C++ static个人总结
一、示例程序
通过示例程序最能说明的就是static关键字所能够出现的位置:
1.全局static(global static),即出现在声明全局静态变量时使用,见注释[8];
2.局部静态变量(local static),即出现在局部函数中的静态变量时使用,见注释[9];
3.类中的静态成员变量(static member variable),即在类中声明静态成员变量,见注释[2];
4.类中的静态成员函数(static member function),即在类中声明静态成员函数,见注释[10];
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class StaticTest{
private:
int member; //belong to the object [1]
static int staticmember; //belong to the class [2]
public:
StaticTest (int m): member(m){ // [10]
//initialize normal member in constructor
cout<<"the mormal member is:"<<member<<" [1]"<<endl;
//static member has already been initialized
cout<<"the static member is:"<<staticmember<<" [2]"<<endl;
};
static void setMember(int m){
//member = m; //complination error! [3]
staticmember = m; // [4]
cout<<"static set m"<<endl;
cout<<"[In setMember] staticmember"<<staticmember<<"[3]&[4]"<<endl;
}
void test(int m){
member = m; // [5]
staticmember = m; // [6]
cout<<"normal set m"<<endl;
cout<<"[In test] member:"<<member<<" [5]"<<endl;
cout<<"[In test] staticmember:"<<staticmember<<" [6]"<<endl;
}
};
//static member variable should be initialize out the class
int StaticTest::staticmember = 3; // [7]
//global static variable
static int globalStatic; // [8]
//local static variable
void localStaticTest(int m){
static int test = 0; // [9]
test +=m ;
cout<<"[localStaticTest] m:"<<test<<" [9]"<<endl;
}
int main(){
StaticTest s(2);
//test static member function
s.setMember(6);
StaticTest::setMember(5);
//test normal member function
s.test(5);
StaticTest t(3);
cout<<globalStatic<<endl;
localStaticTest(1);
localStaticTest(3);
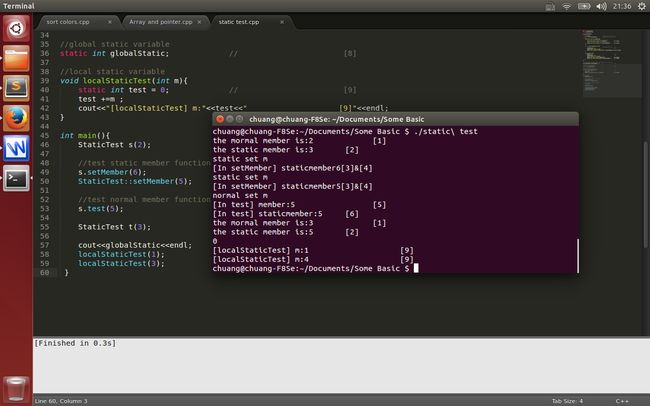
}二、示例程序输出:
三、解析static
下面针对输出和代码中的注释行我们来详细说明static出现在不同地方的作用,以及使用时需要注意的地方:
1.通过注释[1]和[2]以及程序输出中带有[1][2]标号行,我们可以得出以下结论:
a.类中的静态成员变量是属于整个类的;
b.类中的静态成员在类内部声明,但要在类的外部进行初始化(即在类的定义/实现时初始化);
原因在于:a就是b的根本原因;
作特殊说明的是:在main函数中我们声明了两个对象,第一个对象s调用test将静态成员变量更改为5之后,在构造的对象t去访问静态变量所得输出即为5,这更说明两个对象同时使用了一个静态成员变量,也就是说静态成员变量是属于class的。
2.通过注释[3]和[4]以及输出,有以下结论:
a.静态成员函数是属于整个类的,并不隶属于某个类对象;
b.静态成员函数可以使用类的静态成员,但不能使用类的普通成员;
c.同样类的静态成员函数不可以使用累的非静态成员函数;
原因在于:静态成员函数属于整个class,因此其在引用普通成员变量时就无法确定普通成员变量所属的对象;
待续。。。