源码角度深入理解Activity
目录
- 目录
- 前言
- Activity相关类介绍
- ActivityThread
- ApplicationThread
- ActivityClientRecord
- ActivityRecord
- Context
- Activity生命周期分析
- 参考
前言
这篇博客的名字起的很大,我自己也很担心是否有能力来从源码的角度深入分析Activity。
写这篇博客的起因是因为最近一直利用空闲时间在学习《Android开发艺术探索》,今天总算读完一遍,但是其中第九章节“四大组件的工作过程”一直让我介怀,感觉自己并没有真正的搞懂。
所以这里也是花时间从源码角度分析了一下Activity的生命周期流程,并且记录一下自己的学习过程。
另外:推荐一下《Android开发艺术探索》,对Android应用层开发者进阶还是挺有帮助的。是我目前读过的最为推荐的Android书籍。
Activity相关类介绍
在深入理解Activity之前,必须介绍几个跟Activity生命周期息息相关的类。具体内容如下。
ActivityThread
代码路径:/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
代码浅析:对于ActivityThread,我们首先要明确它并不是一个线程类,从它的定义可以看出它并非继承自Thread类。我们从它的main函数入手,看它都做了哪些事情。
public final class ActivityThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter());
Security.addProvider(new AndroidKeyStoreProvider());
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
// 构造UI线程的Looper对象
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// 创建ActivityThread对象,并使用attach方法与ActivityManagerService进行交互
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
AsyncTask.init();
// 轮询处理UI线程的消息
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
}为什么要先介绍一下ActivityThread的main函数呢?是因为Android应用程序框架层创建的应用程序的入口函数是ActivityThread.main()。而ActivityThread的main函数的主要作用就是开启消息循环,处理UI线程中各种消息。
ApplicationThread
ActivityThread在attach方法中与ActivityManagerService进行交互的代码如下:
private void attach(boolean system) {
// ......
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
}可以看出,ActivityManagerService与ActivityThread通信是通过mAppThread对象,而这个对象的定义为:
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();所以,我们还需要来分析一下ApplicationThread的实现,它是ActivityThread的内部类。
private class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
// ......
}
public abstract class ApplicationThreadNative extends Binder {
// ......
}这里我们可以看到,ApplicationThread是Binder的实现类,也就是说,ActivityManagerService拿到ApplicationThread对象BpBinder,然后通过Binder通信与当前Activity所在进程的BnBinder进行通信。
ActivityClientRecord
为什么要介绍这个类呢?因为它是Activity描述的类,对Activity进行了高度抽象。它是ActivityThread的静态final内部类。
每个Activity被创建出来的时候,都对应着一个ActivityClientRecord,用于记录Activity的信息。
static final class ActivityClientRecord {
IBinder token;
int ident;
Intent intent;
IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor;
Bundle state;
PersistableBundle persistendState;
Activity activity;
Window window;
// 这个也是对Activity的具体描述,大家感兴趣可以去看一下源码
ActivityInfo activityInfo;
// .......
}ActivityRecord
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityRecord.java
代码解析:这个ActivityRecord是ActivityManagerService用于描述Activity的高度抽象类。具体源码大家感兴趣的可以自行研究源码,这里不贴代码了。
Context
这是分析Activity源码之前最后也是最重要的相关类。对于Context类,我们首先需要明确几点内容:
1. 它描述的是一个应用程序环境的信息,即上下文。
2. 该类是一个抽象类,Android提供了该抽象类的具体实现类即ContextIml类。
3. 通过它我们可以获取应用程序的资源和类,也包括一些应用级别的操作,例如启动一个Activity或者发送广播。
Context的相关类继承关系如下(从UML图中我们看出Activity也是继承自Context类的):
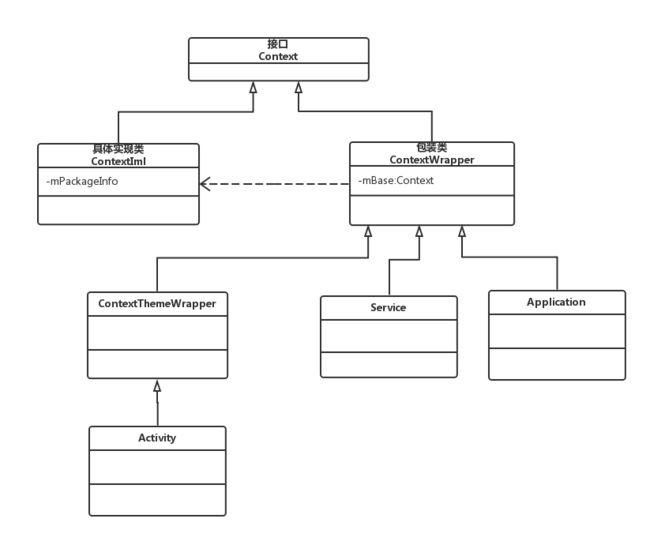
由于Service和Application没有界面,所以可以直接继承ContextWrapper类,而Activity是有UI界面的,所以它要继承ContextThemeWrapper,增加了与主题相关的方法。
Activity生命周期分析
在Android应用中,启动一个Activity是非常容易的一件事情,我们可以通过显示调用启动同一个应用中的其他Activity,示例代码如下:
Intent intent = new Intent(this, SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);通过上述代码,就可以启动一个具体的Activity了,然后新的Activity就会被系统启动并展示在用户的眼前了。但是,知道这些是远远不够的,因为一个Activity的展示和消失均包含了各种生命周期方法的回调,例如onCreate->onStart->onResume->onPause->onStop->onDestory。而这些生命周期方法的回调并不是Activity直接控制的,而是由Android系统通过进程间通信通知Activity的相关类进行具体操作的。接下来,我就带着大家看一下Android系统是如何控制Activity生命周期各种函数回调的。
既然,上述代码是从startActivity函数开始的,那我们也从startActivity函数入手,通过源码分析,我们最终可以知道,startActivity最终都调用了startActivityForResult方法,具体代码如下:
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
startActivity(intent, null);
}
public void startActivity(Intent intent, Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
}
public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode) {
startActivityForResult(intent, requestCode, null);
}
public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
// 一般Activity的mParent变量都为null,mParent常用在ActivityGroup中,目前已被废弃
if (mParent == null) {
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
// 这里会启动新的Activity
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) {
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(
mToken, mEmbeddedID, requestCode, ar.getResultCode(),
ar.getResultData());
}
if (requestCode >= 0) {
mStartedActivity = true;
}
final View decor = mWindow != null ? mWindow.peekDecorView() : null;
if (decor != null) {
decor.cancelPendingInputEvents();
}
}
}Instrumentation的execActivity的方法如下:
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
synchronized(mSync) {
// 先检查是否存在这个Activity
final int N = mActivityMonitors.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++) {
final ActivityMonitor am = mActivityMonitors.get(i);
if (am.match(who, null, intent)) {
am.mHits ++;
if (am.isBlocking()) {
// 如果目标Activity无法打开,则直接return
return requestCode >= 0? am.getResult() : null;
}
break;
}
}
}
}
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess();
// 这里是真正打开Activity的地方,跨进程调用ActivityManagerService的startActivity方法
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
}
return null;
}启动Activity真正的实现是由ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()的startActivity方法来完成的。ActivityManagerNative的getDefault方法源码如下:
public abstrace class ActivityManagerNative extends Binder implements IActivityManager {
static public IActivityManager getDefault() {
return gDefault.get();
}
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> gDefault = new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
protected IActivityManager create() {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity");
if (false) {
Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service binder = " + b);
}
IActivityManager am = asInterface(b);
if (false) {
Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service = " + am);
}
return am;
}
}
}ActivityManagerService继承自ActivityManagerNative,而ActivityManagerNative继承自Binder并实现了IActivityManager这个Binder接口,因此ActivityManagerService也是一个Binder,并且是IActivityManager的具体实现。所以,这里ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()返回的是ActivityManagerService的远程Binder对象。通过远程Binder对象调用ActivityManagerService的startActivity方法。
注意:此时我们已经从Activity进程通过Binder远程通信调用了ActivityManagerService所在进程的方法了。那么接下来,我们就需要研究一下ActivityManagerService的startActivity方法,源码如下:
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
String profileFile, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, Bundle options) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode,
startFlags, profileFile, profileFd, options, UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
}
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
String profileFile, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, Bundle options, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId,
false, true, "startActivity", null);
return mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profileFile, profileFd,
null, null, options, userId);
}从上述源码可以看出,ActivityManagerService的startActivity启动过程又转移到mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait函数了。而mStackSupervisor是ActivityStackSupervisor类的对象。
ActivityStackSupervisor的startActivityMayWait函数源码较长,简单总结起来流程如下:
startActivityMayWait()->startActivityLocked()->startActivityUncheckedLocked()->startSpecificActivityLocked()->realStartActivityLocked()
在关键的realStartActivityLocked函数中,有如下一段代码:
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),
r.compat, r.task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle, r.persistentState,
results, newIntents, !andResume, mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);这段代码非常重要,因为app.thread的类型为IApplicationThread,IApplicationThread的定义如下:
package android.app;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IIntentReceiver;
import android.content.pm.ActivityInfo;
import android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo;
import android.content.pm.ProviderInfo;
import android.content.pm.ServiceInfo;
import android.content.res.CompatibilityInfo;
import android.content.res.Configuration;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Debug;
import android.os.ParcelFileDescriptor;
import android.os.PersistableBundle;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.IInterface;
import android.service.voice.IVoiceInteractionSession;
import com.android.internal.app.IVoiceInteractor;
import java.io.FileDescriptor;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/** * System private API for communicating with the application. This is given to * the activity manager by an application when it starts up, for the activity * manager to tell the application about things it needs to do. * * {@hide} */
public interface IApplicationThread extends IInterface {
void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished, boolean userLeaving,
int configChanges, boolean dontReport) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleStopActivity(IBinder token, boolean showWindow,
int configChanges) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleWindowVisibility(IBinder token, boolean showWindow) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleSleeping(IBinder token, boolean sleeping) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleResumeActivity(IBinder token, int procState, boolean isForward, Bundle resumeArgs)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleSendResult(IBinder token, List<ResultInfo> results) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, int procState, Bundle state,
PersistableBundle persistentState, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults,
List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleRelaunchActivity(IBinder token, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults,
List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, int configChanges,
boolean notResumed, Configuration config) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleNewIntent(List<Intent> intent, IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
int configChanges) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleReceiver(Intent intent, ActivityInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras, boolean sync,
int sendingUser, int processState) throws RemoteException;
static final int BACKUP_MODE_INCREMENTAL = 0;
static final int BACKUP_MODE_FULL = 1;
static final int BACKUP_MODE_RESTORE = 2;
static final int BACKUP_MODE_RESTORE_FULL = 3;
void scheduleCreateBackupAgent(ApplicationInfo app, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
int backupMode) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleDestroyBackupAgent(ApplicationInfo app, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token, ServiceInfo info,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleBindService(IBinder token,
Intent intent, boolean rebind, int processState) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleUnbindService(IBinder token,
Intent intent) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleServiceArgs(IBinder token, boolean taskRemoved, int startId,
int flags, Intent args) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleStopService(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
static final int DEBUG_OFF = 0;
static final int DEBUG_ON = 1;
static final int DEBUG_WAIT = 2;
void bindApplication(String packageName, ApplicationInfo info, List<ProviderInfo> providers,
ComponentName testName, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle testArguments,
IInstrumentationWatcher testWatcher, IUiAutomationConnection uiAutomationConnection,
int debugMode, boolean openGlTrace, boolean restrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent,
Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map<String, IBinder> services,
Bundle coreSettings) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleExit() throws RemoteException;
void scheduleSuicide() throws RemoteException;
void scheduleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config) throws RemoteException;
void updateTimeZone() throws RemoteException;
void clearDnsCache() throws RemoteException;
void setHttpProxy(String proxy, String port, String exclList,
Uri pacFileUrl) throws RemoteException;
void processInBackground() throws RemoteException;
void dumpService(FileDescriptor fd, IBinder servicetoken, String[] args)
throws RemoteException;
void dumpProvider(FileDescriptor fd, IBinder servicetoken, String[] args)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleRegisteredReceiver(IIntentReceiver receiver, Intent intent,
int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras, boolean ordered,
boolean sticky, int sendingUser, int processState) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleLowMemory() throws RemoteException;
void scheduleActivityConfigurationChanged(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
void profilerControl(boolean start, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, int profileType)
throws RemoteException;
void dumpHeap(boolean managed, String path, ParcelFileDescriptor fd)
throws RemoteException;
void setSchedulingGroup(int group) throws RemoteException;
static final int PACKAGE_REMOVED = 0;
static final int EXTERNAL_STORAGE_UNAVAILABLE = 1;
void dispatchPackageBroadcast(int cmd, String[] packages) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleCrash(String msg) throws RemoteException;
void dumpActivity(FileDescriptor fd, IBinder servicetoken, String prefix, String[] args)
throws RemoteException;
void setCoreSettings(Bundle coreSettings) throws RemoteException;
void updatePackageCompatibilityInfo(String pkg, CompatibilityInfo info) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleTrimMemory(int level) throws RemoteException;
void dumpMemInfo(FileDescriptor fd, Debug.MemoryInfo mem, boolean checkin, boolean dumpInfo,
boolean dumpDalvik, String[] args) throws RemoteException;
void dumpGfxInfo(FileDescriptor fd, String[] args) throws RemoteException;
void dumpDbInfo(FileDescriptor fd, String[] args) throws RemoteException;
void unstableProviderDied(IBinder provider) throws RemoteException;
void requestAssistContextExtras(IBinder activityToken, IBinder requestToken, int requestType)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleTranslucentConversionComplete(IBinder token, boolean timeout)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleOnNewActivityOptions(IBinder token, ActivityOptions options)
throws RemoteException;
void setProcessState(int state) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleInstallProvider(ProviderInfo provider) throws RemoteException;
void updateTimePrefs(boolean is24Hour) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleCancelVisibleBehind(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleBackgroundVisibleBehindChanged(IBinder token, boolean enabled) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleEnterAnimationComplete(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
String descriptor = "android.app.IApplicationThread";
int SCHEDULE_PAUSE_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION;
int SCHEDULE_STOP_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+2;
int SCHEDULE_WINDOW_VISIBILITY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+3;
int SCHEDULE_RESUME_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+4;
int SCHEDULE_SEND_RESULT_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+5;
int SCHEDULE_LAUNCH_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+6;
int SCHEDULE_NEW_INTENT_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+7;
int SCHEDULE_FINISH_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+8;
int SCHEDULE_RECEIVER_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+9;
int SCHEDULE_CREATE_SERVICE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+10;
int SCHEDULE_STOP_SERVICE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+11;
int BIND_APPLICATION_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+12;
int SCHEDULE_EXIT_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+13;
int SCHEDULE_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+15;
int SCHEDULE_SERVICE_ARGS_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+16;
int UPDATE_TIME_ZONE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+17;
int PROCESS_IN_BACKGROUND_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+18;
int SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+19;
int SCHEDULE_UNBIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+20;
int DUMP_SERVICE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+21;
int SCHEDULE_REGISTERED_RECEIVER_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+22;
int SCHEDULE_LOW_MEMORY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+23;
int SCHEDULE_ACTIVITY_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+24;
int SCHEDULE_RELAUNCH_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+25;
int SCHEDULE_SLEEPING_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+26;
int PROFILER_CONTROL_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+27;
int SET_SCHEDULING_GROUP_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+28;
int SCHEDULE_CREATE_BACKUP_AGENT_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+29;
int SCHEDULE_DESTROY_BACKUP_AGENT_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+30;
int SCHEDULE_ON_NEW_ACTIVITY_OPTIONS_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+31;
int SCHEDULE_SUICIDE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+32;
int DISPATCH_PACKAGE_BROADCAST_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+33;
int SCHEDULE_CRASH_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+34;
int DUMP_HEAP_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+35;
int DUMP_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+36;
int CLEAR_DNS_CACHE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+37;
int SET_HTTP_PROXY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+38;
int SET_CORE_SETTINGS_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+39;
int UPDATE_PACKAGE_COMPATIBILITY_INFO_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+40;
int SCHEDULE_TRIM_MEMORY_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+41;
int DUMP_MEM_INFO_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+42;
int DUMP_GFX_INFO_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+43;
int DUMP_PROVIDER_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+44;
int DUMP_DB_INFO_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+45;
int UNSTABLE_PROVIDER_DIED_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+46;
int REQUEST_ASSIST_CONTEXT_EXTRAS_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+47;
int SCHEDULE_TRANSLUCENT_CONVERSION_COMPLETE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+48;
int SET_PROCESS_STATE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+49;
int SCHEDULE_INSTALL_PROVIDER_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+50;
int UPDATE_TIME_PREFS_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+51;
int CANCEL_VISIBLE_BEHIND_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+52;
int BACKGROUND_VISIBLE_BEHIND_CHANGED_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+53;
int ENTER_ANIMATION_COMPLETE_TRANSACTION = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION+54;
}因为它继承了IInterface接口,所以它也是一个Binder类型的接口,而它的具体实现是ActivityThread中的ApplicationThread类。
注意:这里通过调用IInterface的scheduleLaunchActivity方法其实是通过了Binder进程间通信,从ActivityManagerService进程又调回了Activity所在进程的ActivityThread类中ApplicationThread的scheduleLaunchActivity方法。
我们又回到了Activity所在进程的ActivityThread类中。我们看一下其内部类ApplicationThread类的scheduleLaunchActivity方法源码如下:
public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) {
sendMessage(
finished ? H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY_FINISHING : H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
token,
(userLeaving ? 1 : 0) | (dontReport ? 2 : 0),
configChanges);
}
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, boolean async) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(
TAG, "SCHEDULE " + what + " " + mH.codeToString(what)
+ ": " + arg1 + " / " + obj);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
msg.obj = obj;
msg.arg1 = arg1;
msg.arg2 = arg2;
if (async) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}在ActivityThread类中,有一个非常重要的成员变量:
final H mH = new H();
private class H extends Handler {
public static final int LAUNCH_ACTIVITY = 100;
// .......
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch(msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
// 获取AMS远程传递过来的Activity描述对象
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(r.activityInfo.application, r.compatInfo);
// 这个是真正启动Activity的方法
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
} break;
}
}
}这个mH就是用来处理ActivityManagerService发送过来的跨进程通信的消息。我们上述代码就描述一个打开Activity的具体操作。Activity的真正启动是通过handleLaunchActivity方法实现的。
handleLaunchActivity的源码如下:
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// ......
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Handling launch of " + r);
// 真正完成Activity调用的地方
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward, !r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed);
// ......
}
// ......
}通过上面的源码可以看出,performLaunchActivity方法最终完成了Activity对象的创建和启动过程,并且ActivityThread通过handleResumeActivity方法来调用被启动Activity的onResume这一生命周期方法。
performLaunchActivity这个方法主要完成了如下几件事情,具体源码如下。
- 从ActivityClientRecord中获取待启动的Activity的组件信息。
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo, Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
// 从intent中解析出目标Activity的启动参数
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName, r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
}- 通过Instrumentation类的newActivity方法使用类加载器创建Activity对象。
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
//......
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectdActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ":" + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}至于Instrumentation的newActivity方法,它的实现非常简单,就是利用了Java的反射机制,源码如下:
public Activity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className, Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (Activity)cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}- 通过LoadedApk类的makeApplication方法来尝试创建Application对象。
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// ......
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
}LoadedApk类的makeApplication方法代码如下:
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass, Instrumentation instrumentation) {
// 判断Application对象是否已经创建过,如果已经创建过,则不会再重复创建。
// 说明,每个应用只有一个Application对象。
if (mApplication != null) {
return mApplication;
}
Application app = null;
String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
appClass = "android.app.Application";
}
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
if (!mPackageName.equals("android")) {
initializeJavaContextClassLoader();
}
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate application " + appClass
+ ":" + e.toString(), e);
}
}
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
if (instrumentation != null) {
try {
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!instrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
// ......
return app;
}可以看到,Application的创建是调用Instrumentation类的newApplication方法,这个方法也是通过Java的反射机制,具体源码如下:
public Application newApplication(ClassLoader cl, String className, Context context)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
return newApplication(cl.loadClass(className), context);
}- 创建ContextImpl对象并通过Activity的attach方法来完成一些重要数据的初始化。
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// ......
if (activity != null) {
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.voiceInteractor);
}
}Activity的attach方法如下:
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachActivity(this, mContainer, null);
// 创建Activity依附的Window对象
mWindow = PolicyManager.makeNewWindow(this);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
if (info.softInputMode != WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNSPECIFIED) {
mWindow.setSoftInputMode(info.softInputMode);
}
if (info.uiOptions != 0) {
mWindow.setUiOptions(info.uiOptions);
}
mUiThread = Thread.currentThread();
sMainThread = aThread;
mInstrumentation = instr;
mToken = token;
mIdent = ident;
mApplication = application;
mIntent = intent;
mComponent = intent.getComponent();
mActivityInfo = info;
mTitle = title;
mParent = parent;
mEmbeddedID = id;
mLastNonConfigurationInstances = lastNonConfigurationInstances;
if (voiceInteractor != null) {
if (lastNonConfigurationInstances != null) {
mVoiceInteractor = lastNonConfigurationInstances.voiceInteractor;
} else {
mVoiceInteractor = new VoiceInteractor(voiceInteractor, this, this, Looper.myLooper());
}
}
// 为window设置WindowManager对象
mWindow.setWidowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
mCurrentConfig = config;
}- 调用Activity的onCreate方法。
通过Instrumentation的callActivityOnCreate方法来回调Activity的onCreate()方法。
参考
- 《Android开发艺术探索》