從DTS到驅動加載的過程分析
一、驅動中的probe函數如何被調用?
首先,我們知道驅動執行的起始函數是init函數。以I2C驅動爲例。
(cm36283.c)
static int __init cm36283_init(void)
{
int err = 0;
<span style="color:#FF0000;">err = i2c_add_driver(&cm36283_driver);</span>
return err;
}
module_init(cm36283_init);
(i2c.h)
#define i2c_add_driver(driver) \ i2c_register_driver(THIS_MODULE, driver)
(i2c-core.c)
int i2c_register_driver(struct module *owner, struct i2c_driver *driver)
{
int res;
/* Can't register until after driver model init */
if (unlikely(WARN_ON(!i2c_bus_type.p)))
return -EAGAIN;
/* add the driver to the list of i2c drivers in the driver core */
driver->driver.owner = owner;
driver->driver.bus = &i2c_bus_type;
/* When registration returns, the driver core
* will have called probe() for all matching-but-unbound devices.
*/
<span style="color:#FF0000;">res = driver_register(&driver->driver);</span>
if (res)
return res;
/* Drivers should switch to dev_pm_ops instead. */
if (driver->suspend)
pr_warn("i2c-core: driver [%s] using legacy suspend method\n",
driver->driver.name);
if (driver->resume)
pr_warn("i2c-core: driver [%s] using legacy resume method\n",
driver->driver.name);
pr_debug("i2c-core: driver [%s] registered\n", driver->driver.name);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&driver->clients);
/* Walk the adapters that are already present */
i2c_for_each_dev(driver, __process_new_driver);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_register_driver);
(driver.c)
int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv)
{
int ret;
struct device_driver *other;
BUG_ON(!drv->bus->p);
if ((drv->bus->probe && drv->probe) ||
(drv->bus->remove && drv->remove) ||
(drv->bus->shutdown && drv->shutdown))
printk(KERN_WARNING "Driver '%s' needs updating - please use "
"bus_type methods\n", drv->name);
other = driver_find(drv->name, drv->bus);
if (other) {
printk(KERN_ERR "Error: Driver '%s' is already registered, "
"aborting...\n", drv->name);
return -EBUSY;
}
<span style="color:#FF0000;">ret = bus_add_driver(drv);</span>
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = driver_add_groups(drv, drv->groups);
if (ret)
bus_remove_driver(drv);
return ret;
}
(bus.c)
int bus_add_driver(struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct bus_type *bus;
struct driver_private *priv;
int error = 0;
bus = bus_get(drv->bus);
if (!bus)
return -EINVAL;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': add driver %s\n", bus->name, drv->name);
priv = kzalloc(sizeof(*priv), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!priv) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto out_put_bus;
}
klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, NULL, NULL);
priv->driver = drv;
drv->p = priv;
priv->kobj.kset = bus->p->drivers_kset;
error = kobject_init_and_add(&priv->kobj, &driver_ktype, NULL,
"%s", drv->name);
if (error)
goto out_unregister;
klist_add_tail(&priv->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_drivers);
if (drv->bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) {
<span style="color:#FF6666;">error = driver_attach(drv);</span>
if (error)
goto out_unregister;
}
module_add_driver(drv->owner, drv);
error = driver_create_file(drv, &driver_attr_uevent);
if (error) {
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: uevent attr (%s) failed\n",
__func__, drv->name);
}
error = driver_add_attrs(bus, drv);
if (error) {
/* How the hell do we get out of this pickle? Give up */
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: driver_add_attrs(%s) failed\n",
__func__, drv->name);
}
if (!drv->suppress_bind_attrs) {
error = add_bind_files(drv);
if (error) {
/* Ditto */
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: add_bind_files(%s) failed\n",
__func__, drv->name);
}
}
kobject_uevent(&priv->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
return 0;
out_unregister:
kobject_put(&priv->kobj);
kfree(drv->p);
drv->p = NULL;
out_put_bus:
bus_put(bus);
return error;
} driver註冊到bus上時,同時會建立uevent屬性文件及bus->attr數組中的屬性文件(如果
bus->attr有的話)。
(dd.c)
int driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv)
{
return bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(driver_attach);
(bus.c)
int bus_for_each_dev(struct bus_type *bus, struct device *start,
void *data, int (*fn)(struct device *, void *))
{
struct klist_iter i;
struct device *dev;
int error = 0;
if (!bus)
return -EINVAL;
klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,
(start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL));
while ((dev = next_device(&i)) && !error)
error = <span style="color:#FF6666;">fn(dev, data);</span>
klist_iter_exit(&i);
return error;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(bus_for_each_dev);
(dd.c)
static int __driver_attach(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
struct device_driver *drv = data;
/*
* Lock device and try to bind to it. We drop the error
* here and always return 0, because we need to keep trying
* to bind to devices and some drivers will return an error
* simply if it didn't support the device.
*
* driver_probe_device() will spit a warning if there
* is an error.
*/
<strong>if (!driver_match_device(drv, dev))</strong>
return 0;
if (dev->parent) /* Needed for USB */
device_lock(dev->parent);
device_lock(dev);
if (!dev->driver)
<strong><span style="color:#FF6666;">driver_probe_device(drv, dev);</span></strong>
device_unlock(dev);
if (dev->parent)
device_unlock(dev->parent);
return 0;
}
driver_match_device调用bus上的match函数进行匹配。具体可以参照各种总线match匹配函数
匹配成功后,会调用driver的probe函数。
int driver_probe_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
{
int ret = 0;
if (!device_is_registered(dev))
return -ENODEV;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: matched device %s with driver %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);
pm_runtime_get_noresume(dev);
pm_runtime_barrier(dev);
<span style="color:#FF6666;">ret = really_probe(dev, drv);</span>
pm_runtime_put_sync(dev);
return ret;
}
static int really_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
int ret = 0;
atomic_inc(&probe_count);
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: probing driver %s with device %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, drv->name, dev_name(dev));
WARN_ON(!list_empty(&dev->devres_head));
dev->driver = drv;
/* If using pinctrl, bind pins now before probing */
ret = pinctrl_bind_pins(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
if (driver_sysfs_add(dev)) {
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: driver_sysfs_add(%s) failed\n",
__func__, dev_name(dev));
goto probe_failed;
}
<span style="background-color: rgb(204, 204, 255);">if (dev->bus->probe) {
ret = dev->bus->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
} else if (drv->probe) {
<span style="color:#FF6666;">ret = drv->probe(dev);</span>
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
}</span>
driver_bound(dev);
ret = 1;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: bound device %s to driver %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);
goto done;
probe_failed:
devres_release_all(dev);
driver_sysfs_remove(dev);
dev->driver = NULL;
if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER) {
/* Driver requested deferred probing */
dev_info(dev, "Driver %s requests probe deferral\n", drv->name);
driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);
} else if (ret != -ENODEV && ret != -ENXIO) {
/* driver matched but the probe failed */
printk(KERN_WARNING
"%s: probe of %s failed with error %d\n",
drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);
} else {
pr_debug("%s: probe of %s rejects match %d\n",
drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);
}
/*
* Ignore errors returned by ->probe so that the next driver can try
* its luck.
*/
ret = 0;
done:
atomic_dec(&probe_count);
wake_up(&probe_waitqueue);
return ret;
}
如果bus->probe爲空,就執行drv->probe
二、驅動中的probe函數參數如何產生的?
int driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv)
{
return bus_for_each_dev(<span style="color:#FF0000;"><strong>drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach</strong></span>);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(driver_attach);
int bus_for_each_dev(struct bus_type *bus, struct device *start,
void *data, int (*fn)(struct device *, void *))
{
struct klist_iter i;
struct device *dev;
int error = 0;
if (!bus)
return -EINVAL;
klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,
(start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL));
while ((<strong><span style="color:#FF0000;">dev = next_device(&i)</span></strong>) && !error)
error = fn(dev, data);
klist_iter_exit(&i);
return error;
}
這樣可以看到klist_iter_init_node實際調用klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,NULL),所以,跟蹤klist_iter_init_node函數,發現並沒做什麼相關重要的東西。
void klist_iter_init_node(struct klist *k, struct klist_iter *i,
struct klist_node *n)
{
i->i_klist = k;
i->i_cur = n;
if (n)
kref_get(&n->n_ref);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(klist_iter_init_node);
static struct device *next_device(struct klist_iter *i)
{
struct klist_node *n = klist_next(i);
struct device *dev = NULL;
struct device_private *dev_prv;
if (n) {
dev_prv =<span style="color:#FF0000;"> to_device_private_bus(n);</span>
<span style="color:#FF0000;">dev = dev_prv->device;</span>
}
return dev;
}
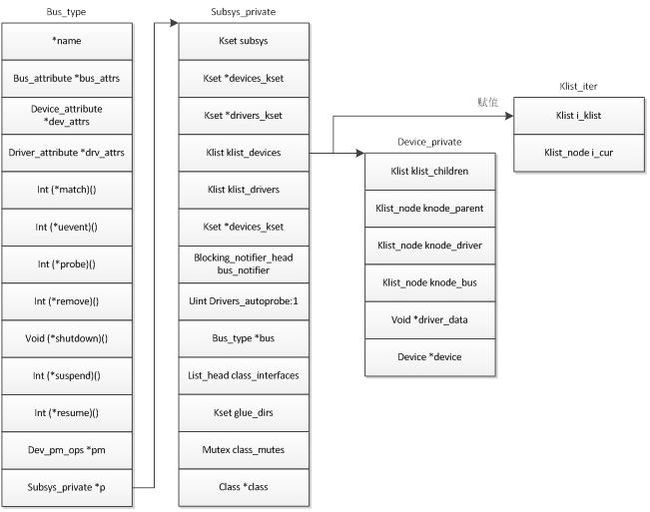
可以看出,只要得到dev_prv就可以得到dev。下面的問題就是dev_prv中的dev如何被添加進去的呢?
#define to_device_private_bus(obj) \ container_of(obj, struct device_private, knode_bus)
這裏引用其他一些文章解釋:
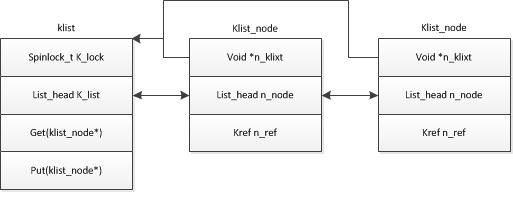
先上几个struct:
struct klist_iter {
struct klist *i_klist;
struct klist_node *i_cur;
};
struct klist {
spinlock_t k_lock;
struct list_head k_list;
void (*get)(struct klist_node *);
void (*put)(struct klist_node *);
} __attribute__ ((aligned (sizeof(void*))));
struct klist_node {
void *n_klist; /* never access directly */
struct list_head n_node;
struct kref n_ref;
};
struct kref {
atomic_t refcount;
};
其中的klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,(start ?&start->p->knode_bus :NULL))作用是定义个klist_iter指向此klist,以便以后直接使用,如图:
static struct device *next_device(struct klist_iter *i)
{
struct klist_node *n =<span style="color:#FF0000;"> <strong>klist_next(i);</strong></span>
struct device *dev = NULL;
struct device_private *dev_prv;
if (n) {
dev_prv = to_device_private_bus(n);
dev = dev_prv->device;
}
return dev;
}
(klist.c)
struct klist_node *klist_next(struct klist_iter *i)
{
void (*put)(struct klist_node *) = i->i_klist->put;
struct klist_node *last = i->i_cur; <span style="color:#FFCCCC;"> <span style="color:#009900;">// NULL</span></span>
struct klist_node *next;
spin_lock(&i->i_klist->k_lock);
if (last) {
next = to_klist_node(last->n_node.next);
if (!klist_dec_and_del(last))
put = NULL;
} else
<span style="color:#FF0000;">next = to_klist_node(i->i_klist->k_list.next);</span>
i->i_cur = NULL;
while (next != to_klist_node(&i->i_klist->k_list)) {
if (likely(!knode_dead(next))) {
kref_get(&next->n_ref);
i->i_cur = next;
break;
}
next = to_klist_node(next->n_node.next);
}
spin_unlock(&i->i_klist->k_lock);
if (put && last)
put(last);
return i->i_cur;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(klist_next);
這裏可以知道i->i_cur=NULL,i->i_klist=&bus->p->klist_devices。 to_klist_node從klist中取得下一個node賦值給next,然後執行一次while循環裏的內容,將next賦值給i->i_cur。這樣就得到了klist_node. to_device_private_bus通過container_of 得到struct device_private。下圖說明其中的關係。
由此,可以知道DTS解析後的設備都是通過klist和klist_node掛載到bus上的。
三、 DTS的解析掛載
dts文件編譯時通過dtc被編譯成了dtb文件。然後在內核啓動時該文件被解析。DTS节点信息保存到allnodes鏈表中。
start_kernel() --> setup_arch() --> unflatten_device_tree()
随后,当系统启动到board文件时,会调用.init_machine,高通8974平台对应的是msm8974_init()。接着调用of_platform_populate(....)接口,加载平台总线和平台设备。
(kernel/arch/arm/mach-msm/board-8226.c)
void __init msm8226_init(void)
{
<span style="color:#FF0000;">board_dt_populate(adata);</span>
msm8226_add_drivers();
}
(kernel/arch/arm/mach-msm/board-dt.c)
void __init board_dt_populate(struct of_dev_auxdata *adata)
{
<span style="color:#CC0000;">of_platform_populate(NULL, of_default_bus_match_table, NULL, NULL);</span>
/* Explicitly parent the /soc devices to the root node to preserve
* the kernel ABI (sysfs structure, etc) until userspace is updated
*/
<span style="color:#FF0000;">of_platform_populate(of_find_node_by_path("/soc"),
of_default_bus_match_table, adata, NULL);</span>
}
上面兩句話,一個是以“/”爲根進行遍歷;一個是遍歷allnodes鏈找到“/soc”,並以這一節點爲根節點進行遍歷。
(kernel/driver/of/platform.c)
int of_platform_populate(struct device_node *root,
const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct of_dev_auxdata *lookup,
struct device *parent)
{
struct device_node *child;
int rc = 0;
root = root ? of_node_get(root) : of_find_node_by_path("/");
if (!root)
return -EINVAL;
for_each_child_of_node(root, child) {
rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, parent, true);
if (rc)
break;
}
of_node_put(root);
return rc;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_OF_ADDRESS */
of_platform_populate遍歷根節點下的所有節點,分配建立platform device。for_each_child_of_node實現遍歷父節點下的所有兄弟節點及孩子節點。
#define for_each_child_of_node(parent, child) \ for (child = of_get_next_child(parent, NULL); child != NULL; \ child = of_get_next_child(parent, child))
struct device_node *of_get_next_child(const struct device_node *node,
struct device_node *prev)
{
struct device_node *next;
read_lock(&devtree_lock);
next = prev ? prev->sibling : node->child;
for (; next; next = next->sibling)
if (of_node_get(next))
break;
of_node_put(prev);
read_unlock(&devtree_lock);
return next;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(of_get_next_child);
(kernel/driver/of/platform.c)
static int of_platform_bus_create(struct device_node *bus,
const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct of_dev_auxdata *lookup,
struct device *parent, bool strict)
{
const struct of_dev_auxdata *auxdata;
struct device_node *child;
struct platform_device *dev;
const char *bus_id = NULL;
void *platform_data = NULL;
int rc = 0;
/* Make sure it has a compatible property */
if (strict && (!of_get_property(bus, "compatible", NULL))) {
pr_debug("%s() - skipping %s, no compatible prop\n",
__func__, bus->full_name);
return 0;
}
auxdata = of_dev_lookup(lookup, bus);
if (auxdata) {
bus_id = auxdata->name;
platform_data = auxdata->platform_data;
}
if (of_device_is_compatible(bus, "arm,primecell")) {
of_amba_device_create(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent);
return 0;
}
<span style="color:#FF0000;">dev = of_platform_device_create_pdata(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent);</span>
if (!dev || !of_match_node(matches, bus))
return 0;
for_each_child_of_node(bus, child) {
pr_debug(" create child: %s\n", child->full_name);
rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, &dev->dev, strict);
if (rc) {
of_node_put(child);
break;
}
}
return rc;
}
struct platform_device *of_platform_device_create_pdata(
struct device_node *np,
const char *bus_id,
void *platform_data,
struct device *parent)
{
struct platform_device *dev;
if (!of_device_is_available(np))
return NULL;
<strong><span style="color:#FF0000;">dev = of_device_alloc(np, bus_id, parent);</span></strong>
if (!dev)
return NULL;
#if defined(CONFIG_MICROBLAZE)
dev->archdata.dma_mask = 0xffffffffUL;
#endif
dev->dev.coherent_dma_mask = DMA_BIT_MASK(sizeof(dma_addr_t) * 8);
dev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type;
dev->dev.platform_data = platform_data;
/* We do not fill the DMA ops for platform devices by default.
* This is currently the responsibility of the platform code
* to do such, possibly using a device notifier
*/
if (of_device_add(dev) != 0) {
platform_device_put(dev);
return NULL;
}
return dev;
}
of_device_alloc根據allnodes的device node分配platform device空間。然後設置platform device的bus總線。
struct platform_device *of_device_alloc(struct device_node *np,
const char *bus_id,
struct device *parent)
{
struct platform_device *dev;
int rc, i, num_reg = 0, num_irq;
struct resource *res, temp_res;
dev = platform_device_alloc("", -1);
if (!dev)
return NULL;
/* count the io and irq resources */
if (of_can_translate_address(np))
while (of_address_to_resource(np, num_reg, &temp_res) == 0)
num_reg++;
num_irq = of_irq_count(np);
/* Populate the resource table */
if (num_irq || num_reg) {
res = kzalloc(sizeof(*res) * (num_irq + num_reg), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!res) {
platform_device_put(dev);
return NULL;
}
dev->num_resources = num_reg + num_irq;
dev->resource = res;
for (i = 0; i < num_reg; i++, res++) {
rc = of_address_to_resource(np, i, res);
WARN_ON(rc);
}
WARN_ON(of_irq_to_resource_table(np, res, num_irq) != num_irq);
}
<span style="color:#FF0000;"> dev->dev.of_node = of_node_get(np);</span>
#if defined(CONFIG_MICROBLAZE)
dev->dev.dma_mask = &dev->archdata.dma_mask;
#endif
dev->dev.parent = parent;
if (bus_id)
dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "%s", bus_id);
else
of_device_make_bus_id(&dev->dev);
return dev;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(of_device_alloc);
分配platform device空間後,注意將device node賦值給dev->dev.of_node,這也就是爲什麼經常在probe函數中見到通過pdev->dev.of_node得到dts 設備節點,並從該節點中讀取相關信息。
I2C platform device驅動加載在i2c-qup.c文件中。下面是i2c-qup platform device驅動加載及i2c-client的驅動加載。
(i2c-qup.c)
static int __devinit
qup_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct qup_i2c_dev *dev;
struct resource *qup_mem, *gsbi_mem, *qup_io, *gsbi_io, *res;
struct resource *in_irq, *out_irq, *err_irq;
struct clk *clk, *pclk;
int ret = 0;
int i;
int dt_gpios[I2C_GPIOS_DT_CNT];
bool use_device_tree = pdev->dev.of_node;
struct msm_i2c_platform_data *pdata;
gsbi_mem = NULL;
dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "qup_i2c_probe\n");
if (use_device_tree) {
pdata = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*pdata), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pdata)
return -ENOMEM;
ret = msm_i2c_rsrcs_dt_to_pdata_map(pdev, pdata, dt_gpios);
if (ret)
goto get_res_failed;
} else
pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data;
if (!pdata) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "platform data not initialized\n");
return -ENOSYS;
}
qup_mem = platform_get_resource_byname(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM,
"qup_phys_addr");
if (!qup_mem) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"platform_get_resource_byname(qup_phys_addr) failed\n");
ret = -ENODEV;
goto get_res_failed;
}
/*
* We only have 1 interrupt for new hardware targets and in_irq,
* out_irq will be NULL for those platforms
*/
in_irq = platform_get_resource_byname(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ,
"qup_in_intr");
out_irq = platform_get_resource_byname(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ,
"qup_out_intr");
err_irq = platform_get_resource_byname(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ,
"qup_err_intr");
if (!err_irq) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no error irq resource?\n");
ret = -ENODEV;
goto get_res_failed;
}
qup_io = request_mem_region(qup_mem->start, resource_size(qup_mem),
pdev->name);
if (!qup_io) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "QUP region already claimed\n");
ret = -EBUSY;
goto get_res_failed;
}
if (!pdata->use_gsbi_shared_mode) {
gsbi_mem = platform_get_resource_byname(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM,
"gsbi_qup_i2c_addr");
if (!gsbi_mem) {
dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "Assume BLSP\n");
/*
* BLSP core does not need protocol programming so this
* resource is not expected
*/
goto blsp_core_init;
}
gsbi_io = request_mem_region(gsbi_mem->start,
resource_size(gsbi_mem),
pdev->name);
if (!gsbi_io) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "GSBI region already claimed\n");
ret = -EBUSY;
goto err_res_failed;
}
}
blsp_core_init:
clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "core_clk");
if (IS_ERR(clk)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Could not get core_clk\n");
ret = PTR_ERR(clk);
goto err_clk_get_failed;
}
pclk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "iface_clk");
if (IS_ERR(pclk)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Could not get iface_clk\n");
ret = PTR_ERR(pclk);
clk_put(clk);
goto err_clk_get_failed;
}
/* We support frequencies upto FAST Mode(400KHz) */
if (pdata->clk_freq <= 0 ||
pdata->clk_freq > 400000) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "clock frequency not supported\n");
ret = -EIO;
goto err_config_failed;
}
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct qup_i2c_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_alloc_dev_failed;
}
dev->dev = &pdev->dev;
if (in_irq)
dev->in_irq = in_irq->start;
if (out_irq)
dev->out_irq = out_irq->start;
dev->err_irq = err_irq->start;
if (in_irq && out_irq)
dev->num_irqs = 3;
else
dev->num_irqs = 1;
dev->clk = clk;
dev->pclk = pclk;
dev->base = ioremap(qup_mem->start, resource_size(qup_mem));
if (!dev->base) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_ioremap_failed;
}
/* Configure GSBI block to use I2C functionality */
if (gsbi_mem) {
dev->gsbi = ioremap(gsbi_mem->start, resource_size(gsbi_mem));
if (!dev->gsbi) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_gsbi_failed;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(i2c_rsrcs); ++i) {
if (use_device_tree && i < I2C_GPIOS_DT_CNT) {
dev->i2c_gpios[i] = dt_gpios[i];
} else {
res = platform_get_resource_byname(pdev, IORESOURCE_IO,
i2c_rsrcs[i]);
dev->i2c_gpios[i] = res ? res->start : -1;
}
}
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, dev);
dev->one_bit_t = (USEC_PER_SEC/pdata->clk_freq) + 1;
dev->pdata = pdata;
dev->clk_ctl = 0;
dev->pos = 0;
ret = i2c_qup_clk_path_init(pdev, dev);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"Failed to init clock path-voting data structs. err:%d", ret);
/* disable i2c_qup_clk_path_xxx() functionality */
dev->pdata->master_id = 0;
}
if (dev->pdata->src_clk_rate <= 0) {
dev_info(&pdev->dev,
"No src_clk_rate specified in platfrom data\n");
dev_info(&pdev->dev, "Using default clock rate %dHz\n",
DEFAULT_CLK_RATE);
dev->pdata->src_clk_rate = DEFAULT_CLK_RATE;
}
ret = clk_set_rate(dev->clk, dev->pdata->src_clk_rate);
if (ret)
dev_info(&pdev->dev, "clk_set_rate(core_clk, %dHz):%d\n",
dev->pdata->src_clk_rate, ret);
clk_prepare_enable(dev->clk);
clk_prepare_enable(dev->pclk);
/*
* If bootloaders leave a pending interrupt on certain GSBI's,
* then we reset the core before registering for interrupts.
*/
writel_relaxed(1, dev->base + QUP_SW_RESET);
if (qup_i2c_poll_state(dev, 0, true) != 0)
goto err_reset_failed;
clk_disable_unprepare(dev->clk);
clk_disable_unprepare(dev->pclk);
/*
* We use num_irqs to also indicate if we got 3 interrupts or just 1.
* If we have just 1, we use err_irq as the general purpose irq
* and handle the changes in ISR accordingly
* Per Hardware guidelines, if we have 3 interrupts, they are always
* edge triggering, and if we have 1, it's always level-triggering
*/
if (dev->num_irqs == 3) {
ret = request_irq(dev->in_irq, qup_i2c_interrupt,
IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING, "qup_in_intr", dev);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "request_in_irq failed\n");
goto err_request_irq_failed;
}
/*
* We assume out_irq exists if in_irq does since platform
* configuration either has 3 interrupts assigned to QUP or 1
*/
ret = request_irq(dev->out_irq, qup_i2c_interrupt,
IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING, "qup_out_intr", dev);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "request_out_irq failed\n");
free_irq(dev->in_irq, dev);
goto err_request_irq_failed;
}
ret = request_irq(dev->err_irq, qup_i2c_interrupt,
IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING, "qup_err_intr", dev);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "request_err_irq failed\n");
free_irq(dev->out_irq, dev);
free_irq(dev->in_irq, dev);
goto err_request_irq_failed;
}
} else {
ret = request_irq(dev->err_irq, qup_i2c_interrupt,
IRQF_TRIGGER_HIGH, "qup_err_intr", dev);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "request_err_irq failed\n");
goto err_request_irq_failed;
}
}
disable_irq(dev->err_irq);
if (dev->num_irqs == 3) {
disable_irq(dev->in_irq);
disable_irq(dev->out_irq);
}
i2c_set_adapdata(&dev->adapter, dev);
dev->adapter.algo = &qup_i2c_algo;
strlcpy(dev->adapter.name,
"QUP I2C adapter",
sizeof(dev->adapter.name));
dev->adapter.nr = pdev->id;
dev->adapter.dev.parent = &pdev->dev;
if (pdata->msm_i2c_config_gpio)
pdata->msm_i2c_config_gpio(dev->adapter.nr, 1);
mutex_init(&dev->mlock);
dev->pwr_state = MSM_I2C_PM_SUSPENDED;
/* If the same AHB clock is used on Modem side
* switch it on here itself and don't switch it
* on and off during suspend and resume.
*/
if (dev->pdata->keep_ahb_clk_on)
clk_prepare_enable(dev->pclk);
ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&dev->adapter);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "i2c_add_adapter failed\n");
if (dev->num_irqs == 3) {
free_irq(dev->out_irq, dev);
free_irq(dev->in_irq, dev);
}
free_irq(dev->err_irq, dev);
} else {
if (dev->dev->of_node) {
dev->adapter.dev.of_node = pdev->dev.of_node;
<strong><span style="color:#CC0000;"> of_i2c_register_devices(&dev->adapter);</span></strong>
}
pm_runtime_set_autosuspend_delay(&pdev->dev, MSEC_PER_SEC);
pm_runtime_use_autosuspend(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_enable(&pdev->dev);
return 0;
}
err_request_irq_failed:
if (dev->gsbi)
iounmap(dev->gsbi);
err_reset_failed:
clk_disable_unprepare(dev->clk);
clk_disable_unprepare(dev->pclk);
i2c_qup_clk_path_teardown(dev);
err_gsbi_failed:
iounmap(dev->base);
err_ioremap_failed:
kfree(dev);
err_alloc_dev_failed:
err_config_failed:
clk_put(clk);
clk_put(pclk);
err_clk_get_failed:
if (gsbi_mem)
release_mem_region(gsbi_mem->start, resource_size(gsbi_mem));
err_res_failed:
release_mem_region(qup_mem->start, resource_size(qup_mem));
get_res_failed:
if (pdev->dev.of_node)
kfree(pdata);
return ret;
}
i2c、spi等都是platform bus,在msm8974_init()時调用of_platform_populate(....)接口註冊到系統中。這樣在i2c bus驅動中就可以調用of_i2c_register_devices,將i2c設備註冊到i2c bus上。
(of_i2c.c)
void of_i2c_register_devices(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
void *result;
struct device_node *node;
/* Only register child devices if the adapter has a node pointer set */
if (!adap->dev.of_node)
return;
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: walking child nodes\n");
for_each_child_of_node(adap->dev.of_node, node) {
struct i2c_board_info info = {};
struct dev_archdata dev_ad = {};
const __be32 *addr;
int len;
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: register %s\n", node->full_name);
if (of_modalias_node(node, info.type, sizeof(info.type)) < 0) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: modalias failure on %s\n",
node->full_name);
continue;
}
addr = of_get_property(node, "reg", &len);
if (!addr || (len < sizeof(int))) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: invalid reg on %s\n",
node->full_name);
continue;
}
info.addr = be32_to_cpup(addr);
if (info.addr > (1 << 10) - 1) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: invalid addr=%x on %s\n",
info.addr, node->full_name);
continue;
}
info.irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(node, 0);
info.of_node = of_node_get(node);
info.archdata = &dev_ad;
request_module("%s%s", I2C_MODULE_PREFIX, info.type);
<span style="color:#FF0000;">result = i2c_new_device(adap, &info);</span>
if (result == NULL) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: Failure registering %s\n",
node->full_name);
of_node_put(node);
irq_dispose_mapping(info.irq);
continue;
}
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(of_i2c_register_devices);
of_i2c_register_devices從解析後的allnodes鏈表信息取出節點,解析具體信息後,放到stuct i2c_board_info中,用於建立i2c-client。
(I2c-core.c)
struct i2c_client *
i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info)
{
struct i2c_client *client;
int status;
client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client)
return NULL;
client->adapter = adap;
client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data;
if (info->archdata)
client->dev.archdata = *info->archdata;
client->flags = info->flags;
client->addr = info->addr;
client->irq = info->irq;
strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name));
/* Check for address validity */
status = i2c_check_client_addr_validity(client);
if (status) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "Invalid %d-bit I2C address 0x%02hx\n",
client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_TEN ? 10 : 7, client->addr);
goto out_err_silent;
}
/* Check for address business */
status = i2c_check_addr_busy(adap, client->addr);
if (status)
goto out_err;
client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev;
client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;
client->dev.type = &i2c_client_type;
client->dev.of_node = info->of_node;
/* For 10-bit clients, add an arbitrary offset to avoid collisions */
dev_set_name(&client->dev, "%d-%04x", i2c_adapter_id(adap),
client->addr | ((client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_TEN)
? 0xa000 : 0));
<strong><span style="color:#FF0000;">status = device_register(&client->dev);</span></strong>
if (status)
goto out_err;
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "client [%s] registered with bus id %s\n",
client->name, dev_name(&client->dev));
return client;
out_err:
dev_err(&adap->dev, "Failed to register i2c client %s at 0x%02x "
"(%d)\n", client->name, client->addr, status);
out_err_silent:
kfree(client);
return NULL;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_new_device);
(bus.c)
int device_register(struct device *dev)
{
device_initialize(dev);
<span style="color:#FF0000;">return device_add(dev);</span>
}
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
struct device *parent = NULL;
struct kobject *kobj;
struct class_interface *class_intf;
int error = -EINVAL;
dev = get_device(dev);
if (!dev)
goto done;
if (!dev->p) {
error = device_private_init(dev);
if (error)
goto done;
}
/*
* for statically allocated devices, which should all be converted
* some day, we need to initialize the name. We prevent reading back
* the name, and force the use of dev_name()
*/
if (dev->init_name) {
dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name);
dev->init_name = NULL;
}
/* subsystems can specify simple device enumeration */
if (!dev_name(dev) && dev->bus && dev->bus->dev_name)
dev_set_name(dev, "%s%u", dev->bus->dev_name, dev->id);
if (!dev_name(dev)) {
error = -EINVAL;
goto name_error;
}
pr_debug("device: '%s': %s\n", dev_name(dev), __func__);
parent = get_device(dev->parent);
kobj = get_device_parent(dev, parent);
if (kobj)
dev->kobj.parent = kobj;
/* use parent numa_node */
if (parent)
set_dev_node(dev, dev_to_node(parent));
/* first, register with generic layer. */
/* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */
error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);
if (error)
goto Error;
/* notify platform of device entry */
if (platform_notify)
platform_notify(dev);
error = device_create_file(dev, &uevent_attr);
if (error)
goto attrError;
if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) {
error = device_create_file(dev, &devt_attr);
if (error)
goto ueventattrError;
error = device_create_sys_dev_entry(dev);
if (error)
goto devtattrError;
devtmpfs_create_node(dev);
}
error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev);
if (error)
goto SymlinkError;
error = device_add_attrs(dev);
if (error)
goto AttrsError;
<strong><span style="color:#CC0000;"> error = bus_add_device(dev);</span></strong><pre name="code" class="cpp"> if (error)
goto BusError;
error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);
if (error)
goto DPMError;
device_pm_add(dev);
/* Notify clients of device addition. This call must come
* after dpm_sysfs_add() and before kobject_uevent().
*/
if (dev->bus)
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE, dev);
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
bus_probe_device(dev);
if (parent)
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_parent,
&parent->p->klist_children);
if (dev->class) {
mutex_lock(&dev->class->p->mutex);
/* tie the class to the device */
klist_add_tail(&dev->knode_class,
&dev->class->p->klist_devices);
/* notify any interfaces that the device is here */
list_for_each_entry(class_intf,
&dev->class->p->interfaces, node)
if (class_intf->add_dev)
class_intf->add_dev(dev, class_intf);
mutex_unlock(&dev->class->p->mutex);
}
done:
put_device(dev);
return error;
DPMError:
bus_remove_device(dev);
BusError:
device_remove_attrs(dev);
AttrsError:
device_remove_class_symlinks(dev);
SymlinkError:
if (MAJOR(dev->devt))
devtmpfs_delete_node(dev);
if (MAJOR(dev->devt))
device_remove_sys_dev_entry(dev);
devtattrError:
if (MAJOR(dev->devt))
device_remove_file(dev, &devt_attr);
ueventattrError:
device_remove_file(dev, &uevent_attr);
attrError:
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_REMOVE);
kobject_del(&dev->kobj);
Error:
cleanup_device_parent(dev);
if (parent)
put_device(parent);
name_error:
kfree(dev->p);
dev->p = NULL;
goto done;
}
<pre name="code" class="cpp">int bus_add_device(struct device *dev)
{
struct bus_type *bus = bus_get(dev->bus);
int error = 0;
if (bus) {
pr_debug("bus: '%s': add device %s\n", bus->name, dev_name(dev));
error = device_add_attrs(bus, dev);
if (error)
goto out_put;
error = sysfs_create_link(&bus->p->devices_kset->kobj,
&dev->kobj, dev_name(dev));
if (error)
goto out_id;
error = sysfs_create_link(&dev->kobj,
&dev->bus->p->subsys.kobj, "subsystem");
if (error)
goto out_subsys;
<strong><span style="color:#CC0000;">klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_devices);</span></strong>
}
return 0;
out_subsys:
sysfs_remove_link(&bus->p->devices_kset->kobj, dev_name(dev));
out_id:
device_remove_attrs(bus, dev);
out_put:
bus_put(dev->bus);
return error;
}
這樣,i2c-client device掛載到了i2c bus上。當i2c 設備驅動添加到系統時,就出現了在前幾部分的東西了。從bus上取下i2c-client與i2c-driver進行匹配。
雖然i2-client怎麼掛載到i2c-bus上知道了(由qup_i2c_probe調用of_i2c_register_device掛載)。新的問題又來了:qup_i2c_probe參數是platform_device,i2c-bus又是如何建立platform_device的。
(kernel/include/linux/init.h)
#define arch_initcall(fn) <span style="color:#FF0000;">__define_initcall("3",fn,3)</span>
#define __define_initcall(level,fn,id) \
static initcall_t __initcall_##fn##id __used \
__attribute__((__section__(".initcall" level ".init"))) = fn
將i2c-bus的driver init函數放到.initcall3.init 代碼段中。
之所以,i2c-bus的driver和i2c 設備的驅動init函數使用的不同的函數放到.initcall代碼段,主要原因是後面調用.initcall中的函數執行順序是按.initcall段的函數順序進行的(按照initcall的level從0到7依次存放的)。
(kernel/include/linux/vmlinux.lds.h)
#define INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(level) \ VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__initcall##level##_start) = .; \ *(.initcall##level##.init) \ *(.initcall##level##s.init) #define INIT_CALLS \ VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__initcall_start) = .; \ *(.initcallearly.init) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(0) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(1) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(2) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(3) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(4) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(5) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(rootfs) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(6) \ INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(7) \ VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__initcall_end) = .;
那麼現在根據前面部分內容,知道driver_register將platform bus上的platform device取下來,與driver進行匹配。到此終於理順了從dts節點信息到驅動註冊的完整過程。
四、module_init()中的驅動初始化後函數何時被調用
(kernel/include/linux/init.h)
#define module_init(x) __initcall(x);
#define __initcall(fn) device_initcall(fn)
#define device_initcall(fn) __define_initcall("6",fn,6)
#define __define_initcall(level,fn,id) /
static initcall_t __initcall_##fn##id __used /
__attribute__((__section__(".initcall" level ".init"))) = fn
initcall_t(typedef int (*initcall_t)(void))
這樣就將module_init傳遞的fn函數放到了制定的.initcall6.init 代碼段中。
在linux /init/main.c 中,
static void __init do_initcalls(void)
{
initcall_t *call;
call = &__initcall_start;
do {
(*call)();
call++;
} while (call < &__initcall_end);
flush_scheduled_tasks();
}
通過do_initcalls就可以吧__initcall section段的函數調用起來。
參考文章: http://blog.csdn.net/MarsWG/archive/2004/11/05/168552.aspx