Android开发实践 界面编程(上)
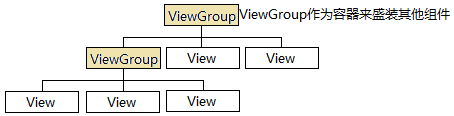
Android应用大部分UI组件都放在android.widget包及其子包、android.view包及其子包中,所有UI组件都继承了View类,Android采用“组合器”设计模式来设计View和ViewGroup(ViewGroup是View的子类),Android图形用户界面的组件层次如下图:
在此强烈建议阅读官方文档(Documentation for Android SDK,打开index.html,Develop -> API Guides / Reference)。
Android中布局建议采用XML布局文件和Java代码(变化多、行为控制复杂的用Java代码)混合控制UI界面
下面我们开始Android界面编程的大探险(一些简单的属性,例如layout_width、layout_height等,下面将不再赘述)。
1.UI控件-布局管理器
所有布局管理器都是ViewGroup的子类,Android布局管理器类图(StarUML绘制)如下:
1)线性布局LinearLayout
<span style="font-size:14px;">android:orientation="" 设置布局管理器内组件的排列方式,horizontal水平、vertical垂直(默认) android:gravity="" 用于控制它所包含的子元素的对齐方式 android:layout_gravity="" 设置该子元素在父容器中的对齐方式</span>
2)表格布局TableLayout
通过添加TableRow、其他组件控制表格行数、列数<TableRow>..</TableRow> 添加1个表格行 android:shrinkColumns="1" 指定第2列允许收缩 android:stretchColumns="2" 指定第3列可以被拉伸 android:stretchColumns="1,2" 指定第2、3列可以被拉伸 android:collapseColumns="1" 指定第2列被隐藏
3)帧布局FrameLayout
android:layout_gravity=""
4)相对布局RelativeLayout
android:gravity="" android:ignoreGravity="" 设置哪个组件不受gravity影响 android:layout_centerHorizontal="" 定义该组件位于父容器水平居中 android:layout_centerInParent="" 定义该组件位于父容器中间 android:layout_above="@id/abc" 定义该组件位于abc组件的上方 android:layout_below="@id/abc" 定义该组件位于abc组件的下方 android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/abc" 定义该组件位于abc组件的左边 android:layout_alignLeft="@id/abc" 控制该组件位于abc的左边界对齐 android:layout_alignParentLeft="@id/abc" 控制该组件是否与布局容器左边对齐
5)网格布局GridLayout
GridLayout是Android4.0新增的布局管理器
<span style="font-size:14px;">android:alignmentMode="" 设置GridLayout采用的对齐模式 android:columnCount="4" 设置网格列数量 android:columnOrderPreserved="" 设置网格容器是否保留列序号 android:rowCount="" 设置网格行数量 android:rowOrderPreserved="" 设置网格容器是否保留行序号 android:useDefaultMargins="" 设置GridLayout是否使用默认的页边距</span>
6)绝对布局AbsoluteLayout
(已过时,这里不再探讨。)
2.UI组件-TextView及其子类
TextView及其子类类图如下:
TextView和EditText最大区别在于TextView不允许用户编辑文本内容。1)TextView属性
android:drawableEnd="@drawable/icon" 设置文本框结尾处绘制图片 android:ellipsize="middle" 设置中间省略 android:textAllCaps="true" 设置所有字母大写 android:autoLink="email|phone" 对邮件、电话增加链接 android:shadowColor="#0000ff" 设置文字阴影 android:shadowDx="10.0" android:shadowDy="8.0" android:shadowRadius="3.0" android:password="true" 设置密码框
2)CheckedTextView属性
<CheckedTextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="可勾选的文本" android:checkMark="@drawable/ok" /> 通过checkMark设置该文本框的勾选图标
3)圆角边框、渐变背景的TextView
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="带边框的文本"
android:background="@drawable/bg_border" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="圆角边框、渐变背景的文本"
android:background="@drawable/bg_border2" />
</LinearLayout>
bg_border.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<solid android:color="#0000"/> <!-- 设置背景色为透明色 -->
<stroke android:width="4px" android:color="#f00" /> <!-- 设置红色边框 -->
</shape>
bg_border2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle">
<!-- 指定圆角矩形的4个圆角的半径 -->
<corners android:topLeftRadius="20px"
android:topRightRadius="5px"
android:bottomRightRadius="20px"
android:bottomLeftRadius="5px"/>
<!-- 指定边框线条的宽度和颜色 -->
<stroke android:width="4px" android:color="#f0f" />
<!-- 指定使用渐变背景色,使用sweep类型的渐变,颜色从红色→绿色→蓝色 -->
<gradient android:startColor="#f00"
android:centerColor="#0f0"
android:endColor="#00f"
android:type="sweep"/>
</shape>
4)EditText组件的用法
<!-- android:selectAllOnFocus="true" 若文本框内容可选择,设置当它获取焦点时自动选中所有文本 --> <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="请填写登录帐号" android:selectAllOnFocus="true" /> <!-- inputType="numberPassword" 表明只能接收数字密码 inputType="number"表明是数值输入框 inputType="date"表明是日期输入框 inputType="phone"表明是输入电话号码的输入框 --> <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType="numberPassword" />
5)Button组件的用法
<!-- 文字带阴影的按钮 --> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="文字带阴影的按钮" android:shadowColor="#aa5" android:shadowRadius="1" android:shadowDx="5" android:shadowDy="5" /> <!-- 普通文字按钮 --> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@drawable/red" android:text="普通按钮" /> <!-- 带文字的图片按钮--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@drawable/button_selector" android:text="带文字的图片按钮" /> <!-- 意图过滤器 --> button_selector.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <!-- 指定按钮按钮下时的图片 --> <item android:state_pressed="true" android:drawable="@drawable/red" /> <!-- 指定按钮松开时的图片 --> <item android:state_pressed="false" android:drawable="@drawable/purple" /> </selector>
6)点9图片
实现只缩放图片中的某个部分的效果(可用于屏幕适配)draw9patch工具 --> sdk\tools\draw9patch.bat

7)单选按钮(RadioButton)与复选框(CheckBox)的用法
RadioButton与CheckBox的不同在于一组RadioButton只能选中其中一个,因此RadioButton常与RadioGroup一起使用,用于定义一组单选按钮。如下定义了一个让用户选择的输入界面:
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TableRow> <!-- 定义一组单选框 --> <RadioGroup android:id="@+id/rg" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"> <!-- 定义两个单选框 --> <RadioButton android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/javaee" android:text="JavaEE" android:checked="true" /> <RadioButton android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/android" android:text="Android" /> </RadioGroup> </TableRow> <TableRow> <!-- 定义一个垂直的线性布局 --> <LinearLayout android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <!-- 定义三个复选框 --> <CheckBox android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="A" android:checked="true" /> <CheckBox android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="B" /> <CheckBox android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="C" /> </LinearLayout> </TableRow> <TextView android:id="@+id/show" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </TableLayout>CheckButtonTest.java
下面添加事件监听采用了“委托式”事件处理机制(当事件源上发生事件时,该事件会激发该事件源上的监听器的特定方法)。
public class CheckButtonTest extends Activity {
private RadioGroup rg;
private TextView show;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
rg = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.rg);
show = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.show);
// 为RadioGroup组件的OnCheck事件绑定事件监听器
rg.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
// 根据用户勾选的单选按钮来动态改变tip字符串的值
String tip = checkedId == R.id.javaee ? "您最热爱的技术是JavaEE": "您最热爱的技术是Android";
// 修改show组件中的文本。
show.setText(tip);
}
});
}
}
8)其他
状态开关按钮(ToggleButton)
开关(Switch)
时钟(AnalogClock和DigitalClock)
计时器(Chronometer)
详细使用方法请查阅Android官方文档,这里不再赘述。
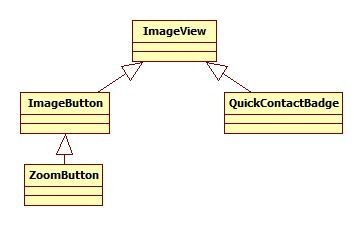
3.UI组件-ImageView及其子类
ImageView及其子类类图如下:
1)图片浏览器 - 实现增大降低透明度、下一张功能
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center"> <Button android:id="@+id/maxus" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="增大透明度" /> <Button android:id="@+id/minus" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="降低透明度" /> <Button android:id="@+id/next" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="下一张" /> </LinearLayout> <!-- 定义显示图片整体的ImageView --> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="240px" android:src="@drawable/image1" android:scaleType="fitCenter"/> <!-- 定义显示图片局部细节的ImageView --> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image2" android:layout_width="120dp" android:layout_height="120dp" android:background="#00f" android:layout_marginTop="10dp"/> </LinearLayout>ImageViewTest.java
public class ImageViewTest extends Activity {
// 一个访问图片的数组
int[] images = new int[]{
R.drawable.image1,
R.drawable.image2,
R.drawable.image3,
R.drawable.image4,
R.drawable.image5,
};
// 默认显示的图片
int currentImg = 2;
// 图片的初始透明度
private int alpha = 255;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
final Button maxus = (Button) findViewById(R.id.maxus);
final Button minus = (Button) findViewById(R.id.minus);
final ImageView image1 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image1);
final ImageView image2 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image2);
final Button next = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
// 查看下一张图片的监听器
next.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 设置ImageView显示下一张图片
image1.setImageResource(images[++currentImg % images.length]);
}
});
// 改变图片透明度的方法
OnClickListener listener = new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (v == maxus) {
alpha += 20;
}
if (v == minus) {
alpha -= 20;
}
if (alpha >= 255) {
alpha = 255;
}
if (alpha <= 0) {
alpha = 0;
}
// 改变图片的透明度
image1.setAlpha(alpha);
}
};
// 为两个按钮添加监听器
maxus.setOnClickListener(listener);
minus.setOnClickListener(listener);
image1.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View view, MotionEvent event) {
BitmapDrawable bitmapDrawable = (BitmapDrawable) image1
.getDrawable();
// 获取第一个图片显示框中的位图
Bitmap bitmap = bitmapDrawable.getBitmap();
// bitmap图片实际大小与第一个ImageView的缩放比例
double scale = bitmap.getWidth() / 320.0;
// 获取需要显示的图片的开始点
int x = (int) (event.getX() * scale);
int y = (int) (event.getY() * scale);
if (x + 120 > bitmap.getWidth()) {
x = bitmap.getWidth() - 120;
}
if (y + 120 > bitmap.getHeight()) {
y = bitmap.getHeight() - 120;
}
// 显示图片的指定区域
image2.setImageBitmap(Bitmap.createBitmap(bitmap, x, y, 120, 120));
image2.setAlpha(alpha);
return false;
}
});
}
}
4.UI组件-AdapterView及其子类(一)
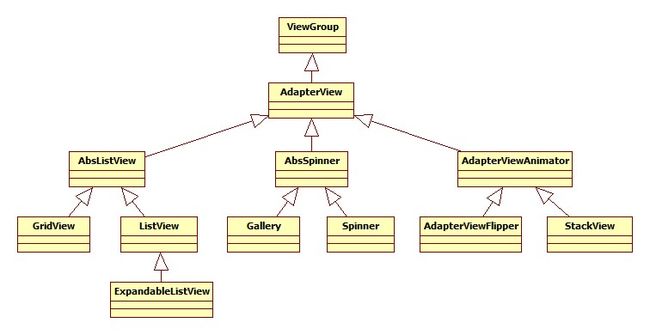
AdapterView继承了ViewGroup,它的本质是容器。AdapterView显示的多个列表项由Adapter提供,调用AdapterView的setAdapter(Adapter)方法设置Adapter即可。
AdapterView派生了三个子类:AbsListView、AbsSpinner、AdapterViewAnimator,这三个子类也是抽象的,实际使用往往采用它们的子类。AdapterView及其子类类图如下:
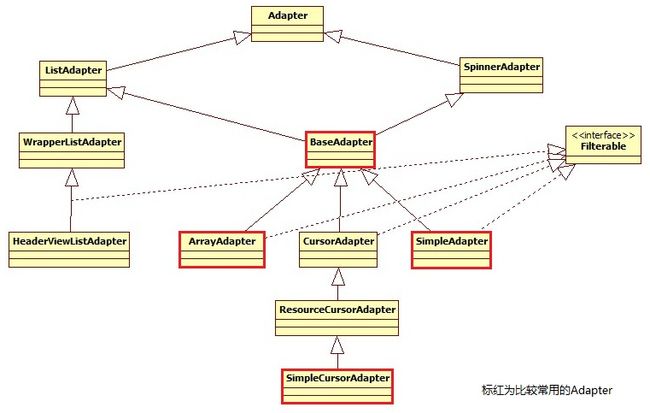
Adapter及其子类类图如下:
1)基于数组的ListView
\res\layout\main.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <!-- 直接使用数组资源给出列表项 设置使用红色的分隔条 --> <ListView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:entries="@array/dev" android:divider="#f00" android:dividerHeight="2px" android:headerDividersEnabled="false" /> </LinearLayout> \res\values\arrays.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <resources> <string-array name="dev"> <item>Java</item> <item>JavaEE</item> <item>Android</item> </string-array> </resources>
2)使用ArrayAdapter创建ListView
布局文件如下:
\res\layout\main.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <!-- divider="#f00" 设置使用红色的分隔条 --> <ListView android:id="@+id/list" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:divider="#f00" android:dividerHeight="2px" android:headerDividersEnabled="false" /> </LinearLayout> \res\layout\array_item.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/TextView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="24dp" android:padding="10px" android:shadowColor="#f0f" android:shadowDx="4" android:shadowDy="4" android:shadowRadius="2"/>
ArrayAdapterTest.java
public class ArrayAdapterTest extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
ListView list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list);
String[] arr = { "Java", "JavaEE", "Android" };
// 创建ArrayAdapter对象
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, R.layout.array_item, arr);
// 设置Adapter
list.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}
另外,基于ListActivity实现列表,只需要去除ListView布局文件,然后修改ArrayAdapterTest.java如下:
public class ArrayAdapterTest extends ListActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//无须使用布局文件
String[] arr = { "Java", "JavaEE", "Android" };
// 创建ArrayAdapter对象
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_multiple_choice, arr);
// 设置Adapter
setListAdapter(adapter);
}
}
3)继承BaseAdapter实现ListView
继承BaseAdapter可取得对Adapter最大的控制权。下面我们简单实现一下, 布局文件如下:main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <ListView android:id="@+id/myList" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"/> </LinearLayout>adapter_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="55dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:singleLine="true"
android:text="哈哈哈"
android:textSize="16sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
下面来看看具体代码实现,首先设置全局变量和编写实体类
/**
* 设置全局变量
* 注意:需要在AndroidManifest.xml中做配置
*/
public class MyApplication extends Application{
private static Context context;//全局的上下文
//app的入口函数
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//初始化COntext
context = this;
}
/**
* 获取全局的上下文
* @return
*/
public static Context getContext(){
return context;
}
}
/**
* 实体类
*/
public class AppInfo {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
然后再来看看BaseAdapterTest.java
public class BaseAdapterTest extends Activity {
private ArrayList<AppInfo> list ;
private ListView myList;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
myList = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.myList);
... // 解析json或者xml,获取请求的数据
myList.setAdapter(new MyAdapter(list));
}
}
MyAdapter.java(已做优化处理)
public class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private ArrayList<AppInfo> list;
public MyAdapter(ArrayList<AppInfo> list) {
super();
this.list = list;
}
/**
* 设置条目个数
*/
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
/**
* 获取对应条目的数据
*/
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return null;
}
/**
* 获取对应条目的id
*/
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return 0;
}
/**
* 设置条目样式
*/
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if(convertView==null){
convertView = View.inflate(MyApplication.getContext(), R.layout.adapter_main, null);
}
ViewHolder holder = ViewHolder.getHolder(convertView);
// 获取实体类<AppInfo>,设置数据
AppInfo appInfo = list.get(position);
holder.tv_name.setText(appInfo.getName());
return convertView;
}
/**
* 利用ViewHolder进行性能优化
*/
static class ViewHolder{
TextView tv_name;
public ViewHolder(View convertView){
tv_name = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
}
public static ViewHolder getHolder(View convertView){
ViewHolder holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
if(holder==null){
holder = new ViewHolder(convertView);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}
return holder;
}
}
}