SGI STL源码之内存配置
好长时间没有写博客了,最近一直忙于看STL源码和实验室其它事情。在骑行了12公里的情况下,终于停歇下
来,静静地坐着,开始思考人生,思考STL是如何配置内存的。
1、SGI STL在配置内存的时候主要考虑了以下几点:
①向堆申请空间
②考虑了多线程
③考虑了内存碎片的问题
④考虑了当内存不足时的应变策略
在C++中申请堆内存使用的是new操作符,释放堆内存使用的是delete操作符,这两个操作符相当于C语言的
malloc()、free()函数。不知道是历史原因还是因为C++中没有realloc这种类似功能的函数(或操作符),SGI STL在申请和释放内存时使用的是C语言函数。
至于多线程,就需要考虑同步的问题,以防多个线程同时修改全局变量。在Linux系统下采用的是互斥锁
(pthread_mutex_lock()、pthread_mutex_unlock()),在windows系统下采用的是临界区。
内存碎片的问题,也是本博客主要讲解的内容。SGI STL在内存碎片处理的问题上采用了两级配置器,第一级配
置器主要是用来配置大于128K字节的内存、第二级配置器主要是用来配置小于128K字节(小块内存)的内存。我们首先来看看第一级配置器做了什么。以下程序是我从源码中提炼出来的关于第一级配置的精华(源码稍后会给出)。
template<int ints>
class __malloc_alloc_template
{
public:
static void *allocate(int n)
{
void *tmp = malloc(n);
if (tmp == 0)
exit(1);
}
static void deallocate(void *p)
{
free(p);
}
static void *reallocate(void*p, int n)
{
void *tmp = realloc(p, n);
if (tmp == 0)
exit(1);
}
};
我们从代码中可以发现,第一级配置器主要是转调用C语言的malloc、free及realloc函数而已,其中的模板参数并没有什么用处。
第二级配置器的做法是如果配置的内存大于128K字节,就移交给第一级配置器去处理。当区块小于128字节时,
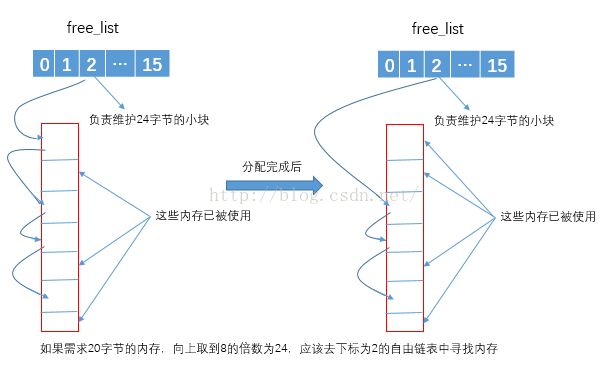
则以内存池的方式来管理:每次配置一大块内存,并维护对于的自由链表。如果下次再有相应大小的内存需求,则直接向自由链表中索取,如果客端释放小额区块,则有配置器回收到自由链表中。设计的理念是防止频繁的对小块内存的申请和释放。为了方便管理内存,SGI采用8字节对齐的方式,比如我需要12字节的内存,SGI会给你配置16个字节的内存,即向上取到8的倍数。第二级配置器维护了16个自由链表,负责维护16种小型区块的配置,下标从0开始,依次维护的内存大小为8、16、24、32、40、48、56、64、72、80、88、96、104、112、120、128(单位为字节)。自由链表的结构为:
union obj
{
union obj*free_list;
char client_data[1];
}
你是否能意识到此联合体的妙用?从第一个字段观之,obj可被看做是一个指针,指向相同形式的另一个obj。从其第二个字段观之,obj可被视为指针,指向实际的区块,一物二用。
下面我们以图解的方式来说明:
内存配置的具体过程:共分为三种情况:
①需求的内存大于128k,就调用第一级配置器,这种情况非常简单,就不做介绍。
②需求的内存小于128k,且自由链表中有可用的空间。根据需求的内存,计算出其应该去哪个自由链表中搜索。然后取出自由链表中第一个可用的空间,并修改自由链表的指针。比如,我们需求的内存为20个字节,向上取到8的倍数为24,因此我们应该去下标为2的自由链表中取内存。
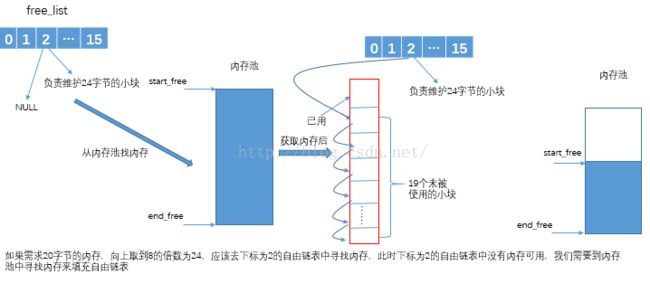
③需求的内存小于128K,且自由链表中没有可用的内存。这时我们需要从内存池中获取内存。我们期望从内存池中一次性获取20个块,来填充自由链表。究竟能得到多少个块,这取决于内存池的当前容量。我们可以分为以下3中情形:
<1>内存池容量足够大。在这种情形下直接从内存池取出20个小块的容量填充到自由链表中。
<2>内存池有容量,但容量的大小只能提供1个及以上的块,不足于20个块的大小。此时,尽可能多地从内存池取内存来填充自由链表。
<3>内存池的容量不足于1个小块的需求。此时我们要把内存池中剩余的那点内存填充到合适的自由链表中,然后使用malloc申请一块大的堆内存,堆内存的大小为2*20*需求的小块。
下面的代码是我从源代码中提取的关于二级配置器分配内存的精华
/*第二级配置器*/
template<bool thread,int inst>
class __default_alloc_template
{
private:
enum{ ALINE = 8,MAXBYTES = 128, NUM_FREE_LIST = MAXBYTES/ALINE};
static char *start;//内存池的起始地址
static char *end;//内存池的结束地址
static int heap_size;//堆上已有内存的大小
union obj
{
union obj *free_list;
char client[1];
};
static obj *free_list[NUM_FREE_LIST];
static int round_up(int bytes)//上调至8的倍数
{
return ((bytes + ALINE - 1) & ~(ALINE - 1));
}
static int free_list_index(int bytes)//寻找自由链表的下标
{
return ((bytes + ALINE - 1) / ALINE - 1);
}
public:
static void *allocate(int size);
static void *refill(int size);
static char *chunk_alloc(int size, int &nobjs);
static void *reallocate(void *p,int old_size,int new_size);
static void deallocate(void *p,int size);
};
template<bool thread, int inst>
char *__default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::start = 0;
template<bool thread, int inst>
char *__default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::end = 0;
template<bool thread, int inst>
typename __default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::obj * __default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::free_list[NUM_FREE_LIST]
= { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
template<bool thread, int inst>
int __default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::heap_size = 0;
template<bool thread, int inst>
void *__default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::allocate(int size)
{
if (size > MAXBYTES)
return __malloc_alloc_template<0>::allocate(size);//使用第一级配置器
obj **my_free_list;
obj *result;
my_free_list = free_list + free_list_index(size);
result = *my_free_list;
if (0 == result)//自由链表没有可用的内存,进行重新填充
{
void *tmp = refill(round_up(size));
return tmp;
}
*my_free_list = result->free_list;
return result;
}
template<bool thread, int inst>
void *__default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::refill(int size)
{
int nobjs = 20;
char *chunk = chunk_alloc(size, nobjs);//nobjs按引用传递
if (1 == nobjs)//如果只够一个块的大小
return chunk;
/*如果有多个小块,则把这几个小块串成链表*/
obj **my_free_list = free_list + free_list_index(size);
obj *next;
next = *my_free_list = (obj*)(chunk + size);
for (int i = 1; i < nobjs - 1; i++)
{
next->free_list = (obj*)((char*)next + size);
next = next->free_list;
}
next->free_list = 0;
return chunk;
}
template<bool thread, int inst>
char *__default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::chunk_alloc(int size, int &nobjs)
{
int need_size = size * nobjs;
int left_size = end - start;
char *result = start;
/*内存池中的内存足够用*/
if (left_size >= need_size)
{
start += need_size;
return result;
}
/*内存池中空间不够,但足够一个以上的块使用*/
else if (left_size >= size)
{
nobjs = left_size / size;
start += nobjs * size;
return result;
}
/*内存池剩余的空间满足不了一个小块的需求*/
else
{
int bytes_to_get = 2 * need_size + round_up(heap_size >> 4);
/*尝试利用内存池剩余的零头*/
if (left_size > 0)
{
obj **my_free_list = free_list + free_list_index(left_size);
obj *tmp = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = (obj *)start;
(*my_free_list)->free_list = tmp;
}
/*配置堆用来补充内存池*/
result = (char *)malloc(bytes_to_get);
/*只做简单的处理:没有足够的内存则终止程序*/
if (result == 0)
exit(1);
start = result + need_size;
end = result + bytes_to_get;
heap_size += bytes_to_get;
return result;
}
}
template<bool thread, int inst>
void *__default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::reallocate(void *p, int old_size, int new_size)
{
/*如果新旧内存都大于MAXBYTES*/
if (old_size > MAXBYTES && new_size > MAXBYTES)
return realloc(p, new_size);
/*如果新旧内存调整到8的倍数后相等*/
if (round_up(old_size) == round_up(new_size))
return p;
void *result = allocate(new_size);
int min_copy = old_size > new_size ? new_size : old_size;
memcpy(result, p, min_copy);
deallocate(p, old_size);
return result;
}
template<bool thread, int inst>
void __default_alloc_template<thread, inst>::deallocate(void *p, int size)
{
if (size > MAXBYTES)
malloc_alloc::deallocate(p);
/*回收到自由列表中*/
else
{
obj**my_free_list = free_list + free_list_index(size);
obj *tmp = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = (obj*)p;
(*my_free_list)->free_list = tmp;
}
}
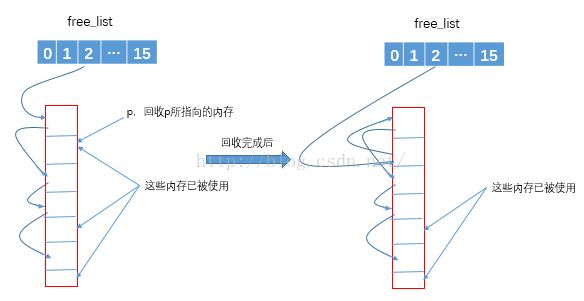
二级配置器又是如何回收内存的呢?如果回收的内存大于128字节,那么直接交给第一级配置器进行free掉;如果回收的内存小于128字节,则直接回收到自由链表中。
SGI STL的源码如下:
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_H
#ifdef __SUNPRO_CC
# define __PRIVATE public
#else
# define __PRIVATE private
#endif
#ifdef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
# define __USE_MALLOC
#endif
/* 这实现了一些标准的节点配置.这些与在C++标准草案或在原STL分配器都不一样。
它们不封装不同的指针类型;事实上,我们假设只有一个指针类型。
配置元素的目的是分配对象,与原来的STL分配器相比没有更大的用途。
*/
/**********************19~28行主要是处理内存溢出***********************************/
#ifndef __THROW_BAD_ALLOC
# if defined(__STL_NO_BAD_ALLOC) || !defined(__STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS)
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
# define __THROW_BAD_ALLOC fprintf(stderr, "out of memory\n"); exit(1)
# else
# include <new>
# define __THROW_BAD_ALLOC throw std::bad_alloc()
# endif
#endif
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#ifndef __RESTRICT
# define __RESTRICT
#endif
#ifdef __STL_THREADS
# include <stl_threads.h>
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true
# ifdef __STL_SGI_THREADS
// We test whether threads are in use before locking.
// Perhaps this should be moved into stl_threads.h, but that
// probably makes it harder to avoid the procedure call when
// it isn't needed.
extern "C" {
extern int __us_rsthread_malloc;
}
// The above is copied from malloc.h. Including <malloc.h>
// would be cleaner but fails with certain levels of standard
// conformance.
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK if (threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) \
{ _S_node_allocator_lock._M_acquire_lock(); }
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK if (threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) \
{ _S_node_allocator_lock._M_release_lock(); }
# else /* !__STL_SGI_THREADS */
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK \
{ if (threads) _S_node_allocator_lock._M_acquire_lock(); }
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK \
{ if (threads) _S_node_allocator_lock._M_release_lock(); }
# endif
#else
// Thread-unsafe
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS false
#endif
__STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma set woff 1174
#endif
// Malloc-based allocator. Typically slower than default alloc below.
// Typically thread-safe and more storage efficient.
#ifdef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
# ifdef __DECLARE_GLOBALS_HERE
void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = 0;
// g++ 2.7.2 does not handle static template data members.
# else
extern void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)();
# endif
#endif
template <int __inst>
class __malloc_alloc_template
{
private:
static void* _S_oom_malloc(size_t);
static void* _S_oom_realloc(void*, size_t);
#ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
static void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)();
#endif
public:
static void* allocate(size_t __n)
{
void* __result = malloc(__n);
if (0 == __result) __result = _S_oom_malloc(__n);
return __result;
}
static void deallocate(void* __p, size_t /* __n */)
{
free(__p);
}
static void* reallocate(void* __p, size_t /* old_sz */, size_t __new_sz)
{
void* __result = realloc(__p, __new_sz);
if (0 == __result) __result = _S_oom_realloc(__p, __new_sz);
return __result;
}
static void (* __set_malloc_handler(void (*__f)()))()
{
void (* __old)() = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
__malloc_alloc_oom_handler = __f;
return(__old);
}
};
// 内存溢出处理函数
#ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
template <int __inst>
void (* __malloc_alloc_template<__inst>::__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = 0;
#endif
template <int __inst>
void*
__malloc_alloc_template<__inst>::_S_oom_malloc(size_t __n)
{
void (* __my_malloc_handler)();
void* __result;
for (;;) {
__my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
if (0 == __my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }
(*__my_malloc_handler)();
__result = malloc(__n);
if (__result) return(__result);
}
}
template <int __inst>
void* __malloc_alloc_template<__inst>::_S_oom_realloc(void* __p, size_t __n)
{
void (* __my_malloc_handler)();
void* __result;
for (;;) {
__my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
if (0 == __my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }
(*__my_malloc_handler)();
__result = realloc(__p, __n);
if (__result) return(__result);
}
}
typedef __malloc_alloc_template<0> malloc_alloc;
/*定义此类的目的是使配置器的接口能够符合STL规格,内部函数
只是转调用而已,或者调用第一级的配置器或调用第二级的配置器*/
template<class _Tp, class _Alloc>
class simple_alloc
{
public:
static _Tp* allocate(size_t __n)
{ return 0 == __n ? 0 : (_Tp*) _Alloc::allocate(__n * sizeof (_Tp)); }
static _Tp* allocate(void)
{ return (_Tp*) _Alloc::allocate(sizeof (_Tp)); }
static void deallocate(_Tp* __p, size_t __n)
{ if (0 != __n) _Alloc::deallocate(__p, __n * sizeof (_Tp)); }
static void deallocate(_Tp* __p)
{ _Alloc::deallocate(__p, sizeof (_Tp)); }
};
// Allocator adaptor to check size arguments for debugging.
// Reports errors using assert. Checking can be disabled with
// NDEBUG, but it's far better to just use the underlying allocator
// instead when no checking is desired.
// There is some evidence that this can confuse Purify.
template <class _Alloc>
class debug_alloc {
private:
enum {_S_extra = 8}; // Size of space used to store size. Note
// that this must be large enough to preserve
// alignment.
public:
static void* allocate(size_t __n)
{
char* __result = (char*)_Alloc::allocate(__n + (int) _S_extra);
*(size_t*)__result = __n;
return __result + (int) _S_extra;
}
static void deallocate(void* __p, size_t __n)
{
char* __real_p = (char*)__p - (int) _S_extra;
assert(*(size_t*)__real_p == __n);
_Alloc::deallocate(__real_p, __n + (int) _S_extra);
}
static void* reallocate(void* __p, size_t __old_sz, size_t __new_sz)
{
char* __real_p = (char*)__p - (int) _S_extra;
assert(*(size_t*)__real_p == __old_sz);
char* __result = (char*)
_Alloc::reallocate(__real_p, __old_sz + (int) _S_extra,
__new_sz + (int) _S_extra);
*(size_t*)__result = __new_sz;
return __result + (int) _S_extra;
}
};
# ifdef __USE_MALLOC
typedef malloc_alloc alloc;
typedef malloc_alloc single_client_alloc;
# else
#if defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__)
// breaks if we make these template class members:
enum {_ALIGN = 8};
enum {_MAX_BYTES = 128};
enum {_NFREELISTS = 16}; // _MAX_BYTES/_ALIGN
#endif
/*第二级配置器*/
template <bool threads, int inst>
class __default_alloc_template
{
private:
#if ! (defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__))
enum {_ALIGN = 8};//对齐字节数
enum {_MAX_BYTES = 128};//块的最大字节数
enum {_NFREELISTS = 16}; // 16个自由链表
# endif
static size_t _S_round_up(size_t __bytes) //将__bytes提升到8的倍数
{
return (((__bytes) + (size_t) _ALIGN-1) & ~((size_t) _ALIGN - 1));
}
__PRIVATE:
union _Obj //自由链表的节点结构
{
union _Obj* _M_free_list_link;
char _M_client_data[1];
};
private:
# if defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__HP_aCC)
static _Obj* __STL_VOLATILE _S_free_list[];
# else
static _Obj* __STL_VOLATILE _S_free_list[_NFREELISTS];
# endif
static size_t _S_freelist_index(size_t __bytes)//__bytes所在自由链表的下标
{
return (((__bytes) + (size_t)_ALIGN-1)/(size_t)_ALIGN - 1);
}
static void* _S_refill(size_t __n);//重新填充自由链表
static char* _S_chunk_alloc(size_t __size, int& __nobjs);//分配大块内存
// 大块内存的状态
static char* _S_start_free;//内存池的起始位置
static char* _S_end_free;//内存池的结束位置
static size_t _S_heap_size;//堆的大小
# ifdef __STL_THREADS
static _STL_mutex_lock _S_node_allocator_lock;//如果定义了线程,则声明一个互斥锁
# endif
class _Lock;
friend class _Lock;
class _Lock //主要是用来线程之间的同步
{
public:
_Lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK; }
~_Lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK; }
};
public:
static void* allocate(size_t __n)//分配内存
{
void* __ret = 0;
if (__n > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES)//如果需求内存大于128,则调用第一级配置器
{
__ret = malloc_alloc::allocate(__n);
}
else
{
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n);
#ifndef _NOTHREADS
_Lock __lock_instance;
#endif
_Obj* __RESTRICT __result = *__my_free_list;
if (__result == 0)
__ret = _S_refill(_S_round_up(__n));//自由链表中没有内存则去内存池中寻找内存来填充自由链表
else
{
*__my_free_list = __result -> _M_free_list_link;
__ret = __result;
}
}
return __ret;
};
static void deallocate(void* __p, size_t __n)//回收内存
{
if (__n > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES)//如果回收内存大于128,则直接交给第一级配置器free掉
malloc_alloc::deallocate(__p, __n);
else
{
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n);
_Obj* __q = (_Obj*)__p;
#ifndef _NOTHREADS
_Lock __lock_instance;
#endif /* _NOTHREADS */
__q -> _M_free_list_link = *__my_free_list;
*__my_free_list = __q;
}
}
static void* reallocate(void* __p, size_t __old_sz, size_t __new_sz);
} ;
typedef __default_alloc_template<__NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS, 0> alloc;
typedef __default_alloc_template<false, 0> single_client_alloc;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
inline bool operator==(const __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>&,const __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>&)
{
return true;
}
# ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
inline bool operator!=(const __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>&,const __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>&)
{
return false;
}
# endif /* __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER */
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
char*__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_chunk_alloc(size_t __size, int& __nobjs)
{
char* __result;
size_t __total_bytes = __size * __nobjs;
size_t __bytes_left = _S_end_free - _S_start_free;
if (__bytes_left >= __total_bytes)
{
__result = _S_start_free;
_S_start_free += __total_bytes;
return(__result);
}
else if (__bytes_left >= __size)
{
__nobjs = (int)(__bytes_left/__size);
__total_bytes = __size * __nobjs;
__result = _S_start_free;
_S_start_free += __total_bytes;
return(__result);
}
else
{
size_t __bytes_to_get = 2 * __total_bytes + _S_round_up(_S_heap_size >> 4);
if (__bytes_left > 0)
{
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list =_S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__bytes_left);
((_Obj*)_S_start_free) -> _M_free_list_link = *__my_free_list;
*__my_free_list = (_Obj*)_S_start_free;
}
_S_start_free = (char*)malloc(__bytes_to_get);
if (0 == _S_start_free)
{
size_t __i;
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list;
_Obj* __p;
for (__i = __size;__i <= (size_t) _MAX_BYTES;__i += (size_t) _ALIGN)
{
__my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__i);
__p = *__my_free_list;
if (0 != __p)
{
*__my_free_list = __p -> _M_free_list_link;
_S_start_free = (char*)__p;
_S_end_free = _S_start_free + __i;
return(_S_chunk_alloc(__size, __nobjs));
}
}
_S_end_free = 0; // In case of exception.
_S_start_free = (char*)malloc_alloc::allocate(__bytes_to_get);
}
_S_heap_size += __bytes_to_get;
_S_end_free = _S_start_free + __bytes_to_get;
return(_S_chunk_alloc(__size, __nobjs));
}
}
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
void*__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_refill(size_t __n)
{
int __nobjs = 20;
char* __chunk = _S_chunk_alloc(__n, __nobjs);
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list;
_Obj* __result;
_Obj* __current_obj;
_Obj* __next_obj;
int __i;
if (1 == __nobjs) return(__chunk);
__my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n);
__result = (_Obj*)__chunk;
*__my_free_list = __next_obj = (_Obj*)(__chunk + __n);
for (__i = 1; ; __i++)
{
__current_obj = __next_obj;
__next_obj = (_Obj*)((char*)__next_obj + __n);
if (__nobjs - 1 == __i)
{
__current_obj -> _M_free_list_link = 0;
break;
}
else
{
__current_obj -> _M_free_list_link = __next_obj;
}
}
return(__result);
}
template <bool threads, int inst>
void*__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::reallocate(void* __p,size_t __old_sz,size_t __new_sz)
{
void* __result;
size_t __copy_sz;
if (__old_sz > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES && __new_sz > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES)
{
return(realloc(__p, __new_sz));
}
if (_S_round_up(__old_sz) == _S_round_up(__new_sz))
return(__p);
__result = allocate(__new_sz);
__copy_sz = __new_sz > __old_sz? __old_sz : __new_sz;
memcpy(__result, __p, __copy_sz);
deallocate(__p, __old_sz);
return(__result);
}
#ifdef __STL_THREADS
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
_STL_mutex_lock
__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_node_allocator_lock
__STL_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
#endif
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
char* __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_start_free = 0;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
char* __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_end_free = 0;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
size_t __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_heap_size = 0;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
typename __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE
__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst> ::_S_free_list[
# if defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__HP_aCC)
_NFREELISTS
# else
__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_NFREELISTS
# endif
] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, };
#endif /* ! __USE_MALLOC */
#ifdef __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS
template <class _Tp>
class allocator
{
typedef alloc _Alloc; // 根本的配置器
public:
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef const _Tp* const_pointer;
typedef _Tp& reference;
typedef const _Tp& const_reference;
typedef _Tp value_type;
template <class _Tp1>
struct rebind
{
typedef allocator<_Tp1> other;
};
allocator() __STL_NOTHROW {}
allocator(const allocator&) __STL_NOTHROW {}
template <class _Tp1>
allocator(const allocator<_Tp1>&) __STL_NOTHROW {}
~allocator() __STL_NOTHROW {}
pointer address(reference __x) const { return &__x; }
const_pointer address(const_reference __x) const { return &__x; }
_Tp* allocate(size_type __n, const void* = 0)
{
return __n != 0 ? static_cast<_Tp*>(_Alloc::allocate(__n * sizeof(_Tp))) : 0;
}
void deallocate(pointer __p, size_type __n)
{ _Alloc::deallocate(__p, __n * sizeof(_Tp)); }
size_type max_size() const __STL_NOTHROW
{ return size_t(-1) / sizeof(_Tp); }
void construct(pointer __p, const _Tp& __val) { new(__p) _Tp(__val); }
void destroy(pointer __p) { __p->~_Tp(); }
};
template<>
class allocator<void> {
public:
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef void* pointer;
typedef const void* const_pointer;
typedef void value_type;
template <class _Tp1> struct rebind {
typedef allocator<_Tp1> other;
};
};
template <class _T1, class _T2>
inline bool operator==(const allocator<_T1>&, const allocator<_T2>&)
{
return true;
}
template <class _T1, class _T2>
inline bool operator!=(const allocator<_T1>&, const allocator<_T2>&)
{
return false;
}
// Allocator adaptor to turn an SGI-style allocator (e.g. alloc, malloc_alloc)
// into a standard-conforming allocator. Note that this adaptor does
// *not* assume that all objects of the underlying alloc class are
// identical, nor does it assume that all of the underlying alloc's
// member functions are static member functions. Note, also, that
// __allocator<_Tp, alloc> is essentially the same thing as allocator<_Tp>.
template <class _Tp, class _Alloc>
struct __allocator {
_Alloc __underlying_alloc;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef const _Tp* const_pointer;
typedef _Tp& reference;
typedef const _Tp& const_reference;
typedef _Tp value_type;
template <class _Tp1> struct rebind {
typedef __allocator<_Tp1, _Alloc> other;
};
__allocator() __STL_NOTHROW {}
__allocator(const __allocator& __a) __STL_NOTHROW
: __underlying_alloc(__a.__underlying_alloc) {}
template <class _Tp1>
__allocator(const __allocator<_Tp1, _Alloc>& __a) __STL_NOTHROW
: __underlying_alloc(__a.__underlying_alloc) {}
~__allocator() __STL_NOTHROW {}
pointer address(reference __x) const { return &__x; }
const_pointer address(const_reference __x) const { return &__x; }
// __n is permitted to be 0.
_Tp* allocate(size_type __n, const void* = 0) {
return __n != 0
? static_cast<_Tp*>(__underlying_alloc.allocate(__n * sizeof(_Tp)))
: 0;
}
// __p is not permitted to be a null pointer.
void deallocate(pointer __p, size_type __n)
{ __underlying_alloc.deallocate(__p, __n * sizeof(_Tp)); }
size_type max_size() const __STL_NOTHROW
{ return size_t(-1) / sizeof(_Tp); }
void construct(pointer __p, const _Tp& __val) { new(__p) _Tp(__val); }
void destroy(pointer __p) { __p->~_Tp(); }
};
template <class _Alloc>
class __allocator<void, _Alloc> {
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef void* pointer;
typedef const void* const_pointer;
typedef void value_type;
template <class _Tp1> struct rebind {
typedef __allocator<_Tp1, _Alloc> other;
};
};
template <class _Tp, class _Alloc>
inline bool operator==(const __allocator<_Tp, _Alloc>& __a1,
const __allocator<_Tp, _Alloc>& __a2)
{
return __a1.__underlying_alloc == __a2.__underlying_alloc;
}
#ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER
template <class _Tp, class _Alloc>
inline bool operator!=(const __allocator<_Tp, _Alloc>& __a1,
const __allocator<_Tp, _Alloc>& __a2)
{
return __a1.__underlying_alloc != __a2.__underlying_alloc;
}
#endif /* __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER */
// Comparison operators for all of the predifined SGI-style allocators.
// This ensures that __allocator<malloc_alloc> (for example) will
// work correctly.
template <int inst>
inline bool operator==(const __malloc_alloc_template<inst>&,
const __malloc_alloc_template<inst>&)
{
return true;
}
#ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER
template <int __inst>
inline bool operator!=(const __malloc_alloc_template<__inst>&,
const __malloc_alloc_template<__inst>&)
{
return false;
}
#endif /* __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER */
template <class _Alloc>
inline bool operator==(const debug_alloc<_Alloc>&,
const debug_alloc<_Alloc>&) {
return true;
}
#ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER
template <class _Alloc>
inline bool operator!=(const debug_alloc<_Alloc>&,
const debug_alloc<_Alloc>&) {
return false;
}
#endif /* __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER */
template <class _Tp, class _Allocator>
struct _Alloc_traits
{
static const bool _S_instanceless = false;
typedef typename _Allocator::__STL_TEMPLATE rebind<_Tp>::other
allocator_type;
};
template <class _Tp, class _Allocator>
const bool _Alloc_traits<_Tp, _Allocator>::_S_instanceless;
// The version for the default allocator.
template <class _Tp, class _Tp1>
struct _Alloc_traits<_Tp, allocator<_Tp1> >
{
static const bool _S_instanceless = true;
typedef simple_alloc<_Tp, alloc> _Alloc_type;
typedef allocator<_Tp> allocator_type;
};
// Versions for the predefined SGI-style allocators.
template <class _Tp, int __inst>
struct _Alloc_traits<_Tp, __malloc_alloc_template<__inst> >
{
static const bool _S_instanceless = true;
typedef simple_alloc<_Tp, __malloc_alloc_template<__inst> > _Alloc_type;
typedef __allocator<_Tp, __malloc_alloc_template<__inst> > allocator_type;
};
template <class _Tp, bool __threads, int __inst>
struct _Alloc_traits<_Tp, __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst> >
{
static const bool _S_instanceless = true;
typedef simple_alloc<_Tp, __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst> >
_Alloc_type;
typedef __allocator<_Tp, __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst> >
allocator_type;
};
template <class _Tp, class _Alloc>
struct _Alloc_traits<_Tp, debug_alloc<_Alloc> >
{
static const bool _S_instanceless = true;
typedef simple_alloc<_Tp, debug_alloc<_Alloc> > _Alloc_type;
typedef __allocator<_Tp, debug_alloc<_Alloc> > allocator_type;
};
// Versions for the __allocator adaptor used with the predefined
// SGI-style allocators.
template <class _Tp, class _Tp1, int __inst>
struct _Alloc_traits<_Tp,
__allocator<_Tp1, __malloc_alloc_template<__inst> > >
{
static const bool _S_instanceless = true;
typedef simple_alloc<_Tp, __malloc_alloc_template<__inst> > _Alloc_type;
typedef __allocator<_Tp, __malloc_alloc_template<__inst> > allocator_type;
};
template <class _Tp, class _Tp1, bool __thr, int __inst>
struct _Alloc_traits<_Tp,
__allocator<_Tp1,
__default_alloc_template<__thr, __inst> > >
{
static const bool _S_instanceless = true;
typedef simple_alloc<_Tp, __default_alloc_template<__thr,__inst> >
_Alloc_type;
typedef __allocator<_Tp, __default_alloc_template<__thr,__inst> >
allocator_type;
};
template <class _Tp, class _Tp1, class _Alloc>
struct _Alloc_traits<_Tp, __allocator<_Tp1, debug_alloc<_Alloc> > >
{
static const bool _S_instanceless = true;
typedef simple_alloc<_Tp, debug_alloc<_Alloc> > _Alloc_type;
typedef __allocator<_Tp, debug_alloc<_Alloc> > allocator_type;
};
#endif /* __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS */
#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma reset woff 1174
#endif
__STL_END_NAMESPACE
#undef __PRIVATE
#endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_H */
// Local Variables:
// mode:C++
// End: