objective-c中的self和super关键字
对于这两个关键字,最重要的是搞清楚两点:
1.self是调用该方法的实体,是类中方法的隐藏变量(还有一个是_cmd代表被调用方法的selector),在调用时动态决议;
2.super是“编译器指示符”,在编译时静态决议。super指的是从当前类的super class开始查找相应的selector,找到后让self来调用。注意:不是用superclass的对象来调用该selector。
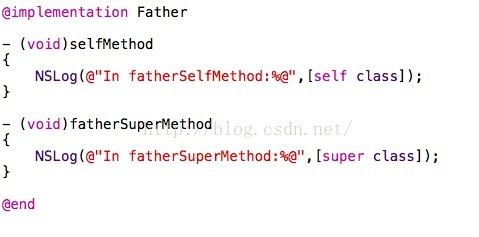
结合一个简单的例子:
其中Son类继承自Father类。
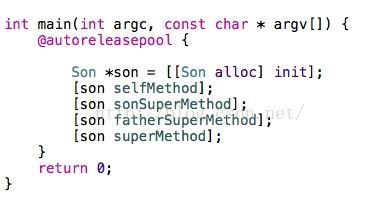
调用:
结果:
从结果可以看到,不管是通过哪种方式来调用class方法,最终输出的都是最初接受消息的Son类的实例对象son的类信息。也就是说,不管使用self或super来调用方法,方法中self指向对象并不会改变。
其实通过super来接收消息时,编译器使用的是以下方法:
/**
* Sends a messagewith a simple return value to the superclass of an instance of a class.
*
* @param super Apointer to an \c objc_super data structure. Pass values identifying the
* context the message was sent to, includingthe instance of the class that is to receive the
* message and the superclass at which to startsearching for the method implementation.
* @param op Apointer of type SEL. Pass the selector of the method that will handle themessage.
* @param ...
* A variable argument list containing thearguments to the method.
*
* @return Thereturn value of the method identified by \e op.
*
* @seeobjc_msgSend
*/
OBJC_EXPORT idobjc_msgSendSuper(struct objc_super *super, SEL op, ...)
__OSX_AVAILABLE_STARTING(__MAC_10_0,__IPHONE_2_0);
其中objc_super结构体定义如下:
/// Specifies the superclass of an instance.
structobjc_super {
/// Specifiesan instance of a class.
__unsafe_unretained id receiver;
/// Specifiesthe particular superclass of the instance to message.
#if!defined(__cplusplus) && !__OBJC2__
/* Forcompatibility with old objc-runtime.h header */
__unsafe_unretained Class class;
#else
__unsafe_unretained Class super_class;
#endif
/* super_classis the first class to search */
};
其中的receiver指向消息中的最初self隐藏参数,区别仅仅是查找对应selector时是从当前类(super关键字所在的类)的super_class的方法列表开始,而不是接收消息的对象isa指针指向的类对象的super_class。但是最终接收该消息的是receiver,还是原来的那个对象,并没有发生改变。