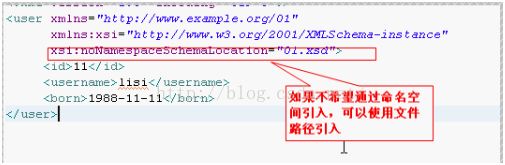
XML:Schema、三种编写Schema的方式
针对DTD文件的不足之处:(不能出现相同名称的元素,DTD的语法不是xml的语法)出现的Schema,需要使用什么命名空间的东西就先引入,使用xmlns,后面加后缀,不加就不用后缀
定义Schema文件,后缀名为xsd
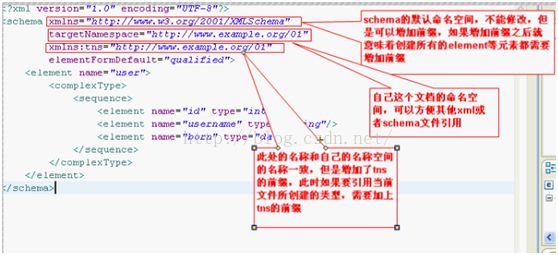
引入XMLSchema那个命名空间,你就可以使用schema、targetNamespace等元素了,它的定义文档在eclipse工具中已经有了,肯定由dtd校验,最初始的。
在xml中引入schema文件校验、提示
DTD和Schema其实可以看做解析XML的程序(比如框架)和书写XML文件之间的约定(比如我们程序员),DTD和Schema由框架提供,就约定了XML的书写模式,你按照这个模式写,那么框架的程序在解析的时候就不会出错。比如dtd中定义*,表示可以定义0到多个元素,那我框架的解析程序就会提供一个list来存储;dtd中定义user?,表示可以出现0或1个User类型,那解析程序就会定义一个User变量来接收。否则你们之间就会出错。
编写Schema的三种方式:
1. Russia Roll(俄罗斯玩偶)
<?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<schemaxmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/02"
xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/02"elementFormDefault="qualified">
<element name="books">
<complexType>
<!-- maxOccurs表示最大出现次数-->
<sequencemaxOccurs="unbounded">
<elementname="book">
<complexType>
<sequenceminOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<elementname="title" type="string" />
<elementname="content" type="string" />
<choice>
<elementname="author" type="string" />
<elementname="authors">
<complexType>
<all><!--每个元素只能出现一次 -->
<elementname="author" type="string"/>
</all>
</complexType>
</element>
</choice>
</sequence>
<attributename="id" type="int" use="required"/>
</complexType>
</element>
</sequence>
</complexType>
</element>
</schema>
优点:结构清晰;缺点:类型不能重用
根据它写的xml文件
<?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<book:booksxmlns:book="http://www.example.org/02"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="02.xsd">
<book:book id="1">
<book:title>Java inaction</book:title>
<book:content>Java isgood</book:content>
<book:author>Bruce</book:author>
</book:book>
<book:book id="2">
<book:title>SOA inaction</book:title>
<book:content>soa isdifficult</book:content>
<book:authors>
<book:author>Jike</book:author>
</book:authors>
</book:book>
</book:books>
2. Salami Slice(腊肉切片)
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<schemaxmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/03"
xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/03"
elementFormDefault="qualified">
<elementname="book" type="tns:bookType"></element>
<elementname="id" type="int"/>
<elementname="title" type="string"/>
<elementname="content" type="string"/>
<complexTypename="bookType">
<sequence>
<elementref="tns:id"/>
<elementref="tns:title"/>
<elementref="tns:content"/>
</sequence>
</complexType>
</schema>
优点:类型最大程度重用;缺点:结构不清晰,根节点都不好确定
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<titlexmlns="http://www.example.org/03"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example.org/03">
12asdasdasd
</title>
3. Venetian Blind(百叶窗)
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<schemaxmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/04"
xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/04"
elementFormDefault="qualified">
<elementname="person" type="tns:personType"/>
<complexTypename="personType">
<sequence>
<elementname="name" type="string"/>
<elementname="age" type="tns:ageType"/>
<elementname="email" type="tns:emailType"/>
</sequence>
<attributename="sex" type="tns:sexType"/>
</complexType>
<simpleTypename="emailType">
<restrictionbase="string">
<patternvalue="(\w+\.*)*\w+@\w+\.[A-Za-z]{2,6}"/>
<minLengthvalue="6"/>
<maxLengthvalue="255"/>
</restriction>
</simpleType>
<simpleTypename="ageType">
<restrictionbase="int">
<minInclusivevalue="1"/>
<maxExclusivevalue="150"/>
</restriction>
</simpleType>
<simpleTypename="sexType">
<restrictionbase="string">
<enumerationvalue="男"/>
<enumerationvalue="女"/>
</restriction>
</simpleType>
</schema>
根据以上写就的xml
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<personxmlns="http://www.example.org/04"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example.org/04"sex="男">
<name>搜索</name>
<age>149</age>
<email>[email protected]</email>
</person>
最好的使用Schema的方式【一个Schema表示一个类,做到分离、模块化】
Student.xsd
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schemaxmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/classroom"
xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/classroom"
elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xsd:elementname="student" type="tns:studentType"/>
<xsd:complexTypename="studentType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:elementname="name" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:elementname="sex" type="tns:sexType"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:simpleTypename="sexType">
<xsd:restrictionbase="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumerationvalue="男"/>
<xsd:enumerationvalue="女"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:schema>
classroom.xsd
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schemaxmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/classroom"
xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/classroom"
elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xsd:includeschemaLocation="student.xsd"/>
<xsd:elementname="classroom" type="tns:classroomType"/>
<xsd:complexTypename="classroomType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:elementname="grade" type="tns:gradeType"/>
<xsd:elementname="name" type="xsd:string"/>
<!-- <xsd:element name="stus">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequenceminOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:elementname="student" type="tns:studentType"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
-->
<xsd:sequenceminOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:elementname="student" type="tns:studentType"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:simpleTypename="gradeType">
<xsd:restrictionbase="xsd:int">
<xsd:minInclusivevalue="2000"/>
<xsd:maxInclusivevalue="3000"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:schema>