16.05.01-16.05.24 题集
练习的故事仍然继续下去,今天写下的题目难度适中,记录自己近段时间的训练成果。涉及数学,动态规划,字符串问题。
poj 2159 Ancient Cipher(规律)
http://poj.org/problem?id=2159
大意:密码加密方法,两种加密方式,第一种,替换加密:Substitution cipher changes all occurrences of each letter to some other letter. Substitutes for all letters must be different(这就是当时做题坑的我一瘸一拐的 一句话).
第二种,排列加密:字符串乱序一下。
分析:那条语句就是精华啊啊啊,告诉我们,在得到每一个字符的出现次数后只需要排列比较是否一样就行。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
char s1[105],s2[105];
int t1[30],t2[30];
int main()
{
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
while(~scanf("%s",s1)){
scanf("%s",s2);
memset(t1,0,sizeof(t1));
memset(t2,0,sizeof(t2));
int len1=strlen(s1),len2=strlen(s2);
for(int i=0;i<len1;i++) t1[s1[i]-'A']++;
for(int i=0;i<len2;i++) t2[s2[i]-'A']++;
bool same=1;
sort(t1,t1+30); sort(t2,t2+30);
for(int i=0;i<30;i++){
if(t1[i]!=t2[i]){ same=0; break; }
}
if(same) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}nefu 1174 Decode(reverse函数)
http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemShow.php?problem_id=1174
大意:将字符串中的小串逆序,然后输出,如:
Sample Input
i evol uoy
doog emag
Sample Output
i love you
good game
linux下用不了个gets(),我的版本号是ubuntu 16.04 LTS:
main.cpp: In function ‘int main()’:
main.cpp:10:12: warning: ‘char* gets(char*)’ is deprecated [-Wdeprecated-declarations]
while(~gets(str)){
^
In file included from main.cpp:1:0:
/usr/include/stdio.h:638:14: note: declared here
extern char *gets (char *__s) __wur __attribute_deprecated__;
^
main.cpp:10:12: warning: ‘char* gets(char*)’ is deprecated [-Wdeprecated-declarations]
while(~gets(str)){
^
In file included from main.cpp:1:0:
/usr/include/stdio.h:638:14: note: declared here
extern char *gets (char *__s) __wur __attribute_deprecated__;
^
main.cpp:10:20: warning: ‘char* gets(char*)’ is deprecated [-Wdeprecated-declarations]
while(~gets(str)){
^
In file included from main.cpp:1:0:
/usr/include/stdio.h:638:14: note: declared here
extern char *gets (char *__s) __wur __attribute_deprecated__;
^
main.cpp:10:20: error: wrong type argument to bit-complement
while(~gets(str)){掌握reverse函数的用法即可。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
char str[1005],s[1005];
int main(){
while(~scanf("%c",&str[0])){
if(str[0]==EOF) break;
int L=1;
while(scanf("%c",&str[L++]) && str[L-1]!='\n');
str[L-1]=0;
int top=0;
for(int i=0;str[i];i++){
if(str[i]==' '){
s[top]=0;
reverse(s,s+top); // 系统函数实现翻转
printf("%s ",s);
top=0;
}
else s[top++]=str[i];
}
s[top]=0;
reverse(s,s+top); // 系统函数实现翻转
printf("%s\n",s);
}
return 0;
}问题拓展:
将字符串整体逆序,小串不逆序
如
asfd dfds fgh jkj
jkj fgh dfds asfd
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char str[100][105],s[105];
char L[10005];
int main()
{
while(gets(L)){
int top=0,len=0;
for(int i=0;L[i];i++){
if(L[i]==' '){
s[top]=0;
strcpy(str[len++],s);
top=0;
}
else s[top++]=L[i];
}
s[top]=0;
strcpy(str[len++],s);
reverse(str,str+len);
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++){
printf("%s ",str[i]);
}
printf("%s\n",str[len-1]);
}
return 0;
}codeforces 645B. Mischievous Mess Makers(贪心)
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/645/B
大意:给出一个1-n的序列,最多进行k次交换,问最大的逆序数是多少?
分析:为了得到最大的逆序数,我们需要交换右边最大的数字和左边最小的数字。最开始的数字有n个,交换一次剩下n-2个数字……如果n是偶数,最后剩下是2个;是奇数的話最后剩下3个。每交换一次,产生的逆序数是n-1+1+1+……+0=2n-3
eg:
1 2 3 4 5
5 2 3 4 1
–>
4 1 1 1 0
设最小n是minm=min(2,n-2k+2) OR min(3,n-2k+2),交换次数c= (n-minm)/2+1
所以最后的逆序数就是2(n+n-2+……+minm)-3c
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main()
{
LL n,k;
while(cin>>n>>k){
if(n==1) {
puts("0"); continue;
}
LL minm=0;
if(n&1) minm=max(3LL,n-2*k+2);
else minm=max(2LL,n-2*k+2); //min n
LL c=(n-minm)/2+1; //swap counts
LL s=c*(n+minm)/2;
s=s*2-3*c;
printf("%I64d\n",s);
}
return 0;
}nefu 1173 Dipper Landlord(规律)
http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemShow.php?problem_id=1173
大意:斗地主游戏。每一次游戏有一个地主两个农民, x=6×2y ,地主赢了加分2x,农民减分x, 农民赢了都加分x, 地主减分2x。现在给出三个数字,问是否合法。
分析:地主每次的变化量是2x,两个农民的变化量是每人x。这样看来它们任意两个数字的差值的绝对值是3x的倍数。同时三个数的和是3000。
当时的思路是比较复杂的。我想着地主,农民,农民: x(2k) -xk -xk
x需要满足的形式是 6×2y , 然后直接判断即可。代码写了老长了,结果还错了T_T
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int r[3];
while(cin>>r[0]>>r[1]>>r[2]){
int sum=r[0]+r[1]+r[2];
int d1=r[0]-r[1];
int d2=r[1]-r[2];
int d3=r[0]-r[2];
if(sum==3000 && d1%18==0 && d2%18==0 && d3%18==0) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
}poj 2262 Goldbach’s Conjecture(简单)
http://poj.org/problem?id=2262
大意:求解6-1000000内的偶数能否写成两个素数之和。
分析:练手
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
vector<int> prim;
int cnt;
bool vis[N];
void getprim(){
for(int i=2;i<N;i++){
if(!vis[i]) prim.push_back(i);
cnt=prim.size();
for(int j=0;j<cnt && prim[j]*i<N;j++){
vis[i*prim[j]]=1;
if(i%prim[j]==0) break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
getprim();
int n;
while(cin>>n&&n){
bool tag=0;
for(int i=1;prim[i]+prim[i]<=n;i++){
int g=n-prim[i];
if(vis[g]==0) {
printf("%d = %d + %d\n",n,prim[i],g);
tag=1;
break;
}
}
if(tag==0) puts("Goldbach's conjecture is wrong.");
}
return 0;
}nyist 368 最长公共子序列(简单)
http://acm.nyist.net/JudgeOnline/problem.php?pid=36&rec=rec
只要求输出字符串的长度:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
char s1[1005],s2[1005];
int g[1005][1005];
int main(){
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%s%s",s1+1,s2+1);
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
for(int i=1;s1[i];i++){
for(int j=1;s2[j];j++){
if(s1[i]==s2[j]){
g[i][j]=g[i-1][j-1]+1;
}
else {
g[i][j]=max(g[i-1][j],g[i][j-1]); //当两者不同时,两个串的当前字符都可能成为LCS的一部分
}
}
}
int len1=strlen(s1+1),len2=strlen(s2+1);
printf("%d\n",g[len1][len2]);
}
return 0;
}问题拓展:
要求输出最长的相同字符子串:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
char s1[1005],s2[1005];
int g[1005][1005];
int dir[1005][1005];
int main(){
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%s%s",s1+1,s2+1);
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
memset(dir,-1,sizeof(dir));
for(int i=1;s1[i];i++){
for(int j=1;s2[j];j++){
if(s1[i]==s2[j]){
g[i][j]=g[i-1][j-1]+1;
dir[i][j]=1; // 左斜上方
}
else {
if(g[i-1][j]>g[i][j-1]) { g[i][j]=g[i-1][j]; dir[i][j]=0; } //上方
else { g[i][j]=g[i][j-1]; dir[i][j]=2; } //左边
}
}
}
int len1=strlen(s1+1),len2=strlen(s2+1);
printf("%d\n",g[len1][len2]);
int x=len1, y=len2, top=0;
char str[1005];
memset(str,0,sizeof(str));
while(x>0 && y>0){
if(s1[x]==s2[y]) str[top++]=s1[x];
if(dir[x][y]==0) x--;
else if(dir[x][y]==1){ x--; y--; }
else if(dir[x][y]==2){ y--; }
}
while(top>0){
printf("%c",str[top-1]);
top--;
}
puts("");
}
return 0;
}codeforces 645A. Amity Assessment(规律)
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/645/A
大意:
能否通过变换使得两者具有相同的结构?
分析:空格相邻的字母来填补空格不会变化的是顺时针的字母顺序。于是整个问题就变成了数组位移问题。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
char B[2][5],E[2][5];
char s1[5],s2[5];
void moves(char ss[]){
char ch=ss[2];
ss[2]=ss[1]; ss[1]=ss[0]; ss[0]=ch;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%s",B[0])){
scanf("%s%s%s",B[1],E[0],E[1]);
s1[0]=B[0][0]; s1[1]=B[0][1]; s1[2]=B[1][1]; s1[3]=B[1][0];
s2[0]=E[0][0]; s2[1]=E[0][1]; s2[2]=E[1][1]; s2[3]=E[1][0];
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
if(s1[i]=='X') {
for(int j=i;j<4;j++) s1[j]=s1[j+1];
}
if(s2[i]=='X') {
for(int j=i;j<4;j++) s2[j]=s2[j+1];
}
}
bool same=0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
if(strcmp(s1,s2)==0) { same=1; break; }
moves(s1);
}
if(same) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}hdu 3853 LOOPS(概率dp)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3853
大意:逃离迷宫,从左上角出发,到达右下角算是成功逃脱。每一个点有三条路径可选,自身,右边,下边,他们的选择概率分别给出,每一次跳跃格子都将花费2份魔力,问逃离迷宫的花费魔力的期望
分析:
假设点(i,j)选择自身,右边,下边的概率分别是
p[i][j][0] , p[i][j][1] , p[i][j][2] 。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const double eps=1e-7;
const int N=1e3+10;
double p[N][N][3],dp[N][N];
int main()
{
freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int r,c;
while(cin>>r>>c){
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(int i=1;i<=r;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=c;j++){
scanf("%lf %lf %lf",&p[i][j][0],&p[i][j][1],&p[i][j][2]);
}
}
for(int i=r;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=c;j>=0;j--){
if(fabs(1-p[i][j][0])<eps) continue;
double t1=1.0-p[i][j][0];
double t2=dp[i][j+1]*p[i][j][1]+dp[i+1][j]*p[i][j][2]+2.0;
dp[i][j]=t2/t1;
}
}
printf("%.3lf\n",dp[1][1]); //现实意义 ~ 左上点
}
return 0;
}poj 1068 Parencodings(简单)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1068
大意:给出q序列求出w序列。q序列——每一个数字qi代表在”)”前面的”(“的个数。w序列——每一个数字wi代表当前”)”和其匹配的”(“之间的”)”的个数。
分析:由q序列推出原来的字符串,然后模拟求出w序列。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
char sta[N];
int main()
{
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int t,n,m;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d",&n);
int top=0,last=0,temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&m);
int temp=m-last;
while(temp--) sta[top++]='(';
sta[top++]=')';
last=m;
}
//cout<<sta<<endl;
int ans[N];
int top2=0;
for(int i=0;i<top;i++){
if(sta[i]==')'){
int l=0,r=1;
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--){
if(sta[j]=='(') {
l++;
if(l==r){ ans[top2++]=r; break; }
}
else {
r++;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<top2-1;i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]);
printf("%d\n",ans[top2-1]);
}
return 0;
}
nefu 1169 The Sequence likes Ladder(数学)
http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemShow.php?problem_id=1169
The sequence Si is defined as:
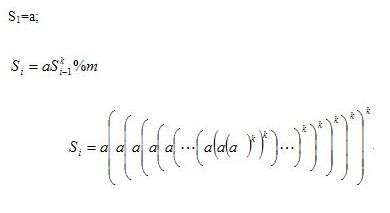
Where a,k,m are positive integer, a and m are relative prime, i.e. (a,m)=1.And % is modulo operation.
Your task is to calculate the Si.
分析:先不写模
同时我们知道,
再由欧拉定理我们知道,
所以,使用快速幂取模,拓展欧几里得求解逆元,欧拉定理降幂后就能得到答案。
但是这是错的。
矩阵做法:
令 ai 的指数是 pi ,那么有递推关系
所以有
推出:
即和上一种做法的唯一区别是a的指数部分用矩阵处理。
同时我们排除了 k-1和phi可能不互素产生错误的情况!(不互素就不能使用逆元)
AC code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
struct matrix {
LL m[2][2];
};
matrix I={
1,0,
0,1
};
matrix multi(matrix a ,matrix b,LL mod){
matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++){
c.m[i][j]+=a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j];
}
c.m[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return c;
}
matrix power(matrix a,LL p,LL mod){
matrix ans=I;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=multi(ans,a,mod);
a=multi(a,a,mod);
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
LL Euler(LL x){
LL ans=x;
for(LL i=2;i*i<=x;i++){
if(x%i==0){
while(x%i==0) x/=i;
ans=ans-ans/i;
}
}
if(x>1) ans=ans-ans/x;
return ans;
}
LL power2(LL a,LL p,LL mod){
LL ans=1;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=ans*a%mod;
a=a*a%mod;
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
LL a,k,m,i;
while(~scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&a,&k,&m,&i)){
matrix A;
A.m[0][0]=k; A.m[0][1]=1;
A.m[1][0]=0; A.m[1][1]=1;
LL phi=Euler(m);
A=power(A,i-1,phi);
LL p=(A.m[0][0]+A.m[0][1])%phi;
LL ans=power2(a,p,m);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}hdu 5159 Card(概率)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5159
大意:X张卡片,抽取b次,每次把卡片上的数字(1——X)加起来,问最后的点数和的期望
分析:每一张卡片贡献的点数的期望是 E(i)=i×p(i) ,i被抽中的概率是 p(i)=1−(1−1x)b
那么 S=∑i=1xE(i)=(1+x)x2[1−(1−1x)b]
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t,x,b,ca=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d",&x,&b);
double ans=(1.0+x)*x/2.0;
ans=ans*(1-pow((1-1.0/x),b));
printf("Case #%d: %.3lf\n",ca++,ans);
}
return 0;
}codeforces 645 C. Enduring Exodus(二分)
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/645/C
大意:n个房间有一部分是空着能用的,现在要分配给1个牧人和 k头牛,求解人和牛的最远距离最小值。
分析:数据范围是100000,应该和二分相关。
如何写好这个二分就是难点了。
自己一开始将所有的0记录在一个数组中,数值就是在源字符串中的位置,假设最左边的位置是p[d1],最右边的位置是p[d2],那么最远的距离就是两者到p[d]牧人位置的最大值。
d1=d-x
d2=d+k-x
然后就形成了
一个凹函数distance=f(x)。
然后写二分我就懵逼了,思路复杂了。
因为自己给自己构造了distance=f(x)的函数。。。
不把k看作变量的一部分,先忽略掉它,使用二分,k作为二分的满足要求。即hasRoom(x)>=k
x就是答案。
——最小最大距离是变量,不是所求量!
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
char str[N];
int sum[N];
int n,k;
int cows(int d,int dex){
int dex1=max(1,dex-d);
int dex2=min(n,dex+d);
int gs=sum[dex2]-sum[dex1];
if(str[dex1]=='0') gs++;
return gs;
}
int midfind(int dex){
int l=1,r=n,mid;
int ans=0;
while(l<=r){
mid=(l+r)>>1;
int sum=cows(mid,dex);
if(sum<=k){
ans=mid;
l=mid+1;
}
else r=mid-1;
}
return ans+1;
}
int main(){
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
while(cin>>n>>k){
scanf("%s",str+1);
memset(sum,0,sizeof(sum));
for(int i=1;str[i];i++){
sum[i]=sum[i-1];
if(str[i]=='0') sum[i]++;
}
int ans=1<<30;
for(int i=1;str[i];i++){
if(str[i]=='0'){
ans=min(ans,midfind(i));
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}bad code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
char str[N];
int bit[N];
int n,k;
int dis(int x,int d,int c){
int d1=d-x, d2=d+k-x;
if(d1<0 || d2>=c) return n+10;
int y1=bit[x]-bit[d1];
int y2=bit[d2]-bit[x];
return max(y1,y2);
}
int midfind(int d,int c){ // 二分查找最小值,最小值未知
int l=0,r=k,mid;
int ans=0; //找到和0最接近的dex, so we have to find min x >= 0 where x=abs(df)
while(l<=r){
mid=(l+r)>>1;
int dex1=d-mid;
int dex2=d+k-mid;
if(dex1<0){ r=mid-1; continue; }
else if(dex2>=c){ l=mid+1; continue; }
int df=bit[d]-bit[dex1]-(bit[dex2]-bit[d]);
if(df<0) {
ans=mid;
l=mid+1;
}
else r=mid-1;
}
return ans+1; // >= 0
}
int main(){
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
while(cin>>n>>k){
scanf("%s",str);
int c=0;
for(int i=0;str[i];i++){
if(str[i]=='0'){
bit[c++]=i;
}
}
int ans=n+10;
for(int i=0;i<c;i++){
int x=midfind(i,c);
if(x<0) continue;
ans=min(ans,dis(x,i,c));
ans=min(ans,dis(x-1,i,c));
ans=min(ans,dis(x+1,i,c));
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}POJ 1743 Musical Theme(后缀数组)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1743
大意:在一个音符串中寻找主题串。主题串有这样的特征——至少5个音调字符;在其他地方也出现主题串,可能潜在变换(potentially transposed,指每一个数字都相同的增加或者减少);没有重叠部分(is disjoint from (i.e., non-overlapping with) at least one of its other appearance(s),我的英语~)
分析:这相当于求解最长重复子串。任意子串都是后缀串的一部分,所以后缀数组值得拥有。
但是他要求求解潜在变换的数字主题串,所以我们把数组中的每两个相邻的元素做差存储起来即可,最后统计新数组的最长重复串。由于要求不能有公共部分,所以我们需要: sa[i]-sa[j]>=len。公共部分越小匹配的成功率越高,越小成功率越低,所以以公共部分的长度为基准二分加速。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e4+10;
int t1[N],t2[N],c[N];
bool cmp(int *r,int a,int b,int l){
return r[a]==r[b] && r[a+l]==r[b+l];
}
void suffix(int str[],int sa[],int Rank[],int height[],int n,int m){
n++; // length+1
int i,j,p,*x=t1,*y=t2;
for(i=0;i<m;i++) c[i]=0; // c[i]=value: value是排名
for(i=0;i<n;i++) c[x[i]=str[i]]++;
for(i=1;i<m;i++) c[i]+=c[i-1]; //排序完成
for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--) {
sa[c[x[i]]-1]=i;
c[x[i]]--; //start at 0
}
for(j=1;j<=n;j<<=1){
p=0;
for(i=n-j;i<n;i++) y[p++]=i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
if(sa[i]>=j) y[p++]=sa[i]-j;
for(i=0;i<m;i++) c[i]=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) c[x[y[i]]]++;
for(i=1;i<m;i++) c[i]+=c[i-1];
for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--) sa[--c[x[y[i]]]]=y[i];
swap(x,y); //x --> y
p=1;
x[sa[0]]=0;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
x[sa[i]]=cmp(y,sa[i-1],sa[i],j)?p-1:p++;
if(p>=n) break;
m=p;
}
int k=0;
n--;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++) Rank[sa[i]]=i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
if(k)k--;
j=sa[Rank[i]-1]; // 相似的字符子串 Rank[n]=0
while(str[i+k]==str[j+k]) k++;
height[Rank[i]]=k; //最大相同部分的长度
}
}
int str[N],sa[N],Rank[N],height[N];
bool check(int len,int n){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(height[i]<len) continue; //保证向下可行
for(int j=i-1;j>=1;j--){
if(abs(sa[j]-sa[i])>=len) return 1; //没有公共部分
if(height[j]<len) break;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int n;
while(cin>>n&&n){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&str[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
str[i]=str[i+1]-str[i];
str[i]+=90;
}
str[n-1]=0;
suffix(str,sa,Rank,height,n-1,200); //最长重复子串
int ans=0;
int l=1,r=n-1,mid;
while(l<=r){
mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(check(mid,n-1)){
l=mid+1;
ans=mid;
}
else r=mid-1;
}
if(ans<4) printf("0\n");
else printf("%d\n",ans+1);
}
return 0;
}nefu 1166 Lazy People (几何*有意思)
http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemShow.php?problem_id=1166
大意:给出起点和终点,n个直线方程将二维平面分成了不同的区域,每次到达新的区域会消耗一单位的能量值,问最少需要消耗的能量值。
分析:注意,穿过两条直线的交点算是穿过两条直线(从例子可以看出),由此相当于是要求求出过起点和终点的直线和其他的直线的交点的个数。
数学判别:将起点S和终点E的坐标带入直线方程乘积结果是负数一定会穿过!(等于0是相接触)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
struct point {
LL x,y;
}s,e;
int main()
{
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
LL t,n;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&s.x,&s.y,&e.x,&e.y);
scanf("%lld",&n);
LL ans=0;
LL a,b,c;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&c);
point t;
LL t1=a*s.x+b*s.y+c;
LL t2=a*e.x+b*e.y+c;
if(t1*t2<0) ans++;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}nefu1163 Cut The Cake(有意思)
http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemShow.php?problem_id=1163
大意:蛋糕已经切成了n块,现在需要多切几刀将其变成n+m块,问最少再切多少刀?
分析:请看下图。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a,int b){
return b==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);
}
int main() {
int t,n,m;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int g=gcd(n,n+m);
printf("%d\n",n+m-g);
}
return 0;
}nefu 1175 So Easy(概率)
http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemShow.php?problem_id=1175
大意:翻n个硬币,问连续出现至少k个正面向上的硬币段的段落区间数的期望。
分析:第一种做法,直接二进制枚举暴力得到答案。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
double dp[20];
int main()
{
int n,k;
while(cin>>n>>k){
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
double ans=0;
double p=pow(0.5,n);
for(int i=1;i<(1<<n);i++){
int one=0,pre=0,maxm=0,temp=0;
bool OK=0;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if((i&(1<<j))) {
one++;
if(j>0 && (i&(1<<(j-1)))) pre++;
}
else {
one=0;
pre=0;
}
if(k>1){
if(one>=k && pre+1>=k) OK=1;
}
else {
if(one>=k) OK=1;
}
}
if(OK) {
ans+=p;
} //cout<<endl;
}
printf("%.4lf\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}第二种做法,数学分析推公式。
因为k教育等于n,所以以第一点为出发点,一定有可能出现连续k个正面向上的硬币区间—— 2(−k)
寻找剩余的可能的出发点,2~n-k+1. 他们对应的概率是 2(−k−1) (我们还要保证出发点前的一点不是正面向上的,即不是出发点!)
所以结果就是 2(−k)+∑i=2n−k+12(−k−1)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,k;
while(cin>>n>>k){
double ans=1+(n-k)/2.0;
ans=ans/(1<<k);
printf("%.4lf\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}nyist 814 又见导弹拦截(经典贪心)
http://acm.nyist.net/JudgeOnline/problem.php?pid=814
大意:求解拦截所有的导弹需要的拦截系统。
分析:经典贪心
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int h[3005],dp[3005];
int main(){
int n;
while(cin>>n){
if(n==-1) break;
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&h[i]);
}
int temp=0,ans=0;
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
if(dp[i]==0){
dp[i]=1;
temp=h[i];
ans++;
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--){
if(h[j]>=temp && dp[j]==0){
dp[j]=1;
temp=h[j];
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
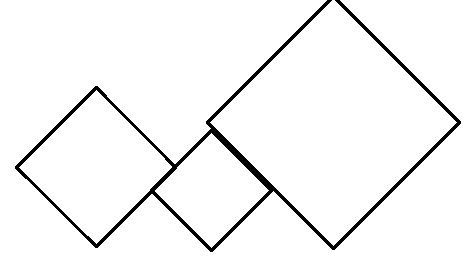
poj 3347 Kadj Squareshd(有意思)
http://poj.org/problem?id=3347
大意:给出n个正方形的边长,求解从上方向下看能看到多少的正方形?
分析:
边长a在x轴上的投影是 2√2a ,为了避免浮点数的出现,我们把其长度扩大 2√ 倍。以后的计算直接有这样的概念:边长a的水平投影就是a。
然后就是投影转化,投影后的问题就是线段问题。设每一个正方形有一个最左边的点 l和最右边的点 r,如果投影后满足r>l就是能看见的。
如图,设从左到右的正方形分别是p[0],p[1],p[2].
for p[1]:
p[0].len>p[1].len.
p[1].l = p[0].r-(p[0].len-p[1].len)
for p[2]:
p[1].len \< p[2].len
p[2].l=p[1].r-(p[2].len-p[1].len)
为了防止出现
的极端情况。应该用一个循环不断向左或者向右更新。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int l,r,len;
}p[55];
int main()
{
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n){
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&p[i].len);
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
if(p[j].len>p[i].len)
p[i].l=max(p[i].l,p[j].r-(p[j].len-p[i].len));
else p[i].l=max(p[i].l,p[j].r-(p[i].len-p[j].len));
p[i].r=p[i].l+2*p[i].len;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
if(p[j].len>p[i].len && p[j].r>p[i].l) p[i].l=p[j].r;
if(p[j].len<p[i].len && p[j].r>p[i].l) p[j].r=p[i].l;
}
}
/*for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++) if(p[i].l<p[i].r) printf("%d ",i+1);
if(p[n-1].l<p[n-1].r) printf("%d\n",n);*/
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) if(p[i].l<p[i].r) printf("%d ",i+1);
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
最后,一首优美的歌曲谢谢你的阅读。
此心安处 Everseeping