计算机图形学(二)输出图元_20_章节总结_程序展示_蜗形线、心形线、螺旋线
蜗形线、心形线、螺旋线
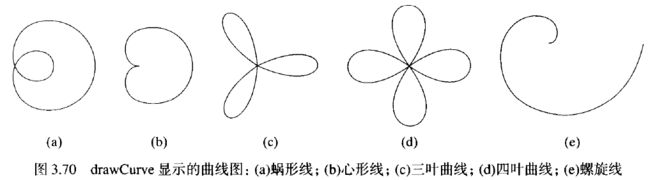
最后一个程序显示了圆公式的某些变化,其中使用了参数极坐标方程(3.28)来计算曲线路径的点。这些点用做显示弧的逼近折线中直线段的端点。图3.70中的弧通过圆半径r的变化来生成。按照r的不同变化,可生成蜗形线、心形线、螺旋线或其他类似的图形。
#include <GL/glut.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream.h>
struct screenPt
{
GLint x;
GLint y;
};
typedef enum {limacon = 1, cardioid, threeLeaf, fourLeaf, spiral} curveName;
GLsizei winWidth = 600, winHeight = 500; //Initial display window size.
void init (void)
{
glClearColor (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
glMatrixMode (GL_PROJECTION);
gluOrtho2D (0.0, 200.0, 0.0, 150.0);
}
void lineSegment (screenPt pt1, screenPt pt2)
{
glBegin (GL_LINES);
glVertex2i (pt1.x, pt1.y);
glVertex2i (pt2.x, pt2.y);
glEnd ( );
}
void drawCurve (GLint curveName)
{
/* The limacon of Pascal is a modification of the circle equation
* with the radius varying as r = a * cos (theta) + b, where a
* and b are constants. A cardioid is a limacon with a = b.
* Three-leaf and four-leaf curves are generated when
* r = a * cos (n * theta), with n = 3 and n = 2, respectively.
* A spiral is displayed when r is a multiple of theta.
*/
const GLdouble twoPi = 6.283185;
const GLint a = 175, b = 60;
GLfloat r, theta, dtheta = 1.0 / float (a);
GLint x0 = 200; y0 = 250; // Set an initial screen position.
screenPt curvePt[2];
glColor3f (0.0, 0.0, 0.0); // Set curve position.
curvePt[0].x = x0; // Initialize curve position.
curvePt[0].y = y0;
switch (curveName){
case limacon: curvePt[0].x += a + b; break;
case cardioid: curvePt[0].x += a + a; break;
case threeLeaf: curvePt[0].x += a; break;
case fourLeaf: curvePt[0].x += a; break;
case spiral: break;
default: break;
}
theta = dtheta;
while (theta < two_Pi){
switch (curveName){
case limacon:
r = a * cos (theta) + b; break;
case cardioid:
r = a * (1 + cos (theta)); break;
case threeLeaf:
r = a * cos (3 * theta); break;
case fourLeaf:
r = a * cos (2 * theta); break;
case spiral:
r = (a / 4.0) * theta; break;
default: break;
}
curvePt[1].x = x0 + r * cos (theta);
curvePt[1].y = y0 + r * sin (theta);
lineSegment (curvePt[0], curvePt[1]);
curvePt[0].x = curvePt[1].x;
curvePt[0].y = curvePt[1].y;
theta += dtheta;
}
}
void displayFcn (void)
{
GLint curveNum;
glClear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear display window.
cout << "\nEnter the integer value corresponding to\n";
cout << "one of the following curve names.\n";
cont << "Press any other key to exit.\n";
cout << "\n1-limacon, 2-cardioid, 3-threeLeaf, 4-fourLeaf, 5-spiral: ";
cin >> curveNum;
if (curveNum == 1 || curveNum == 2 || curveNum == 3 || curveNum == 4 || curveNum == 5)
drawCurve (curveNum);
else
exit (0);
glFlush ( );
}
void winReshpeFcn (GLint newWidth, GLint newHeight)
{
glMatrixMode (GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdetity ( );
gluOrtho2D (0.0, (GLdouble) newWidth, 0.0, (GLdouble) newHeight);
glClear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
}
void main (int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit (&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode (GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowPosition (100, 100);
glutInitWindowSize (winWidth, winHeight);
glutCreateWindow ("Draw Curves");
init ( );
glutDisplayFunc(displayFcn);
glutReshapeFunc(winReshpeFcn);
glutMainLoop ( );
}