Collection集合 框架图 及 Collections帮助类
目录:
一. Collection集合 框架图
二. MAP框架图
三. Collections帮助类
四. 自定义对List/Map进行排序
五. 对ArrayList进行初始化
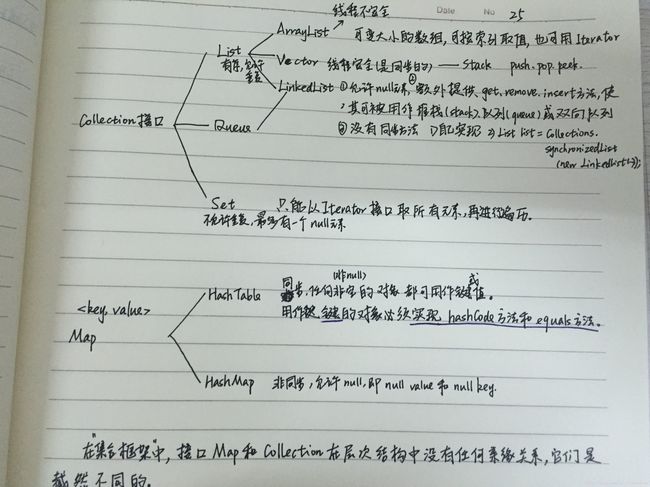
一. Collection集合 框架图
查看了一些资料将Collection接口及Map接口的框架总结如下,方便以后学习使用。
java.util.Collection接口
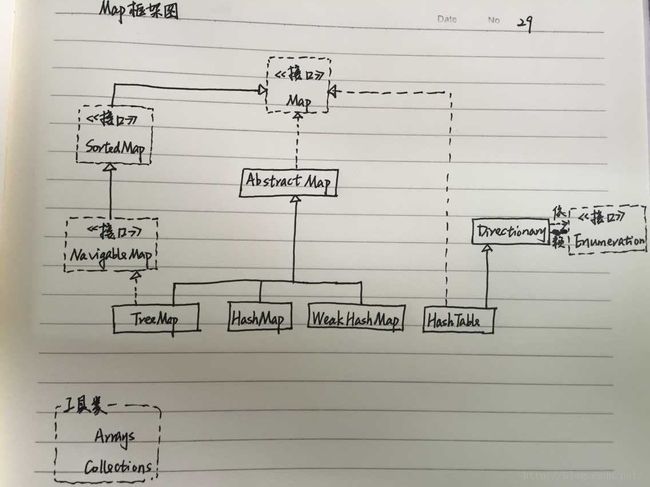
二. MAP框架图
参考:http://www.chawenti.com/articles/20110.html
Hashtable(同步)没有自定义哈希算法,而直接采用的key的hashCode()。
HashMap(非同步)添加元素时,是使用自定义的哈希算法。
TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的。
TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合。
TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法。比如返回有序的key集合。
TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆。
TreeMap 实现了java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化。
TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
另外,TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fastl的。
三. Collections帮助类
Collections是个类,不是接口,是一个为集合提供处理功能的工具类/帮助类。
1. 对List进行升序排序。public static void sort(List list)
列表中的所有元素都必须实现 Comparable接口。此列表内的所有元素都必须是使用指定比较器可相互比较的。
double array[] = {112, 111, 23, 456, 231 };
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
list.add(new Double(array[i]));
}
Collections.sort(list);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.println(li.get(i));
}
//结果:112,111,23,456,231
如果要降序排列,可以在sort函数中指定降序。可以选择:public static void sort(List list, Comparator c),其中,参数可以用java.util.Collections的reverseOrder()方法返回。
2. 返回指定collection中等于指定对象的元素数。public static int frequency(Collection c, Object o)
3. 判断两个指定collection中有无相同的元素。public static boolean disjoint(Collection c1, Collection c2)
4. 寻找集合中的最大/最小值。public static Object max/min(Collection coll)
double array[] = {112, 111, 23, 456, 231 };
List list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
list.add(new Double(array[i]));
}
Collections.max(list);
for (int i = 0; i <list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("list[" + i + "]=" + list.get(i));
}
//结果:456
5. 对于集合中的元素进行 替换。public static boolean replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal)
6. 混排
混排算法所做的正好与 sort 相反: 它打乱在一个 List 中可能有的任何排列的踪迹。也就是说,基于随机源的输入重排该 List,这样的排列具有相同的可能性(假设随机源是公正的)。这个算法在实现一个碰运气的游戏中是非常有用的。例如,它可被用来混排代表一副牌的Card 对象的一个 List 。另外,在生成测试案例时,它也是十分有用的。
double array[] = {112, 111, 23, 456, 231 };
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
list.add(new Double(array[i]));
}
Collections.shuffle(list);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.println(li.get(i));
}
//结果:112,111,23,456,231
7. 反转
使用Reverse方法可以根据元素的自然顺序 对指定列表按降序进行排序。
Collections.reverse(list)
double array[] = {112, 111, 23, 456, 231 };
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
list.add(new Double(array[i]));
}
Collections. reverse (list);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.println(li.get(i));
}
//结果:231,456,23,111,112
8. 替换所有的元素
String str[] = {"dd","aa","bb","cc","ee"};
for(int j=0;j<str.length;j++){
li.add(new String(str[j]));
}
Collections.fill(li,"aaa");
for (int i = 0; i < li.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("list[" + i + "]=" + li.get(i));
}
//结果:aaa,aaa,aaa,aaa,aaa
9. 拷贝(copy)
用两个参数,一个目标 List 和一个源 List, 将源的元素拷贝到目标,并覆盖它的内容。目标 List至少与源一样长。如果它更长,则在目标 List 中的剩余元素不受影响。
Collections.copy(list,li): 后面一个参数是目标列表 ,前一个是源列表
double array[] = {112, 111, 23, 456, 231 };
List list = new ArrayList();
List li = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
list.add(new Double(array[i]));
}
double arr[] = {1131,333};
for(int j=0;j<arr.length;j++){
li.add(new Double(arr[j]));
}
Collections.copy(list,li);
for (int i = 0; i <list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("list[" + i + "]=" + list.get(i));
}
//结果:1131,333,23,456,231
10. lastIndexOfSubList
返回指定源列表中最后一次出现指定目标列表的起始位置。
List list = new ArrayList();
List li = new ArrayList();
int count = Collections.lastIndexOfSubList(list,li);
double array[] = {112, 111, 23, 456, 231 };
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
list.add(new Double(array[i]));
}
double arr[] = {111};
String str[] = {"dd","aa","bb","cc","ee"};
for(int j=0;j<arr.length;j++){
li.add(new Double(arr[j]));
}
int locations = Collections. lastIndexOfSubList (list,li);
System.out.println(" == "+ locations);
//结果 1
11. indexOfSubList
返回指定源列表中第一次出现指定目标列表的起始位置。
12. Rotate
根据指定的距离循环移动指定列表中的元素。
Collections.rotate(list,-1);
如果是负数,则正向移动,正数则方向移动
double array[] = {112, 111, 23, 456, 231 };
List list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
list.add(new Double(array[i]));
}
Collections.rotate(list,-1);
for (int i = 0; i <list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("list[" + i + "]=" + list.get(i));
}
//结果:111,23,456,231,112
这一部分参考链接:http://blog.csdn.net/lskyne/article/details/8961014
13. unmodifiableMap
用于实现一个不可修改的Map
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CreateMap {
private static Map<String, String> map;
static {
// 按照存入顺序的Map
map = new LinkedHashMap();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key3", "value3");
map.put("key2", "value2");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateMap cm = new CreateMap();
cm.map.put("test", "test");
// java中提供了很多方法都可以实现对一个Map的复制,但是那些方法不见得会时时同步。
// 简单说,就是一个Map发生的变化,而复制的那个依然保持原样。下面是一个比较高效的实现方法
Map<String, String> copiedMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(map);
cm.setUnmodifiable();
copiedMap.put("test2", "test2");// 不会报错
System.out.println("Travese copiedMap:");
traveseMap(copiedMap);
System.out.println("Travese cm.map");
traveseMap(cm.map);
cm.map.put("test2", "test2");// 报错
}
public void setUnmodifiable() {
// 禁止修改,修改会抛出UnsupportedOperationException异常来禁止修改。
this.map = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
}
public static void traveseMap (Mapmap) {
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> ite = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(ite.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = ite.next();
System.out.println("key = " + entry.getKey() + " and value = " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
四. 自定义对List/Map进行排序
最后补充,对Map实现自定义排序,借助Comparator http://www.cnblogs.com/xiohao/p/4314326.html
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class TestCompare {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new TestCompare().testCompare();
}
private void testCompare() {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("张三", 7);
map.put("李四", 1);
map.put("王五", 9);
map.put("赵六", 8);
ArrayList<Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Entry<String, Integer>>(
map.entrySet());
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Entry<String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Entry<String, Integer> o1,
Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
return o1.getValue() - o2.getValue();
}
});
// map按照指定格式排序后的结果
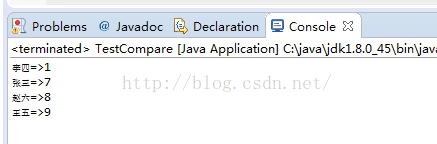
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : list) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=>" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
运行结果:
重要的一点:实现对List或Map的排序有两种方法,参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/wentiertong/archive/2011/03/07/1973698.html
第一种方法,就是list中对象实现Comparable接口,实现compareTo方法,代码如下:
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private Integer order;
/**
* @return the name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* @param name
* the name to set
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* @return the order
*/
public Integer getOrder() {
return order;
}
/**
* @param order
* the order to set
*/
public void setOrder(Integer order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person arg0) {
return this.getOrder().compareTo(arg0.getOrder());
}
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> listA = new ArrayList<Person>();
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
Person p3 = new Person();
p1.setName("name1");
p1.setOrder(1);
p2.setName("name2");
p2.setOrder(2);
p3.setName("name3");
p3.setOrder(3);
listA.add(p2);
listA.add(p1);
listA.add(p3);
Collections.sort(listA);
for (Person p : listA) {
System.out.println(p.getName());
}
}
第二种方法,就是在 重载Collections.sort方法,代码如下:
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer order;
/**
* @return the name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* @param name
* the name to set
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* @return the order
*/
public Integer getOrder() {
return order;
}
/**
* @param order
* the order to set
*/
public void setOrder(Integer order) {
this.order = order;
}
}
使用Collections.sort方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> listA = new ArrayList<Person>();
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
Person p3 = new Person();
p1.setName("name1");
p1.setOrder(1);
p2.setName("name2");
p2.setOrder(2);
p3.setName("name3");
p3.setOrder(3);
listA.add(p2);
listA.add(p1);
listA.add(p3);
Collections.sort(listA, new Comparator<Person>() {
public int compare(Person arg0, Person arg1) {
return arg0.getOrder().compareTo(arg1.getOrder());
}
});
for (Person p : listA) {
System.out.println(p.getName());
}
}
两次执行的结果都是:
name1
name2
name3
五. 对ArrayList进行初始化
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList("Ryan", "Julie", "Bob"));
2. 常用的初始化方法
//初始化List
List<string> list = new ArrayList<string>(){{
add("string1");
add("string2");
//some other add() code......
add("stringN");
}};
//初始化Map
Map<string , String> map = new HashMap<string , String>(){{
put("key1", "value1");
put("key2", "jb51.net");
//.... some other put() code
put("keyN", "valueN");
}};