apache shiro的工作流程分析
原址:点击打开链接
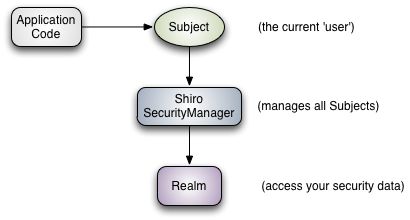
本文基于shiro的web环境,用宏观(也就是不精确)的角度去理解shiro的工作流程,先看shiro官方的一张图。
和应用程序直接交互的对象是Subject,securitymanager为Subject服务。可以把Subject看成一个用户,你的所有的代码都由用户来执行。suject.execute(callable),这个callable里面就是你的代码。
一、shiro如何介入你的webapp
它是如何初始化的?servletContextListener。它是如何在每个http请求中介入的?ServletFilter.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
<
listener
>
<
listener-class
>org.apache.shiro.web.env.EnvironmentLoaderListener</
listener-class
>
</
listener
>
<
filter
>
<
filter-name
>ShiroFilter</
filter-name
>
<
filter-class
>org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.ShiroFilter</
filter-class
>
</
filter
>
<
filter-mapping
>
<
filter-name
>ShiroFilter</
filter-name
>
<
url-pattern
>/*</
url-pattern
>
<
dispatcher
>REQUEST</
dispatcher
>
<
dispatcher
>FORWARD</
dispatcher
>
<
dispatcher
>INCLUDE</
dispatcher
>
<
dispatcher
>ERROR</
dispatcher
>
</
filter-mapping
>
|
EnvironmentLoaderListener会根据你在web.xml中的配置读取对应的配置文件(默认读取/WEB-INF/shiro.ini,或者classroot的对应文件),构建一个shiro环境,该环境保存在servletcontext中,所有的filter都可以获取。里面就包括一个单例的securityManager,该securityManager已经根据ini的内容进行了配置。
再看shiroFilter:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@Override
public
void
init()
throws
Exception {
WebEnvironment env = WebUtils.getRequiredWebEnvironment(getServletContext());
setSecurityManager(env.getWebSecurityManager());
FilterChainResolver resolver = env.getFilterChainResolver();
if
(resolver !=
null
) {
setFilterChainResolver(resolver);
}
}
|
这样filter里面就可以使用securityManager了。
下面的一段代码就是本文开头提到的Subject(用户)的创建了,因为是web环境所以每次请求都需要创建一个subject对象,在filter里面给你准备好,在你的servlet里面就可以直接使用了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
final
ServletRequest request = prepareServletRequest(servletRequest, servletResponse, chain);
final
ServletResponse response = prepareServletResponse(request, servletResponse, chain);
final
Subject subject = createSubject(request, response);
//noinspection unchecked
subject.execute(
new
Callable() {
public
Object call()
throws
Exception {
updateSessionLastAccessTime(request, response);
executeChain(request, response, chain);
return
null
;
}
});
|
看一下subject.execute的javadoc,写道:
Associates the specified Callable with this Subject instance and then executes it on the currently running thread. If you want to execute the Callable on a different thread, it is better to use the associateWith(Callable)} method instead.
将callable(你的所有代码都在里面执行)和当前的subject实例相关联,并且在当前的thread中执行...
二、securityManage如何为subject服务
请注意看上面最后一段java代码,里面有一个createSubject(request,response)方法,也在filter里面,它的代码如下:
|
1
2
3
|
protected
WebSubject createSubject(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {
return
new
WebSubject.Builder(getSecurityManager(), request, response).buildWebSubject();
}
|
看到没有?subject的构造用到了securityManager,所有shiro的魔法都被隐藏在securityManager里面了。接下来提一些问题,试着发现securityManager需要完成哪些工作。
-
如果保证每次http请求得到同一个(确切说应该是一样的)subject?这里关系到session管理了吧。
-
如何登陆用户,subject.login?这里关系到认证,授权,用户realm了吧。
-
....