Android 动画详解之属性动画(Property Animation)(下)
Hello,大家好,最近好长时间没有写博客了,因为我决定辞职了。
废话不多说,我们还是来看属性动画在上一篇 Android 动画详解之属性动画(Property Animation)中我们简单的介绍了一下属性动画的用法,其实属性动画还有更多有趣的用法。
1,在xml中使用
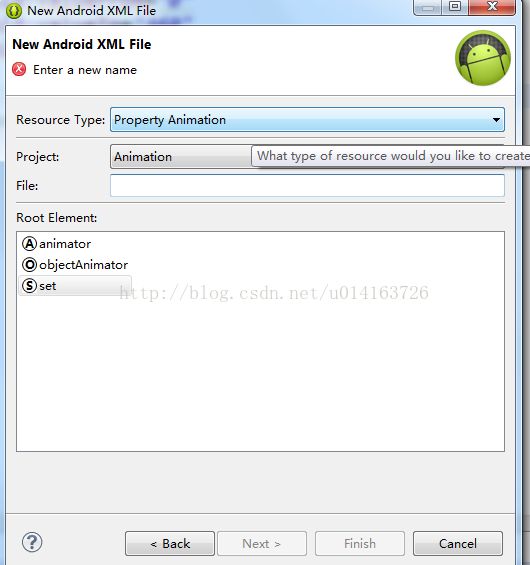
在eclipse中我们右键新建xml可以选择新建属性动画,如图
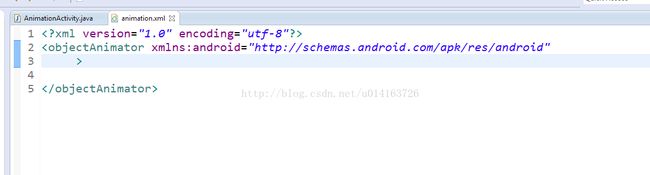
我们选择objectAnimator,然后我们就会看到熟悉的一幕
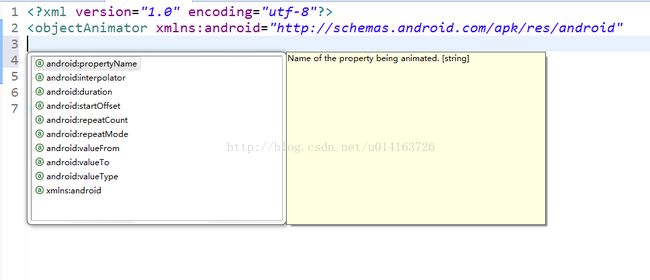
然后我们用智能提示就可以看到更熟悉的
没错,这下我们应该知道怎么用xml布局来写属性动画了吧
<span style="font-size:14px;"><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="3000"
android:propertyName="Rotation"
android:valueFrom="0"
android:valueTo="360"
android:valueType="floatType"
>
</objectAnimator></span>
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_animation);
button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_anim);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Animator animator = AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(
AnimationActivity.this, R.animator.animation);
animator.setTarget(button);
animator.start();
}
});
}
效果

同时我们可以看到在新建xml的时候是有set的,set的用法同样很简单
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:ordering="sequentially" >
<!-- ordering="together"同时播放
ordering="sequentially"次序播放
-->
<objectAnimator />
<objectAnimator />
</set>
2,布局动画
当容器中的视图层次发生变化时存在过渡的动画效果,这个我们先来看看ApiDemo的效果。
可以看到我们勾选了in于out之后我们新增的button或者remove掉的button会有一个动画效果,接下来我们来看代码
// Check for disabled animations
CheckBox appearingCB = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.appearingCB);
appearingCB.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
setupTransition(transitioner);
}
});
CheckBox disappearingCB = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.disappearingCB);
disappearingCB.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
setupTransition(transitioner);
}
});
这是俩个checkbox,我们再看setupTransition方法
private void setupTransition(LayoutTransition transition) {
CheckBox customAnimCB = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.customAnimCB);
CheckBox appearingCB = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.appearingCB);
CheckBox disappearingCB = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.disappearingCB);
CheckBox changingAppearingCB = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.changingAppearingCB);
CheckBox changingDisappearingCB = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.changingDisappearingCB);
transition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.APPEARING, appearingCB.isChecked() ?
(customAnimCB.isChecked() ? customAppearingAnim : defaultAppearingAnim) : null);
transition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.DISAPPEARING, disappearingCB.isChecked() ?
(customAnimCB.isChecked() ? customDisappearingAnim : defaultDisappearingAnim) : null);
transition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.CHANGE_APPEARING, changingAppearingCB.isChecked() ?
(customAnimCB.isChecked() ? customChangingAppearingAnim :
defaultChangingAppearingAnim) : null);
transition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.CHANGE_DISAPPEARING,
changingDisappearingCB.isChecked() ?
(customAnimCB.isChecked() ? customChangingDisappearingAnim :
defaultChangingDisappearingAnim) : null);
}
我们可以发现关键就是LayoutTransition,而且动画产生也是依据
LayoutTransition.APPEARING;
LayoutTransition.DISAPPEARING;
LayoutTransition.CHANGE_APPEARING;
LayoutTransition.CHANGE_DISAPPEARING;
APPEARING新增view的动画CHANGE_APPEARING对布局产生改变的动画,那么我们就可以依葫芦画瓢。
private RelativeLayout relativeLayout;
private Button mAdbtn;
private int count = 0;
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_animation);
relativeLayout = (RelativeLayout)findViewById(R.id.relative);
mAdbtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn);
final GridLayout gridLayout = new GridLayout(this);
gridLayout.setColumnCount(5);
relativeLayout.addView(gridLayout);
gridLayout.setLayoutTransition(new LayoutTransition());
mAdbtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
count++;
Button button = new Button(AnimationActivity.this);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
gridLayout.removeView(v);
}
});
button.setText("btn"+count);
gridLayout.addView(button);
}
});
}
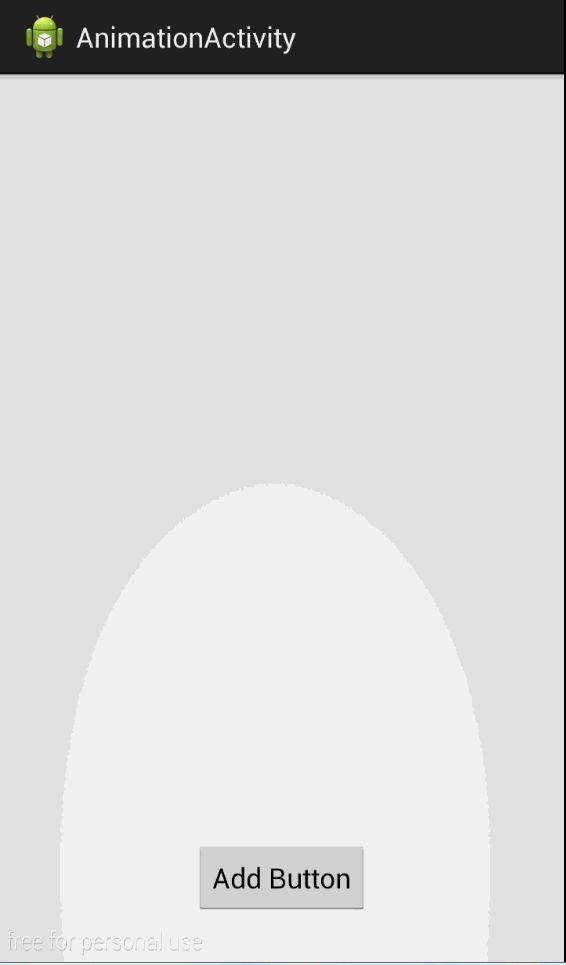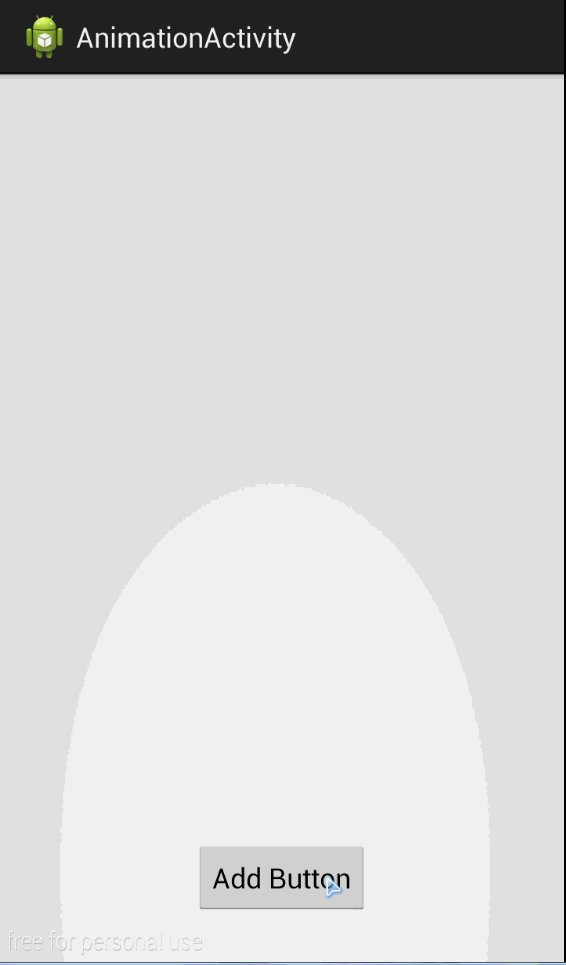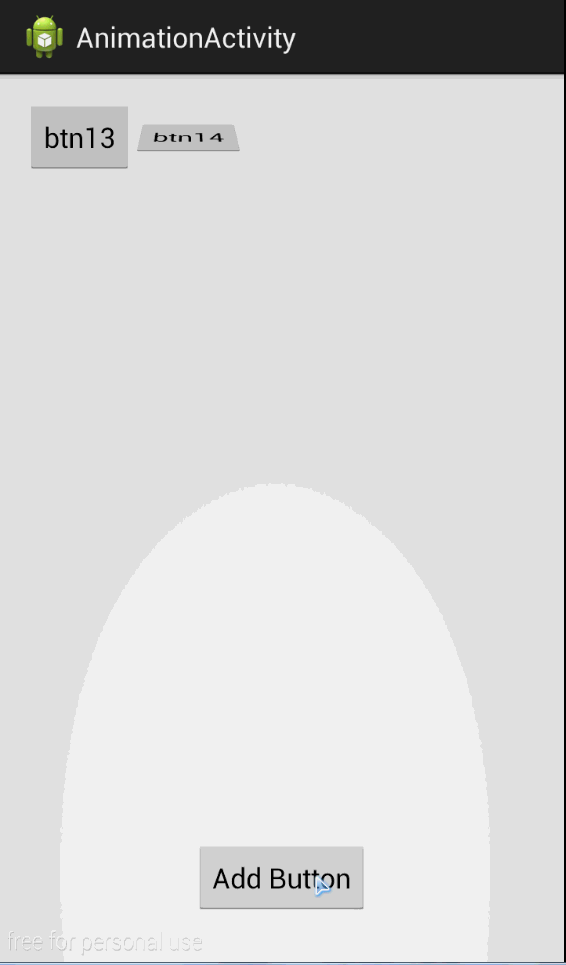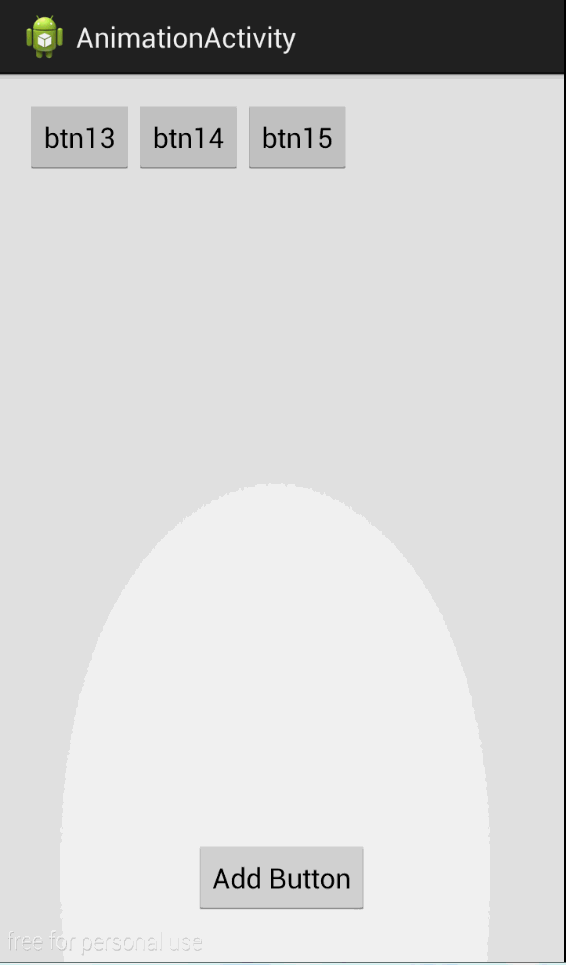
效果
同时如果我们不喜欢默认的动画效果也可以替换为自己喜欢的效果。
mAdbtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
count++;
Button button = new Button(AnimationActivity.this);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
gridLayout.removeView(v);
}
});
button.setText("btn" + count);
layoutTransition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.APPEARING,
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(button, "RotationX", 0, 360).setDuration(2000));
gridLayout.setLayoutTransition(layoutTransition);
gridLayout.addView(button);
}
});
ok,属性动画就介绍到这里吧,也预祝大家都工作顺利天天开心