本文源码寄放于github:https://github.com/w392807287/Design_pattern_of_python
参考文献:
《大话设计模式》——吴强
《Python设计模式》——pythontip.com
《23种设计模式》——http://www.cnblogs.com/beijiguangyong/
一、设计模式是什么?
设计模式:经过总结、优化的,对我们经常会碰到的编程问题的可重用解决方案(通俗:解决问题的思路,类似作文模板)。
设计模式特点:
- 设计模式并不像类或库那样能够直接作用于我们的代码。
- 设计模式更为高级,是一种必须在特定情形下实现的一种方法模板。
- 设计模式不绑定具体的编程语言。好的设计模式应该能够用大部分编程语言实现(做不到全部的话,具体取决于语言特性)。
- 设计模式是一把双刃剑,用在不恰当的情形下将会带来无穷的麻烦。在正确的时间被用在正确地地方,将是你的救星。
设计设计模式六大原则:
- 开闭原则:开发拓展,关闭修改,不用多言。
- 里氏替换原则:所有引用基类(父类)的地方必须能够透明的使用其子类的对象。
- 依赖倒置原则:高层模块不应该依赖低层模块,二者都应该依赖其抽象。抽象不应该依赖细节,细节应该依赖抽象,换言之,针对接口编程,不针对实现编程。
- 接口隔离原则: 使用多个专门接口,而不用单一接口,亦不应该依赖那些它不需要的接口。
- 迪米特法则:一个软件实体应该尽可能少的与其他实体发生相互作用。
- 单一职责原则:不要存在多于一个导致类变更的原因。通俗的讲,一个类只负责一项职责。
设计模式的分类:
- 创建模式,提供实例化的方法,为适合的状况提供相应的对象创建方法。
- 结构化模式,通常用来处理实体之间的关系,使得这些实体能够更好地协同工作。
- 行为模式,用于在不同的实体建进行通信,为实体之间的通信提供更容易,更灵活的通信方法。
创建型:
- 1. Factory Method(工厂方法)
- 2. Abstract Factory(抽象工厂)
- 3. Builder(创建者)
- 4. Prototype(原型)
- 5. Singleton(单例)
结构型:
- 6. Adapter Class/Object(适配器)
- 7. Bridge(桥接)
- 8. Composite(组合)
- 9. Decorator(装饰)
- 10. Facade(外观)
- 11. Flyweight(享元)
- 12. Proxy(代理)
行为型:
- 13. Interpreter(解释器)
- 14. Template Method(模板方法)
- 15. Chain of Responsibility(责任链)
- 16. Command(命令)
- 17. Iterator(迭代器)
- 18. Mediator(中介者)
- 19. Memento(备忘录)
- 20. Observer(观察者)
- 21. State(状态)
- 22. Strategy(策略)
- 23. Visitor(访问者)
二、创建型
1.Factory Method(工厂方法)
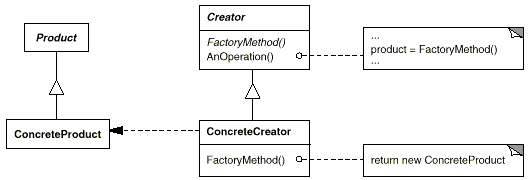
意图:
定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类。Factory Method 使一个类的实例化延迟到其子类。
适用性:
- 需要生产多种,大量复杂对象的时候。
- 需要降低耦合的时候。
- 当系统中的产品种类需要经常拓展的时候。
优点:
- 隐藏了对象创建的实现细节。
- 每个具体产品都对应一个具体的工厂类,不需要修改工厂代码。
缺点:
- 当添加具体产品类的时候,需要修改工厂代码,违反了开闭原则。
实现:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Factory Method
'''
class ChinaGetter:
"""A simple localizer a la gettext"""
def __init__(self):
self.trans = dict(dog=u"小狗", cat=u"小猫")
def get(self, msgid):
"""We'll punt if we don't have a translation"""
try:
return self.trans[msgid]
except KeyError:
return str(msgid)
class EnglishGetter:
"""Simply echoes the msg ids"""
def get(self, msgid):
return str(msgid)
def get_localizer(language="English"):
"""The factory method"""
languages = dict(English=EnglishGetter, China=ChinaGetter)
return languages[language]()
# Create our localizers
e, g = get_localizer("English"), get_localizer("China")
# Localize some text
for msgid in "dog parrot cat bear".split():
print(e.get(msgid), g.get(msgid))
|
2. Abstract Factory(抽象工厂)
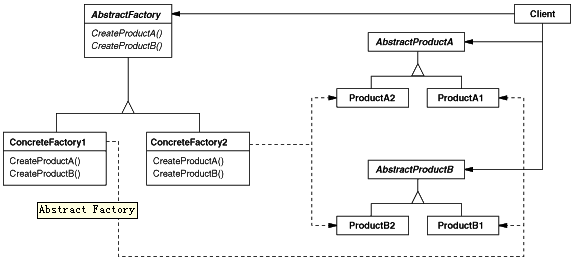
意图:
提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。 (例如:生产手机,需要手机壳CPU操作系统等,进行组装,每种对象都有不同的类,对每个具体工厂,分别生产一部手机需要的几个对象。)
相比工厂方法模式,抽象工厂模式中每个具体工厂都生产一套产品。
适用性:
- 一个系统要独立于它的产品的创建、组合和表示时。
- 强调一系列相关产品对象的设计以便进行联合使用。
- 提供一个产品类库,想隐藏产品的具体实现时。
优点:
- 将客户端与类的具体实现相分离。
- 每个工厂创建了一个 完整的产品系列,使得抑郁交换产品的系列。
- 有利于产品的一致性。
缺点:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Abstract Factory
'''
import random
class PetShop:
"""A pet shop"""
def __init__(self, animal_factory=None):
"""pet_factory is our abstract factory.
We can set it at will."""
self.pet_factory = animal_factory
def show_pet(self):
"""Creates and shows a pet using the
abstract factory"""
pet = self.pet_factory.get_pet()
print("This is a lovely", str(pet))
print("It says", pet.speak())
print("It eats", self.pet_factory.get_food())
# Stuff that our factory makes
class Dog:
def speak(self):
return "woof"
def __str__(self):
return "Dog"
class Cat:
def speak(self):
return "meow"
def __str__(self):
return "Cat"
# Factory classes
class DogFactory:
def get_pet(self):
return Dog()
def get_food(self):
return "dog food"
class CatFactory:
def get_pet(self):
return Cat()
def get_food(self):
return "cat food"
# Create the proper family
def get_factory():
"""Let's be dynamic!"""
return random.choice([DogFactory, CatFactory])()
# Show pets with various factories
if __name__ == "__main__":
shop = PetShop()
for i in range(3):
shop.pet_factory = get_factory()
shop.show_pet()
print("=" * 20)
|
3. Builder(建造者)
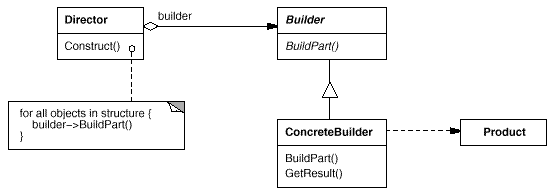
意图:
将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。
与抽象工厂模式相似,也用来创建复杂对象,主要区别是建造者模式着重一步步的构造一个复杂对象,而抽象工厂模式着重于多个系列的产品对象。
适用性:
当创建复杂对象的算法应该独立于该对象的组成部分以及它们的装配方式时。
当构造过程必须允许被构造的对象有不同的表示时。
优点:
隐藏了一个产品的内部结构与装配过程。
将构造代码与表示代码分开。
可以对构造过程进行更精细的控制。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
"""
Builder
"""
# Director
class Director(object):
def __init__(self):
self.builder = None
def construct_building(self):
self.builder.new_building()
self.builder.build_floor()
self.builder.build_size()
def get_building(self):
return self.builder.building
# Abstract Builder
class Builder(object):
def __init__(self):
self.building = None
def new_building(self):
self.building = Building()
# Concrete Builder
class BuilderHouse(Builder):
def build_floor(self):
self.building.floor = 'One'
def build_size(self):
self.building.size = 'Big'
class BuilderFlat(Builder):
def build_floor(self):
self.building.floor = 'More than One'
def build_size(self):
self.building.size = 'Small'
# Product
class Building(object):
def __init__(self):
self.floor = None
self.size = None
def __repr__(self):
return 'Floor: %s | Size: %s' % (self.floor, self.size)
# Client
if __name__ == "__main__":
director = Director()
director.builder = BuilderHouse()
director.construct_building()
building = director.get_building()
print(building)
director.builder = BuilderFlat()
director.construct_building()
building = director.get_building()
print(building)
|
4. Prototype(原型)
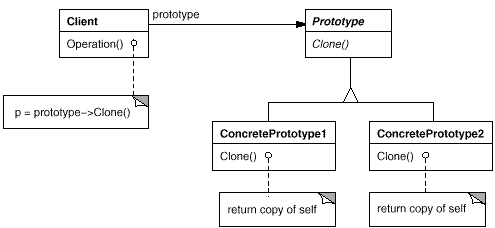
意图:
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
适用性:
当要实例化的类是在运行时刻指定时,例如,通过动态装载;或者为了避免创建一个与产品类层次平行的工厂类层次时;或者当一个类的实例只能有几个不同状态组合中的一种时。建立相应数目的原型并克隆它们可能比每次用合适的状态手工实例化该类更方便一些。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Prototype
'''
import copy
class Prototype:
def __init__(self):
self._objects = {}
def register_object(self, name, obj):
"""Register an object"""
self._objects[name] = obj
def unregister_object(self, name):
"""Unregister an object"""
del self._objects[name]
def clone(self, name, **attr):
"""Clone a registered object and update inner attributes dictionary"""
obj = copy.deepcopy(self._objects.get(name))
obj.__dict__.update(attr)
return obj
def main():
class A:
def __str__(self):
return "I am A"
a = A()
prototype = Prototype()
prototype.register_object('a', a)
b = prototype.clone('a', a=1, b=2, c=3)
print(a)
print(b.a, b.b, b.c)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
|
5. Singleton(单例)
意图:
保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点。
与单例模式功能相似的概念:全局变量、静态变量(方法)
适用性:
当类只能有一个实例而且客户可以从一个众所周知的访问点访问它时。
当这个唯一实例应该是通过子类化可扩展的,并且客户应该无需更改代码就能使用一个扩展的实例时。
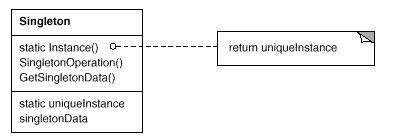
优点:
- 对唯一实例的受控访问。
- 单例相当于全局变量,但放置了命名空间被污染。
实现:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Singleton
'''
class Singleton(object):
''''' A python style singleton '''
def __new__(cls, *args, **kw):
if not hasattr(cls, '_instance'):
org = super(Singleton, cls)
cls._instance = org.__new__(cls, *args, **kw)
return cls._instance
if __name__ == '__main__':
class SingleSpam(Singleton):
def __init__(self, s):
self.s = s
def __str__(self):
return self.s
s1 = SingleSpam('spam')
print id(s1), s1
s2 = SingleSpam('spa')
print id(s2), s2
print id(s1), s1
|
创建型模式小结:
- 依赖于继承的创建模式:工厂方法模式
- 依赖于组合的创建型模式:抽象工厂模式、创建者模式。
结构型
6. Adapter Class/Object(适配器)
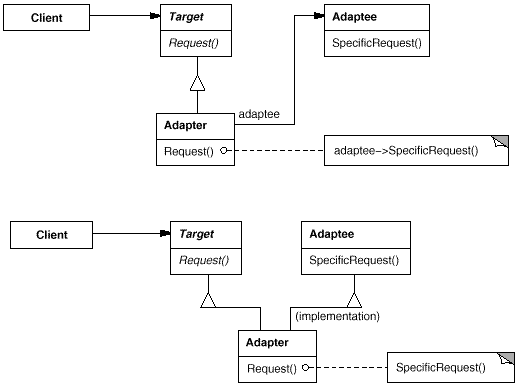
意图:
将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口。Adapter 模式使原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。
两种实现方式:类适配器(使用多继承), 对象适配器(使用组合)。
适用性:
使用一个已经存在的类,而它的接口不符合你的需求。
想创建一个可以复用的类,该类可以与其他不相关的类或不可预见的类(即那些接口可能不一定兼容的类)协同工作。
(仅适用于对象Adapter )你想使用一些已经存在的子类,但是不可能对每一个都进行子类化以匹配它们的接口。对象适配器可以适配它的父类接口。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Adapter
'''
import os
class Dog(object):
def __init__(self):
self.name = "Dog"
def bark(self):
return "woof!"
class Cat(object):
def __init__(self):
self.name = "Cat"
def meow(self):
return "meow!"
class Human(object):
def __init__(self):
self.name = "Human"
def speak(self):
return "'hello'"
class Car(object):
def __init__(self):
self.name = "Car"
def make_noise(self, octane_level):
return "vroom%s" % ("!" * octane_level)
class Adapter(object):
"""
Adapts an object by replacing methods.
Usage:
dog = Dog
dog = Adapter(dog, dict(make_noise=dog.bark))
"""
def __init__(self, obj, adapted_methods):
"""We set the adapted methods in the object's dict"""
self.obj = obj
self.__dict__.update(adapted_methods)
def __getattr__(self, attr):
"""All non-adapted calls are passed to the object"""
return getattr(self.obj, attr)
def main():
objects = []
dog = Dog()
objects.append(Adapter(dog, dict(make_noise=dog.bark)))
cat = Cat()
objects.append(Adapter(cat, dict(make_noise=cat.meow)))
human = Human()
objects.append(Adapter(human, dict(make_noise=human.speak)))
car = Car()
car_noise = lambda: car.make_noise(3)
objects.append(Adapter(car, dict(make_noise=car_noise)))
for obj in objects:
print "A", obj.name, "goes", obj.make_noise()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
|
7. Bridge(桥接)
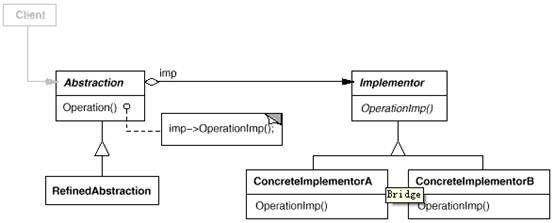
意图:
将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化。
适用性:
你不希望在抽象和它的实现部分之间有一个固定的绑定关系。例如这种情况可能是因为,在程序运行时刻实现部分应可以被选择或者切换。
类的抽象以及它的实现都应该可以通过生成子类的方法加以扩充。这时Bridge 模式使你可以对不同的抽象接口和实现部分进行组合,并分别对它们进行扩充。
对一个抽象的实现部分的修改应对客户不产生影响,即客户的代码不必重新编译。
(C++)你想对客户完全隐藏抽象的实现部分。在C++中,类的表示在类接口中是可见的。
有许多类要生成。这样一种类层次结构说明你必须将一个对象分解成两个部分。Rumbaugh 称这种类层次结构为“嵌套的普化”(nested generalizations )。
你想在多个对象间共享实现(可能使用引用计数),但同时要求客户并不知道这一点。一个简单的例子便是Coplien 的String 类[ Cop92 ],在这个类中多个对象可以共享同一个字符串表示(StringRep)。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Bridge
'''
# ConcreteImplementor 1/2
class DrawingAPI1(object):
def draw_circle(self, x, y, radius):
print('API1.circle at {}:{} radius {}'.format(x, y, radius))
# ConcreteImplementor 2/2
class DrawingAPI2(object):
def draw_circle(self, x, y, radius):
print('API2.circle at {}:{} radius {}'.format(x, y, radius))
# Refined Abstraction
class CircleShape(object):
def __init__(self, x, y, radius, drawing_api):
self._x = x
self._y = y
self._radius = radius
self._drawing_api = drawing_api
# low-level i.e. Implementation specific
def draw(self):
self._drawing_api.draw_circle(self._x, self._y, self._radius)
# high-level i.e. Abstraction specific
def scale(self, pct):
self._radius *= pct
def main():
shapes = (
CircleShape(1, 2, 3, DrawingAPI1()),
CircleShape(5, 7, 11, DrawingAPI2())
)
for shape in shapes:
shape.scale(2.5)
shape.draw()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
|
8. Composite(组合)
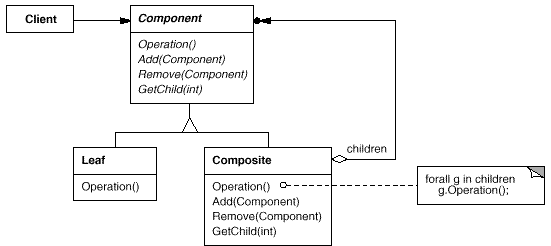
意图:
将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构。C o m p o s i t e 使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
适用性:
你想表示对象的部分-整体层次结构。
你希望用户忽略组合对象与单个对象的不同,用户将统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
"""
Composite
"""
class Component:
def __init__(self,strName):
self.m_strName = strName
def Add(self,com):
pass
def Display(self,nDepth):
pass
class Leaf(Component):
def Add(self,com):
print "leaf can't add"
def Display(self,nDepth):
strtemp = "-" * nDepth
strtemp=strtemp+self.m_strName
print strtemp
class Composite(Component):
def __init__(self,strName):
self.m_strName = strName
self.c = []
def Add(self,com):
self.c.append(com)
def Display(self,nDepth):
strtemp = "-"*nDepth
strtemp=strtemp+self.m_strName
print strtemp
for com in self.c:
com.Display(nDepth+2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
p = Composite("Wong")
p.Add(Leaf("Lee"))
p.Add(Leaf("Zhao"))
p1 = Composite("Wu")
p1.Add(Leaf("San"))
p.Add(p1)
p.Display(1);
|
9. Decorator(装饰)
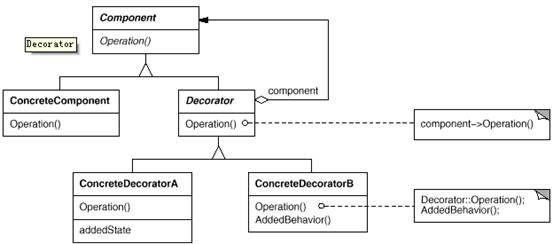
意图:
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,Decorator 模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
适用性:
在不影响其他对象的情况下,以动态、透明的方式给单个对象添加职责。
处理那些可以撤消的职责。
当不能采用生成子类的方法进行扩充时。一种情况是,可能有大量独立的扩展,为支持每一种组合将产生大量的子类,使得子类数目呈爆炸性增长。另一种情况可能是因为类定义被隐藏,或类定义不能用于生成子类。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Decorator
'''
class foo(object):
def f1(self):
print("original f1")
def f2(self):
print("original f2")
class foo_decorator(object):
def __init__(self, decoratee):
self._decoratee = decoratee
def f1(self):
print("decorated f1")
self._decoratee.f1()
def __getattr__(self, name):
return getattr(self._decoratee, name)
u = foo()
v = foo_decorator(u)
v.f1()
v.f2()
|
10. Facade(外观)
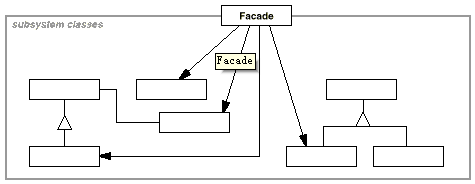
意图:
为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,Facade模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
适用性:
当你要为一个复杂子系统提供一个简单接口时。子系统往往因为不断演化而变得越来越复杂。大多数模式使用时都会产生更多更小的类。这使得子系统更具可重用性,也更容易对子系统进行定制,但这也给那些不需要定制子系统的用户带来一些使用上的困难。Facade 可以提供一个简单的缺省视图,这一视图对大多数用户来说已经足够,而那些需要更多的可定制性的用户可以越过facade层。
客户程序与抽象类的实现部分之间存在着很大的依赖性。引入facade 将这个子系统与客户以及其他的子系统分离,可以提高子系统的独立性和可移植性。
当你需要构建一个层次结构的子系统时,使用facade模式定义子系统中每层的入口点。如果子系统之间是相互依赖的,你可以让它们仅通过facade进行通讯,从而简化了它们之间的依赖关系。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Decorator
'''
import time
SLEEP = 0.5
# Complex Parts
class TC1:
def run(self):
print("###### In Test 1 ######")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Setting up")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Running test")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Tearing down")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Test Finished\n")
class TC2:
def run(self):
print("###### In Test 2 ######")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Setting up")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Running test")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Tearing down")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Test Finished\n")
class TC3:
def run(self):
print("###### In Test 3 ######")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Setting up")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Running test")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Tearing down")
time.sleep(SLEEP)
print("Test Finished\n")
# Facade
class TestRunner:
def __init__(self):
self.tc1 = TC1()
self.tc2 = TC2()
self.tc3 = TC3()
self.tests = [i for i in (self.tc1, self.tc2, self.tc3)]
def runAll(self):
[i.run() for i in self.tests]
# Client
if __name__ == '__main__':
testrunner = TestRunner()
testrunner.runAll()
|
11. Flyweight(享元)

意图:
运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象。
适用性:
一个应用程序使用了大量的对象。
完全由于使用大量的对象,造成很大的存储开销。
对象的大多数状态都可变为外部状态。
如果删除对象的外部状态,那么可以用相对较少的共享对象取代很多组对象。
应用程序不依赖于对象标识。由于Flyweight 对象可以被共享,对于概念上明显有别的对象,标识测试将返回真值。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Flyweight
'''
import weakref
class Card(object):
"""The object pool. Has builtin reference counting"""
_CardPool = weakref.WeakValueDictionary()
"""Flyweight implementation. If the object exists in the
pool just return it (instead of creating a new one)"""
def __new__(cls, value, suit):
obj = Card._CardPool.get(value + suit, None)
if not obj:
obj = object.__new__(cls)
Card._CardPool[value + suit] = obj
obj.value, obj.suit = value, suit
return obj
# def __init__(self, value, suit):
# self.value, self.suit = value, suit
def __repr__(self):
return "" % (self.value, self.suit)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# comment __new__ and uncomment __init__ to see the difference
c1 = Card('9', 'h')
c2 = Card('9', 'h')
print(c1, c2)
print(c1 == c2)
print(id(c1), id(c2))
|
12. Proxy(代理)
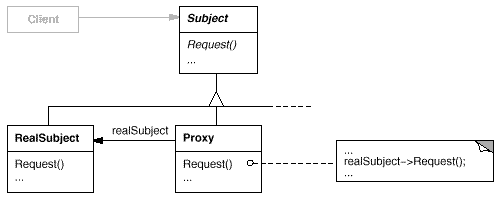
意图:
为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。
适用性:
在需要用比较通用和复杂的对象指针代替简单的指针的时候,使用Proxy模式。下面是一 些可以使用Proxy 模式常见情况:
1) 远程代理(Remote Proxy )为一个对象在不同的地址空间提供局部代表。 NEXTSTEP[Add94] 使用NXProxy 类实现了这一目的。Coplien[Cop92] 称这种代理为“大使” (Ambassador )。
2 )虚代理(Virtual Proxy )根据需要创建开销很大的对象。在动机一节描述的ImageProxy 就是这样一种代理的例子。
3) 保护代理(Protection Proxy )控制对原始对象的访问。保护代理用于对象应该有不同 的访问权限的时候。例如,在Choices 操作系统[ CIRM93]中KemelProxies为操作系统对象提供 了访问保护。
4 )智能指引(Smart Reference )取代了简单的指针,它在访问对象时执行一些附加操作。 它的典型用途包括:对指向实际对象的引用计数,这样当该对象没有引用时,可以自动释放它(也称为SmartPointers[Ede92 ] )。
当第一次引用一个持久对象时,将它装入内存。
在访问一个实际对象前,检查是否已经锁定了它,以确保其他对象不能改变它。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Proxy
'''
import time
class SalesManager:
def work(self):
print("Sales Manager working...")
def talk(self):
print("Sales Manager ready to talk")
class Proxy:
def __init__(self):
self.busy = 'No'
self.sales = None
def work(self):
print("Proxy checking for Sales Manager availability")
if self.busy == 'No':
self.sales = SalesManager()
time.sleep(2)
self.sales.talk()
else:
time.sleep(2)
print("Sales Manager is busy")
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = Proxy()
p.work()
p.busy = 'Yes'
p.work()
|
行为型
13. Interpreter(解释器)
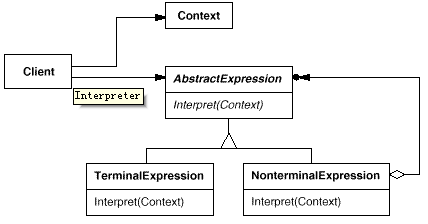
意图:
给定一个语言,定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,这个解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。
适用性:
当有一个语言需要解释执行, 并且你可将该语言中的句子表示为一个抽象语法树时,可使用解释器模式。而当存在以下情况时该模式效果最好:
该文法简单对于复杂的文法, 文法的类层次变得庞大而无法管理。此时语法分析程序生成器这样的工具是更好的选择。它们无需构建抽象语法树即可解释表达式, 这样可以节省空间而且还可能节省时间。
效率不是一个关键问题最高效的解释器通常不是通过直接解释语法分析树实现的, 而是首先将它们转换成另一种形式。例如,正则表达式通常被转换成状态机。但即使在这种情况下, 转换器仍可用解释器模式实现, 该模式仍是有用的。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Interpreter
'''
class Context:
def __init__(self):
self.input=""
self.output=""
class AbstractExpression:
def Interpret(self,context):
pass
class Expression(AbstractExpression):
def Interpret(self,context):
print "terminal interpret"
class NonterminalExpression(AbstractExpression):
def Interpret(self,context):
print "Nonterminal interpret"
if __name__ == "__main__":
context= ""
c = []
c = c + [Expression()]
c = c + [NonterminalExpression()]
c = c + [Expression()]
c = c + [Expression()]
for a in c:
a.Interpret(context)
|
14. Template Method(模板方法)
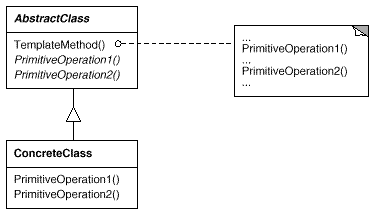
意图:
定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。TemplateMethod 使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
适用性:
一次性实现一个算法的不变的部分,并将可变的行为留给子类来实现。
各子类中公共的行为应被提取出来并集中到一个公共父类中以避免代码重复。这是Opdyke 和Johnson所描述过的“重分解以一般化”的一个很好的例子[ OJ93 ]。首先识别现有代码中的不同之处,并且将不同之处分离为新的操作。最后,用一个调用这些新的操作的模板方法来替换这些不同的代码。
控制子类扩展。模板方法只在特定点调用“hook ”操作(参见效果一节),这样就只允许在这些点进行扩展。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Template Method
'''
ingredients = "spam eggs apple"
line = '-' * 10
# Skeletons
def iter_elements(getter, action):
"""Template skeleton that iterates items"""
for element in getter():
action(element)
print(line)
def rev_elements(getter, action):
"""Template skeleton that iterates items in reverse order"""
for element in getter()[::-1]:
action(element)
print(line)
# Getters
def get_list():
return ingredients.split()
def get_lists():
return [list(x) for x in ingredients.split()]
# Actions
def print_item(item):
print(item)
def reverse_item(item):
print(item[::-1])
# Makes templates
def make_template(skeleton, getter, action):
"""Instantiate a template method with getter and action"""
def template():
skeleton(getter, action)
return template
# Create our template functions
templates = [make_template(s, g, a)
for g in (get_list, get_lists)
for a in (print_item, reverse_item)
for s in (iter_elements, rev_elements)]
# Execute them
for template in templates:
template()
|
15. Chain of Responsibility(责任链)
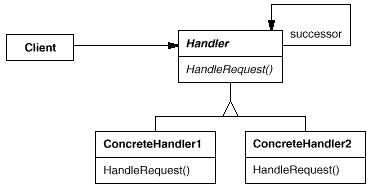
意图:
使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系。将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止。
适用性:
有多个的对象可以处理一个请求,哪个对象处理该请求运行时刻自动确定。
你想在不明确指定接收者的情况下,向多个对象中的一个提交一个请求。
可处理一个请求的对象集合应被动态指定。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
"""
Chain
"""
class Handler:
def successor(self, successor):
self.successor = successor
class ConcreteHandler1(Handler):
def handle(self, request):
if request > 0 and request <= 10:
print("in handler1")
else:
self.successor.handle(request)
class ConcreteHandler2(Handler):
def handle(self, request):
if request > 10 and request <= 20:
print("in handler2")
else:
self.successor.handle(request)
class ConcreteHandler3(Handler):
def handle(self, request):
if request > 20 and request <= 30:
print("in handler3")
else:
print('end of chain, no handler for {}'.format(request))
class Client:
def __init__(self):
h1 = ConcreteHandler1()
h2 = ConcreteHandler2()
h3 = ConcreteHandler3()
h1.successor(h2)
h2.successor(h3)
requests = [2, 5, 14, 22, 18, 3, 35, 27, 20]
for request in requests:
h1.handle(request)
if __name__ == "__main__":
client = Client()
|
16. Command(命令)
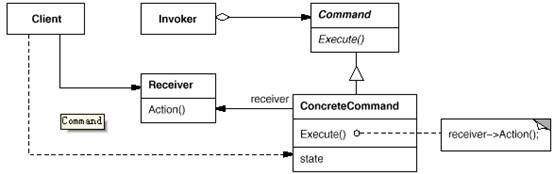
意图:
将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤消的操作。
适用性:
抽象出待执行的动作以参数化某对象,你可用过程语言中的回调(call back)函数表达这种参数化机制。所谓回调函数是指函数先在某处注册,而它将在稍后某个需要的时候被调用。Command 模式是回调机制的一个面向对象的替代品。
在不同的时刻指定、排列和执行请求。一个Command对象可以有一个与初始请求无关的生存期。如果一个请求的接收者可用一种与地址空间无关的方式表达,那么就可将负责该请求的命令对象传送给另一个不同的进程并在那儿实现该请求。
支持取消操作。Command的Excute 操作可在实施操作前将状态存储起来,在取消操作时这个状态用来消除该操作的影响。Command 接口必须添加一个Unexecute操作,该操作取消上一次Execute调用的效果。执行的命令被存储在一个历史列表中。可通过向后和向前遍历这一列表并分别调用Unexecute和Execute来实现重数不限的“取消”和“重做”。
支持修改日志,这样当系统崩溃时,这些修改可以被重做一遍。在Command接口中添加装载操作和存储操作,可以用来保持变动的一个一致的修改日志。从崩溃中恢复的过程包括从磁盘中重新读入记录下来的命令并用Execute操作重新执行它们。
用构建在原语操作上的高层操作构造一个系统。这样一种结构在支持事务( transaction)的信息系统中很常见。一个事务封装了对数据的一组变动。Command模式提供了对事务进行建模的方法。Command有一个公共的接口,使得你可以用同一种方式调用所有的事务。同时使用该模式也易于添加新事务以扩展系统。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
"""
Command
"""
import os
class MoveFileCommand(object):
def __init__(self, src, dest):
self.src = src
self.dest = dest
def execute(self):
self()
def __call__(self):
print('renaming {} to {}'.format(self.src, self.dest))
os.rename(self.src, self.dest)
def undo(self):
print('renaming {} to {}'.format(self.dest, self.src))
os.rename(self.dest, self.src)
if __name__ == "__main__":
command_stack = []
# commands are just pushed into the command stack
command_stack.append(MoveFileCommand('foo.txt', 'bar.txt'))
command_stack.append(MoveFileCommand('bar.txt', 'baz.txt'))
# they can be executed later on
for cmd in command_stack:
cmd.execute()
# and can also be undone at will
for cmd in reversed(command_stack):
cmd.undo()
|
17. Iterator(迭代器)
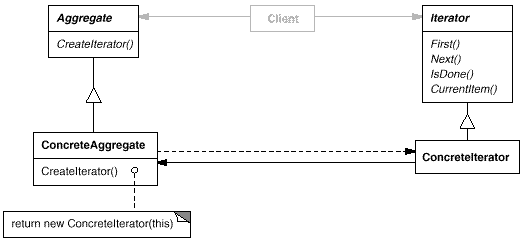
意图:
提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素, 而又不需暴露该对象的内部表示。
适用性:
访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示。
支持对聚合对象的多种遍历。
为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口(即, 支持多态迭代)。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Interator
'''
def count_to(count):
"""Counts by word numbers, up to a maximum of five"""
numbers = ["one", "two", "three", "four", "five"]
# enumerate() returns a tuple containing a count (from start which
# defaults to 0) and the values obtained from iterating over sequence
for pos, number in zip(range(count), numbers):
yield number
# Test the generator
count_to_two = lambda: count_to(2)
count_to_five = lambda: count_to(5)
print('Counting to two...')
for number in count_to_two():
print number
print " "
print('Counting to five...')
for number in count_to_five():
print number
print " "
|
18. Mediator(中介者)
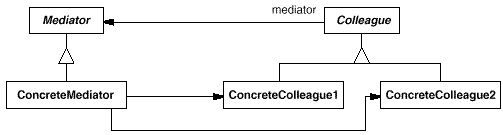
意图:
用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互。中介者使各对象不需要显式地相互引用,从而使其耦合松散,而且可以独立地改变它们之间的交互。
适用性:
一组对象以定义良好但是复杂的方式进行通信。产生的相互依赖关系结构混乱且难以理解。
一个对象引用其他很多对象并且直接与这些对象通信,导致难以复用该对象。
想定制一个分布在多个类中的行为,而又不想生成太多的子类。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Mediator
'''
"""http://dpip.testingperspective.com/?p=28"""
import time
class TC:
def __init__(self):
self._tm = tm
self._bProblem = 0
def setup(self):
print("Setting up the Test")
time.sleep(1)
self._tm.prepareReporting()
def execute(self):
if not self._bProblem:
print("Executing the test")
time.sleep(1)
else:
print("Problem in setup. Test not executed.")
def tearDown(self):
if not self._bProblem:
print("Tearing down")
time.sleep(1)
self._tm.publishReport()
else:
print("Test not executed. No tear down required.")
def setTM(self, TM):
self._tm = tm
def setProblem(self, value):
self._bProblem = value
class Reporter:
def __init__(self):
self._tm = None
def prepare(self):
print("Reporter Class is preparing to report the results")
time.sleep(1)
def report(self):
print("Reporting the results of Test")
time.sleep(1)
def setTM(self, TM):
self._tm = tm
class DB:
def __init__(self):
self._tm = None
def insert(self):
print("Inserting the execution begin status in the Database")
time.sleep(1)
#Following code is to simulate a communication from DB to TC
import random
if random.randrange(1, 4) == 3:
return -1
def update(self):
print("Updating the test results in Database")
time.sleep(1)
def setTM(self, TM):
self._tm = tm
class TestManager:
def __init__(self):
self._reporter = None
self._db = None
self._tc = None
def prepareReporting(self):
rvalue = self._db.insert()
if rvalue == -1:
self._tc.setProblem(1)
self._reporter.prepare()
def setReporter(self, reporter):
self._reporter = reporter
def setDB(self, db):
self._db = db
def publishReport(self):
self._db.update()
rvalue = self._reporter.report()
def setTC(self, tc):
self._tc = tc
if __name__ == '__main__':
reporter = Reporter()
db = DB()
tm = TestManager()
tm.setReporter(reporter)
tm.setDB(db)
reporter.setTM(tm)
db.setTM(tm)
# For simplification we are looping on the same test.
# Practically, it could be about various unique test classes and their
# objects
while (True):
tc = TC()
tc.setTM(tm)
tm.setTC(tc)
tc.setup()
tc.execute()
tc.tearDown()
|
19. Memento(备忘录)
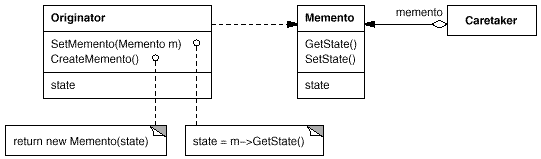
意图:
在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样以后就可将该对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
适用性:
必须保存一个对象在某一个时刻的(部分)状态, 这样以后需要时它才能恢复到先前的状态。
如果一个用接口来让其它对象直接得到这些状态,将会暴露对象的实现细节并破坏对象的封装性。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Memento
'''
import copy
def Memento(obj, deep=False):
state = (copy.copy, copy.deepcopy)[bool(deep)](obj.__dict__)
def Restore():
obj.__dict__.clear()
obj.__dict__.update(state)
return Restore
class Transaction:
"""A transaction guard. This is really just
syntactic suggar arount a memento closure.
"""
deep = False
def __init__(self, *targets):
self.targets = targets
self.Commit()
def Commit(self):
self.states = [Memento(target, self.deep) for target in self.targets]
def Rollback(self):
for st in self.states:
st()
class transactional(object):
"""Adds transactional semantics to methods. Methods decorated with
@transactional will rollback to entry state upon exceptions.
"""
def __init__(self, method):
self.method = method
def __get__(self, obj, T):
def transaction(*args, **kwargs):
state = Memento(obj)
try:
return self.method(obj, *args, **kwargs)
except:
state()
raise
return transaction
class NumObj(object):
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
def __repr__(self):
return '<%s: %r>' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.value)
def Increment(self):
self.value += 1
@transactional
def DoStuff(self):
self.value = '1111' # <- invalid value
self.Increment() # <- will fail and rollback
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = NumObj(-1)
print(n)
t = Transaction(n)
try:
for i in range(3):
n.Increment()
print(n)
t.Commit()
print('-- commited')
for i in range(3):
n.Increment()
print(n)
n.value += 'x' # will fail
print(n)
except:
t.Rollback()
print('-- rolled back')
print(n)
print('-- now doing stuff ...')
try:
n.DoStuff()
except:
print('-> doing stuff failed!')
import traceback
traceback.print_exc(0)
pass
print(n)
|
20. Observer(观察者)
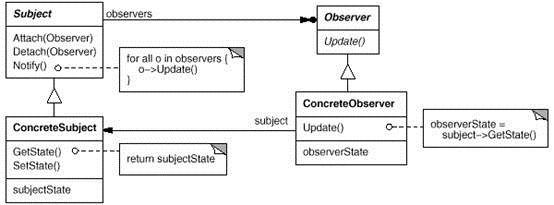
意图:
定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变时, 所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并被自动更新。
适用性:
当一个抽象模型有两个方面, 其中一个方面依赖于另一方面。将这二者封装在独立的对象中以使它们可以各自独立地改变和复用。
当对一个对象的改变需要同时改变其它对象, 而不知道具体有多少对象有待改变。
当一个对象必须通知其它对象,而它又不能假定其它对象是谁。换言之, 你不希望这些对象是紧密耦合的。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Observer
'''
class Subject(object):
def __init__(self):
self._observers = []
def attach(self, observer):
if not observer in self._observers:
self._observers.append(observer)
def detach(self, observer):
try:
self._observers.remove(observer)
except ValueError:
pass
def notify(self, modifier=None):
for observer in self._observers:
if modifier != observer:
observer.update(self)
# Example usage
class Data(Subject):
def __init__(self, name=''):
Subject.__init__(self)
self.name = name
self._data = 0
@property
def data(self):
return self._data
@data.setter
def data(self, value):
self._data = value
self.notify()
class HexViewer:
def update(self, subject):
print('HexViewer: Subject %s has data 0x%x' %
(subject.name, subject.data))
class DecimalViewer:
def update(self, subject):
print('DecimalViewer: Subject %s has data %d' %
(subject.name, subject.data))
# Example usage...
def main():
data1 = Data('Data 1')
data2 = Data('Data 2')
view1 = DecimalViewer()
view2 = HexViewer()
data1.attach(view1)
data1.attach(view2)
data2.attach(view2)
data2.attach(view1)
print("Setting Data 1 = 10")
data1.data = 10
print("Setting Data 2 = 15")
data2.data = 15
print("Setting Data 1 = 3")
data1.data = 3
print("Setting Data 2 = 5")
data2.data = 5
print("Detach HexViewer from data1 and data2.")
data1.detach(view2)
data2.detach(view2)
print("Setting Data 1 = 10")
data1.data = 10
print("Setting Data 2 = 15")
data2.data = 15
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
|
21. State(状态)
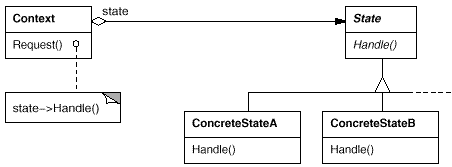
意图:
允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为。对象看起来似乎修改了它的类。
适用性:
一个对象的行为取决于它的状态, 并且它必须在运行时刻根据状态改变它的行为。
一个操作中含有庞大的多分支的条件语句,且这些分支依赖于该对象的状态。这个状态通常用一个或多个枚举常量表示。通常, 有多个操作包含这一相同的条件结构。State模式将每一个条件分支放入一个独立的类中。这使得你可以根据对象自身的情况将对象的状态作为一个对象,这一对象可以不依赖于其他对象而独立变化。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
State
'''
class State(object):
"""Base state. This is to share functionality"""
def scan(self):
"""Scan the dial to the next station"""
self.pos += 1
if self.pos == len(self.stations):
self.pos = 0
print("Scanning... Station is", self.stations[self.pos], self.name)
class AmState(State):
def __init__(self, radio):
self.radio = radio
self.stations = ["1250", "1380", "1510"]
self.pos = 0
self.name = "AM"
def toggle_amfm(self):
print("Switching to FM")
self.radio.state = self.radio.fmstate
class FmState(State):
def __init__(self, radio):
self.radio = radio
self.stations = ["81.3", "89.1", "103.9"]
self.pos = 0
self.name = "FM"
def toggle_amfm(self):
print("Switching to AM")
self.radio.state = self.radio.amstate
class Radio(object):
"""A radio. It has a scan button, and an AM/FM toggle switch."""
def __init__(self):
"""We have an AM state and an FM state"""
self.amstate = AmState(self)
self.fmstate = FmState(self)
self.state = self.amstate
def toggle_amfm(self):
self.state.toggle_amfm()
def scan(self):
self.state.scan()
# Test our radio out
if __name__ == '__main__':
radio = Radio()
actions = [radio.scan] * 2 + [radio.toggle_amfm] + [radio.scan] * 2
actions = actions * 2
for action in actions:
action()
|
22. Strategy(策略)
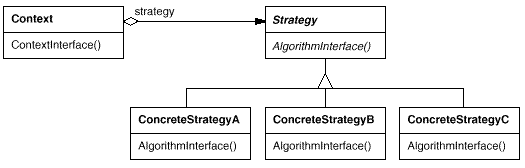
意图:
定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来, 并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法可独立于使用它的客户而变化。
适用性:
许多相关的类仅仅是行为有异。“策略”提供了一种用多个行为中的一个行为来配置一个类的方法。
需要使用一个算法的不同变体。例如,你可能会定义一些反映不同的空间/时间权衡的算法。当这些变体实现为一个算法的类层次时[H087] ,可以使用策略模式。
算法使用客户不应该知道的数据。可使用策略模式以避免暴露复杂的、与算法相关的数据结构。
一个类定义了多种行为, 并且这些行为在这个类的操作中以多个条件语句的形式出现。将相关的条件分支移入它们各自的Strategy类中以代替这些条件语句。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
"""
Strategy
In most of other languages Strategy pattern is implemented via creating some base strategy interface/abstract class and
subclassing it with a number of concrete strategies (as we can see at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strategy_pattern),
however Python supports higher-order functions and allows us to have only one class and inject functions into it's
instances, as shown in this example.
"""
import types
class StrategyExample:
def __init__(self, func=None):
self.name = 'Strategy Example 0'
if func is not None:
self.execute = types.MethodType(func, self)
def execute(self):
print(self.name)
def execute_replacement1(self):
print(self.name + ' from execute 1')
def execute_replacement2(self):
print(self.name + ' from execute 2')
if __name__ == '__main__':
strat0 = StrategyExample()
strat1 = StrategyExample(execute_replacement1)
strat1.name = 'Strategy Example 1'
strat2 = StrategyExample(execute_replacement2)
strat2.name = 'Strategy Example 2'
strat0.execute()
strat1.execute()
strat2.execute()
|
23. Visitor(访问者)
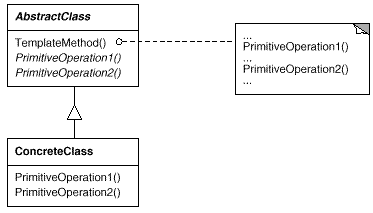
意图:
定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。TemplateMethod 使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
适用性:
一次性实现一个算法的不变的部分,并将可变的行为留给子类来实现。
各子类中公共的行为应被提取出来并集中到一个公共父类中以避免代码重复。这是Opdyke和Johnson所描述过的“重分解以一般化”的一个很好的例子[OJ93]。首先识别现有代码中的不同之处,并且将不同之处分离为新的操作。最后,用一个调用这些新的操作的模板方法来替换这些不同的代码。
控制子类扩展。模板方法只在特定点调用“hook ”操作(参见效果一节),这样就只允许在这些点进行扩展。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf8
'''
Visitor
'''
class Node(object):
pass
class A(Node):
pass
class B(Node):
pass
class C(A, B):
pass
class Visitor(object):
def visit(self, node, *args, **kwargs):
meth = None
for cls in node.__class__.__mro__:
meth_name = 'visit_'+cls.__name__
meth = getattr(self, meth_name, None)
if meth:
break
if not meth:
meth = self.generic_visit
return meth(node, *args, **kwargs)
def generic_visit(self, node, *args, **kwargs):
print('generic_visit '+node.__class__.__name__)
def visit_B(self, node, *args, **kwargs):
print('visit_B '+node.__class__.__name__)
a = A()
b = B()
c = C()
visitor = Visitor()
visitor.visit(a)
visitor.visit(b)
visitor.visit(c)
|
以上
欢迎多来访问博客:http://liqiongyu.com/blog






















