R 分析两个变量
ggplot2:数据分析与图形艺术- Hadley Wickham
8 过度绘制和领域知识
每用户都有一定的朋友数,x是实际的看的人数的百分比,y是猜想的看的人数的百分比。
9 条件均值
install.packages('dplyr')
library(dplyr)
# 其中的常见函数
filter()
group_by()
mutate()
arrange()更多关于 dplyr 包的信息
Hadley Wickham 于 2014 年在 useR 公布的教程:
dplyr 简介
dplyr 教程(第 1 部分)
dplyr 教程(第 2 部分)
12 相关性
# 方法一
cor.test(pf$age, pf$friend_count, method = "pearson")
# 方法二
with(pf, cor.test(age, friend_count, method = "pearson"))
Pearson's product-moment correlation
data: pf$age and pf$friend_count
t = -8.6268, df = 99001, p-value < 2.2e-16
alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.03363072 -0.02118189
sample estimates:
cor
-0.02740737 pearson product-moment correlation
pearson 积矩关联
绝对值0.3左右,代表两者之间是相关性比较弱;0.5左右代表相关性较强,0.7左右相关性很强。
13 子集、相关性
# 某个子集 的 相关系数
with(subset(pf, age <= 70), cor.test(age, friend_count))tip:相关 不代表 因果,需要从实验性研究中获取数据,然后使用推论统计学来得出因果关系,而不是描述性统计学。
14 相关分析法
R Tutorial - Correlation Coefficient
相关分析法: Pearson’s r, Spearman’s ρ 及 Kendall’s τ
15 创建散点图
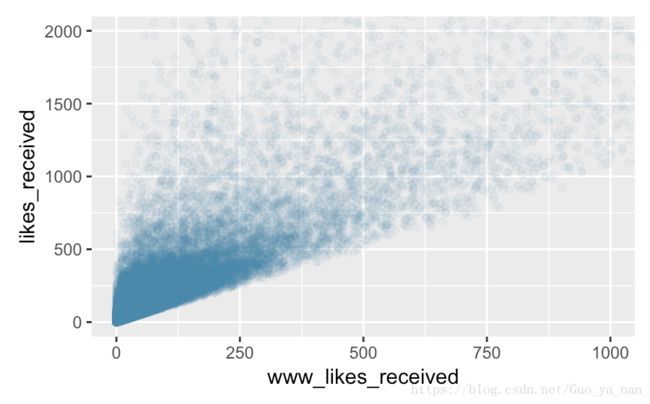
ggplot(aes(x = www_likes_received, y = likes_received), data = pf) +
geom_point(alpha = 1/20,
color = "steelblue") +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(0, 1000), ylim = c(0, 2000))16 强相关
with(pf, cor.test(www_likes_received, likes_received))
Pearson's product-moment correlation
data: www_likes_received and likes_received
t = 937.1, df = 99001, p-value < 2.2e-16
alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
0.9473553 0.9486176
sample estimates:
cor
0.9479902 相关系数在 X 或 Y 的线性转换下是不变的,并且当 X 和 Y 都被转换为 z 分数时,回归线的斜率就是相关系数。
17 对于相关性的研究
对facebook的研究,用户在过去一个月内更新多少状态,与很多变量强相关,比如 过去一个月内登录的天数,好友的个数,过去一个月内上传的照片数。所有这些变量都高度相关,因为它们衡量的东西都差不多,就是用户的互动频率。
通常在开始一项研究之前,做一些回归建模会很有帮助,看看变量之间是相互独立的还是相关的,可以帮助决定保留、舍弃哪些变量。
18 参数的传递
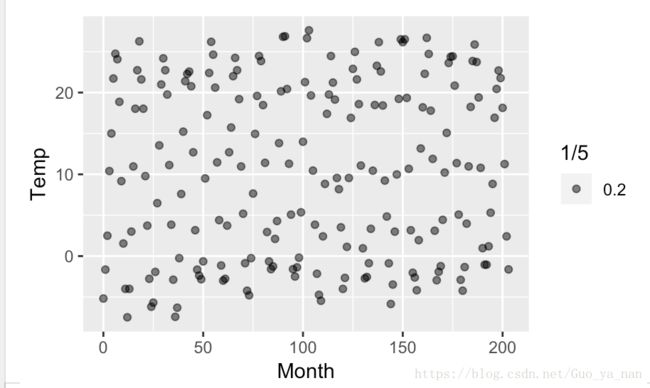
ggplot(aes(x = Month, y = Temp), data = Mitchell) +
geom_point(alpha = 1/5)
qplot(data = Mitchell, Month, Temp, alpha = 1/5)qplot 中除了精确匹配之外,剩下的 Month, Temp按照字母顺序传递参数给x,y。
21 数据可视化
数据可视化先驱:John Tukey,William Playfair
William Playfair 和图形心理学
数据的本质应该暗示图形的形状。
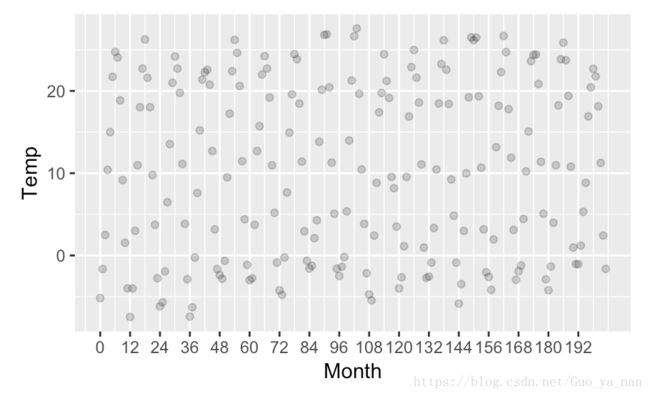
library(alr3)
data("Mitchell")
ggplot(data = Mitchell, aes(x = Month, y = Temp)) +
geom_point(alpha = 1/5) +
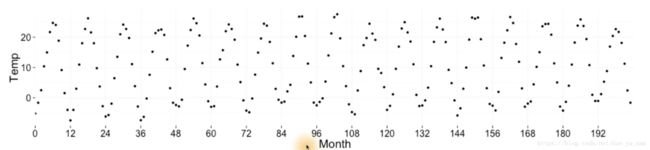
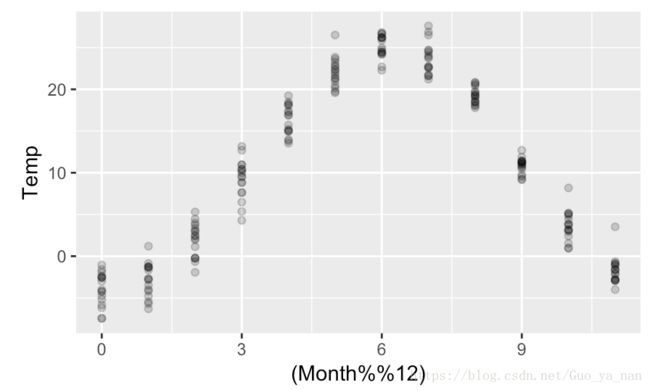
scale_x_continuous(breaks = seq(0, 203, 12))ggplot(data = Mitchell, aes(x = (Month%%12), y = Temp)) +
geom_point(alpha = 1/5)22 了解噪声:年龄到月龄
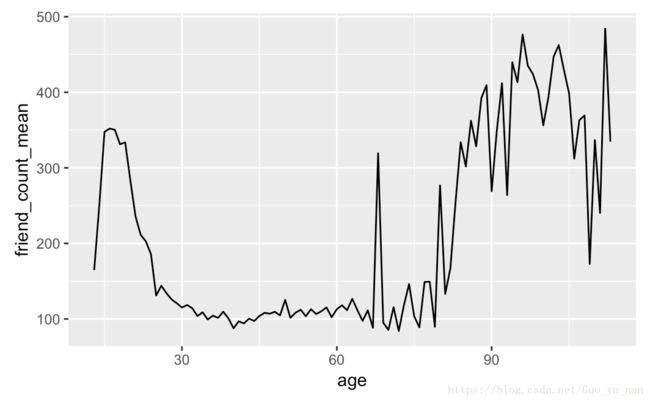
ggplot(aes(x = age, y = friend_count), data = pf) +
geom_line(stat = "summary", fun.y = mean)
ggplot(aes(x = age, y = friend_count_mean), data = pf.fc_by_age) + geom_line()pf$age_with_months <- pf$age + (1 - pf$dob_month/12)
pf$age_with_months <- with(pf, age + (1 - dob_month / 12))23 带有月均值的年龄
# 方法一
age_months_groups <- group_by(pf, age_with_months)
pf.fc_by_age_months <- summarise(age_months_groups,
friend_count_mean = mean(friend_count),
friend_count_median = median(friend_count),
n = n())
pf.fc_by_age <- arrange(pf.fc_by_age, age)
# 以下可以省略,以上得到的即为排序后的结果
pf.fc_by_age_months <- arrange(pf.fc_by_age_months2, age_with_months)
> head(pf.fc_by_age_months)
# A tibble: 6 x 4
age_with_months friend_count_mean friend_count_median n
1 13.2 46.3 30.5 6
2 13.2 115. 23.5 14
3 13.3 136. 44 25
4 13.4 164. 72 33
5 13.5 131. 66 45
6 13.6 157. 64 54 # 方法二
library(dplyr)
pf.fc_by_age_months2 <- pf %>%
group_by(age_with_months) %>%
summarise(friend_count_mean = mean(friend_count),
friend_count_median = median(friend_count),
n = n()) %>%
arrange(age_with_months)24 条件均值中的噪声
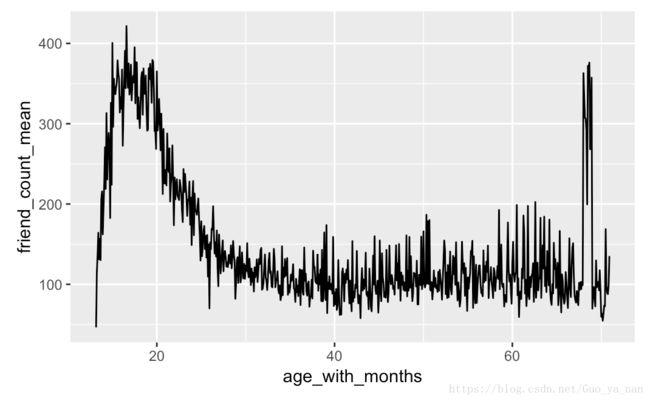
# 以上结果进行 画图
ggplot(data = subset(pf.fc_by_age_months, age_with_months < 71), aes(x = age_with_months, y = friend_count_mean)) +
geom_line()25 平滑化条件均值
p1 <- ggplot(aes(x = age, y = friend_count_mean),
data = subset(pf.fc_by_age, age < 71)) +
geom_line()
p2 <- ggplot(aes(x = age_with_months, y = friend_count_mean),
data = subset(pf.fc_by_age_months, age_with_months < 71)) +
geom_line()
library(gridExtra)
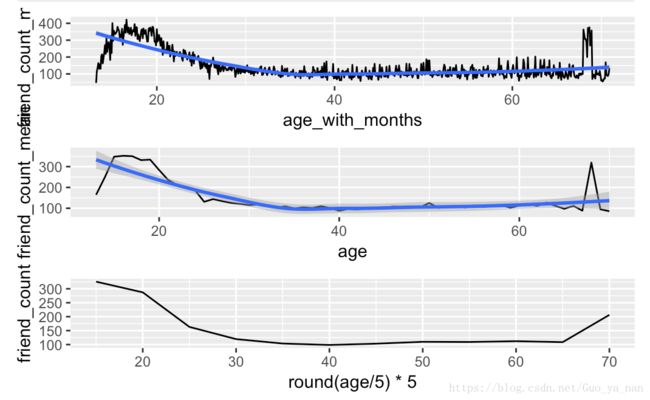
grid.arrange(p2, p1, ncol = 1)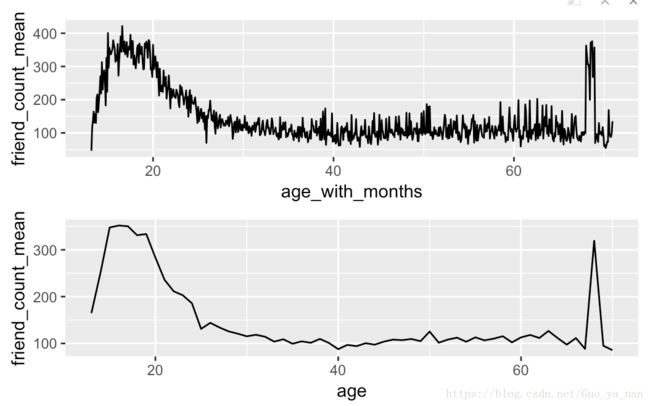
第一幅图采用了更精细的分组,噪声更多。增加分组,能够让图形变得更平滑。
p1 <- ggplot(aes(x = age, y = friend_count_mean),
data = subset(pf.fc_by_age, age < 71)) +
geom_line() +
geom_smooth()
p2 <- ggplot(aes(x = age_with_months, y = friend_count_mean),
data = subset(pf.fc_by_age_months, age_with_months < 71)) +
geom_line() +
geom_smooth()
# 此处代码没看懂
p3 <- ggplot(aes(x = round(age / 5) * 5, y = friend_count),
data = subset(pf, age < 71)) +
geom_line(stat = "summary", fun.y = "mean")
grid.arrange(p2, p1, p3, ncol = 1)局部回归 (LOESS) 的直观解释
Local regression的wiki解释
27 总结
散点图
在散点图的基础上增加 条件汇总(比如 平均值,百分位数)
相关系数
调整可视化效果:设置透明度,抖动,变换坐标轴,温度数据的月份调整。