Tensorflow实现ResNet及其原理
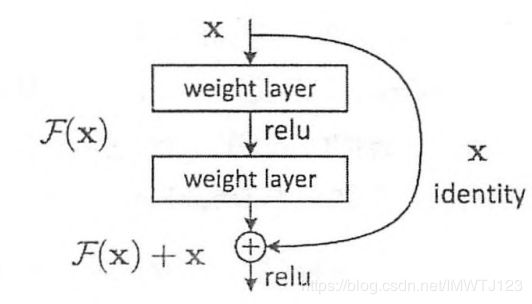
一、ResNet由微软研究院的Kaiming He等4名华人提出,有152层深的神经网络,在ILSVRC 2015比赛中获得冠军,其top-5错误率为3.57%,但参数量比VGGNet低,可以说效果很好了。ResNet和HighWay Network非常类似,也是允许原始输入信息直接传输到后面的层中,如图1所示,这就是一个ResNet的残差学习单元,ResNet相当于将学习目标改变,不再是学习一个完整的输出H(x),只是输出和输入的差别H(x)-x,即残差。
图1.ResNet的残差学习模块
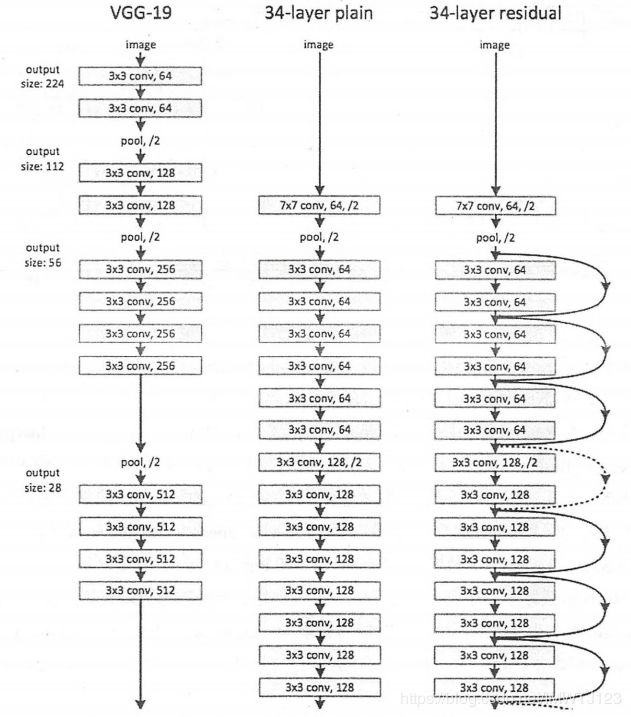
我们从图2可以看出普通直连的卷积神经网络和ResNet的最大区别在于,ResNet有很多旁路的支线将输入直接连在后面的层,使得后面的层可以直接学习残差,这种结构也称shortcut或skip connections。传统的卷积层或全连接层在信息传递时,或多或少存在信息丢失,损耗的问题。ResNet在某种程度上解决了这个问题,通过直接将输入信息绕道传到输出,保护信息的完整性,整个网络则只需要学习输入、输出差别的那一部分,简化学习目标和难度。
图2.VGGNet-19、34层深的普通卷积神经网络、34层深的ResNet的对比图
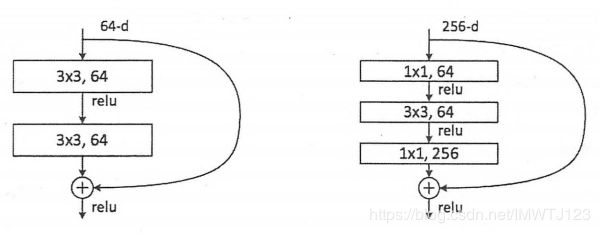
除了图1提出的两层学习单元,还有三层的残差学习单元,如图3,两层的残差学习单元包括两个相同输出通道数的3X3卷积。而3层的使用了Network In Network和Inception Net中的1*1的卷积,并且在3*3的前后都使用了1*1卷积,先降维再升维的操作。如果输入和输出的维度不同,可以先对x做一个线性映射变换维度,在连接到后面的层。
图3 两层和三层的ResNet残差学习模块
图4所示的为ResNet在不同层数时的网络配置,其他基本结构很类似,都是前面提到的两层和三层的残差学习单元的堆叠。
下面我们使用Tensorflow实现一个ResNet V2的网络:
#contrib.slim库辅助创建ResNet
import collections
import tensorflow as tf
slim=tf.contrib.slim
from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
tf.reset_default_graph()#出现后面所示错误所加的
#设计ResNet基本Block模块组的named tuple,并用它创建Block的类
#但只包含数据结构,不包含具体方法
class Block(collections.namedtuple('Block',['scope','unit_fn','args'])):
'A named tuple describing a ResNet block.'
#定义一个降采样的subsample的方法,factor为采样因子
def subsample(inputs,factor,scope=None):
if factor==1:
return inputs
else:
return slim.max_pool2d(inputs,[1,1],stride=factor,scope=scope)
#定义一个conv2d_same函数创建卷积层
def conv2d_same(inputs,num_outputs,kernel_size,stride,scope=None):
if stride==1:
return slim.conv2d(inputs,num_outputs,kernel_size,stride=1,
padding='SAME',scope=scope)
else:
pad_total=kernel_size-1
pad_beg=pad_total//2
pad_end=pad_total-pad_beg
inputs=tf.pad(inputs,[[0,0],[pad_beg,pad_end],#用tf.pad对输入变量进行补零操作
[pad_beg,pad_end],[0,0]])
return slim.conv2d(inputs,num_outputs,kernel_size,stride=stride,
padding='VALID',scope=scope)
#定义堆叠Blocks的函数,net为输入
#使用两层循环,逐个Block,逐个Residual Unit的堆叠
@slim.add_arg_scope
def stack_blocks_dense(net,blocks,outputs_collections=None):
for block in blocks:
with tf.variable_scope(block.scope,'block',[net]) as sc:
for i,unit in enumerate(block.args):
with tf.variable_scope('unit_%d' % (i+1),values=[net]):
unit_depth,unit_depth_bottleneck,unit_stride=unit
net=block.unit_fn(net,#顺序的创建并连接所有的残差学习单元
depth=unit_depth,
depth_bottleneck=unit_depth_bottleneck,
stride=unit_stride)
net=slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections,sc.name,net)
return net
#创建arg_scope,用于定义某些函数的参数默认值
def resnet_arg_scope(is_training=True,
weight_decay=0.0001,
batch_norm_decay=0.997,
batch_norm_epsilon=1e-5,
batch_norm_scale=True):
batch_norm_params={
'is_training':is_training,
'decay':batch_norm_decay,
'epsilon':batch_norm_epsilon,
'scale':batch_norm_scale,
'updates_collections':tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
}
with slim.arg_scope(
[slim.conv2d],
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay),
weights_initializer=slim.variance_scaling_initializer(),
activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm,
normalizer_params=batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm],**batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d],padding='SAME') as arg_sc:
return arg_sc
#定义核心的bottleneck残差学习单元
@slim.add_arg_scope
def bottleneck(inputs,depth,depth_bottleneck,stride,
outputs_collections=None,scope=None):
with tf.variable_scope(scope,'bottleneck_v2',[inputs]) as sc:
depth_in=slim.utils.last_dimension(inputs.get_shape(),min_rank=4)
preact=slim.batch_norm(inputs,activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
scope='preact')
if depth==depth_in:
shortcut=subsample(inputs,stride,'shortcut')
else:
shortcut=slim.conv2d(preact,depth,[1,1],stride=stride,
normalizer_fn=None,activation_fn=None,
scope='shortcut')
residual = slim.conv2d(preact, depth_bottleneck, [1, 1], stride=1,
scope='conv1')
residual = slim.conv2d(residual, depth_bottleneck, 3, stride,
scope='conv2')
residual = slim.conv2d(residual, depth, [1, 1], stride=1,
normalizer_fn=None, activation_fn=None,
scope='conv3')
output = shortcut + residual
return slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections,
sc.name, output)#生成主函数
def resnet_v2(inputs,
blocks,
num_classes=None,
global_pool=True,
include_root_block=True,
reuse=None,
scope=None):
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'resnet_v2', [inputs], reuse=reuse) as sc:
end_points_collection = sc.original_name_scope + '_end_points'
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, bottleneck,
stack_blocks_dense],
outputs_collections=end_points_collection):
net = inputs
if include_root_block:
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], activation_fn=None,
normalizer_fn=None):
net = conv2d_same(net, 64, 7, stride=2, scope='conv1')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='pool1')
net = stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks)
net = slim.batch_norm(net, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, scope='postnorm')
if global_pool:
net = tf.reduce_mean(net, [1, 2], name='pool5', keep_dims=True)
if num_classes is not None:
net = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None,
normalizer_fn=None, scope='logits')
end_points = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(end_points_collection)
if num_classes is not None:
end_points['predictions'] = slim.softmax(net, scope='predictions')
return net, end_points
#50层的残差网络
#4个残差学习的Blocks的units数量分别是3、4、6、3
def resnet_v2_50(inputs,
num_classes=None,
global_pool=True,
reuse=None,
scope='resnet_v2_50'):
bolcks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(255, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 3 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 5 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3 )]
return resnet_v2(inputs, bolcks,num_classes, global_pool,
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
#101层的残差网络
#4个残差学习的Blocks的units数量分别是3、4、23、3
def resnet_v2_101(inputs,
num_classes=None,
global_pool=True,
reuse=None,
scope='resnet_v2_101'):
bolcks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(255, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 3 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 22 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3 )]
return resnet_v2(inputs, bolcks,num_classes, global_pool,
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
#152层的残差网络
#4个残差学习的Blocks的units数量分别是3、8、36、3
def resnet_v2_152(inputs,
num_classes=None,
global_pool=True,
reuse=None,
scope='resnet_v2_152'):
bolcks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(255, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 7 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 35 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3 )]
return resnet_v2(inputs, bolcks,num_classes, global_pool,
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
#200层的残差网络
#4个残差学习的Blocks的units数量分别是3、23、23、3
def resnet_v2_200(inputs,
num_classes=None,
global_pool=True,
reuse=None,
scope='resnet_v2_200'):
bolcks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(255, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 23 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 35 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3 )]
return resnet_v2(inputs, bolcks,num_classes, global_pool,
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)使用测评函数time_tensorflow_run来测试152层深的ResNet
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
num_steps_burn_in = 10
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print ('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %
(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print ('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %
(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
batch_size = 32
height, width = 244, 244
inputs = tf.random_uniform((batch_size, height, width, 3))
with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=False)):
net, end_points = resnet_v2_152(inputs, 1000)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
num_batches = 100
time_tensorflow_run(sess,net,"Forward")结果如下:
2018-11-25 16:55:38.335185: step 0, duration = 6.397
2018-11-25 16:56:44.237910: step 10, duration = 6.460
2018-11-25 16:57:49.805304: step 20, duration = 6.631
2018-11-25 16:58:57.578776: step 30, duration = 6.936
2018-11-25 17:00:03.611065: step 40, duration = 6.510
2018-11-25 17:01:09.255940: step 50, duration = 6.534
2018-11-25 17:02:15.865199: step 60, duration = 7.002
2018-11-25 17:03:21.257175: step 70, duration = 6.674
2018-11-25 17:04:27.042940: step 80, duration = 6.641
2018-11-25 17:05:33.334293: step 90, duration = 6.589
2018-11-25 17:06:33.003457: Forward across 100 steps, 6.611 +/- 0.132 sec / batch我在cpu上跑的可以说很慢了,大家可以在GPU上跑跑,会发现,相比VGGNet和Inception V3,大概增加50%,每batch位0.202秒
在运行程序时如果出现下面的错误则:
方法一、重新开一个控制台
方法二、在代码开头加上一句话:tf.reset_default_graph()
runfile('D:/anaconda4.3/spyder_work/untitled9.py', wdir='D:/anaconda4.3/spyder_work')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
runfile('D:/anaconda4.3/spyder_work/untitled9.py', wdir='D:/anaconda4.3/spyder_work')
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\spyder\utils\site\sitecustomize.py", line 710, in runfile
execfile(filename, namespace)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\spyder\utils\site\sitecustomize.py", line 101, in execfile
exec(compile(f.read(), filename, 'exec'), namespace)
File "D:/anaconda4.3/spyder_work/untitled9.py", line 488, in
net, end_points = resnet_v2_152(inputs, 1000)
File "D:/anaconda4.3/spyder_work/untitled9.py", line 418, in resnet_v2_152
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
File "D:/anaconda4.3/spyder_work/untitled9.py", line 338, in resnet_v2
net = conv2d_same(net, 64, 7, stride=2, scope='conv1')
File "D:/anaconda4.3/spyder_work/untitled9.py", line 98, in conv2d_same
return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride=stride, padding='VALID', scope=scope)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\framework\python\ops\arg_scope.py", line 182, in func_with_args
return func(*args, **current_args)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\layers\python\layers\layers.py", line 1154, in convolution2d
conv_dims=2)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\framework\python\ops\arg_scope.py", line 182, in func_with_args
return func(*args, **current_args)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\layers\python\layers\layers.py", line 1057, in convolution
outputs = layer.apply(inputs)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\keras\engine\base_layer.py", line 828, in apply
return self.__call__(inputs, *args, **kwargs)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\layers\base.py", line 364, in __call__
outputs = super(Layer, self).__call__(inputs, *args, **kwargs)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\keras\engine\base_layer.py", line 759, in __call__
self.build(input_shapes)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\keras\layers\convolutional.py", line 161, in build
dtype=self.dtype)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\layers\base.py", line 278, in add_weight
getter=vs.get_variable)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\keras\engine\base_layer.py", line 586, in add_weight
aggregation=aggregation)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\training\checkpointable\base.py", line 591, in _add_variable_with_custom_getter
**kwargs_for_getter)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\variable_scope.py", line 1484, in get_variable
aggregation=aggregation)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\variable_scope.py", line 1234, in get_variable
aggregation=aggregation)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\variable_scope.py", line 521, in get_variable
return custom_getter(**custom_getter_kwargs)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\layers\python\layers\layers.py", line 1749, in layer_variable_getter
return _model_variable_getter(getter, *args, **kwargs)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\layers\python\layers\layers.py", line 1740, in _model_variable_getter
aggregation=aggregation)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\framework\python\ops\arg_scope.py", line 182, in func_with_args
return func(*args, **current_args)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\framework\python\ops\variables.py", line 350, in model_variable
aggregation=aggregation)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\framework\python\ops\arg_scope.py", line 182, in func_with_args
return func(*args, **current_args)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\framework\python\ops\variables.py", line 277, in variable
aggregation=aggregation)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\variable_scope.py", line 492, in _true_getter
aggregation=aggregation)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\variable_scope.py", line 859, in _get_single_variable
name, "".join(traceback.format_list(tb))))
ValueError: Variable resnet_v2_152/conv1/weights already exists, disallowed. Did you mean to set reuse=True or reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE in VarScope? Originally defined at:
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\framework\ops.py", line 1768, in __init__
self._traceback = tf_stack.extract_stack()
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\framework\ops.py", line 3272, in create_op
op_def=op_def)
File "C:\Users\2018061801\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\util\deprecation.py", line 488, in new_func
return func(*args, **kwargs) 至此卷积神经网络就学完了,将卷积神经网络的发展可概括为如下图:在AlexNet之后将卷积
神经网络分为两类,一是网络结构上的改变调整(左侧分支),一类是网络深度的加深(右侧分支)。
参考文献:
TensorFlow(黄文坚)