HBase二级索引实现方案
Hbase简介
HBASE是在hadoop之上构建非关系型,面向列存储的开源分布式结构化数据存储系统。
HBase表分区与索引管理
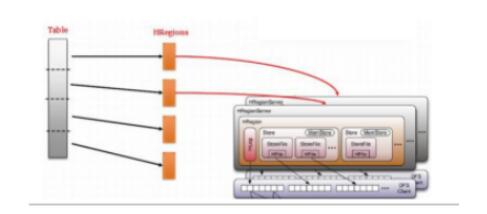
•将Table中的数据根据rowKey字段划分为多个HRegion
•HRegion分配给RegionServer管理
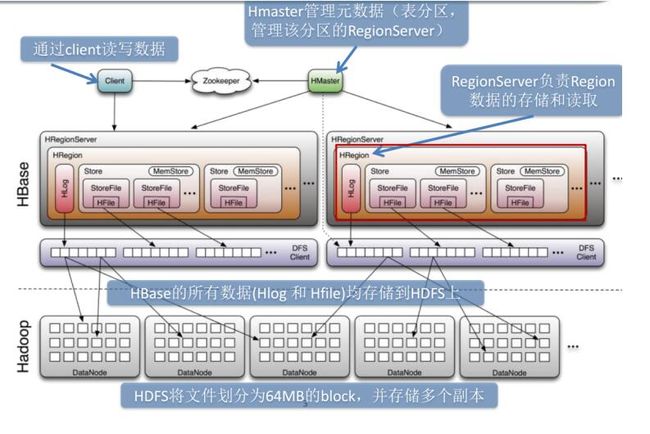
HBase系统架构
HBase的局限性
HBase本身只提供基于行键和全表扫描的查询,而行键索引单一,对于多维度的查询困难。
常见的二级索引方案
HBase的一级索引就是rowkey,我们只能通过rowkey进行检索。如果我们相对hbase里面列族的列列进行一些组合查询,就需要采用HBase的二级索引方案来进行多条件的查询。
1. MapReduce方案
2. ITHBASE(Indexed-Transanctional HBase)方案
3. IHBASE(Index HBase)方案
4. Hbase Coprocessor(协处理器)方案
5. Solr+hbase方案
6. CCIndex(complementalclustering index)方案
HBase二级索引种类
2.1创建单列索引
2.2同时创建多个单列索引
2.3创建联合索引(最多同时支持3个列)
2.4只根据rowkey创建索引
建立全局二级索引
1. 全局建立索引,可以修改hbase-site.xml文件
为所有table加载了一个cp class,可以用”,”分割加载多个class
单表建立二级索引
2. 单个表建立索引
1.首先disable ‘表名’
2.然后修改表
alter 'LogTable',METHOD=>'table_att','coprocessor'=>'hdfs:///test.jar|www.aboutyun.com.hbase.HbaseCoprocessor|1001'
3. enable '表名'
卸载二级索引
3. 卸载索引
alter 'LogTable', METHOD => 'table_att_unset', NAME => 'coprocessor$1‘
二级索引的设计
设计思路:
图1
二级索引的本质就是建立各列值与行键之间的映射关系
如上图1,当要对F:C1这列建立索引时,只需要建立F:C1各列值到其对应行键的映射关系,如C11->RK1等,这样就完成了对F:C1列值的二级索引的构建,当要查询符合F:C1=C11对应的F:C2的列值时(即根据C1=C11来查询C2的值,图1青色部分)
其查询步骤如下:
1. 根据C1=C11到索引数据中查找其对应的RK,查询得到其对应的RK=RK1
2. 得到RK1后就自然能根据RK1来查询C2的值了 这是构建二级索引大概思路,其他组合查询的联合索引的建立也类似。
MapReduce方式创建二级索引
使用整合MapReduce的方式创建hbase索引。主要的流程如下:
1.1扫描输入表,使用hbase继承类TableMapper
1.2获取rowkey和指定字段名称和字段值
1.3创建Put实例, value=rowkey, rowkey=columnName +"_" +columnValue
1.4使用IdentityTableReducer将数据写入索引表
继承TableMapper
GenerateIndexMapper继承TableMapper类
LoadIndexMapper类数据批量导入hbase
SecondIndexMain是驱动类
实例
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Scan;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.MultiTableOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapReduceUtil;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @Description:Mapreduce构建hbase二级索引
*/
public class MyIndexBuilder {
private class MyIndexMapper extends TableMapper {
//create the map object
private Map indexes = new HashMap();
//make the cloumnfamily
private String columnFamily;
/**
* Called once for each key/value pair in the input split. Most applications
* should override this, but the default is the identity function.
*/
@Override
protected void map(ImmutableBytesWritable key, Result value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Set keys = indexes.keySet();
for (byte[] k : keys) {
ImmutableBytesWritable indexTableName = indexes.get(k);
byte[] val = value.getValue(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), k);
// 索引表的rowkey为原始表的值
Put put = new Put(val);
// 索引表的内容为原始表的rowkey
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("id"), key.get());
//context write
context.write(indexTableName, put);
}
// super.map(key, value, context);
}
/**
* Called once at the beginning of the task.
*/
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();
String tableName = conf.get("tableName");
columnFamily = conf.get("columnFamily");
String[] qualifiers = conf.getStrings("qualifiers");
// indexes的key为列名,value为索引表名
for (String q : qualifiers) {
indexes.put(
Bytes.toBytes(q),
new ImmutableBytesWritable(Bytes.toBytes(tableName
+ "-" + q)));
}
}
// super.setup(context);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
String[] otherargs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args)
.getRemainingArgs();// 去除掉没有用的命令行参数
// 输入参数:表名,列族名,列名
if (otherargs.length < 3) {
System.exit(-1);
}
String tableName = otherargs[0];
String columnFamily = otherargs[1];
conf.set("tableName", tableName);
conf.set("columnFamily", columnFamily);
String[] qualifiers = new String[otherargs.length - 2];
for (int i = 0; i < qualifiers.length; i++) {
qualifiers[i] = otherargs[i + 2];
}
conf.setStrings("qualifiers", qualifiers);
Job job = new Job(conf, tableName);
job.setJarByClass(MyIndexBuilder.class);
job.setMapperClass(MyIndexMapper.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
job.setInputFormatClass(TableInputFormat.class);
// 可以输出多张表
job.setOutputFormatClass(MultiTableOutputFormat.class);
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.setCaching(1000);
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableMapperJob(tableName, scan, MyIndexMapper.class,
ImmutableBytesWritable.class, Put.class, job);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
HBase 协处理器(coprocessor)实现二级索引
HBase在0.92之后引入了coprocessors,提供了一系列的钩子,让我们能够轻易实现访问控制和二级索引的特性。
HBase Coprocessor简介
•HBase Coprocessor受启发于Google的Jeff Dean在LADIS’09 上的报告
–Google BigTable的Coprocessor特点
•在每个表服务器的任何tablet上均可执行用户代码
•提供客户端调用接口 (coprocessor客户端lib将可定位每个row/range的位置;多行读写将自
动分片为多个并行的RPC调用)
•提供可构建分布式服务的灵活的编程模型
•可以自动扩展,负载均衡等
–与Google Bigtable Coprocessor相比
•Bigtable coprocessor 以独立的进程执行,可以更好的控制CP计算所需资源
•HBase coprocessor是一个在Master/RegionServer进程内的框架,通过在运行时执行用户的代码,在HBase内实现灵活的分布式数据处理功能
•HBase Coprocessor的主要应用场景
–secondary indexing
–complex filtering
–access control
HBase Coprocessor 的实现类型
•HBase Coprocessor的实现分为Observer和Endpoint两种
–Observer类似于触发器,工作在服务器端。可以实现权限管理、监控等
–Endpoint类似于存储过程,工作在服务器端和客户端。可以实现min/max等计算
•Coprocessor的作用范围
–System coprocessor: 对所有table的所有region
–Table coprocessor:对某个table的所有region
•RegionObserver:提供表数据操作事件的钩子函数:Get、Put、Scan等的pre/post处理。
•WALObserver:提供WAL相关操作钩子。
•MasterObserver:提供DDL类型的操作钩子。如创建、删除、修改数据表等。
Endpoint:只适用于RegionServer, 对应于每个table 的Region的处理。
想要更详细的介绍请查阅:
https://blogs.apache.org/hbase/entry/coprocessor_introduction
observers分为三种:
RegionObserver:提供数据操作事件钩子;
WALObserver:提供WAL(write ahead log)相关操作事件钩子;
MasterObserver:提供DDL操作事件钩子。
实例
该例子使用RegionObserver实现在写主表之前将索引数据先写到另外一个表
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.Cell;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.KeyValue;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Durability;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.BaseRegionObserver;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.ObserverContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.RegionCoprocessorEnvironment;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.wal.WALEdit;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class IndexHBaseCoprocessor extends BaseRegionObserver {
@Override
public void prePut(ObserverContext e, Put put, WALEdit edit, Durability durability) throws IOException {
//set configuration
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//need conf.set...
HTable table = new HTable(conf, "indexTableName");
List kv = put.get("familyName".getBytes(), "columnName".getBytes());
Iterator kvItor = kv.iterator();
while (kvItor.hasNext()) {
Cell tmp = kvItor.next();
final byte[] value = tmp.getValue();
Put indexPut = new Put(value);
indexPut.add("familyName".getBytes(), "columnName".getBytes(), tmp.getRow());
table.put(indexPut);
}
table.close();
// super.prePut(e, put, edit, durability);
}
}
这是类之间的继承关系和实现里面的方法:
public class IndexHBaseCoprocessor extends BaseRegionObserver {
public class BaseRegionObserver implements RegionObserver {
public interface RegionObserver extends Coprocessor {
void prePut(ObserverContext var1, Put var2, WALEdit var3, Durability var4) throws IOException;
} | |
写完后要加载到table里面去,先把该文件打包indexTest.jar并上传到hdfs的/hbase-test路径下,然后操作如下:
进入hbase shell ,执行一下命令行:
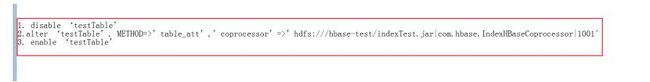
1. disable ‘testTable’
2.alter ‘testTable’,
METHOD=>’table_att’,’coprocessor’=>’hdfs:///hbase-test/indexTest.jar|com.hbase
.IndexHBaseCoprocessor|1001′
enable ‘testTable’
然后往testTable里面插数据就会自动往indexTableName写数据了。
这就是用coprocessor实现二级索引的例子。
HBase IndexBuilder.java源码
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/140ZTLE-pFJZXeMRo6QQuNg 密码:ql9d
参考博文:
1.http://www.aboutyun.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=8857&highlight=hbase%2B%B6%FE%BC%B6
2.https://www.cnblogs.com/MOBIN/p/5579088.html