基于Tensorflow的LSTM-CNN文本分类模型
题记
前段时间再看QA方面的文章,读了一篇paper(《LSTM-based deep learning model for non-factoid answer selection》)中,使用了LSTM-CNN模型来做answer与question的语义抽取。受此启发,使用这个模型对文本语义信息进行抽取,加上一个softmax函数形成文本分类模型。
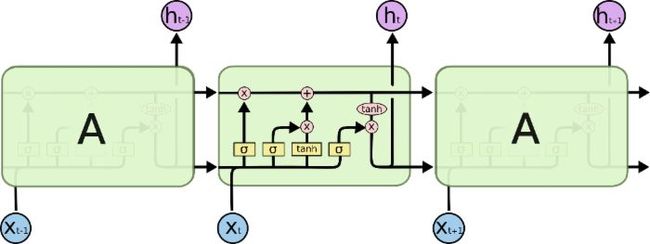
1.LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory)
LSTM在NLP中的应用实在太广泛了,在Machine Translation,Text Classification,QA等领域都有着成熟的应用,具体通过对RNN的结构进行改进,加入Memory Cell与三个门控单元,对历史信息进行有效的控制。而不是像RNN一样每次都将前一时刻的hidden state完全洗掉,从而增强了其处理长文本序列的能力,也解决了vanishing gradient的问题。
具体结构如图所示:
Input Gate决定当前时刻LSTM单元的Input vector对memory cell中信息的改变量,Forget Gate决定上一时刻历史信息对当前时刻memory cell中的信息的影响程度,Output Gate对memory cell中信息的输出量进行控制。
将Input Gate,Output Gate,Forget Gate表示为:![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,LSTM更新方法为:
,LSTM更新方法为:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
当前时刻的cell state 为![]() ,
,![]() 为LSTM单元最终输出,使用sigmoid function 作为activation function,
为LSTM单元最终输出,使用sigmoid function 作为activation function,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() 为LSTM的权重矩阵与偏置量。
为LSTM的权重矩阵与偏置量。
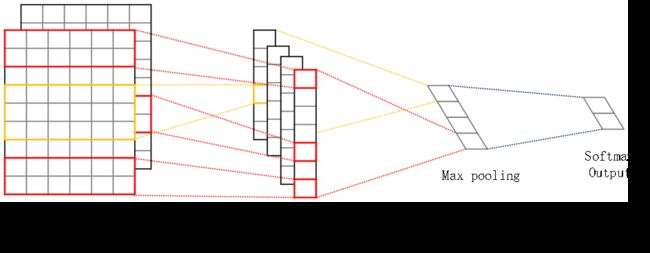
2.CNN(Convolutional Neural Network)
CNN的结构类似Yoon Kim在《Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification》中提出的结构。
其中,卷积窗口的大小设置对最终的分类结果影响较大,借鉴N-gram语言模型的思想,通过提取相邻n个词进行局部特征的提取,从而捕捉上下文搭配词语的语义信息,对整个文本的语义进行表示。根据这种思想,将卷积窗口大小设置为n*m,n为窗口内词的个数,m为词向量维度。
同时使用多个卷积核生成feature maps,再进行max pooling操作,最后使用sotfmax进行分类。
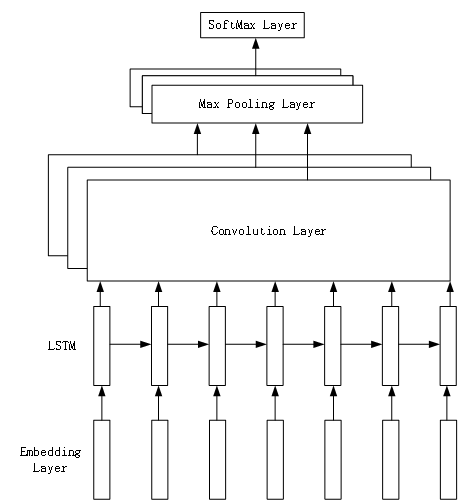
3.LSTM-CNN Model
首先通过Embedding Layer将单词转化为词向量,再输入LSTM进行语义特征提取,由于原始语料处理时进行了padding的操作,所以在LSTM输出时乘以MASK矩阵来减小padding所带来的影响。下一步将LSTM的输出作为CNN的输入,进行进一步的特征提取。最后得到分类结果。
整个模型的结构如下:
4.代码
class LSTM_CNN_Model(object):
def __init__(self,config,is_training=True):
self.keep_prob=config.keep_prob
self.batch_size = 64
num_step=config.num_step
self.input_data=tf.placeholder(tf.int32,[None,num_step])
self.target = tf.placeholder(tf.int64,[None])
self.mask_x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[num_step,None])
class_num=config.class_num
hidden_neural_size=config.hidden_neural_size
vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
embed_dim=config.embed_dim
hidden_layer_num=config.hidden_layer_num
#build LSTM network
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(hidden_neural_size,forget_bias=0.0,state_is_tuple=True)
if self.keep_prob<1:
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(
lstm_cell,output_keep_prob=self.keep_prob
)
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([lstm_cell]*hidden_layer_num,state_is_tuple=True)
self._initial_state = cell.zero_state(self.batch_size,tf.float32)
#embedding layer
with tf.device("/cpu:0"),tf.name_scope("embedding_layer"):
embedding = tf.get_variable("embedding",[vocabulary_size,embed_dim],dtype=tf.float32)
inputs=tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding,self.input_data)
if self.keep_prob<1:
inputs = tf.nn.dropout(inputs,self.keep_prob)
out_put=[]
state=self._initial_state
with tf.variable_scope("LSTM_layer"):
for time_step in range(num_step):
if time_step>0: tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
(cell_output,state)=cell(inputs[:,time_step,:],state)
out_put.append(cell_output)
out_put=out_put*self.mask_x[:,:,None]
with tf.name_scope("Conv_layer"):
out_put = tf.transpose(out_put,[1,2,0])
out_put = tf.reshape(out_put , [self.batch_size,hidden_neural_size,num_step,-1])
W_conv = tf.get_variable(name="conv_w" , initializer=tf.truncated_normal(shape=[600,5,1,200],stddev=0.1))
B_conv = tf.get_variable(name="conv_b", initializer=tf.constant(0.1,shape=[200]))
conv_output = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(out_put , W_conv , strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID') + B_conv)
conv_output = tf.reshape(conv_output,[self.batch_size,36,200,1])
max_pool_out = tf.nn.max_pool(conv_output,ksize=[1,36,1,1],strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID')
max_pool_out = tf.reshape(max_pool_out,[self.batch_size,200])
with tf.name_scope("Softmax_layer_and_output"):
softmax_w = tf.get_variable("softmax_w",[200,class_num],dtype=tf.float32)
softmax_b = tf.get_variable("softmax_b",[class_num],dtype=tf.float32)
self.logits = tf.matmul(max_pool_out,softmax_w)+softmax_b
with tf.name_scope("loss"):
self.loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=self.logits+1e-10,labels=self.target)
self.cost = tf.reduce_mean(self.loss)
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
self.prediction = tf.argmax(self.logits,1)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(self.prediction,self.target)
self.correct_num=tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32),name="accuracy")
#add summary
loss_summary = tf.summary.scalar("loss",self.cost)
#add summary
accuracy_summary=tf.summary.scalar("accuracy_summary",self.accuracy)
if not is_training:
return
self.globle_step = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0),dtype=tf.int32,name="globle_step",trainable=False)
self.lr = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.8),dtype=tf.float32,trainable=False)
tvars = tf.trainable_variables()
grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(self.cost, tvars),
config.max_grad_norm)
# Keep track of gradient values and sparsity (optional)
grad_summaries = []
for g, v in zip(grads, tvars):
if g is not None:
grad_hist_summary = tf.summary.histogram("{}/grad/hist".format(v.name), g)
sparsity_summary = tf.summary.scalar("{}/grad/sparsity".format(v.name), tf.nn.zero_fraction(g))
grad_summaries.append(grad_hist_summary)
grad_summaries.append(sparsity_summary)
self.grad_summaries_merged = tf.summary.merge(grad_summaries)
self.summary =tf.summary.merge([loss_summary,accuracy_summary,self.grad_summaries_merged])
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self.lr)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, tvars))
self.train_op=optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, tvars))
self.new_lr = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[],name="new_learning_rate")
self._lr_update = tf.assign(self.lr,self.new_lr)
def assign_new_lr(self,session,lr_value):
session.run(self._lr_update,feed_dict={self.new_lr:lr_value})5.实验结果
实验环境如下
GPU:NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080
OS:Ubuntu 16.04
开发环境:Anaconda 2.3.1,TensorFlow 1.5.0rc1
实验结果如下
训练集准确率:
Loss Function:
最终在测试集和验证集上准确率分别为:87.31%,91.17%
相较LSTM模型提高4%~5%
最后附上源代码:https://github.com/zjrn/LSTM-CNN_CLASSIFICATION
https://github.com/zjrn/LSTM-CNN_CLASSIFICATION.git
https://github.com/zjrn/LSTM-CNN_CLASSIFICATION.git