Spark2.x学习笔记:7、Spark应用程序设计
7、 Spark应用程序设计
7.1 基本流程
1.创建SparkContext对象
- 每个Spark应用程序有且仅有一个SparkContext对象,封装了Spark执行环境信息
2.创建RDD
- 可以冲Scala集合或者Hadoop数据集上创建
3.在RDD之上进行转换和Action
- MapReduce只提供了map和reduce两种操作,而Spark提供了多种转换和action函数
4.返回结果
- 保存到HDFS中,或者直接输出到终端
7.2 创建SparkContext对象
(1)创建SparkConf对象
val conf=new SparkConf()
conf.setAppName(appName)
conf.set(“spark.app.name”,”MySpark”)
conf.set(“spark.yarn.queue”,”infrastructure”)不过,不建议这样设置参数。可以在提交Spark作业时,通过spark-submit –conf设置。
(2)创建SparkContext对象,封装了调度器等信息
val sc=new SparkContext(conf)7.3 创建RDD
(1)Scala集合
sc.parallelize(List(1,2,3),2)(2)本地文件/HDFS文件
- 1) 文本文件
sc.textFile(“file:///data/a.txt”) //将本地文件加载成RDD
sc.textFile(“hdfs:///data/inpt”)
sc.textFile(“hdfs://nn:9000/path”)//HDFS文件或目录以hdfs://开头的文件表示HDFS上的文件,以hdfs://开头的文件表示本地文件;
- 2) sequenceFile文件
处理图片、语音、视频等二进制文件
sc.sequenceFile(“file.mp3”)
sc.sequenceFile[String,Int](“hdfs://nn:9000/path”)(3)使用任意自定义的Hadoop InputFormat
sc.hadoopFile(path,inputFmt,keyClass,valCLass)7.4 在RDD之上进行转换和Action
- Transformation:将一个RDD通过一种规则,映射成另一种RDD;
- Action:返回结果或者保存结果,只有action才出发程序的执行。
(1)RDD transformation
//创建RDD
val listRdd =sc.parallelize(List(1,2,3),3)
//将RDD传入函数,生成新的RDD
val squares =listRdd.map(x=>x*x)//{1,4,9}
//对RDD中的元素进行过滤,生产新的RDD
val even=sequres.filter(_%2==0)//{4}
//将一个元素映射成多个,生成新的RDD
nums.flatMap(x=>1 to x)//{1,1,2,1,2,3}注解:
- map:一一映射,元素数量不变
- filter:过滤,输出元素数量小于等于
- flatMap:展开,放大,输出元素数大于原来
(2)RDD Action
//创建新的RDD
val nums=sc.parallelize(List(1,2,3),2)
//将RDD保存为本地集合(返回到driver端)
nums.collect() //Array(1,2,3)
//返回前k个元素
nums.take(2)//Array(1,2)
//计算集合大小
nums.count()//3
合并集合元素
nums.reduce(_+_)//6
//将RDD写到HDFS中,注意该输出目录不能存在,Hadoop自动创建
//输出文件数和patition数相同
nums.saveAsTextFile(“hdfs://nn:8020/output”)
nums.saveAsSequenceFile(“hdfs://nn:8020/output”)7.5 Key/Value类型RDD操作
(1)KV型的RDD
Spark提供了强大的算子来处理KV型的RDD
Val pets=sc.parallelize(List((“cat”,1),(“dog”,1,(“cat”,2)) ))
pets.reduceByKey(_+_) //{(“cat”,3),(“dog”,1)}
pets.groupByKey() //{(“cat”,seq(1,2)),(dog,seq(1))}
pets.sortByKey() //{(“cat”,1),(“cat”,2),(“dog”,1)}(2)级联操作
由于Transformation返回都是RDD,所以可以将Transformation进行级联操作,
比如
val resultRdd = rowRdd.flatMap(line => line.split("\\s+"))
.map(word => (word, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)7.6 join
- def cogroup[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))]
- def cogroup[W](other: RDD[(K, W)], numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))]
- def join[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (V, W))]
- def join[W](other: RDD[(K, W)], numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, (V, W))]
说明:
1)cogroup函数对两个RDD(如:(K,V)和(K,W))相同Key的元素先分别做聚合,最后返回(K,Iterator,Iterator)形式的RDD。numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度。
2)join相当于SQL中的内关联join,只返回两个RDD根据K可以关联上的结果,join只能用于两个RDD之间的关联,如果要多个RDD关联,多关联几次即可。numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度
package cn.hadron
import org.apache.spark._
object JoinDemo {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val masterUrl = "local[1]"
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster(masterUrl).setAppName("JoinDemo")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val visits=sc.parallelize(List(
("index.jsp","192.168.1.100"),("about.jsp","192.168.1.101"),("index.jsp","192.168.1.102")
))
val pageNames=sc.parallelize(List(
("index.jsp","Home"),("about.jsp","About")
))
val cogRdd=visits.cogroup(pageNames)
cogRdd.take(2).foreach(println)
println("--------------")
val joinRdd=visits.join(pageNames)
joinRdd.take(3).foreach(println)
}
}
输出结果
(index.jsp,(CompactBuffer(192.168.1.100, 192.168.1.102),CompactBuffer(Home)))
(about.jsp,(CompactBuffer(192.168.1.101),CompactBuffer(About)))
--------------
(index.jsp,(192.168.1.100,Home))
(index.jsp,(192.168.1.102,Home))
(about.jsp,(192.168.1.101,About))7.7 cache
(1)Spark RDD Cache允许将RDD缓存到内存中,以便重用
(2)Spark提供了多种缓存级别,以便用户根据实际需求进行调整
rdd.chache()等价于rdd.persist(StorageLevel.DISK_ONLY_2)
(3)实例分析
val rdd=sc.textFile("hdfs://master:8020/input")
rdd.chache()
rdd.fileter(_.startWith("error")).count
rdd.fileter(_.endWith("hadoop")).count
rdd.fileter(_.endWith("hbase")).count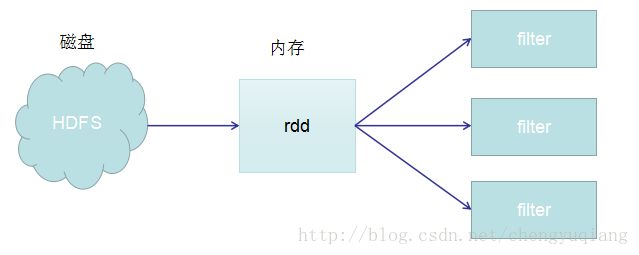
上面代码使用cache后,从HDFS(磁盘)读取1次,之后从内存中读取3次
如果不使用chache,则上面代码从HDFS读取3次。

7.8 控制ReduceTask数目
所有Key/value型RDD操作符均包含一个整形可选参数,表示reduce task并发度。
比如:
def cogroup[W](other: RDD[(K, W)], numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))]
def join[W](other: RDD[(K, W)], numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, (V, W))]
用户也可以通过修改spark.default.parallelism设置默认并行度(默认并行度是最初RDD partition数目)
7.9 其他RDD操作符
- samaple():从数据集中采样
- union():合并多个RDD
- cartesian():求笛卡尔积
- pipe():传入一个外部程序