ignite分布式计算
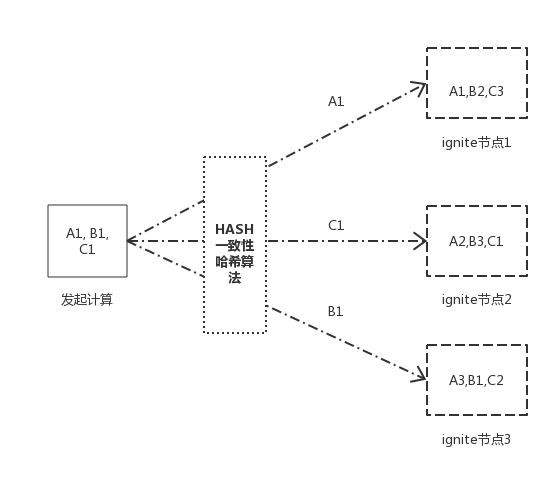
在ignite中,有传统的MapReduce模型的分布式计算,也有基于分布式存储的并置计算,当数据分散到不同的节点上时,根据提供的并置键,计算会传播到数据所在的节点进行计算,再结合数据并置,相关联的数据存储在相同节点,这样可以避免在计算过程中涉及到大量的数据移动,有效保证计算的性能。
ignite分布式计算的主要特点如下:
| 特性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 自动部署 | 计算用到的类可以自动传播,而不需要在每个节点都部署相关的类,这个可以通过配置peerClassLoadingEnabled选项开启计算类的自动传播,但是缓存的实体类是无法自动传播的。 |
| 平衡加载 | 数据在加载之后会在集群中进行一个再平衡的过程,保证数据均匀分布在各个节点,当有计算在集群中执行的时候,可以根据提供的并置键定位到数据所在节点进行计算,也就是并置计算。 |
| 故障转移 | 当节点出现故障或者其它计算的时候,任务会自动转移到集群中的其他节点执行 |
1.分布式闭包:
Ignite计算网格可以对集群或者集群组内的任何闭包进行广播和负载平衡,包括纯Java的
runnables和callables
| 闭包类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| broadcast | 将任务传播到部分指定节点或者全部节点 |
| call/run | 执行单个任务或者任务集 |
| apply | apply接收一个闭包和一个集合作为参数,生成与参数数量等量的任务,每个任务分别是将闭包应用在其中一个参数上,并且会返回结果集。 |
ComputeTestController.java
/** broadCast测试*/
@RequestMapping("/broadcast")
String broadcastTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
// IgniteCompute compute = ignite.compute(ignite.cluster().forRemotes()); //只传播远程节点
IgniteCompute compute = ignite.compute();
compute.broadcast(() -> System.out.println("Hello Node: " + ignite.cluster().localNode().id()));
return "all executed.";
}
/** call和run测试 */
@RequestMapping("/call")
public @ResponseBody
String callTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Collection> calls = new ArrayList<>();
/** call */
System.out.println("-----------call-----------");
for(String word : "How many characters".split(" ")) {
calls.add(word::length);
// calls.add(() -> word.length());
}
Collection res = ignite.compute().call(calls);
int total = res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
System.out.println(String.format("the total lengths of all words is [%s].", total));
/** run */
System.out.println("-----------run-----------");
for (String word : "Print words on different cluster nodes".split(" ")) {
ignite.compute().run(() -> System.out.println(word));
}
/** async call */
System.out.println("-----------async call-----------");
IgniteCompute asyncCompute = ignite.compute().withAsync();
asyncCompute.call(calls);
asyncCompute.future().listen(fut -> {
Collection result = (Collection)fut.get();
int t = result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
System.out.println("Total number of characters: " + total);
});
/** async run */
System.out.println("-----------async run-----------");
Collection> futs = new ArrayList<>();
asyncCompute = ignite.compute().withAsync();
for (String word : "Print words on different cluster nodes".split(" ")) {
asyncCompute.run(() -> System.out.println(word));
futs.add(asyncCompute.future());
}
futs.stream().forEach(ComputeTaskFuture::get);
return "all executed.";
}
/** apply测试 */
@RequestMapping("/apply")
public @ResponseBody
String applyTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
/** apply */
System.out.println("-----------apply-----------");
IgniteCompute compute = ignite.compute();
Collection res = compute.apply(
String::length,
Arrays.asList("How many characters".split(" "))
);
int total = res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
System.out.println(String.format("the total lengths of all words is [%s].", total));
/** async apply */
IgniteCompute asyncCompute = ignite.compute().withAsync();
res = asyncCompute.apply(
String::length,
Arrays.asList("How many characters".split(" "))
);
asyncCompute.future().listen(fut -> {
int t = ((Collection)fut.get()).stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
System.out.println(String.format("Total number of characters: " + total));
});
return "all executed.";
} 2. MapReduce:
在ignite中MapReduce的实现是ComputeTask,其主要方法是map()和reduce(),map()可以控制任务映射到节点的过程,而reduce()则是对最终计算结果集的一个处理。ComputeTask有两个主要实现ComputeTaskAdapter和ComputeTaskSplitAdapter, 主要的区别在于ComputeTaskAdapter需要手动实现map()方法,而ComputeTaskSplitAdapter可以自动映射任务。
ComputeTaskAdapter:
/**ComputeTaskAdapter*/
@RequestMapping("/taskMap")
public @ResponseBody
String taskMapTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
/**ComputeTaskMap*/
int cnt = ignite.compute().execute(MapExampleCharacterCountTask.class, "Hello Ignite Enable World!");
System.out.println(String.format(">>> Total number of characters in the phrase is %s.", cnt));
return "all executed.";
}
private static class MapExampleCharacterCountTask extends ComputeTaskAdapter {
/**节点映射*/
@Override
public Map map(List nodes, String arg) throws IgniteException {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
Iterator it = nodes.iterator();
for (final String word : arg.split(" ")) {
// If we used all nodes, restart the iterator.
if (!it.hasNext()) {
it = nodes.iterator();
}
ClusterNode node = it.next();
map.put(new ComputeJobAdapter() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws IgniteException {
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println(String.format(">>> Printing [%s] on this node from ignite job.", word));
return word.length();
}
}, node);
}
return map;
}
/**结果汇总*/
@Override
public Integer reduce(List results) throws IgniteException {
int sum = 0;
for (ComputeJobResult res : results) {
sum += res.getData();
}
return sum;
}
} 运行结果:
-------------------------------------
>>> Printing [Ignite] on this node from ignite job.
-------------------------------------
>>> Printing [World!] on this node from ignite job.
>>> Total number of characters in the phrase is 23.ComputeTaskSplitAdapter:
/**ComputeTaskSplitAdapter*/
@RequestMapping("/taskSplit")
public @ResponseBody
String taskSplitTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
/**ComputeTaskSplitAdapter(自动映射) */
int result = ignite.compute().execute(SplitExampleDistributedCompute.class, null);
System.out.println(String.format(">>> result: [%s]", result));
return "all executed.";
}
private static class SplitExampleDistributedCompute extends ComputeTaskSplitAdapter {
@Override
protected Collection split(int gridSize, String arg) throws IgniteException {
Collection jobs = new LinkedList<>();
jobs.add(new ComputeJobAdapter() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws IgniteException {
// IgniteCache cache = Ignition.ignite().cache(CacheKeyConstant.STUDENT);
IgniteCache cache = Ignition.ignite().cache(CacheKeyConstant.STUDENT).withKeepBinary();
/**普通查询*/
String sql_query = "name = ? and email = ?";
// SqlQuery cSqlQuery = new SqlQuery<>(Student.class, sql_query);
SqlQuery cSqlQuery = new SqlQuery<>(Student.class, sql_query);
cSqlQuery.setReplicatedOnly(true).setArgs("student_54", "student_54gmail.com");
// List> result = cache.query(cSqlQuery).getAll();
List> result = cache.query(cSqlQuery).getAll();
System.out.println("--------------------");
result.stream().map(x -> {
Integer studId = x.getValue().field("studId");
String name = x.getValue().field("name");
return String.format("name=[%s], studId=[%s].", name, studId);
}).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println(String.format("the query size is [%s].", result.size()));
return result.size();
}
});
return jobs;
}
@Override
public Integer reduce(List results) throws IgniteException {
int sum = results.stream().mapToInt(x -> x.getData()).sum();
return sum;
}
} 运行结果:
--------------------
name=[student_54], studId=[54].
the query size is [1].
>>> result: [1]MapReduce的局限性:
MapReduce适合解决并行和批处理的场景,不适合串行,迭代和递归一类无法并行和分割任务的场景。
分布式计算存在的问题以及注意点
在使用ignite的分布式计算功能的时候,如果用到了缓存, 并且缓存value不是平台类型(java基础类型),则需要考虑反序列化的问题。现有两种解决方案:
- 部署缓存实体类包到ignite节点
缓存实体类得实现Serializable接口,并且得指定serialVersionUID
serialVersionUID表示实体类的当前版本,每个实现Serializable接口的类都有,如果没有的设置该值,java序列化机制会帮你默认生成一个。最好在使用serializable接口时,设定serialVersionUID为某个值,不然当在传输的某一端修改实体类时,serialVersionUID会被虚拟机设置成一个新的值,造成两端的serialVersionUID不一致会发生异常。
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5941489737545326242L;
....
}将实体类打包成普通jar包,并放在$IGNITE_HOME/libs/路径下面:
注意:打包的时候不能打包成spring-boot的可执行包,要打包成普通jar包,这样相关类才能正常加载。当然如果集群里的节点均为应用节点,则可以不用考虑这个问题。
使用二进制对象对缓存进行操作
Ignite默认使用反序列化值作为最常见的使用场景,要启用
BinaryObject处理,需要获得一个IgniteCache的实例然后使用withKeepBinary()方法。启用之后,如果可能,这个标志会确保从缓存返回的对象都是BinaryObject格式的。
IgniteCache cache = ignite.cache("student").withKeepBinary();
BinaryObject obj = cache.get(k); //获取二进制对象
String name = obj.field("name"); //读取二进制对象属性值<使用field方法> 3.并置计算:
affinityCall(...)和affinityRun(...)方法使作业和缓存着数据的节点位于一处,换句话说,给定缓存名字和关系键,这些方法会试图在指定的缓存中定位键所在的节点,然后在那里执行作业。
并置的两种类型以及区别:
| 并置 | 特点 |
|---|---|
| 数据并置 | 将相关的缓存数据并置到一起,确保其所有键会缓存在同一个节点上,避免节点间数据移动产生的网络开销。 |
| 计算并置 | 根据关系键和缓存名称,定位关系键所在节点,并在该节点执行作业单元。 |
ComputeTestController.class
/**并置计算测试*/
@RequestMapping("/affinity")
public @ResponseBody
String affinityTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
/** affinityRun call */
System.out.println("-----------affinityRun call-----------");
IgniteCompute compute = ignite.compute();
// IgniteCompute compute = ignite.compute(ignite.cluster().forRemotes());
for(int key = 0; key < 100; key++) {
// final long k = key;
//生成随机k值
final long k = IntStream.generate(() -> (int)(System.nanoTime() % 100)).limit(1).findFirst().getAsInt();
compute.affinityRun(CacheKeyConstant.STUDENT, k, () -> {
IgniteCache cache = ignite.cache(CacheKeyConstant.STUDENT).withKeepBinary();
BinaryObject obj = cache.get(k);
if(obj!=null) {
System.out.println(String.format("Co-located[key= %s, value= %s]", k, obj.field("name")));
}
});
}
IgniteCache cache = ignite.cache(CacheKeyConstant.STUDENT).withKeepBinary();
cache.forEach(lo -> compute.affinityRun(CacheKeyConstant.STUDENT, lo.getKey(), () -> {
System.out.println(lo.getValue().field("name"));
}));
return "all executed.";
} 运行结果:
-----------affinityRun call-----------
student_495
student_496
student_498
...至此,ignite分布式计算完毕。