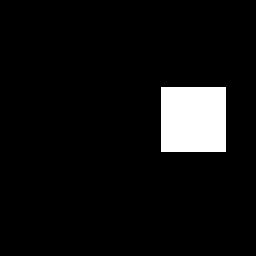图像修复实例解析(二)
Generative Image Inpainting with Contextual Attention
今天介绍CVPR 2018的Generative Image Inpainting with Contextual Attention
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.07892, demo http://jiahuiyu.com/deepfill
github:https://github.com/JiahuiYu/generative_inpainting
先看效果:
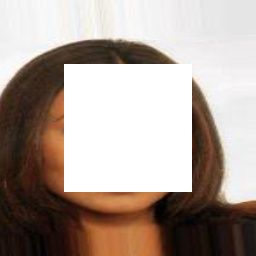
上述是作者修复的结果,我自己训练后修复的如下:
这里生成了两个不同情况的图,因为使用了两个不同的pre-train Model
下面介绍如何使用:
- Requirements:
- Install python3.
- Install tensorflow (tested on Release 1.3.0, 1.4.0, 1.5.0, 1.6.0, 1.7.0).
- Install tensorflow toolkit neuralgym (run
pip install git+https://github.com/JiahuiYu/neuralgym).
- Training:
- Prepare training images filelist and shuffle it (example).
- Modify inpaint.yml to set DATA_FLIST, LOG_DIR, IMG_SHAPES and other parameters.
- Run
python3 train.py.
这里重点介绍如何准备自己的训练集,直接写了个python脚本自动处理即可。gen_flist.py自动将源数据集划分为训练集和验证集。并生成项目需要的格式。
# 将原数据集分为training ,validation by gavin
import os
import random
import argparse
#划分验证集训练集
_NUM_TEST = 20000
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--folder_path', default='/home/gavin/Dataset/celeba', type=str,
help='The folder path')
parser.add_argument('--train_filename', default='./data/celeba/train_shuffled.flist', type=str,
help='The train filename.')
parser.add_argument('--validation_filename', default='./data/celeba/validation_static_view.flist', type=str,
help='The validation filename.')
def _get_filenames(dataset_dir):
photo_filenames = []
image_list = os.listdir(dataset_dir)
photo_filenames = [os.path.join(dataset_dir, _) for _ in image_list]
return photo_filenames
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = parser.parse_args()
data_dir = args.folder_path
# get all file names
photo_filenames = _get_filenames(data_dir)
print("size of celeba is %d" % (len(photo_filenames)))
# 切分数据为测试训练集
random.seed(0)
random.shuffle(photo_filenames)
training_file_names = photo_filenames[_NUM_TEST:]
validation_file_names = photo_filenames[:_NUM_TEST]
print("training file size:",len(training_file_names))
print("validation file size:", len(validation_file_names))
# make output file if not existed
if not os.path.exists(args.train_filename):
os.mknod(args.train_filename)
if not os.path.exists(args.validation_filename):
os.mknod(args.validation_filename)
# write to file
fo = open(args.train_filename, "w")
fo.write("\n".join(training_file_names))
fo.close()
fo = open(args.validation_filename, "w")
fo.write("\n".join(validation_file_names))
fo.close()
# print process
print("Written file is: ", args.train_filename)
最终生成的格式如下图:
- Resume training:
- Modify MODEL_RESTORE flag in inpaint.yml. E.g., MODEL_RESTORE: 20180115220926508503_places2_model.
- Run
python3 train.py.
- Testing:
- Run
python test.py --image examples/input.png --mask examples/mask.png --output examples/output.png --checkpoint model_logs/your_model_dir.
- Run
大概就是以上操作,后面贴上我实际训练和测试的脚本。
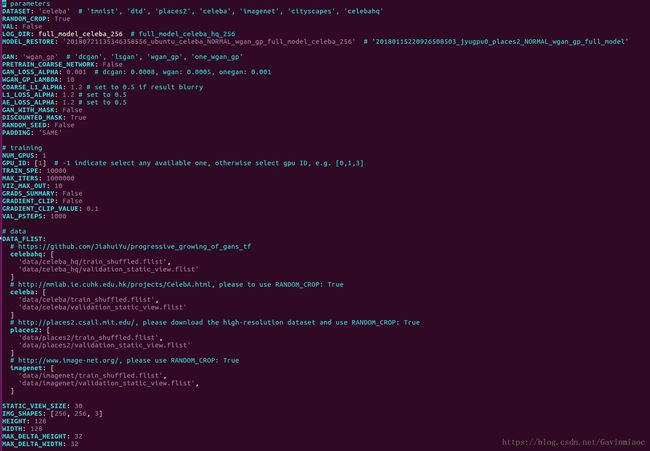
配置文件
其中inpaint.yml中要注意的是,在恢复训练模型的时候,MODEL_RESTORE的值:
多GPU模式训练
如果使用多个GPU训练,需要改三处地方,分别是inpaint.yml中两处,如下
# training
NUM_GPUS: 2
GPU_ID: [0,1] # -1 indicate select any available one, otherwise select gpu ID, e.g. [0,1,3]分别指定将gpu使用的个数及各自的id,第三处,也是最重要而且特别容易忽略的,在train.py中修改这里
# train generator with primary trainer ,MultiGPUTrainer. for multi gpu,and add num_gpus=config.NUM_GPUS
trainer = ng.train.Trainer(
optimizer=g_optimizer,
var_list=g_vars,
max_iters=config.MAX_ITERS,
graph_def=multigpu_graph_def,
grads_summary=config.GRADS_SUMMARY,
gradient_processor=gradient_processor,
graph_def_kwargs={
'model': model, 'data': data, 'config': config, 'loss_type': 'g'},
spe=config.TRAIN_SPE,
log_dir=log_prefix,
)
'''
trainer = ng.train.MultiGPUTrainer(
optimizer=g_optimizer,
var_list=g_vars,
max_iters=config.MAX_ITERS,
graph_def=multigpu_graph_def,
grads_summary=config.GRADS_SUMMARY,
gradient_processor=gradient_processor,
graph_def_kwargs={
'model': model, 'data': data, 'config': config, 'loss_type': 'g'},
spe=config.TRAIN_SPE,
log_dir=log_prefix,
num_gpus = config.NUM_GPUS,
)
'''即有两种调用方式,一种单GPU跑,一种多GPU模式,而多GPU模式下需要加上参数
num_gpus = config.NUM_GPUS,
脚本:
# training
python3 train.py
# Resume training:
Modify MODEL_RESTORE flag in inpaint.yml. E.g., MODEL_RESTORE: 20180115220926508503_places2_model.
Run python3 train.py.
#Testing:
python3 test.py --image examples/input.png --mask examples/mask.png --output examples/output.png --checkpoint model_logs/your_model_dir.
python3 test.py --image examples/celeba/celebahr_patches_164787_input.png --mask examples/center_mask_256.png
--output examples/output_celeba.png --checkpoint_dir model_logs/celebA_model/snap-60000
# for any other image,you can generate mask and masked image first ,then predict
1. python3 generate_mask.py --img ./examples/celeba/000035.jpg --HEIGHT 64 --WIDTH 64
2. python3 test.py --image ./data/mask_img/masked/000035.jpg --mask ./data/mask_img/mask/000035.jpg \
--output examples/output_000035.png --checkpoint_dir model_logs/celebA_model/snap-90000测试
实际测试过程中,对于任一张图,需要输入mask,和input,这里需要我们自己生成,为了便于随机生成mask,我写了如下代码,可以随机生成规则及不规则的mask
'''
利用opencv随机给图像生成带mask区域的图
author:gavin
'''
# import itertools
# import matplotlib
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from copy import deepcopy
from random import randint
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
import sys
import tensorflow as tf
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--img', default='./examples/celeba/000042.jpg', type=str,
help='The input img for single image ')
parser.add_argument('--input_dirimg', default='./data/mask_img/src_img/', type=str,
help='The input folder path for multi-images')
parser.add_argument('--output_dirmask', default='./data/mask_img/mask/', type=str,
help='The output file path of mask.')
parser.add_argument('--output_dirmasked', default='./data/mask_img/masked/', type=str,
help='The output file path of masked.')
parser.add_argument('--MAX_MASK_NUMS', default='16', type=int,
help='max numbers of masks')
parser.add_argument('--MAX_DELTA_HEIGHT', default='32', type=int,
help='max height of delta')
parser.add_argument('--MAX_DELTA_WIDTH', default='32', type=int,
help='max width of delta')
parser.add_argument('--HEIGHT', default='128', type=int,
help='max height of delta')
parser.add_argument('--WIDTH', default='128', type=int,
help='max width of delta')
parser.add_argument('--IMG_SHAPES', type=eval, default=(256, 256, 3))
# 随机生成不规则掩膜
def random_mask(height, width, config,channels=3):
"""Generates a random irregular mask with lines, circles and elipses"""
img = np.zeros((height, width, channels), np.uint8)
# Set size scale
size = int((width + height) * 0.02)
if width < 64 or height < 64:
raise Exception("Width and Height of mask must be at least 64!")
# Draw random lines
for _ in range(randint(1, config.MAX_MASK_NUMS)):
x1, x2 = randint(1, width), randint(1, width)
y1, y2 = randint(1, height), randint(1, height)
thickness = randint(3, size)
cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (1, 1, 1), thickness)
# Draw random circles
for _ in range(randint(1, config.MAX_MASK_NUMS)):
x1, y1 = randint(1, width), randint(1, height)
radius = randint(3, size)
cv2.circle(img, (x1, y1), radius, (1, 1, 1), -1)
# Draw random ellipses
for _ in range(randint(1, config.MAX_MASK_NUMS)):
x1, y1 = randint(1, width), randint(1, height)
s1, s2 = randint(1, width), randint(1, height)
a1, a2, a3 = randint(3, 180), randint(3, 180), randint(3, 180)
thickness = randint(3, size)
cv2.ellipse(img, (x1, y1), (s1, s2), a1, a2, a3, (1, 1, 1), thickness)
return 1 - img
'''
# this for test
# %matplotlib inline ==> plt.show()
# Plot the results
_, axes = plt.subplots(5, 5, figsize=(20, 20))
axes = list(itertools.chain.from_iterable(axes))
for i in range(len(axes)):
# Generate image
img = random_mask(500, 500)
# Plot image on axis
axes[i].imshow(img * 255)
plt.show()
'''
def random_bbox(config):
"""Generate a random tlhw with configuration.
Args:
config: Config should have configuration including IMG_SHAPES,
VERTICAL_MARGIN, HEIGHT, HORIZONTAL_MARGIN, WIDTH.
Returns:
tuple: (top, left, height, width)
"""
img_shape = config.IMG_SHAPES
img_height = img_shape[0]
img_width = img_shape[1]
maxt = img_height - config.HEIGHT
maxl = img_width - config.WIDTH
t = tf.random_uniform(
[], minval=0, maxval=maxt, dtype=tf.int32)
l = tf.random_uniform(
[], minval=0, maxval=maxl, dtype=tf.int32)
h = tf.constant(config.HEIGHT)
w = tf.constant(config.WIDTH)
return (t, l, h, w)
def bbox2mask(bbox, config, name='mask'):
"""Generate mask tensor from bbox.
Args:
bbox: configuration tuple, (top, left, height, width)
config: Config should have configuration including IMG_SHAPES,
MAX_DELTA_HEIGHT, MAX_DELTA_WIDTH.
Returns:
tf.Tensor: output with shape [1, H, W, 1]
"""
def npmask(bbox, height, width, delta_h, delta_w):
mask = np.zeros((1, height, width, 1), np.float32)
h = np.random.randint(delta_h//2+1)
w = np.random.randint(delta_w//2+1)
mask[:, bbox[0]+h:bbox[0]+bbox[2]-h,
bbox[1]+w:bbox[1]+bbox[3]-w, :] = 1.
return mask
with tf.variable_scope(name), tf.device('/cpu:0'):
img_shape = config.IMG_SHAPES
height = img_shape[0]
width = img_shape[1]
mask = tf.py_func(
npmask,
[bbox, height, width,
config.MAX_DELTA_HEIGHT, config.MAX_DELTA_WIDTH],
tf.float32, stateful=False)
mask.set_shape([1] + [height, width] + [1])
return mask
# 对于矩形mask随机生成
def random_mask_rect(img_path,config,bsave=True):
# Load image
img_data = cv2.imread(img_path)
#img_data = cv2.cvtColor(img_data, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
'''
# generate mask, 1 represents masked point
bbox = random_bbox(config)
mask = bbox2mask(bbox, config, name='mask_c')
img_pos = img_data / 127.5 - 1.
masked_img = img_pos * (1. - mask)
'''
# 创建矩形区域,填充白色255
img_shape = config.IMG_SHAPES
img_height = img_shape[0]
img_width = img_shape[1]
image = cv2.resize(img_data, (img_width, img_height))
rectangle = np.zeros(image.shape[0:2], dtype=np.uint8)
maxt = img_height - config.HEIGHT
maxl = img_width - config.WIDTH
h = config.HEIGHT
w = config.WIDTH
x = randint(0, maxt - 1)
y = randint(0, maxl - 1)
mask = cv2.rectangle(rectangle,(x, y), (x+w, y+h) , 255, -1) # 修改这里 (78, 30), (98, 46)
masked_img = deepcopy(image)
masked_img[mask == 255] = 255
print("shape of mask:",mask.shape)
print("shape of masked_img:",masked_img.shape)
if bsave:
save_name_mask = os.path.join(config.output_dirmask, img_path.split('/')[-1])
cv2.imwrite(save_name_mask,mask)
save_name_masked = os.path.join(config.output_dirmasked, img_path.split('/')[-1])
cv2.imwrite(save_name_masked, masked_img)
return masked_img,mask
def get_path(config):
if not os.path.exists(config.input_dirimg):
os.mkdir(config.input_dirimg)
if not os.path.exists(config.output_dirmask):
os.mkdir(config.output_dirmask)
if not os.path.exists(config.output_dirmasked):
os.mkdir(config.output_dirmasked)
# 给单个图像生成带mask区域的图
def load_mask(img_path,config,bsave=False):
# Load image
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
shape = img.shape
print("Shape of image is: ",shape)
# Load mask
mask = random_mask(shape[0], shape[1],config)
# Image + mask
masked_img = deepcopy(img)
masked_img[mask == 0] = 255
mask = mask * 255
if bsave:
save_name_mask = os.path.join(config.output_dirmask, img_path.split('/')[-1])
cv2.imwrite(save_name_mask,mask)
save_name_masked = os.path.join(config.output_dirmasked, img_path.split('/')[-1])
cv2.imwrite(save_name_masked, masked_img)
return masked_img,mask
# 批量生成带mask区域的图像
def img2maskedImg(dataset_dir):
files = []
image_list = os.listdir(dataset_dir)
files = [os.path.join(dataset_dir, _) for _ in image_list]
length = len(files)
for index,jpg in enumerate(files):
try:
sys.stdout.write('\r>>Converting image %d/%d ' % (index,length))
sys.stdout.flush()
load_mask(jpg,config,True)
# 将已经转换的图片移动到指定位置
#shutil.move(png, output_dirHR)
except IOError as e:
print('could not read:',jpg)
print('error:',e)
print('skip it\n')
sys.stdout.write('Convert Over!\n')
sys.stdout.flush()
# python3 generate_mask.py --img ./examples/celeba/000042.jpg --HEIGHT 64 --WIDTH 64
if __name__ == '__main__':
config = parser.parse_args()
get_path(config)
# 单张图像生成mask
#img = './data/test.jpg'
#masked_img,mask = load_mask(img,config,True)
# 批量图像处理==>圆形,椭圆,直线
#img2maskedImg(config.input_dirimg)
# 矩形特殊处理 处理同样shape的图片(256,256,3) fix me
#img = './examples/celeba/000042.jpg'
img = config.img
masked_img, mask = random_mask_rect(img,config)
'''
# Show side by side
_, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(20, 5))
axes[0].imshow(img)
axes[1].imshow(mask*255)
axes[2].imshow(masked_img)
plt.show()
'''
效果:
mask,masked,output