用TensorFlow构建基础的神经网络(一):MLP
源代码下载:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kUAsk5L
作者:XJTU_Ironboy
时间:2017年8月
开头语
由于最近在学习Deep Learning方面的知识,并尝试着用Google近些年刚提出的TensorFlow框架来搭建各种经典的神经网络,如MLP、LeNet-5、AlexNet、VGG、GoogleNet、ResNet、DenseNet、SqueezeNet,所以在接下来的学习过程中我将逐个地介绍MLP、LeNet-5和AlexNet三个基础的神经网络的结构细节,因为其他的神经网络都可以说是在AlexNet上进行结构的修改而得到的,所以说如果学会了这三个基本网络的构建,那么其他结构的构建就是套路了。
一、MLP
1.单层感知机
在我的理解中,Deep Learning的学习大多数都是从感知机(perceptron)开始的,因为它是神经网络的开山鼻祖,一种最最简单的神经网络结构。
感知机是一种二分类模型,输入实例的特征向量,输出实例的±类别。由于这个模型过于简单,懒得废话,还是直接上图吧。

其中输入(Input)是一个m维的向量: [X1,X2,X3,...,Xi,...,Xm] ,权重(Weight)也是一个m维的向量: [W1,W2,W3,...,Wi,...,Wm] ,偏置项(Bias)是: [b] ,输出(Output)是一个标量输出: y ,激活函数(Activation Function)是: 符号函数(signum:x大于0的时候为1;x等于0的时候为0,x小于0的时候为-1)。
2.多层感知机
多层感知器(MLP,Multilayer Perceptron)是一种前馈人工神经网络模型,其将输入的多个数据集映射到单一的输出的数据集上。
接下来讲一下如何用TensorFlow来实现这个简单的多层感知机(MLP):
1.数据库: MNIST数字手写体数据库
2.编程配置: Python3.5 + TensorFlow1.2.0
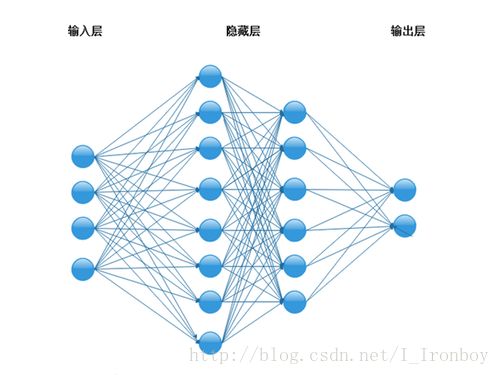
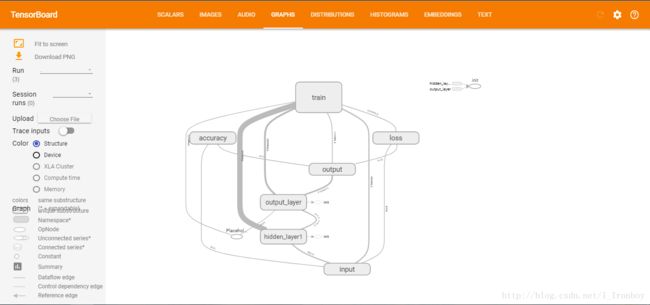
3.结构: 输入层+一个隐含层+输出层
输入图像大小: 28×28 ;
隐含层神经元个数: 300;
输出神经元个数: 10;
激活函数: ReLU
优化器: Adagrad
训练集上的batch size: 1000
测试集上的batch size: 10000
4.TensorFlow上实现
① 首先,导入tensorflow和MNIST数据集
import tensorflow as tf
# 导入MNIST数字手写体数据库
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/",one_hot = True)② 开始定义MLP的整体结构
# 定义输入层、隐含层、输出层的神经元个数
in_units = 784
h1_units = 300
out_units = 10③ 输入层,with tf.name_scope是TensorFlow中的命名空间,便于在tensorboard可视化整体的结构
# 定义输入层,keep_prob是dropout的比例
with tf.name_scope("input"):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,in_units])
y_= tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,out_units])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)④ 隐含层:权重、偏置的初始值都是正态分布的随机数
# 定义隐含层的权重、偏置、激活函数
with tf.name_scope("hidden_layer1"):
with tf.name_scope("w1"):
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_units,h1_units],stddev = 0.1))
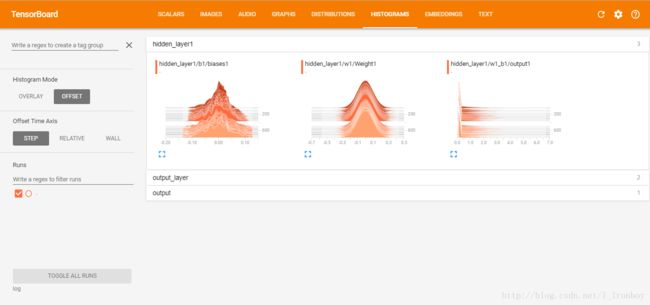
tf.summary.histogram('Weight1',w1)
with tf.name_scope("b1"):
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([h1_units])) + 0.01
tf.summary.histogram('biases1',b1)
with tf.name_scope("w1_b1"):
hidden1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x,w1) + b1)
tf.summary.histogram('output1',hidden1)⑤ 输出层:权重、偏置的初始值都是正态分布的随机数
# 定义输出层的权重、偏置、激活函数
with tf.name_scope("output_layer"):
with tf.name_scope("w2"):
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([h1_units,out_units],stddev = 0.1))
tf.summary.histogram('Weight2',w2)
with tf.name_scope("b2"):
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_units]))
tf.summary.histogram('biases2',b2)
with tf.name_scope("w2_b2"):
hidden1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(hidden1,keep_prob)
with tf.name_scope("output"):
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(hidden1_drop,w2)+b2)
tf.summary.histogram('output',y)⑥ 损失函数、准确率、优化器
# 定义损失函数———交叉熵
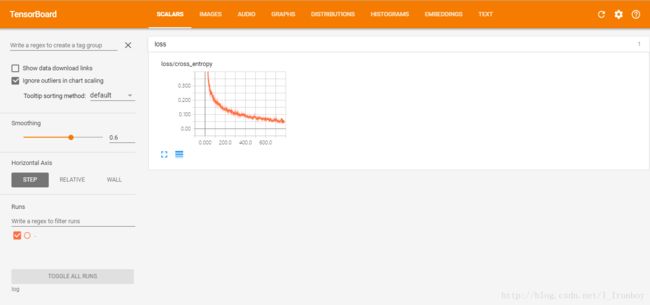
with tf.name_scope("loss"):
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y),reduction_indices = [1]))
tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy)
# 计算准确率
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
# 定义优化器——Adagrad,和学习率:0.3
with tf.name_scope("train"):
train_step = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(0.3).minimize(cross_entropy)⑦ 框架搭好了,正式开始计算
# 初始化所有的变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开始导入数据,正式计算,迭代3000步,训练时batch size=100
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
merge = tf.summary.merge_all()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("log",sess.graph)
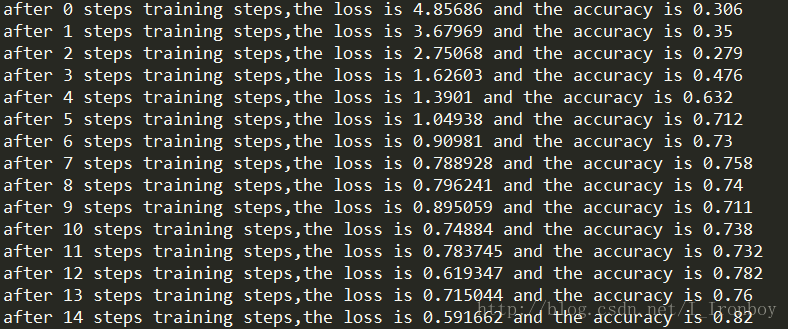
for i in range(3000):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(1000)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict = {x:batch_xs,y_:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.75})
loss_run = sess.run(cross_entropy,feed_dict = {x:batch_xs,y_:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.75})
accuracy_run = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict = {x:batch_xs,y_:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.75})
print('after %d steps training steps,the loss is %g and the accuracy is %g'%(i,loss_run,accuracy_run))
result = sess.run(merge,feed_dict = {x:batch_xs,y_:batch_ys,keep_prob:1})
writer.add_summary(result,i)
# 训练完后直接加载测试集数据,进行测试
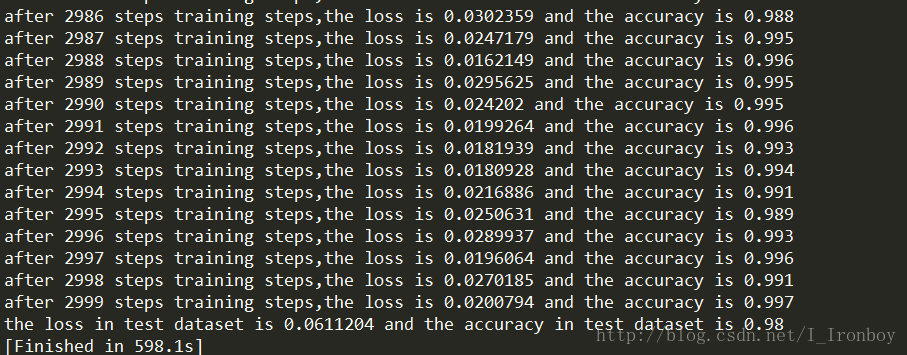
if i == 2999:
loss_run = sess.run(cross_entropy,feed_dict = {x:mnist.test.images,y_:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1})
accuracy_run = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict = {x:mnist.test.images,y_:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1})
print('the loss in test dataset is %g and the accuracy in test dataset is %g'%(loss_run,accuracy_run))5 .运行结果:
测试集上的准确度:98.00%
6. TensorBoard可视化:
① 在MLP.py程序的所在文件夹下打开cmd窗口(针对Windows)
方法一:打开cmd,然后用“cd + 路径”的方式找到该位置
方法二:定位到MLP.py所在文件的位置,点击左上角的“文件”,然后点击“打开命令提示符”
② 输入: tensorboard - -logdir=log ,回车
③ 复制上面的地址到浏览器,如我这上面的地址是:http://Ironboy:6006
④ 可视化结果: