cocos2d-x 世界坐标与模型坐标互相转换
世界坐标与模型坐标互相转换
世界坐标与模型坐标的互相转换分别是通过convertToNodeSpace和convertToWorldSpace函数来实现的
1.世界坐标转换为模型坐标
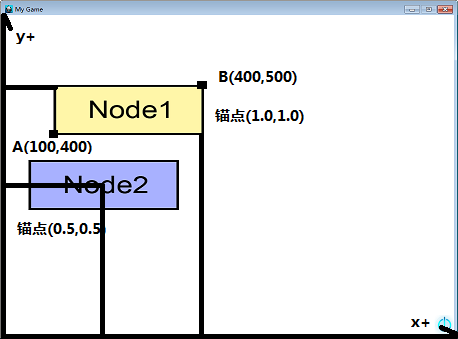
示例:(Node1、Node2大小均为300*100)
代码实现:
//添加精灵1 auto node1 = Sprite::create("node1.png"); node1->setPosition(Point(400,500)); node1->setAnchorPoint(Point(1.0,1.0)); this->addChild(node1, 0);auto node2 = Sprite::create("node2.png");node2->setPosition(Point(200,300));node2->setAnchorPoint(Point(0.5, 0.5));this->addChild(node2, 0);//添加精灵2
//世界坐标转换为模型坐标Point point1 = node1->convertToNodeSpace(node2->getPosition());Point point2 = node1->convertToNodeSpaceAR(node2->getPosition());
//打印
log("Node2 NodeSpace = (%f,%f)",point1.x,point1.y);log("Node2 NodeSpaceAR = (%f,%f)",point2.x,point2.y); 结果:Node2 NodeSpace = (100.000000,-100.000000)Node2 NodeSpaceAR = (-200.000000,-200.000000)
解读:
在这里,Point point1 = node1->convertToNodeSpace(node2->getPosition());node2->getPosition()的结果为Point(200,300)(即在上文中设置node2->setPosition(200,300)的坐标),被视为一个世界坐标。
node1->convertToNodeSpace(node2->getPosition())将获得的世界坐标转换为相对于node1原点的模型坐标。
同理,node1->convertToNodeSpaceAR(node2->getPosition())将获得的世界坐标转换为相对于node1锚点的模型坐标。
2.模型坐标转换为世界坐标
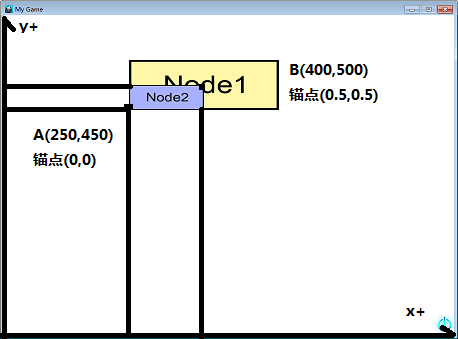
示例:(Node1大小为300*100,Node2大小为150*50)
代码实现:
结果://添加精灵1 auto node1 = Sprite::create("node1.png"); node1->setPosition(Point(400, 500)); node1->setAnchorPoint(Point(0.5, 0.5)); this->addChild(node1, 0); //添加精灵2 auto node2 = Sprite::create("node2.png"); node2->setPosition(Point(0.0, 0.0)); node2->setAnchorPoint(Point(0.0, 0.0)); node1->addChild(node2, 0);//注意,node2是添加在node1里的 //模型坐标转换为世界坐标 Point point1 = node1->convertToWorldSpace(node2->getPosition()); Point point2 = node1->convertToWorldSpaceAR(node2->getPosition()); //打印 log("Node2 WorldSpace = (%f,%f)",point1.x,point1.y); log("Node2 WorldSpaceAR = (%f,%f)",point2.x,point2.y);Node2 WorldSpace = (250.000000,450.000000)
Node2 WorldSpaceAR = (400.000000,500.000000)解读:
Point point1 = node1->convertToWorldSpace(node2->getPosition());在这里,
node2->getPosition()的结果为Point(0,0)(即在上文中设置node2->setPosition(0,0)的坐标),被视为一个模型坐标。
node1->convertToWorldSpace(node2->getPosition())将获得的模型坐标转换为相对于node1原点的世界坐标。
同理,node1->convertToWorldSpaceAR(node2->getPosition())将获得的模型坐标转换为相对于node1锚点的世界坐标。