PyTorch深度学习60分钟快速上手(三),神经网络。
神经网络
使用torch.nn可以很方便地构建神经网络。
到目前为止,我们已经对autograd有所了解,nn依靠autograd来定义模型,并求微分。nn.Module包含了许多网络层,forward(input)能返回输出结果output。
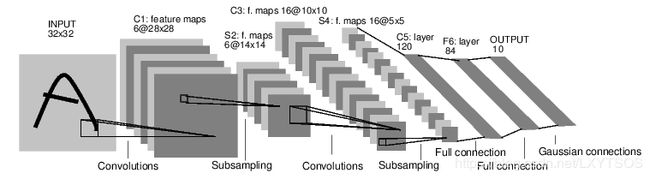
下面是分类数字图片的网络结构图:
这是一个非常简单的前向网络,将输入经过若干网络层的处理,最后得出结果。
神经网络的典型训练过程有以下几点:
- 定义网络结构,包含可学习的参数(或权重);
- 遍历数据集;
- 用网络处理输入;
- 计算损失(网络的输出离正确的值相差多少);
- 将梯度值反向传回给网络的参数;
- 更新网络的权重,一般使用:
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient来更新权重。
定义网络结构
现在,我们将使用Pytorch定义上述图中的网络:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 输入1通道图像, 输出6通道, 卷积核5x5
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
# an affine operation: y = Wx + b
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# 在(2, 2) 的窗口上做最大池化
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
# 如果池化窗口大小是个方阵,那么可以直接设定一个值
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
def num_flat_features(self, x):
size = x.size()[1:] # 除去批次这个维度
num_features = 1
for s in size:
num_features *= s
return num_features
输入是1 * 32 * 32大小的图像,经过第一次卷积之后,生成6 * 28 * 28的tensor,因此卷积层conv1的参数为,输入1通道tensor,输出6通道tensor,卷积核为5 * 5(32 - 5 + 1 = 28),步长为1,代码对应为:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)
接下来,卷积层的输出经过一个线性整流单元(ReLU),再经过一个池化层,输入为6 * 28 * 28,输出为6 * 14 * 14,因此池化窗口大小为2 * 2,步长为2,这里使用最大池化:
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
然后经过第二次卷积,得到16 * 10 * 10大小的tensor:
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
同样经过ReLU后做池化操作:
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
在进行全连接之前,我们需要把输出的16 * 5 * 5展开:
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
定义第一个全连接层,输入大小为16 * 5 * 5,输出120:
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
同理定义第二个全连接层,输入大小为上一层的输出:
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
定义最后一个全连接层,因为网络是用来分类数字的,而数字一共有10个,因此输出为10:
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
我们来把网络结构打印下出来看看:
net = Net()
print(net)
Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
我们只需要定义好网络的前向传播——forward函数,而反向传播backward则由autograd自动计算。
通过net.parameters()可以获取网络中的可学习参数:
params = list(net.parameters())
print(len(params))
print(params[0].size()) # conv1的权重
10
torch.Size([6, 1, 5, 5])
我们来随机生成一个32 * 32的输入,因为这个网络(LeNet)要求的输入为32 * 32:
input = torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 32)
out = net(input)
print(out)
tensor([[-0.0027, 0.0397, -0.0506, 0.1499, -0.0068, -0.0074, 0.0797, -0.0323,
-0.0592, 0.0341]], grad_fn=)
由于每次tensor的梯度都是累积在grad属性中,因此在反向传播之前需要梯度归零,这里在反向传播中传入随机的梯度值进行反向传播:
net.zero_grad()
out.backward(torch.randn(1, 10))
注意:
torch.nn只支持小批次的数据输入,不支持输入单个样本。比如nn.Conv2d接收4D tensor作为输入:nSamples x nChannels x Height x Width,如果只有一个样本,那么使用input.unsqueeze(0)来增加一个批次维度。
到现在为止,我们已经学会了:
- 定义网络结构
- 处理输入并且进行反向传播
接下来将讲述:
- 计算损失
- 更新网络权重
损失函数(Loss Function)
损失函数将(output, target)作为输入,计算出一个数值来估计output与target相差多少。
nn包下面有很多不同的损失函数,比如nn.MSELoss损失函数用来计算均方误差。
比如:
output = net(input)
target = torch.randn(10) # 随机生成的target
target = target.view(1, -1) # 与输出大小保持一致
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
loss = criterion(output, target)
print(loss)
tensor(0.8012, grad_fn=)
当调用loss.backward(),整个网络就开始计算关于loss的梯度,网络中所有requires_grad=True的参数都会将梯度累积到grad属性里。
我们来看看几个反向传播步骤:
print(loss.grad_fn) # MSELoss
print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0]) # Linear
print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0].next_functions[0][0]) # ReLU
反向传播(Backprop)
将损失反向传播,我们只需要调用loss.backward(),不过要记得清空梯度,否则所有梯度都会累积起来。
现在我们调用一下反向传播,并看看conv1层的偏置在反向传播前后的变化:
net.zero_grad() # 所有参数梯度归零
print('conv1.bias.grad before backward')
print(net.conv1.bias.grad)
loss.backward()
print('conv1.bias.grad after backward')
print(net.conv1.bias.grad)
conv1.bias.grad before backward
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
conv1.bias.grad after backward
tensor([-0.0122, -0.0004, -0.0031, -0.0044, -0.0003, -0.0003])
现在我们已经知道如何使用损失函数了,只剩下如何更新网络权重啦。
更新权重
在实际应用中,最简单的更新方法是使用随机梯度下降(Stochastic Gradient Descent,SGD):
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient
使用Python实现如下:
learning_rate = 0.01
for f in net.parameters():
f.data.sub_(f.grad.data * learning_rate)
然而,在使用神经网络时,我们通常想用不同的更新策略,比如SGD,Nesterov-SGD,Adam,RMSProp等,因此,在torch.optim包中实现了各种优化方法,使用起来非常方便:
import torch.optim as optim
# 创建优化器
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# 训练过程:
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度归零
output = net(input)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step() # 更新权重