深度学习与PyTorch入门实战(二) 线性回归问题
2 回归问题
简单线性回归:
对数据进行线性拟合
y = w x + b y = wx + b y=wx+b
从
到
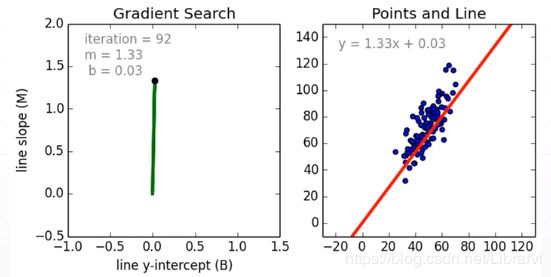
进行曲线拟合
1、目标
l o s s = Σ ( W X + b − y ) 2 loss = Σ(WX + b - y)^2 loss=Σ(WX+b−y)2
求 loss 最小值,对应的 w 和 b
2、通过数据信息,对其梯度下降,在迭代过程中获得最优解(凸优化)
w ‘ = w − l r ∗ d l o s s / d w w` = w - lr * dloss / dw w‘=w−lr∗dloss/dw
代码
import numpy as np
# loss = Σ(WX + b - y)^2
def conpute_error_for_line_given_points(b, w, points):
totalError = 0
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
totalError += (y - (w * x + b)) ** 2
return totalError / float(len(points))
# w` = w - lr * δloss / δw
def step_gradient(b_current, w_current, points, learningRate):
b_gradient = 0
w_gradient = 0
N = float(len(points))
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
b_gradient += -(2/N) * (y - ((w_current * x) + b_current))
w_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y - ((w_current * x) + b_current))
new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient)
new_w = w_current - (learningRate * w_gradient)
return [new_b, new_w]
# Iterate to optimize
def gradient_descent_runner(points, starting_b, starting_w, learning_rate, num_iterations):
b = starting_b
w = starting_w
for i in range(num_iterations):
b, w = step_gradient(b, w, np.array(points), learning_rate)
return [b, w]
def run():
points = np.genfromtxt("./Deep-Learning-with-PyTorch-Tutorials/lesson04-简单回归案例实战/data.csv", delimiter=",")
learning_rate = 0.0001
initial_b = 0
initial_w = 0
num_iterations = 1000
print("Starting gradient descent at b = {0}, m = {1}, error = {2}"
.format(initial_b, initial_w,
conpute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_w, points)))
print("running...")
[b, w] = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_w, learning_rate, num_iterations)
print("After {0} iterations b = {1}, w = {2}, error = {3}"
.format(num_iterations, b, w,
conpute_error_for_line_given_points(b, w, points)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
结果: