codeforces787D. Legacy(线段树+最短路)
D. Legacy
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Rick and his co-workers have made a new radioactive formula and a lot of bad guys are after them. So Rick wants to give his legacy to Morty before bad guys catch them.
There are n planets in their universe numbered from 1 to n. Rick is in planet number s (the earth) and he doesn't know where Morty is. As we all know, Rick owns a portal gun. With this gun he can open one-way portal from a planet he is in to any other planet (including that planet). But there are limits on this gun because he's still using its free trial.
By default he can not open any portal by this gun. There are q plans in the website that sells these guns. Every time you purchase a plan you can only use it once but you can purchase it again if you want to use it more.
Plans on the website have three types:
- With a plan of this type you can open a portal from planet v to planet u.
- With a plan of this type you can open a portal from planet v to any planet with index in range [l, r].
- With a plan of this type you can open a portal from any planet with index in range [l, r] to planet v.
Rick doesn't known where Morty is, but Unity is going to inform him and he wants to be prepared for when he finds and start his journey immediately. So for each planet (including earth itself) he wants to know the minimum amount of money he needs to get from earth to that planet.
Input
The first line of input contains three integers n, q and s (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 105, 1 ≤ s ≤ n) — number of planets, number of plans and index of earth respectively.
The next q lines contain the plans. Each line starts with a number t, type of that plan (1 ≤ t ≤ 3). If t = 1 then it is followed by three integers v, u and w where w is the cost of that plan (1 ≤ v, u ≤ n, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109). Otherwise it is followed by four integers v, l, r and w where w is the cost of that plan (1 ≤ v ≤ n, 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109).
Output
In the first and only line of output print n integers separated by spaces. i-th of them should be minimum money to get from earth to i-th planet, or - 1 if it's impossible to get to that planet.
Examples
input
Copy
3 5 1
2 3 2 3 17
2 3 2 2 16
2 2 2 3 3
3 3 1 1 12
1 3 3 17
output
Copy
0 28 12
input
Copy
4 3 1
3 4 1 3 12
2 2 3 4 10
1 2 4 16
output
Copy
0 -1 -1 12
Note
In the first sample testcase, Rick can purchase 4th plan once and then 2nd plan in order to get to get to planet number 2.
一、原题地址
点我传送
二、大致题意
给出n个点,m个传送的方案,起点为s.
传送方案有3种。
1、从u传送到v费用为w
2、从u传送到[ l , r ]范围上任意一点,费用为w
3、从[l ,r ]范围上任意一点传送到u,费用为w.
现在询问到达每个点的最短路。
三、大致思路
肯定是建图跑一个最短路,但是按照正常的建边方法,在一个范围内连接边的话会导致最后边数过多超时。
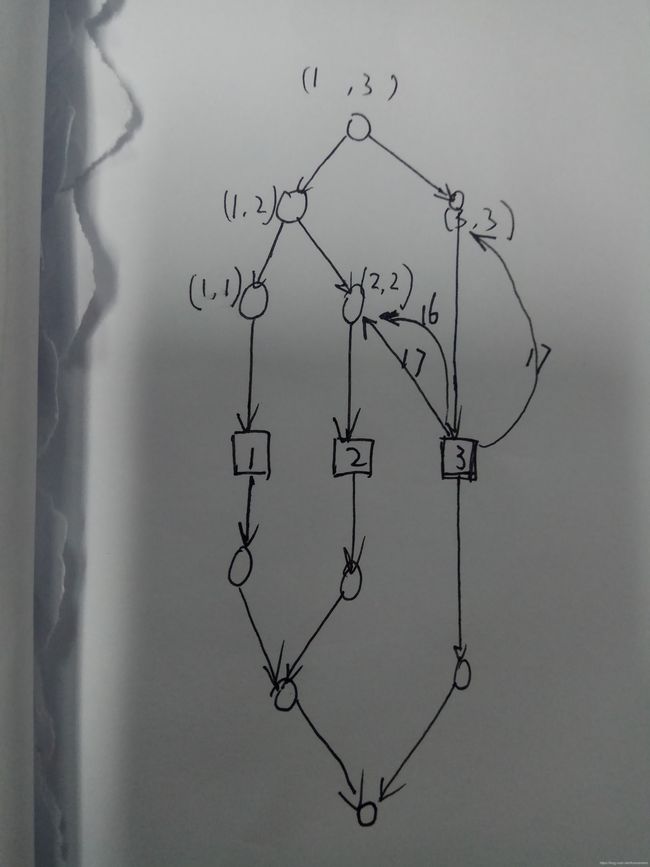
所以要用线段树来辅助建图。如样例1可以建立下图的路径(仅画了前两条边):
利用线段树的节点,大幅度减少了重复边。
四、代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include