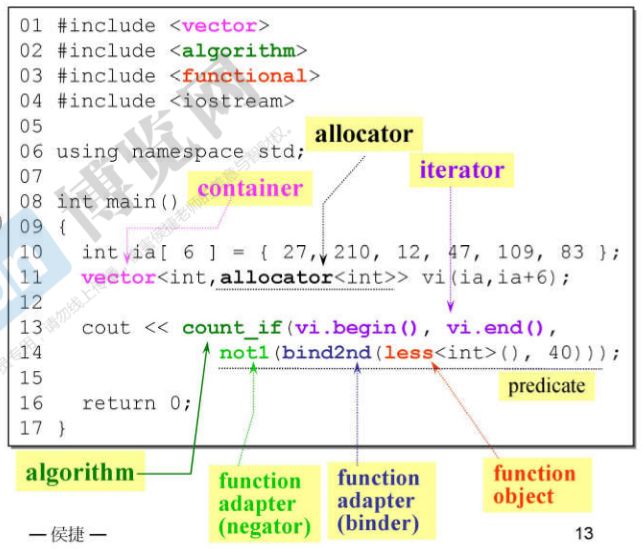
一 认识header、版本、重要资源
1.C++ Standard Library(C++标准库)
2.Standard Template Library(STL标准模板库)
STL标准模板库占用了C++标准库的大部分。
标准库以header files形式呈现
(1)C++标准库的header files 不带副档名(.h),例如#include
(2)新式C header files 不带副档名.h,例如#include
(3)旧式C header files 带有副档名.h,例如#include
(4)新式headers内的组件封装于namespace“std”:using namespace std;using std::cout;(for example)
(5)旧式headers内的组件不封装于namespace“std”
重要参考C++库参考链接:
1.CPlusPlus.com
2.CppReference.com
3.gcc.gnu.org
二 STL体系结构基础介绍
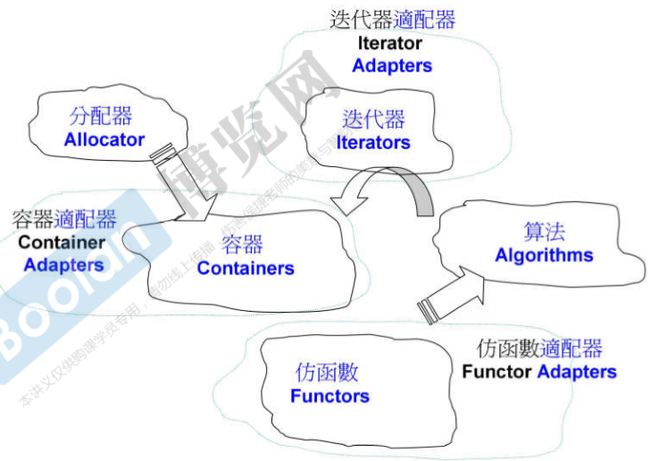
STL六大部件——《STL源码剖析》
- 容器:各种数据结构,如Vector,List,Deque,Set,Map,用来存放数据,STL容器是一种Class Template,就体积而言,这一部分很像冰山载海面的比率。
- 分配器:负责空间配置与管理,从实现的角度来看,配置器是一个实现了动态空间配置、空间管理、空间释放的Class Template。
- 算法:各种常用算法如Sort,Search,Copy,Erase,从实现的角度来看,STL算法是一种Function Templates。
- 迭代器:扮演容器与算法之间的胶合剂,是所谓的“泛型指针”,共有五种类型,以及其它衍生变化,从实现的角度来看,迭代器是一种将Operators*,Operator->,Operator++,Operator--等相关操作予以重载的Class Template。所有STL容器都附带有自己专属的迭代器——是的,只有容器设计者才知道如何遍历自己的元素,原生指针(Native pointer)也是一种迭代器。
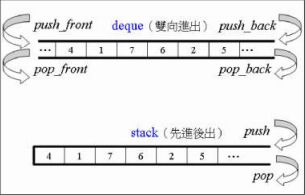
- 适配器:一种用来修饰容器(Containers)或仿函数(Functors)或迭代器(Iterators)接口的东西,例如:STL提供的Queue和Stack,虽然看似容器,其实只能算是一种容器配接器,因为 它们的底部完全借助Deque,所有操作有底层的Deque供应。改变Functor接口者,称为Function Adapter;改变Container接口者,称为Container Adapter;改变Iterator接口者,称为Iterator Adapter。配接器的实现技术很难一言蔽之,必须逐一分析。
- 仿函数:行为类似函数,可作为算法的某种策略(Policy),从实现的角度来看,仿函数是一种重载了Operator()的Class 或 Class Template。一般函数指针可视为狭义的仿函数。
程序实例:
三 容器之分类与各种测试
小Tips:
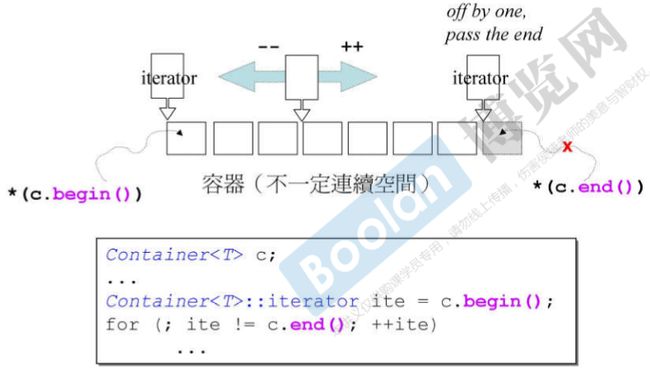
如图所示容器是一种[)的结构,迭代器指向最后一个数据的下一个地址,所以*(c.end())是不允许的。
STL中的常用容器包括:
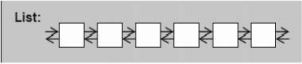
(1)顺序性容器(array、vector、deque、list、forward-list);
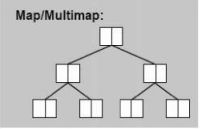
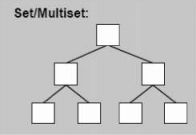
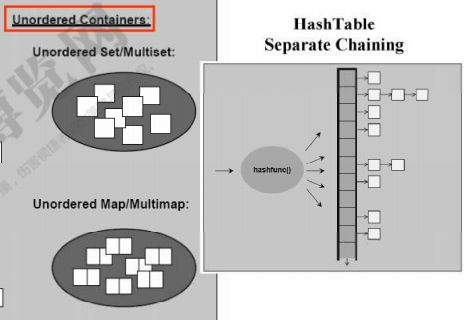
(2)关联容器(map/multimap、set/multiset、unordered set/multiset、unordered map/multimap);
(3)容器适配器(queue、stac)
参考链接:深入解析C++ STL中的常用容器
顺序性容器:
-
array:array是一个固定大小的顺序容器,不能动态改变大小,array内的元素在内存中以严格的线性顺序存储与普通数组声明存储空间大小[]的方式是一样有效的,只是加入了一些成员函数和全局函数[get (array)、operators (array)],以便当作标准容器使用。零大小的array是有效的,但是不可以被成员函数front、back、data间接引用,array的swap是一个线性操作交换所有的元素,通常是非常低效的
-
vector:vector是一种动态数组,在内存中具有连续的存储空间,支持快速随机访问。由于具有连续的存储空间,所以在插入和删除操作方面,效率比较慢。vector有多个构造函数,默认的构造函数是构造一个初始长度为0的内存空间,且分配的内存空间是以2的倍数动态增长的,即内存空间增长是按照20,21,22,23.....增长的,在push_back的过程中,若发现分配的内存空间不足,则重新分配一段连续的内存空间,其大小是现在连续空间的2倍,再将原先空间中的元素复制到新的空间中,性能消耗比较大,尤其是当元素是非内部数据时(非内部数据往往构造及拷贝构造函数相当复杂)。
-
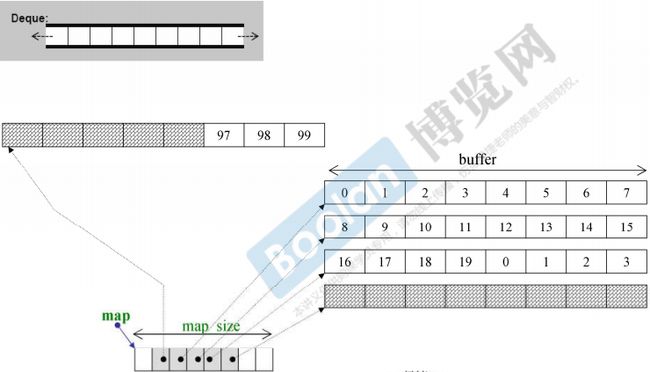
deque:deque和vector类似,支持快速随机访问。二者最大的区别在于,vector只能在末端插入数据,而deque支持双端插入数据。deque的内存空间分布是小片的连续,小片间用链表相连,实际上内部有一个map的指针。deque空间的重新分配要比vector快,重新分配空间后,原有的元素是不需要拷贝的。
-
list:list是一个双向链表,因此它的内存空间是可以不连续的,通过指针来进行数据的访问,这使list的随机存储变得非常低效,因此list没有提供[]操作符的重载。但list可以很好地支持任意地方的插入和删除,只需移动相应的指针即可。
-
forward_list:前向链表是用单链表实现的,可在常量时间内在链表中做插入或删除操作。list比之forward_list,双向链表要消耗额外的空间存储每个元素和在插入和删除元素时一个轻微的更高的时间开销,所以forward_list更有效率,虽然只能向前遍历。forward_list是唯一的标准容器中故意不给出size()成员函数的,这样是为了更高效而考虑,可以用distance(c.begin(),c.end())来得到forward_list的大小,这将消耗一个线性时间,而如果同list一样实现size()成员函数的话,那样要消耗一些额外的存储空间[用于链表中的内部计数得出size()]和使得插入和删除元素时有一个轻微的效率降低,实现size()要消耗一个常量的时间。
关联容器:
-
map:map是一种关联容器,该容器用唯一的关键字来映射相应的值,即具有key-value功能。map内部自建一棵红黑树(一种自平衡二叉树),这棵树具有数据自动排序的功能,所以在map内部所有的数据都是有序的,以二叉树的形式进行组织。
-
set:set也是一种关联性容器,它同map一样,底层使用红黑树实现,插入删除操作时仅仅移动指针即可,不涉及内存的移动和拷贝,所以效率比较高。set中的元素都是唯一的,而且默认情况下会对元素进行升序排列。所以在set中,不能直接改变元素值,因为那样会打乱原本正确的顺序,要改变元素值必须先删除旧元素,再插入新元素。不提供直接存取元素的任何操作函数,只能通过迭代器进行间接存取。
-
unordered set/multiset 、unordered map/multimap:散列容器比二叉树的存储方式可以提供更高的访问效率,unordered库提供两个散列集合类unordered_set和unordered_multiset,STLport也提供hash_set和hash_multiset,它们的接口,用法与stl里的标准关联容器set/multiset相同,只是内部使用散列表代替了二叉树实现,因此查找复杂度由数降为常数。
容器适配器:
-
queue:queue是一个队列,实现先进先出功能,queue不是标准的STL容器,却以标准的STL容器为基础。queue是在deque的基础上封装的。之所以选择deque而不选择vector是因为deque在删除元素的时候释放空间,同时在重新申请空间的时候无需拷贝所有元素。
-
stack:stack是实现先进后出的功能,和queue一样,也是内部封装了deque,这也是为啥称为容器适配器的原因吧(纯属猜测)。自己不直接维护被控序列的模板类,而是它存储的容器对象来为它实现所有的功能。stack的源代码原理和实现方式均跟queue相同。
使用实例代码如下:
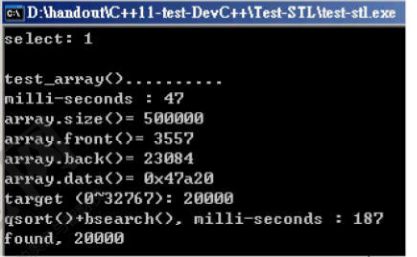
(1)array:
#include
#include
#include
#include //qsort, bsearch, NULL
namespace jj01
{
void test_array()
{
cout << "\ntest_array().......... \n";
array c;
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< ASIZE; ++i) {
c[i] = rand();
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; //
cout << "array.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "array.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "array.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "array.data()= " << c.data() << endl;
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
::qsort(c.data(), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
long* pItem = (long*)::bsearch(&target, (c.data()), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
cout << "qsort()+bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; //
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
(2) vector
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include
#include
#include //sort()
namespace jj02
{
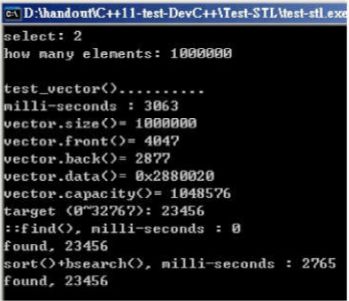
void test_vector(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_vector().......... \n";
vector c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
//曾經最高 i=58389486 then std::bad_alloc
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "vector.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //1073747823
cout << "vector.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "vector.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "vector.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "vector.data()= " << c.data() << endl;
cout << "vector.capacity()= " << c.capacity() << endl << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin(), c.end());
cout << "sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
timeStart = clock();
string* pItem = (string*)::bsearch(&target, (c.data()),
c.size(), sizeof(string), compareStrings);
cout << "bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(vector(),vector(), value);
}
}
(3) list
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include //find()
#include
#include
namespace jj03
{
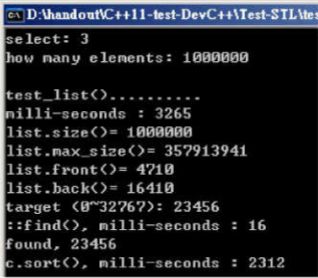
void test_list(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_list().......... \n";
list c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "list.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
cout << "list.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "list.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
test_moveable(list(),list(), value);
}
}
(4) forward_list
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include
#include
namespace jj04
{
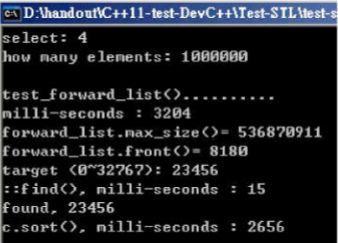
void test_forward_list(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_forward_list().......... \n";
forward_list c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_front(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "forward_list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //536870911
cout << "forward_list.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
}
}
(5) slist
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include
#include
namespace jj10
{
void test_slist(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_slist().......... \n";
__gnu_cxx::slist c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_front(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
}
}
(6) deque
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include
#include
namespace jj05
{
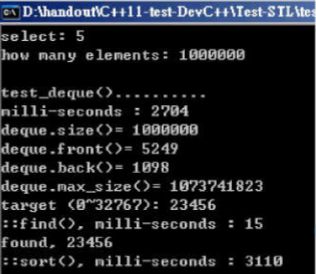
void test_deque(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_deque().......... \n";
deque c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "deque.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "deque.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "deque.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "deque.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //1073741821
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin(), c.end());
cout << "sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
test_moveable(deque(),deque(), value);
}
}
(7) multiset
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include
#include
namespace jj06
{
void test_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_multiset().......... \n";
multiset c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //214748364
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(multiset(),multiset(), value);
}
}
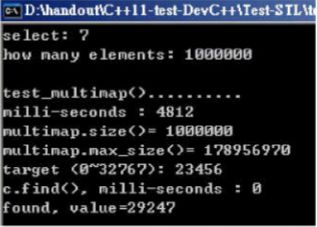
(8) multimap
#include (9) unordered_multiset
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include
#include
namespace jj08
{
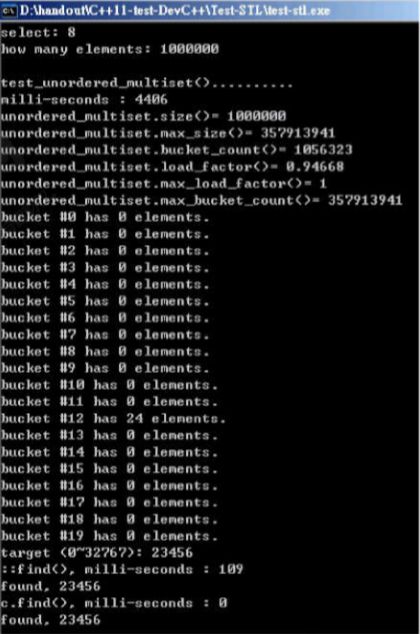
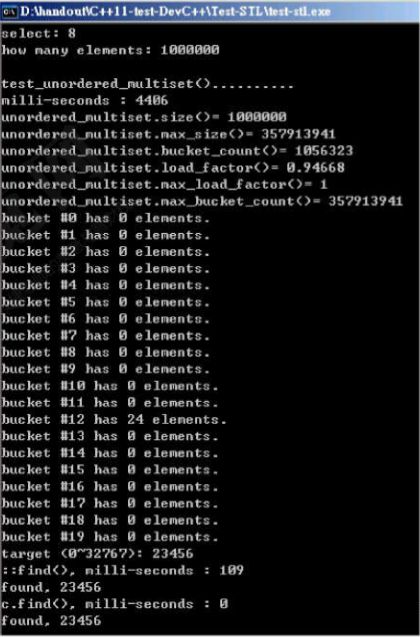
void test_unordered_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multiset().......... \n";
unordered_multiset c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
cout << "unordered_multiset.bucket_count()= " << c.bucket_count() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.load_factor()= " << c.load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_load_factor()= " << c.max_load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_bucket_count()= " << c.max_bucket_count() << endl;
for (unsigned i=0; i< 20; ++i) {
cout << "bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements.\n";
}
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(unordered_multiset(),unordered_multiset(), value);
}
}
(10) unordered_multimap
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include
#include
namespace jj09
{
void test_unordered_multimap(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multimap().......... \n";
unordered_multimap c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
//multimap 不可使用 [] 進行 insertion
c.insert(pair(i,buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_multimap.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multimap.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
四 分配器之测试
#include
#include
#include
#include //abort()
#include //snprintf()
#include //find()
#include
#include
#include
#include //內含 std::allocator
//欲使用 std::allocator 以外的 allocator, 得自行 #include
#ifdef __GNUC__
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#endif
namespace jj20
{
//pass A object to function template impl(),
//而 A 本身是個 class template, 帶有 type parameter T,
//那麼有無可能在 impl() 中抓出 T, 創建一個 list> object?
//以下先暫時迴避上述疑問.
void test_list_with_special_allocator()
{
#ifdef __GNUC__
cout << "\ntest_list_with_special_allocator().......... \n";
//不能在 switch case 中宣告,只好下面這樣. //1000000次
list> c1; //3140
list> c2; //3110
list> c3; //3156
list> c4; //4922
list> c5; //3297
list> c6; //4781
int choice;
long value;
cout << "select: "
<< " (1) std::allocator "
<< " (2) malloc_allocator "
<< " (3) new_allocator "
<< " (4) __pool_alloc "
<< " (5) __mt_alloc "
<< " (6) bitmap_allocator ";
cin >> choice;
if ( choice != 0 ) {
cout << "how many elements: ";
cin >> value;
}
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", i);
switch (choice)
{
case 1 : c1.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 2 : c2.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 3 : c3.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 4 : c4.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 5 : c5.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 6 : c6.push_back(string(buf));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "a lot of push_back(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
//test all allocators' allocate() & deallocate();
int* p;
allocator alloc1;
p = alloc1.allocate(1);
alloc1.deallocate(p,1);
__gnu_cxx::malloc_allocator alloc2;
p = alloc2.allocate(1);
alloc2.deallocate(p,1);
__gnu_cxx::new_allocator alloc3;
p = alloc3.allocate(1);
alloc3.deallocate(p,1);
__gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc alloc4;
p = alloc4.allocate(2);
alloc4.deallocate(p,2); //我刻意令參數為 2, 但這有何意義!! 一次要 2 個 ints?
__gnu_cxx::__mt_alloc alloc5;
p = alloc5.allocate(1);
alloc5.deallocate(p,1);
__gnu_cxx::bitmap_allocator alloc6;
p = alloc6.allocate(3);
alloc6.deallocate(p,3); //我刻意令參數為 3, 但這有何意義!! 一次要 3 個 ints?
#endif
}
}