tensorflow中张量的提取值和赋值操作
tf.gather和gather_nd从params中收集数值,tf.scatter_nd 和 tf.scatter_nd_update用updates更新某一张量。严格上说,tf.gather_nd和tf.scatter_nd_update互为逆操作。
已知数值的位置,从张量中提取数值:tf.gather, tf.gather_nd
tf.gather indices每个元素(标量)是params某个axis的索引,tf.gather_nd 中indices最后一个阶对应于索引值。
tf.gather函数
函数原型
gather(
params,
indices,
validate_indices=None,
name=None,
axis=0
)params是要查找的张量,indices是要查找值的索引(int32或int64),axis是查找轴,name是操作名。
如果indices是标量
![]()
如果indices是向量
![]()
如果indices是高阶张量
![]()
返回值:
该函数返回值类型与params相同,具体值是从params中收集过来的,形状为![]() 。
。
tf.gather_nd函数
函数原型
gather_nd(
params,
indices,
name=None
)indices是K阶张量,包含K-1阶的索引值。它最后一阶是索引,最后一阶维度必须小于等于params的秩。indices最后一阶的维数等于params的秩时,我们得到params的某些元素;indices最后一阶的维数小于params的秩时,我们得到params的切片。
![]()
输出张量的形状由indices的K-1阶和params索引到的形状拼接而成,如下面
indices.shape[:-1] + params.shape[indices.shape[-1]:]参数:
- params:被收集的张量。
- indices:索引张量。必须是以下类型之一:int32,int64。
- name:操作的名称(可选)。
返回值:
该函数返回一个张量.与params具有相同的类型。张量值从indices所给定的索引中收集,并且具有这样的形状:![]() 。
。
已知赋值的位置,向张量赋值:tf.scatter_nd, tf.scatter_nd_update
tf.scatter_nd对零张量进行赋值,tf.scatter_nd_update对已有可变的张量进行赋值。
tf.scatter_nd函数
scatter_nd(
indices,
updates,
shape,
name=None
)创建一个形状为shape的零张量,将updates赋值到indices指定的位置。
indices是整数张量,最内部维度对应于索引。
indices.shape[-1] <= shape.rank如果indices.shape[-1] = shape.rank,那么indices直接对应到新张量的单个元素。如果indices.shape[-1] < shape.rank,那么indices中每个元素对新张量做切片操作。updates的形状应该如下所示
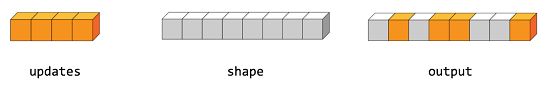
indices.shape[:-1] + shape[indices.shape[-1]:]如果我们要把形状为(4,)的updates赋值给形状为(8,)的零张量,如下图所示。
我们需要这样子做
indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1], [7]])
updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])
shape = tf.constant([8])
scatter = tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(scatter))我们得到这样子的张量
[0, 11, 0, 10, 9, 0, 0, 12]上面代码中,indices的形状是(4,1),updates的形状是(4,),shape的形状是(8,)。
indices.shape[:-1]+shape[indices.shape[-1]:] = (4,)+(,)=(4,)如果我们要在三阶张量中插入两个切片,如下图所示,则应该像下面代码里所说的那样子做。
indices = tf.constant([[0], [2]])
updates = tf.constant([[[5, 5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6, 6],
[7, 7, 7, 7], [8, 8, 8, 8]],
[[5, 5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6, 6],
[7, 7, 7, 7], [8, 8, 8, 8]]])
shape = tf.constant([4, 4, 4])
scatter = tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(scatter))indices的形状是(2,1),updates的形状是(2,4,4),shape的形状是(4,4,4)。
indices.shape[:-1]+shape[indices.shape[-1]:]=(2,)+(4,4)=(2,4,4)我们会得到这样子的张量
[[[5, 5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6, 6], [7, 7, 7, 7], [8, 8, 8, 8]],
[[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]],
[[5, 5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6, 6], [7, 7, 7, 7], [8, 8, 8, 8]],
[[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]]]函数参数
- indices:Tensor;必须是以下类型之一:int32,int64;索引值张量。
- updates:Tensor;分散到输出的更新。
- shape:Tensor;必须与indices具有相同的类型;1-d;得到的张量的形状。
- name:操作的名称(可选)。
返回值
此函数返回一个Tensor,它与updates有相同的类型;一个有shape形状的新张量,初始化值为0,部分值根据indices用updates进行更新。
tf.scatter_nd_update函数
函数原型
scatter_nd_update(
ref,
indices,
updates,
use_locking=True,
name=None
)scatter_nd_update也是把updates里面的值根据indices赋值到另外一个张量中,与scatter_nd不同的是,它是赋值到ref。
ref是秩为P的张量,indices是秩为Q的张量。
indices是整数类型的张量,必须具有这样的形状![]() 。
。
indices最内部的维度对应于ref的某个元素或切片。
updates的形状是![]() ,是秩为Q-1+P-K的张量。
,是秩为Q-1+P-K的张量。
如果我们想要把(4,)的向量赋值到(8,)的ref中,我们可以像下面这样子操作。
ref = tf.Variable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1] ,[7]])
updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])
update = tf.scatter_nd_update(ref, indices, updates)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print sess.run(update)我们可以得到这样的ref
[1, 11, 3, 10, 9, 6, 7, 12]函数参数
- ref:一个可变的Tensor。
- indices:一个 int32 或 int64 Tensor;一个对ref进行索引的张量.
- updates:一个Tensor.必须与ref具有相同的类型;更新值张量.
- use_locking:可选的bool;如果为True,则赋值将受锁定的保护;否则行为是不确定的,但可能表现出较少的争用.
- name:操作的名称(可选).
返回值:
经过更新的ref。