【十八掌●武功篇】第七掌:MapReduce之序列化和压缩
这一篇博文是【大数据技术●降龙十八掌】系列文章的其中一篇,点击查看目录:![]() 大数据技术●降龙十八掌
大数据技术●降龙十八掌
- 系列文章
-
【十八掌●武功篇】第七掌:MapReduce之工作机制
【十八掌●武功篇】第七掌:MapReduce之序列化和压缩
一、序列化类型
1、 Hadoop为什么要对数据序列化
序列化是将数据采用流的形式进行存储,以便于数据在网络传输或者写入磁盘。
Hadoop对数据进行序列化的好处:
(1) 格式确定:存为特定的格式后,数据接收方可以根据约定对数据进行可逆的操作。
(2) 便于传输:Hadoop上的程序在运行过程中,需要大量的网络传输,对数据进行序列化后,可以更好地在两端进行传输。
(3) 易于程序后期的管理:Hadoop是个平台,之后在平台上添加新的功能时,只需要遵守序列化和反序列化就好。
2、 Text
Hadoop中的Text是替代String类的,用于对一般的字符串进行操作。一般先将Text转换为String类型再做处理,处理后再转为Text类型进行存储。
3、 IntWritable
IntWritable可以理解为Hadoop对int类型的包装,对IntWritable类型数据的处理时应该首先将它转换为int再做处理。
IntWritable类型的值比较可以用compareTo方法,也可以实现WritableComparator接口用compare方法比较。第一种是将IntWritable转换为int后进行比较,第二种是对字节数组直接比较,会快一些,但是编码比较困难。
4、 ObjectWritable
ObjectWritable并不是对Java中Objece类的封装,而是对某些类型的封装,比如:String、int、enum等Java常见基本类型。
5、 NullWritable
NullWritable并不是一个null的封装,而是一个单独的特殊的Hadoop的基本类型。
NullWritable类存在的目的就是一个占位符,如果在Hadoop中的某一个位置不需要使用一个具体的值,就可以将之声明为NullWritable。
6、 ByteWritable
ByteWritable是用来包装二进制数组的一个序列化类。
7、 自定义Writable类型
通过查看IntWritable、Text等源代码可以看出,自定义一个Writable类型需要继承自WritableCompareable接口,并实现write、readFields、compareTo方法。
实例:
package mapreduce.sort;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Created by 鸣宇淳 on 2017/5/15.
*/
public class MyDataTypeWritable implements WritableComparable<MyDataTypeWritable> {
private Integer first;
private Integer second;
public Integer getFirst() {
return first;
}
public Integer getSecond() {
return second;
}
public MyDataTypeWritable() {
}
public MyDataTypeWritable(Integer f, Integer s) {
this.set(f, s);
}
public void set(Integer f, Integer s) {
this.first = f;
this.second = s;
}
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeInt(first);
dataOutput.writeInt(second);
}
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
this.first = dataInput.readInt();
this.second = dataInput.readInt();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return first + "|" + second;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return false;
}
if (!(obj instanceof MyDataTypeWritable)) {
return false;
} else {
MyDataTypeWritable other = (MyDataTypeWritable) obj;
return this.first.equals(other.first) && this.second.compareTo(other.second) == 0;
}
}
public int compareTo(MyDataTypeWritable o) {
/*
默认的排序规则,会使用这个compartTo方法进行
这里是先比较第一个,降序排序,如果第一个相同,比较第二个升序排序
*/
int comp = this.first.compareTo(o.first) * -1;
if (comp == 0) {
comp = this.second.compareTo(o.second);
}
return comp;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
//默认的分区规则里,会根据key的hashCode分区(可以参考HashPartitioner类的getPartition方法)
//这里将first的第一个字符char做为hashCode,如果使用默认的分区规则,会保证first 相同开头的分到一个分区里
//但是不能保证一个分区里只有一种first开头的数据
return first.toString().toCharArray()[0];
}
}
8、 SequenceFile文件
- (1) SequenceFile作用
-
Hadoop天生是为了处理大型文件而诞生的,HDFS存储的每一个文件的元数据都会保存在NameNode的内存中,如果存储的是大量的小文件,就会占用大量的NameNode内存空间,严重影响NameNode的性能,另外如果读取大量小文件,就会产生大量对文件的生成和释放资源的操作,影响性能。
但是Hadoop并不是不能处理大量的小文件(小文件是指小于一个块的文件),可以使用SequenceFile格式对小文件进行处理。
Map和Reduce的中间结果就是用SequenceFile存储的。 - (2) SequenceFile格式
-
SequenceFile是将文件进行二进制处理后,生成的具有特定键值对的二进制文件流。格式如下:
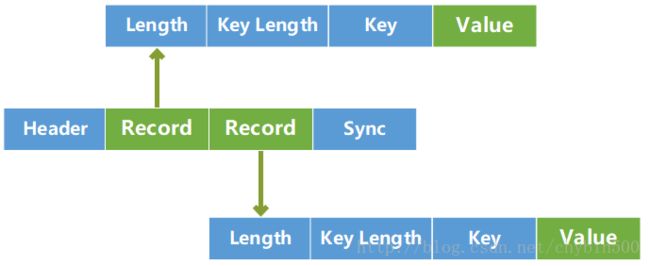
一个SequenceFile是由四部分组成的:
- Header
- 用于存储当前SequenceFile中的一些信息,例如:SEQ标志、后面跟随一个字节表示此SequenceFile的版本号、键值对的类型、压缩格式
- Record
- Header后面是对数据的存储,是SequenceFile文件存储数据的地方。每个Record由数据长度、键长度、键信息、值组成。如果是被压缩的,值就是存储的是压缩后的值。然后每隔若干阶段就会对Record设置一个分界点。
- Sync
- 它是设置Record中的分界点。SequenceFile.Writer实例写入数据时,会隐藏地为每一行添加一个偏移量,用于获取当前文件的移动位置,并按照一定顺序生成相应的同步位置。
(3) 读写实例
package mapreduce.datetype;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Created by 鸣宇淳 on 2017/5/22.
*/
public class SeqDemo {
static Path path = null;
static Configuration configuration = null;
static FileSystem fs = null;
static SequenceFile.Writer writer = null;
static SequenceFile.Reader reader = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
path = new Path(args[0]);
configuration = new Configuration();
try {
fs = FileSystem.get(configuration);
Writen();
Read();
} catch (IOException e) {
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
IOUtils.closeStream(reader);
}
if (writer != null) {
IOUtils.closeStream(writer);
}
}
}
private static void Read() throws IOException {
reader = new SequenceFile.Reader(fs, path, configuration);
IntWritable key = new IntWritable();
Text value = new Text();
while (reader.next(key, value)) {
System.out.println(key + "____" + value);
}
}
private static void Writen() {
String meg = "hello world !";
Random random = new Random();
try {
writer = SequenceFile.createWriter(fs, configuration, path, IntWritable.class, Text.class);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
writer.append(new IntWritable(random.nextInt(100)), new Text(meg + "_" + i));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
} finally {
if (writer != null) {
IOUtils.closeStream(writer);
}
}
}
}
9、 MapFile
(1) MapFile介绍
MapFile继承自SequenceFile,是一个可进行查询操作的文件类,它提供了一个继承了WritableComparable的类作为key,以便在计算时进行排序。
MapFile是一种基于键值对的用于查找的SequenceFile,在生成运算结果的时候一般会分别生成关联的索引与数据文件。MapFile文件写入的时候,要保证key是排好序的,如果写入一个不符合的数据,则会抛出异常。
(2) 示例代码
package mapreduce.datetype;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.MapFile;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Created by 鸣宇淳 on 2017/5/22.
*/
public class MapFileWriteDemo {
static Path path = null;
static String pathStr = "";
static Configuration configuration = null;
static FileSystem fs = null;
static MapFile.Writer writer = null;
static MapFile.Reader reader = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
path = new Path(args[0]);
pathStr = args[0];
configuration = new Configuration();
try {
fs = FileSystem.get(configuration);
Writen();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
IOUtils.closeStream(reader);
}
if (writer != null) {
IOUtils.closeStream(writer);
}
}
}
/*
MapFile文件写入数据,会生成两个文件:index和data
*/
private static void Writen() {
String meg = "hello world !";
Random random = new Random();
try {
writer = new MapFile.Writer(configuration, fs, pathStr, IntWritable.class, Text.class);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("index:" + i);
writer.append(new IntWritable(i), new Text(meg + "_" + i));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} finally {
if (writer != null) {
IOUtils.closeStream(writer);
}
}
}
}
package mapreduce.datetype;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.MapFile;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ReflectionUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Created by 鸣宇淳 on 2017/5/22.
*/
public class MapFileReadDemo {
static Path path = null;
static String pathStr = "";
static Configuration configuration = null;
static FileSystem fs = null;
static MapFile.Writer writer = null;
static MapFile.Reader reader = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
path = new Path(args[0]);
pathStr = args[0];
configuration = new Configuration();
try {
fs = FileSystem.get(configuration);
Read();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
IOUtils.closeStream(reader);
}
if (writer != null) {
IOUtils.closeStream(writer);
}
}
}
private static void Read() throws IOException {
reader = new MapFile.Reader(fs, pathStr, configuration);
IntWritable rInt = new IntWritable();
Text rText = new Text();
while (reader.next(rInt, rText)) {
System.out.println(rInt + ":" + rText);
}
Text value = (Text) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(reader.getValueClass(), configuration);
reader.get(new IntWritable(20), value);
System.out.println(value.toString());
value.clear();
reader.getClosest(new IntWritable(20), value);
System.out.println(value.toString());
}
}
二、压缩
1、 压缩的原因
Hive最终是转为MapReduce程序来执行的,而MapReduce的性能瓶颈在于网络IO和磁盘IO,要解决性能瓶颈,最主要的是减少数据量,对数据进行压缩是个好的方式。
压缩虽然是减少了数据量,但是压缩过程要消耗CPU的,但是在Hadoop中,往往性能瓶颈不在于CPU,CPU压力并不大,所以压缩充分利用了比较空闲的CPU。
2、 压缩格式与算法
| 压缩格式 | 是否可拆分 | 是否自带 | 压缩率 | 速度 | 是否hadoop自带 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gzip | 否 | 是 | 很高 | 比较快 | 是 |
| lzo | 是 | 是 | 比较高 | 很快 | 否,要安装 |
| snappy | 否 | 是 | 比较高 | 很快 | 否,要安装 |
| bzip2 | 是 | 否 | 最高 | 慢 | 是 |
各个压缩格式对应的类:
| 压缩格式 | 类 |
|---|---|
| Zlib | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec |
| Gzip | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec |
| Bzip2 | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec |
| Lzo | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.lzo.LzoCodec |
| Lz4 | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Lz4Codec |
| Snappy | org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec |
(1) 压缩方式选择原则:
● 压缩比率
● 压缩解压速度
● 是否支持split
所有的压缩算法都是空间和时间上做出的一种权衡,即牺牲时间换空间还是牺牲空间换时间。例如:在对实时性比较高的应用场景中,一般要求压缩和解压的速度高;而对一般的大文件存储时,则更注重节省压缩存储空间。
(2) map的输入压缩
最好选择一种支持split的压缩方式,如果选择不支持split的压缩方式,大文件将会由一个map进程进行处理。如果要选择不支持的split压缩方式,那么就先将大文件进行分割成大小接近128M的小文件,然后对这些小文件进行单独压缩。
(3) map的输出压缩
map的输出压缩,要注重考虑压缩解压速度,常用的用snappy压缩,
(4) reduce端的输出
很少对reduce端的输出进行压缩,但是一下两个场景会对使用压缩
● reduce输出结果后面甚少使用,一般要用压缩以提高性能。一般使用压缩比率比较高的压缩格式。
● 迭代计算时,reduce输出结果要给下一个job做为输入使用,着重使用压缩解压速度比较快的方式。
3、 在配置文件中配置压缩
默认是不启用压缩的,如果对整个集群启用压缩,可以在mapred-site.xml中修改参数:
(1) mapreduce.map.output.compress 是否对map任务输出进行压缩,默认是false。
(2) mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec 设置map输出所用的压缩codec,默认是org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec。
4、 在程序中配置压缩
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.set("mapreduce.map.output.compress.","true");
configuration.setClass("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec", SnappyCodec.class, CompressionCodec.class);
5、 压缩池
Hadoop中的压缩和解压是个重量级的任务,需要消耗大量的资源去满足,可以使用压缩池完成任务,压缩池包括两个方法:getCompressor和returnCompressor。
getCompressor是从压缩池中获取一个闲置资源。
returnCompressor是将压缩资源归还到压缩池中。
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.*;
/**
* Created by 鸣宇淳 on 2017/5/10.
*/
public class CodecsPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取环境变量
Configuration configuration=new Configuration();
//Gzip压缩格式
CompressionCodec gzipCodec=new GzipCodec();
//Bzip压缩格式
CompressionCodec bzip2Codec=new BZip2Codec();
//定义压缩池对象实例
Compressor compressor=null;
//获取一个Gzip格式压缩实例
compressor= CodecPool.getCompressor(gzipCodec);
//归还压缩资源
CodecPool.returnCompressor(compressor);
//获取一个Bzip2压缩格式的实例
compressor=CodecPool.getCompressor(bzip2Codec);
}
}