快速排序递归与非递归实现
算法概述:
分而治之。
选出一个元素作为主元,它可以把集合中的元素分成两部分,一部分都是大于它的,一部分都小于它的。
我们先用伪代码描述。
void QuickSort(ElementType A[],int N)
{
//如果只剩一个元素了直接返回
if(N<2) return;
pivot=从A[]选出一个主元;
将S={ A[]\pivot }分成两个独立的子集;
A1={ a∈S | a≤ pivot }和A2={ a∈S | a≥ pivot};
A[]=QuickSort(A1,N1)∪ pivot ∪ QuickSort(A2,N2);
}选主元
选主元一定要慎重。如果是下面这种情况
共有5个元素,1 2 3 4 5
选1作为主元那么比1小的为空,比1大的有4个。这样进行的快排是一点也不快的。
取头,中,尾的三个元素比较,选出中间大小的元素作为主元
ElementType Median(ElementType A[],int left, int right)
{
int center=(left+right)/2;
if(A[left]>A[center])
{
Swap(&A[left],&A[center]);
}
if(A[left]>A[right])
{
Swap(&A[left],&A[right]);
}
if(A[center]>A[right])
{
Swap(&A[center],&A[right]);
}
//将pivot放到right-1的位置,我们知道A[left]肯定小于主元A[right]肯定大于主元
//只需要考虑A[left+1]~A[right-2]
Swap(&A[center],&A[right-1]);
return A[right-1];
}子集划分
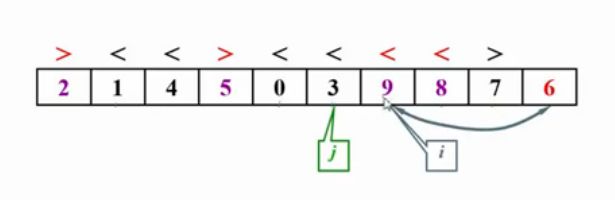
6是主元,被放在最右端。
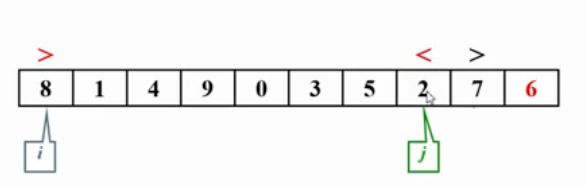
当i对应的元素大于主元,j对应的元素小于主元,停下来,进行交换
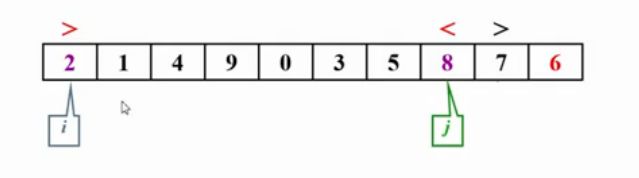
当i>j时,停止交换。并把主元与i位置元素交换。选出来的主元,在完成一次子集划分后,主元会被放到最终应在的位置。
小规模数据的处理
因为使用了递归,对于小规模的数据,可能快排还没有如插入排序的简单排序快。
所以我们可以设定一个阈值Cutoff,当递归时的数据规模足够小,我们就停止递归了,直接调用简单排序。
递归
代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include<string.h>
#include
using namespace std;
int median(int* arr, int left, int right){
int center = (left + right) / 2;
if (arr[left] > arr[center]){
swap(arr[left],arr[center]);
}
if (arr[left] > arr[right]){
swap(arr[left],arr[right]);
}
if (arr[center] > arr[right]){
swap(arr[center],arr[right]);
}
swap(arr[center],arr[right-1]);
return arr[right - 1];
}
void insertSort(int* arr,int n){
int tmp;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
tmp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j>0 && arr[j - 1] > tmp; j--){
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
}
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
int cutoff = 5;
void quickSort(int* arr,int left,int right){
if (cutoff <= (right - left)){
int pivot = median(arr,left,right);
int i = left;
int j = right - 1;
while (1){
while (arr[++i] < pivot){
}
while (arr[--j]>pivot){
}
if (i < j){
swap(arr[i],arr[j]);
}
else{
break;
}
}
swap(arr[i],arr[right-1]);
quickSort(arr,left,i-1);
quickSort(arr,i+1,right);
}
else{
insertSort(arr+left,right-left+1);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[20] = {20,19,18,10,17,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,8,1,2,3,11,4,12};
quickSort(arr,0,19);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 非递归,手动利用栈来存储每次分块时快排的起始点。这种写法的执行效率低于递归算法。
#includeint j;
for (j = i; j>0 && arr[j - 1] >= tmp; j--){
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
}
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
int median(int* arr, int left, int right){
int center = (left + right) / 2;
if (arr[left] > arr[center]){
swap(arr[left],arr[center]);
}
if (arr[left] > arr[right]){
swap(arr[left],arr[right]);
}
if (arr[center] > arr[right]){
swap(arr[center],arr[right]);
}
swap(arr[center],arr[right-1]);
return arr[right - 1];
}
int partition(int* arr,int left,int right){
int pivot = median(arr,left,right);
int i = left;
int j = right - 1;
while (iwhile (arr[++i] < pivot){}
while (arr[--j] > pivot){}
if (i < j){
swap(arr[i],arr[j]);
}
else{
break;
}
}
swap(arr[i],arr[right-1]);
return i;
}
void quickSort(int* arr,int left,int right){
stack