在matlab上实现遗传算法解决TSP旅行者问题
TSP问题指的是从一个节点开始遍历其他所有节点并回到初始节点,构成一个哈密顿回路,节点与节点之间距离不同,目标是找到一条回路使得总路程最短,也即就是走最短的路遍历所有节点回到起点。
遗传算法模仿达尔文进化论中优胜劣汰的思想,从随机初始总群开始,不断进化最终选出接近最优解的一代,从而求解出近似最优解
问题描述
下图矩阵展示了不同城市之间的距离,城市到自身的距离为0,现要求从Hong Kong出发,找一条最短的旅游顺序,使得游览所有城市后回到Hong Kong。

基本思路
主要是问题的编码阶段,对于TSP问题在遗传算法中编码使用整数编码,使用整数来代表每一个城市,比如这里可以依次使用1,2,3,…,13表示这13个城市,9则代表Hong Kong。
| 城市 | 编码基因 |
|---|---|
| Amsterdam | 1 |
| Athens | 2 |
| Auckland | 3 |
| Bahrain | 4 |
| Bangkok | 5 |
| Colombo | 6 |
| Dubai | 7 |
| Frankflurt | 8 |
| HK | 9 |
| Jakarta | 10 |
| Kuala Lumpur | 11 |
| London | 12 |
| Manila | 13 |
这13个数字的一个排列即是一种路径方案,但注意这条路径是一个环,收尾相接,因此起点是哪个城市是无所谓的,只要数字的相对位置确定,那13种(谁是起点)归并为同一种方案。因此所有可能的方案数为:13!/13 (全排列除以13)
示例染色体:[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13],同[2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 1]等属于同一种方案。
这种方案的路程代价为:F = 2.2+17.5+14.7+5.4+2.4+3.3+4.8+9.2+3.3+1.2+10.5+10.7+10.4
= 95.6 (thousand kilometers)
每种方案的路程代价即个体的适应度,路程越短代价越小适应度越高。
函数解释
- cost.m:用来计算一种方案的路程代价,参数为方案数列染色体和代价矩阵。算法中优选代价小的,淘汰代价大的;
- crossover.m:染色体交叉,参数为两个父代染色体,交叉失败返回0,否则返回交叉后的两个子代染色体;
- crosscheck.m:检查两个父代是否可交叉得到有效的子代染色体,因为交叉后如果染色体中出现重复的数字是无效的方案,等于某个城市走了两次同时有的城市没遍历到;
- generate.m:产生一个随机的染色体,实际是将实力染色体中的基因顺序随机打乱得到;
- mutation.m:按照一定基因突变概率使参数染色体发生基因突变得到突变后的子代染色体;
- TSP.m:遗传算法主体,其中采用了精英选择法,将父代的优秀个体加入到下一代的竞争中。
Matlab代码清单
cost.m
% 根据代价矩阵costM计算种群pop的总路程代价
function [value] = cost(pop,costM)
% 求得种群的个体数量,从而对每个个体计算代价
[NumP,tmp]=size(pop);
% 循环对每个个体计算代价
for i=1:NumP
parent_i = pop(i,:);
value_i = 0;
% 累加相邻两个城市之间的距离
for j=1:12
value_i = value_i + costM(parent_i(j),parent_i(j+1));
end
% 将最后一个城市和出发城市的距离加上,组成闭合回路
value_i = value_i + costM(parent_i(13),parent_i(1));
% 结果组装
value(i,1) = value_i;
end
endcrosscheck.m
% 检查两个父代个体是否可以交叉得到有效的两个子代个体
function res = crosscheck(parent1,parent2)
res = 0;
% 对每个交叉点进行交叉看是否至少有一个交叉点是有效的
for i = 1:12
p1 = [parent1(:,1:i) parent2(:,i+1:13)];
p2 = [parent2(:,1:i) parent1(:,i+1:13)];
% 如果子代基因没有重复的则是有效子代
if length(p1)==length(unique(p1)) && length(p2)==length(unique(p2))
res = 1;
end
end
endcrossover.m
% 染色体交叉
function [child1, child2]=crossover(parent1, parent2)
% 如果父代不可交叉子代置0表示无效
child1 = 0;
child2 = 0;
if crosscheck(parent1,parent2) == 1
p1 = [1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1];
p2 = [2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2];
% 确保子代有效
while length(p1)>length(unique(p1)) || length(p2)>length(unique(p2))
% 随机选择交叉点
crossPoint = randi([1 12]);
p1 = [parent1(:,1:crossPoint) parent2(:,crossPoint+1:13)];
p2 = [parent2(:,1:crossPoint) parent1(:,crossPoint+1:13)];
end
child1 = p1;
child2 = p2;
end
endgenerate.m
% 将基本的染色体序列随机打乱构造随机个体,可以构建num个随机个体
function pop = generate(num)
res = [];
% 算法思路是将tmp0中剩余的基因随机抽取依次填入tmp,当tmp0中的基因全部随机填入tmp后得到随机个体
for i = 1:num
tmp = [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0];
tmp0 = [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13];
for j = 1:13
% 随机下标
index = randi([1 14-j]);
tmp(j) = tmp0(index);
% 删除从tmp0染色体中被随机选中的基因
tmp0(:,index) = [];
end
% 组装得到的随机个体
res = [res;tmp];
end
pop = res;
endmutation.m
% 基因突变,按照突变概率,随机交换个体中的某两个基因
function [child]=mutation(parent,probability)
if rand() <= probability
P = parent;
% 随机选择两个不同的基因交换位置
random1 = 0;
random2 = 0;
while random1 == random2
random1 = randi([1 13]);
random2 = randi([1 13]);
end
% 开始突变(交换位置)
P(:,[random1,random2]) = P(:,[random2,random1]);
child=P;
else
% 没有发生突变
child = 0;
end
endTSP.m
% 遗传算法求解TSP旅行商问题
function tmp = TSP()
% 清空
close all;
clc;
%----------------------------data area-------------------------------------
% distance from a city to others
Amsterdam = [0 2.2 18.1 4.8 9.2 8.4 5.2 0.4 9.3 11.3 10.2 0.4 10.4]; %1
Athens = [2.2 0 17.5 2.8 7.9 6.6 3.3 1.8 8.5 9.8 8.7 2.4 9.6]; %2
Auckland = [18.1 17.5 0 14.7 9.6 10.9 14.2 18.2 9.1 7.6 8.7 18.3 8.0]; %3
Bahrain = [4.8 2.8 14.7 0 5.4 3.8 0.5 4.4 6.4 7.0 6.0 5.1 7.4]; %4
Bangkok = [9.2 7.9 9.6 5.4 0 2.4 4.9 9.0 1.7 2.3 1.2 9.5 2.2]; %5
Colombo = [8.4 6.6 10.9 3.8 2.4 0 3.3 8.1 4.1 3.3 2.5 8.7 4.6]; %6
Dubai = [5.2 3.3 14.2 0.5 4.9 3.3 0 4.8 6.0 6.6 5.5 5.5 6.9]; %7
Frankflurt = [0.4 1.8 18.2 4.4 9.0 8.1 4.8 0 9.2 11.1 10.0 0.6 10.3]; %8
HK = [9.3 8.5 9.1 6.4 1.7 4.1 6.0 9.2 0 3.3 2.5 9.6 1.1]; %9
Jakarta = [11.3 9.8 7.6 7.0 2.3 3.3 6.6 11.1 3.3 0 1.2 11.7 2.8]; %10
KualaLumpur = [10.2 8.7 8.7 6.0 1.2 2.5 5.5 10.0 2.5 1.2 0 10.5 2.5]; %11
London = [0.4 2.4 18.3 5.1 9.5 8.7 5.5 0.6 9.6 11.7 10.5 0 10.7]; %12
Manila = [10.4 9.6 8.0 7.4 2.2 4.6 6.9 10.3 1.1 2.8 2.5 10.7 0]; %13
costM = [Amsterdam;Athens;Auckland;Bahrain;Bangkok;Colombo;Dubai;Frankflurt;HK;Jakarta;KualaLumpur;London;Manila];
%mutation probability
pmutation = 1.0;
%max generation
MaxGeneration = 200;
%poputation size
popsize = 20;
%select popsize parents from randomsize generated possible parents
randsize = 200;
%parent generations
parentpop = [];
%best parent of every generation
best_cost = [];
%-------------------generate parent generation-----------------------------
preparentpop = generate(randsize);
[A,index] = sort(cost(preparentpop,costM),1,'ascend');
%orderd preparentpop
orderedpreparentpop = preparentpop(index,:);
%selected top popsize parentpop
parentpop = orderedpreparentpop([1:popsize],:);
%---------------------main revolution loop---------------------------------
for igen = 1:MaxGeneration
childpop = [];
childpopsize = [0 0];
%generate enough children
while childpopsize(1) < popsize
% To generate the random index for crossover and mutation
ind=randi(popsize,[1 2]) ;
parent1 = parentpop(ind(1),:);
parent2 = parentpop(ind(2),:);
[child1,child2] = crossover(parent1,parent2);
[child3] = mutation(parent1,pmutation);
if child1~=0
childpop = [childpop;child1];
end
if child2~=0
childpop = [childpop;child2];
end
if child3~=0
childpop = [childpop;child3];
end
childpopsize = size(childpop);
end
% Elite: parentpop and childpop are added together before sorting for the best popsize to continue
allpop = [parentpop;childpop];
[A,index] = sort(cost(allpop,costM),1,'ascend');
orderdallpop = allpop(index,:);
%parentpop of current generation
parentpop = orderdallpop([1:popsize],:);
best_cost(igen)=A(1);
end
%display
display('the best parentpop:')
parentpop
display('the lowest cost of every generation:')
best_cost'
figure,plot(1:igen,best_cost,'b')
title('GA algorithm for TSP problem')
end结果
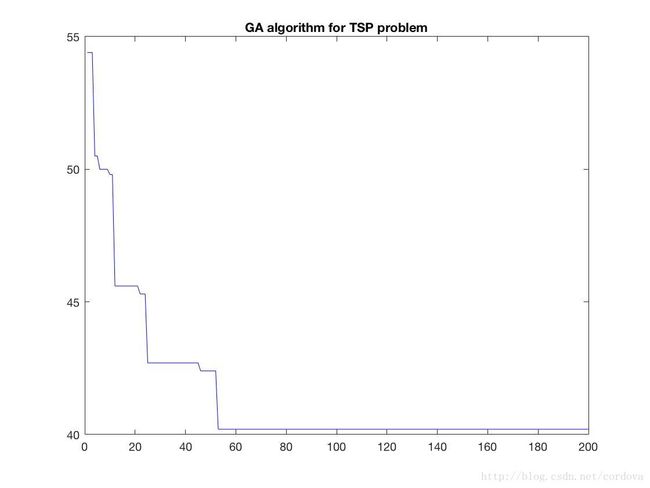
进行了200代进化,大约在50代以后收敛,得到近似最优方案的最小路程代价为40.2。
最优染色体为:
[2 8 12 1 9 13 3 10 11 5 6 7 4]
等效于Hong Kong为起点的:
[9 13 3 10 11 5 6 7 4 2 8 12 1]
解码得到最佳方案为:
Hong Kong - Manila - Auckland - Jakarta - Kuala Lumpur - Bangkok - Colombo - Dubai - Bahrain - Athens - Frankflurt - London - Amsterdam - Hong Kong
并不是每次运行都会得到绝对最优解,遗传算法容易早熟陷入局部最优解。
Github源码下载:https://github.com/jiangxh1992/GA4TSPProblem