EventBus原理详解
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/michael_yt/article/details/52014022
在EventBus 3.0 使用介绍 这篇博客中介绍了关于EventBus的一些使用方法,下面我们就来看看它内部的具体实现吧!
流程图
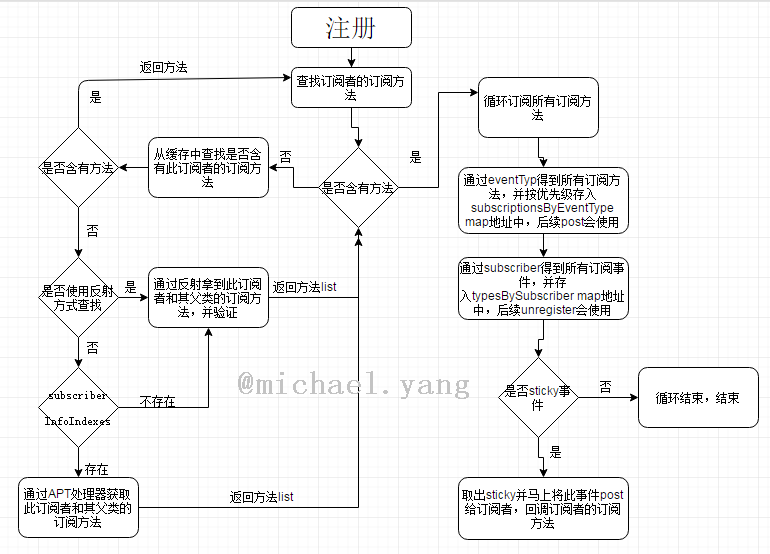
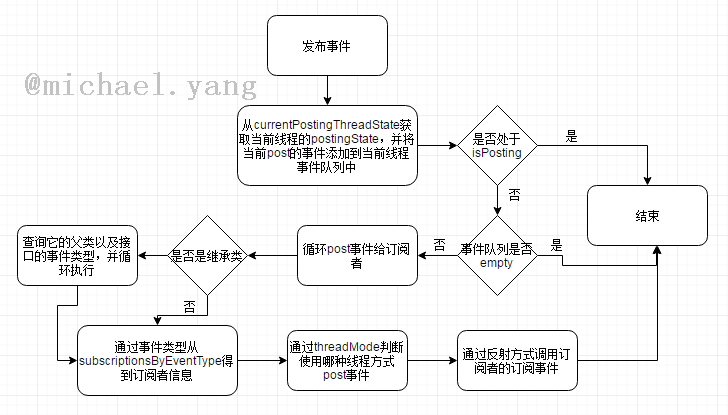
先来一张整体流程图:
思路图
在看看register 和 post 的过程思路图:
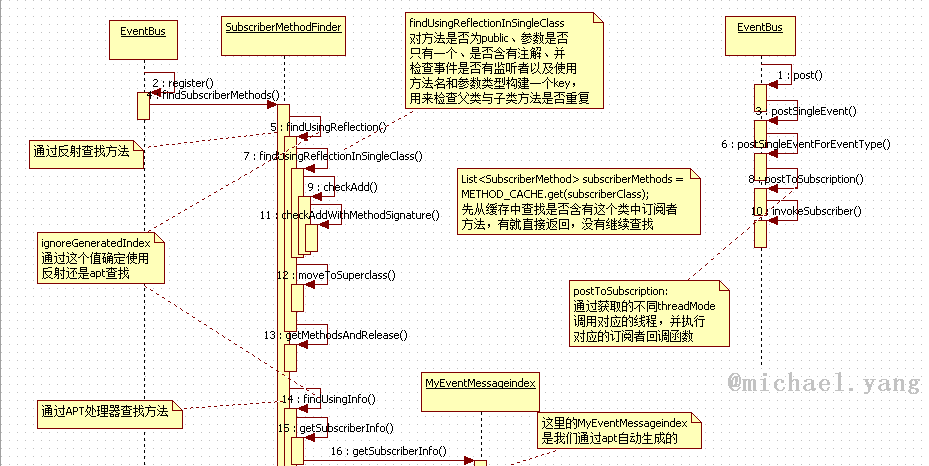
register
post
通过上面的几张图,我们可以大致了解eventbus的工作流程,下面我们在来介绍一下这个流程中比较重要的几个方法
重要的方法
register中重要的方法
List findSubscriberMethods(Class subscriberClass) {
List subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass);//先从缓存中查找是否存在订阅者的方法
if (subscriberMethods != null) {
return subscriberMethods;
}
if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {
subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);//使用反射方法拿到订阅者中的订阅方法
} else {
subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);//使用apt处理器拿到订阅者中的订阅方法
}
if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty()) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass
+ " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation");
} else {
METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods);//将查到的方法放到缓存中,以便下次使用
return subscriberMethods;
}
} 通过反射获取方法
//准备一个FindState 来装订阅者的方法
private FindState prepareFindState() {
synchronized (FIND_STATE_POOL) {
for (int i = 0; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) {
FindState state = FIND_STATE_POOL[i];
if (state != null) { //得到一个state并将相应的引用变量置为null
FIND_STATE_POOL[i] = null;
return state;
}
}
}
return new FindState();
}//将FindState 里面的方法放入subscriberMethods list中,并将FindState 放回去继续使用
private List getMethodsAndRelease(FindState findState) {
List subscriberMethods = new ArrayList<>(findState.subscriberMethods);
findState.recycle();
synchronized (FIND_STATE_POOL) {
for (int i = 0; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) {
if (FIND_STATE_POOL[i] == null) {//如果引用变量为null将当前这个findState赋值过去,和上面的方法相对应
FIND_STATE_POOL[i] = findState;
break;
}
}
}
return subscriberMethods;
} private void findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(FindState findState) {
Method[] methods;
try {
// This is faster than getMethods, especially when subscribers are fat classes like Activities
methods = findState.clazz.getDeclaredMethods();//通过反射方法得到订阅者类里面的订阅方法
} catch (Throwable th) {
// Workaround for java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError, see https://github.com/greenrobot/EventBus/issues/149
methods = findState.clazz.getMethods();
findState.skipSuperClasses = true;
}
for (Method method : methods) {
int modifiers = method.getModifiers();
if ((modifiers & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0 && (modifiers & MODIFIERS_IGNORE) == 0) { //判断方法是不是public
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 1) {//方法参数是不是一个
Subscribe subscribeAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Subscribe.class);
if (subscribeAnnotation != null) {//是否有注解
Class eventType = parameterTypes[0];
if (findState.checkAdd(method, eventType)) { //检查方法和参数(事件)类型是否合法
ThreadMode threadMode = subscribeAnnotation.threadMode();
findState.subscriberMethods.add(new SubscriberMethod(method, eventType, threadMode,
subscribeAnnotation.priority(), subscribeAnnotation.sticky())); //都满足将方法加入findState中
}
}
} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
throw new EventBusException("@Subscribe method " + methodName +
"must have exactly 1 parameter but has " + parameterTypes.length);
}
} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
throw new EventBusException(methodName +
" is a illegal @Subscribe method: must be public, non-static, and non-abstract");
}
}
}通过apt的到方法
private List findUsingInfo(Class subscriberClass) {
FindState findState = prepareFindState();
findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass);
while (findState.clazz != null) {
findState.subscriberInfo = getSubscriberInfo(findState);//通过apt获取方法
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null) {
SubscriberMethod[] array = findState.subscriberInfo.getSubscriberMethods();
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : array) {
if (findState.checkAdd(subscriberMethod.method, subscriberMethod.eventType)) {
findState.subscriberMethods.add(subscriberMethod);
}
}
} else {
findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState);//如果没有获取到再通过反射获取方法
}
findState.moveToSuperclass();
}
return getMethodsAndRelease(findState);
} private SubscriberInfo getSubscriberInfo(FindState findState) {
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null && findState.subscriberInfo.getSuperSubscriberInfo() != null) {
SubscriberInfo superclassInfo = findState.subscriberInfo.getSuperSubscriberInfo();
if (findState.clazz == superclassInfo.getSubscriberClass()) {//先判断缓存中是否存在
return superclassInfo;
}
}
if (subscriberInfoIndexes != null) {//subscriberInfoIndexes 是通过apt处理器自动生成的文件
for (SubscriberInfoIndex index : subscriberInfoIndexes) {
SubscriberInfo info = index.getSubscriberInfo(findState.clazz);
if (info != null) {
return info;
}
}
}
return null;
}订阅
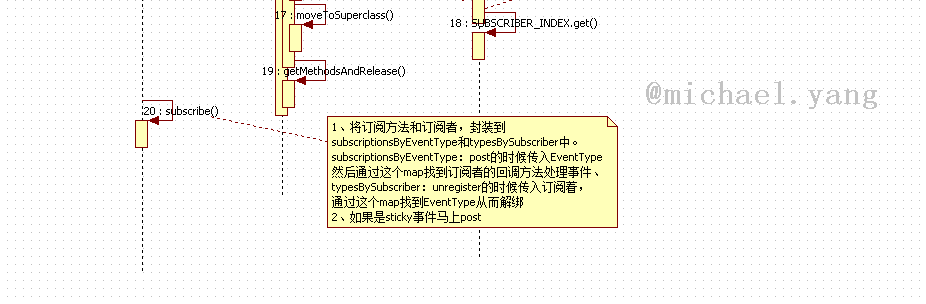
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {
Class eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;
Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
CopyOnWriteArrayList subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions == null) {
subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);//获取subscriptionsByEventType map对象,用于post的时候通过eventtype获取订阅者的信息
} else {
if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event "
+ eventType);
}
}
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {
subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);
break;
}
}
List> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedEvents == null) {
subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();
typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);//获取typesBySubscriber map对象,unregister时会用到
}
subscribedEvents.add(eventType);
if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {//如果是sticky事件,马上post
if (eventInheritance) {
// Existing sticky events of all subclasses of eventType have to be considered.
// Note: Iterating over all events may be inefficient with lots of sticky events,
// thus data structure should be changed to allow a more efficient lookup
// (e.g. an additional map storing sub classes of super classes: Class -> List).
Set, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry, Object> entry : entries) {
Class candidateEventType = entry.getKey();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {
Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
} else {
Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
} 发布事件
//通过threadMode来确认使用哪个线程执行订阅者的订阅函数
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) {
switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {
case POSTING:
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
break;
case MAIN:
if (isMainThread) {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
} else {
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
}
break;
case BACKGROUND:
if (isMainThread) {
backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
} else {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
case ASYNC:
asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);
}
}其中mainThreadPoster继承自Handler、backgroundPoster和asyncPoster都继承自Runnable