gmapping源码分析以及收获
大神的分析博客:http://blog.csdn.net/roadseek_zw/article/details/53316177
功能:创建线程
boost::thread举例说明:
#include 功能:互斥体
boost::mutex任何写过多线程的人都知道,避免不同线程同时访问共享区域的重要性。如果一个线程想要更改他共享区域中的某个数据,这时,另一个线程正在读取这个数据。在这个时候就要用到互斥体。一个互斥体只允许一个线程访问共享区。当另一个线程想要访问共享区的时候,首先要做的就是锁住(lock)
参考博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/chengmin/archive/2011/12/29/2306416.html
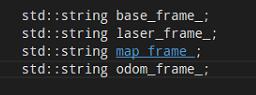
从地图到世界坐标
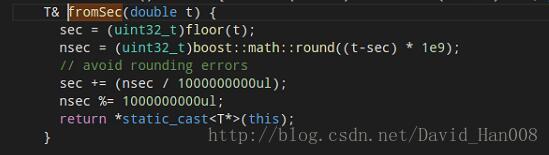
map_to_odom_(tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY( 0, 0, 0 ), tf::Point(0, 0, 0 )))从RPY中创造四元数
laser_count_(0),激光雷达计数
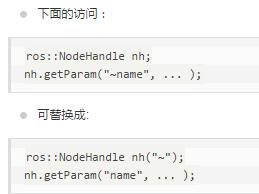
private_nh_("~"),私有的句柄
scan_filter_sub_(NULL),激光雷达订阅
scan_filter_(NULL),激光雷达滤波器
transform_thread_(NULL),变换的线程, unsigned long int seed_;这是一个长整型目前是用roboware进行跳转,真的很easy。

这里构造函数三次重载。
在定义的时候,用一个*,然后将来实例化的就是&
![]()
gmapping这个命名空间是在basic GridFastSLAM算法的基础上,每个粒子都有其自己的地图和机器人的位姿。
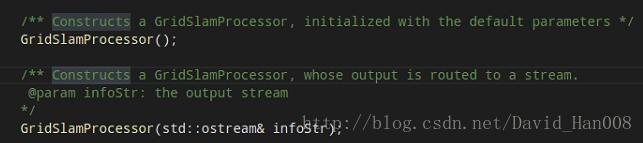
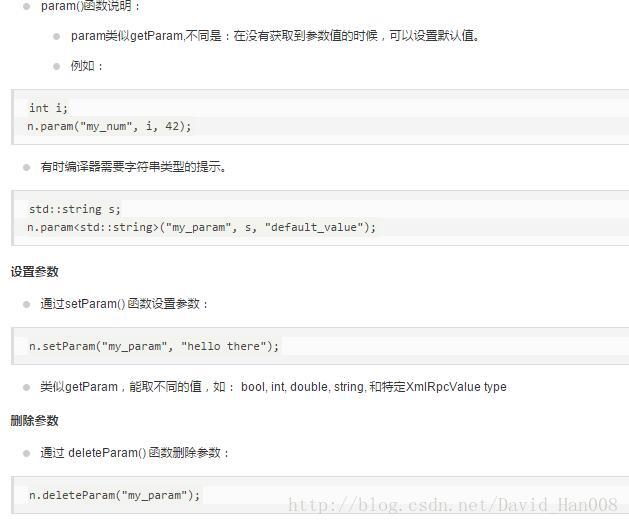
第一个是初始化默认参数
第二个是默认的输出流 infoStr是输出流
所以,这里的 是为了初始化参数
是为了初始化参数
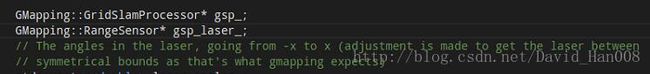
然后跳转到这里,是传递的参数
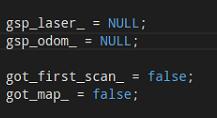
让其里程计的数据为NULL,空指针
![]()
bool类型的采用false
然后进行实时的传值

throttle_scans表示处理的容忍度吧,最小的容忍度。如果设置很高,就会漏掉更多的点
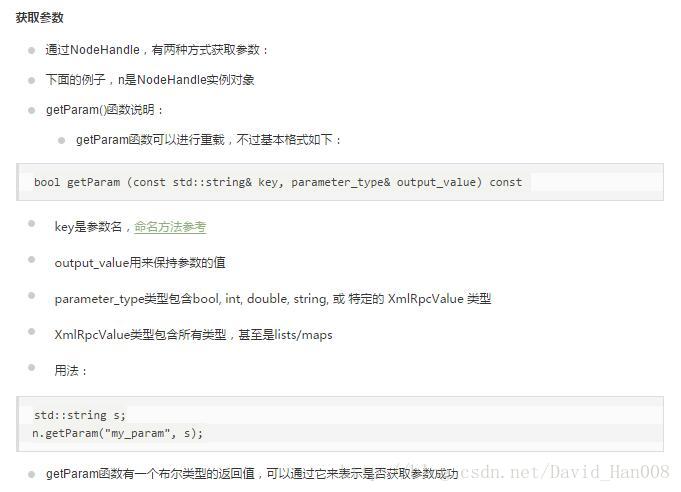
设置参数的名字,已经数字,和string类型,都可以,然后对这个参数进行设置
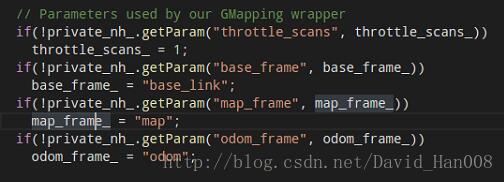
这些参数都是关于gmapping的封装wrapper
gmapping自己的参数
minmumScore最小化评分,来评价scan的数据是不是好,也就是对他的置信度,在小范围饿激光雷达例如5米的情况下
srr里程计的平移的/平移
srt里程计的平移/旋转
stt里程计的旋转/旋转
str里程计的旋转/平移
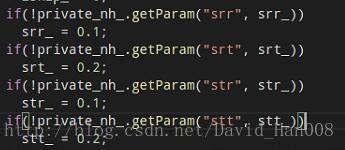
NULL是宏 false是关键字
lskip 每束激光雷达跳过的激光束
ogain为了重新采样而评估的增益
lstep 平移优化的步长
astep 旋转优化的步长
kernelSize寻找关联的
sigma用于暴力匹配
lsigma 每束激光雷达扫描的可能性
void startLiveSlam:
entropy熵(平均值)
![]()
这三个参数依次是 话题的名称,队列的长度,和是否发布消息
这里是发布的消息

订阅的话题
![]()
最后开始一个线程
![]()
开始一个回应startReplay
输入的的 bag的的名字 和 激光雷达的topic
打开一个新的

如果不能够处理的话,5条消息。
std::queue是容器适配器用来适配FIFO
std::pair,float>将两个数据融合成一个数据。 ![]()
这里是实例化了一个对象,下面肯定会有s_queue.first 和 s_queue.second
![]() 这里是一个智能指针
这里是一个智能指针
foreach用来遍历
在32位系统中的size_t是4个字节,size_t是8个字节 size_t一般用来表示计数,比如有多少东西拷贝
这是使用了一个定时器
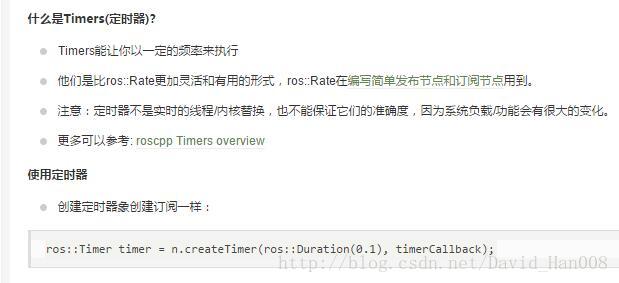
示例程序:
#include "ros/ros.h"
d callback1(const ros::TimerEvent&)
{
ROS_INFO("Callback 1 triggered");
}
void callback2(const ros::TimerEvent&)
{
ROS_INFO("Callback 2 triggered");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "talker");
ros::NodeHandle n;
ros::Timer timer1 = n.createTimer(ros::Duration(0.1), callback1);
ros::Timer timer2 = n.createTimer(ros::Duration(1.0), callback2);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}TimerEvent结构体提供当前定时器的时间信息

callbacks回调函数
单线程spinning
ros::spin();在这个程序中,用户的回调函数在ros::spin()中被调用,ros::spin()在节点关闭或者在ros::shutdown();或者按下ctrl+c才会返回。
定期运行ros::spinonce();
ros::Rate r(19);//19Hz的发布频率
while(ros::ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();//会调用所有的回调函数
r.sleep();
}ros当中的多线程
方式1:这是一种阻塞式的
ros::MultiThreadedSpinner spinner(4);//使用了4个线程
spinner.spin();//spin()直到节点被关闭方式2:这是一个非阻塞式的
ros::AsyncSpinner spinner(4);
spinner.start();
ros::waitForShutdown();callbackqueue回调队列
#includeLogging(日志)
ROS_DEBUG(...)
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM(args)举例
#include cond表示 condition(条件)
当条件为真,就会输出日志信息
include
ROS_DEBUG_COND(x < 0, "Uh oh, x = %d, this is bad", x); ros当中转换时间和持续时间
double secs =ros::Time::now().toSec();
ros::Duration d(0.5);
secs = d.toSec();指定程序的休眠时间
ros::Duration(0.5).sleep(); // sleep for half a secondros的发布和订阅
ros::Publisher pub = nh.advertise("topic_name", 5);
std_msgs::String str;
str.data = "hello world";
pub.publish(str); 后面那个参数表示队列的长度。

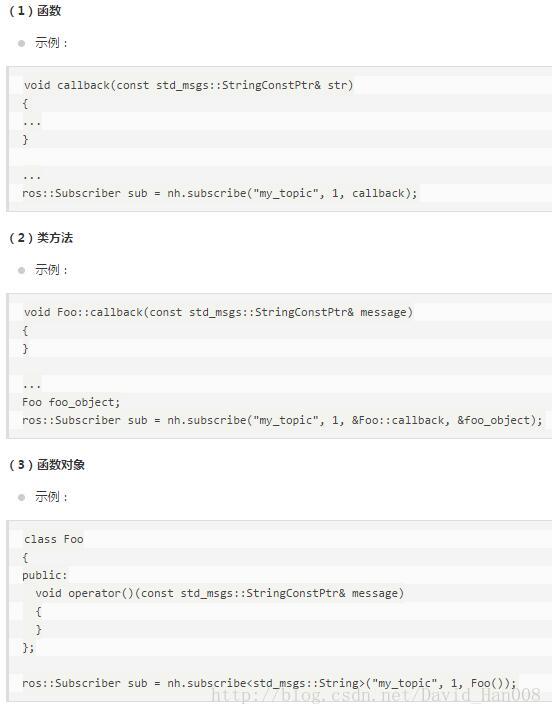
tf的数据结构:
tf::Quaternion tf::Vector3 tf::Point tf::Pose tf::Transform
tf::Stamped模板,就是一个模板类 附带元素 frame_id_和stamp_
tf::StampedTransform 是tf::Transforms的特例,它要求frame_id、stamp、child_frame_id
函数:tf::Quaternion createIdentityQuaternion()
作用:返回四元数句柄
函数:tf::Quaternion createQuaternionFromRPY(double roll,double pitch,double yaw)
作用:返回从固定轴的Roll, Pitch and Yaw(滚动,俯仰和偏转)构造的tf::Quaternion四元数
函数:geometry_msgs::Quaternion createQuaternionMsgFromRollPitchYaw(double roll,double pitch,double yaw)
作用:返回从固定轴的Roll, Pitch and Yaw(滚动,俯仰和偏转)构造geometry_msgs::Quaternion四元数
tf::TransformBroadcaster();发送变换。
发送变换通过调用sendTransform()函数实现
canTransform()函数 返回bool ,判断能否实现变换。不会抛出异常,如果出错,会返回error_msg的内容。
waitForTransform()函数 返回bool值,评估变换是否有效
异常类:tf::ConnectivityException
作用:如果由于两个坐标系ID不在同一个连接的树中而无法完成请求,则抛出。
异常类:tf::ExtrapolationException
作用:如果请求的坐标系id之间存在连接,但一个或多个变换已过期,则抛出。
异常类:tf::InvalidArgument
作用:如果参数无效则抛出。 最常见的情况是非规范化的四元数。
异常类:tf::LookupException
作用:如果引用了未发布的坐标系ID,则抛出。
#include 在C语言当中 atan2(double x,double y)返回的原点到(x,y)的方位角,也就是与x轴的夹角。
#include ("spawn");
turtlesim::Spawn srv;
add_turtle.call(srv);
ros::Publisher turtle_vel =
node.advertise("turtle2/cmd_vel", 10);
tf::TransformListener listener;
ros::Rate rate(10.0);
while (node.ok()){
tf::StampedTransform transform;
try{
listener.lookupTransform("/turtle2", "/turtle1",
ros::Time(0), transform);
}
catch (tf::TransformException &ex) {
ROS_ERROR("%s",ex.what());
ros::Duration(1.0).sleep();
continue;
}
geometry_msgs::Twist vel_msg;
vel_msg.angular.z = 4.0 * atan2(transform.getOrigin().y(),
transform.getOrigin().x());
vel_msg.linear.x = 0.5 * sqrt(pow(transform.getOrigin().x(), 2) +
pow(transform.getOrigin().y(), 2));
turtle_vel.publish(vel_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}; 增加一个carrot的坐标系
#include tf::TransformBroadcaster br;
tf::Transform transform;
transform.setOrigin( tf::Vector3(0.0, 2.0, 0.0) );
transform.setRotation( tf::Quaternion(0, 0, 0, 1) );
br.sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(transform, ros::Time::now(), "turtle1", "carrot1")同样这各也是一个框架希望自己在使用的时候能够记住
ros::Rate rate(10.0);
while(ros::ok())
{
rate.sleep();
}ros::Time(0); 说明察觉到这个时间之后立即行动。迟疑的时间是0秒。同样的意思
ros::Time::now();ros::Duration(3.0);持续时间是3秒ros 里的action; service是同步的通信机制。ros还有另外的一些通信机制action
相关参考链接http://www.cnblogs.com/cv-pr/p/5800270.html
actionlib里面很多内容暂时跳过去,因为在gmapping里面看到的比较少。
pluginlib插件的介绍
在package.xml文件中包含export项
这里写学的不是很好
nodelet的用途和使用
nodelet包用来设计在算法之间的具有零拷贝传输相同的进程中运行多个算法
基本的用法:
nodelet usage:
nodelet load pkg/Type manager - launch一个nodelet的管理器
nodelet standalone pkg/Type - 导入一个单个节点 node
nodelet unload name manager - 从manager导入输出一个单个的节点
nodelet manager - 开始manager的节点同时我们可以开发属于自己的基控制器然后把这个事情做好。
我觉得这个nodelet的地方,到时候需要看看一下
然后这个下面还有一些实现路径规划功能的包。
言归正传,我们接着看gmapping的源码
找到一个不错的看源码的工具scientific toolworks understand,然后安装连接啥的,大家自行百度,刚刚没存档,就给没了,哈哈。
其实我觉着就是一个很好的图像化显示的东西,能够让你很直观的看到
然你旋转用ctrol flow的时候,一定要注意这点着函数然后走,我尝试过,这个软件不能看ros的源码,只能在几个头文件当中相互跳转,但是实际用的时候,还是可以用roboware跳转来看ros的源码
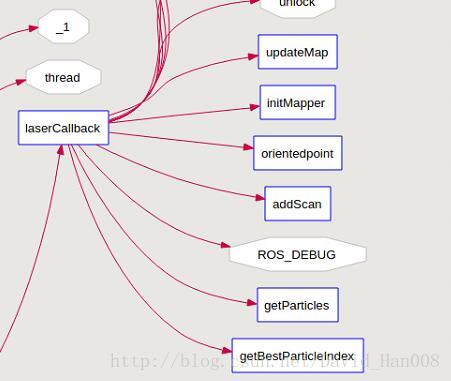
就是先从这个laserCallback函数,然后中间嵌套了
void
SlamGMapping::laserCallback(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan::ConstPtr& scan)
{
laser_count_++;
if ((laser_count_ % throttle_scans_) != 0)
return;
static ros::Time last_map_update(0,0);
// We can't initialize the mapper until we've got the first scan
if(!got_first_scan_)
{
if(!initMapper(*scan))
return;
got_first_scan_ = true;
}
GMapping::OrientedPoint odom_pose;
if(addScan(*scan, odom_pose))
{
ROS_DEBUG("scan processed");
GMapping::OrientedPoint mpose = gsp_->getParticles()[gsp_->getBestParticleIndex()].pose;
ROS_DEBUG("new best pose: %.3f %.3f %.3f", mpose.x, mpose.y, mpose.theta);
ROS_DEBUG("odom pose: %.3f %.3f %.3f", odom_pose.x, odom_pose.y, odom_pose.theta);
ROS_DEBUG("correction: %.3f %.3f %.3f", mpose.x - odom_pose.x, mpose.y - odom_pose.y, mpose.theta - odom_pose.theta);
tf::Transform laser_to_map = tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0, 0, mpose.theta), tf::Vector3(mpose.x, mpose.y, 0.0)).inverse();
tf::Transform odom_to_laser = tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0, 0, odom_pose.theta), tf::Vector3(odom_pose.x, odom_pose.y, 0.0));
map_to_odom_mutex_.lock();
map_to_odom_ = (odom_to_laser * laser_to_map).inverse();
map_to_odom_mutex_.unlock();
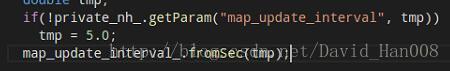
if(!got_map_ || (scan->header.stamp - last_map_update) > map_update_interval_)
{
updateMap(*scan);
last_map_update = scan->header.stamp;
ROS_DEBUG("Updated the map");
}
} else
ROS_DEBUG("cannot process scan");
}bool
SlamGMapping::initMapper(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& scan)
{
laser_frame_ = scan.header.frame_id;
tf::Stamped ident; 设置单位矩阵
tf::Stamped laser_pose; 这是他的激光雷达的位姿
ident.setIdentity(); 设置单位矩阵
ident.frame_id_ = laser_frame_; 这是frameid
ident.stamp_ = scan.header.stamp; 这是ID
try 这里用来抛出一个异常,其实就是查看着两个TF之间的关系
{
tf_.transformPose(base_frame_, ident, laser_pose);两个TF之间的关系
}
catch(tf::TransformException e)这里输出一个e
{
ROS_WARN("Failed to compute laser pose, aborting initialization (%s)",
e.what());
return false;
}
创造一个点在激光雷达laser_pose是他的位姿。然后就是在原点
// create a point 1m above the laser position and transform it into the laser-frame
tf::Vector3 v; 其实激光雷达的位姿,然后
v.setValue(0, 0, 1 + laser_pose.getOrigin().z());
tf::Stamped up(v, scan.header.stamp,
base_frame_);
try
{
tf_.transformPoint(laser_frame_, up, up);
ROS_DEBUG("Z-Axis in sensor frame: %.3f", up.z());
}
catch(tf::TransformException& e)
{
ROS_WARN("Unable to determine orientation of laser: %s", 这里就是抛出一个异常
e.what());
return false;
}
// gmapping doesnt take roll or pitch into account. So check for correct sensor alignment.
if (fabs(fabs(up.z()) - 1) > 0.001)
{
ROS_WARN("Laser has to be mounted planar! Z-coordinate has to be 1 or -1, but gave: %.5f",
up.z());
return false;
}
gsp_laser_beam_count_ = scan.ranges.size();对gmapping 进行计算数值
double angle_center = (scan.angle_min + scan.angle_max)/2;得到中间的角度值。
if (up.z() > 0)
{
do_reverse_range_ = scan.angle_min > scan.angle_max;如果最小的值比最大的值大的话,那么返回一个bool值
centered_laser_pose_ = tf::Stamped(tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0,0,angle_center),
tf::Vector3(0,0,0)), ros::Time::now(), laser_frame_);得到中心值,激光雷达啊的TF。然后这个里面实现的过就是通欧拉角转换输出的四元数,然后设置3维的限量,最后输出的laser_frame,执行时间的话是立即生效。
ROS_INFO("Laser is mounted upwards.");
}
else
{
do_reverse_range_ = scan.angle_min < scan.angle_max;
centered_laser_pose_ = tf::Stamped(tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(M_PI,0,-angle_center),
tf::Vector3(0,0,0)), ros::Time::now(), laser_frame_);
ROS_INFO("Laser is mounted upside down.");
}
// Compute the angles of the laser from -x to x, basically symmetric and in increasing order
laser_angles_.resize(scan.ranges.size());
// Make sure angles are started so that they are centered
double theta = - std::fabs(scan.angle_min - scan.angle_max)/2;
for(unsigned int i=0; istd::fabs(scan.angle_increment);
}
ROS_DEBUG("Laser angles in laser-frame: min: %.3f max: %.3f inc: %.3f", scan.angle_min, scan.angle_max,
scan.angle_increment);
ROS_DEBUG("Laser angles in top-down centered laser-frame: min: %.3f max: %.3f inc: %.3f", laser_angles_.front(),
laser_angles_.back(), std::fabs(scan.angle_increment));
GMapping::OrientedPoint gmap_pose(0, 0, 0);
// setting maxRange and maxUrange here so we can set a reasonable default
ros::NodeHandle private_nh_("~");
if(!private_nh_.getParam("maxRange", maxRange_))
maxRange_ = scan.range_max - 0.01;
if(!private_nh_.getParam("maxUrange", maxUrange_))
maxUrange_ = maxRange_;
// The laser must be called "FLASER".
// We pass in the absolute value of the computed angle increment, on the
// assumption that GMapping requires a positive angle increment. If the
// actual increment is negative, we'll swap the order of ranges before
// feeding each scan to GMapping.
gsp_laser_ = new GMapping::RangeSensor("FLASER",
gsp_laser_beam_count_,
fabs(scan.angle_increment),
gmap_pose,
0.0,
maxRange_);
ROS_ASSERT(gsp_laser_);
GMapping::SensorMap smap;
smap.insert(make_pair(gsp_laser_->getName(), gsp_laser_));
gsp_->setSensorMap(smap);
gsp_odom_ = new GMapping::OdometrySensor(odom_frame_);
ROS_ASSERT(gsp_odom_);
/// @todo Expose setting an initial pose
GMapping::OrientedPoint initialPose;
if(!getOdomPose(initialPose, scan.header.stamp))
{
ROS_WARN("Unable to determine inital pose of laser! Starting point will be set to zero.");
initialPose = GMapping::OrientedPoint(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
gsp_->setMatchingParameters(maxUrange_, maxRange_, sigma_,
kernelSize_, lstep_, astep_, iterations_,
lsigma_, ogain_, lskip_);
gsp_->setMotionModelParameters(srr_, srt_, str_, stt_);
gsp_->setUpdateDistances(linearUpdate_, angularUpdate_, resampleThreshold_);
gsp_->setUpdatePeriod(temporalUpdate_);
gsp_->setgenerateMap(false);
gsp_->GridSlamProcessor::init(particles_, xmin_, ymin_, xmax_, ymax_,
delta_, initialPose);
gsp_->setllsamplerange(llsamplerange_);
gsp_->setllsamplestep(llsamplestep_);
/// @todo Check these calls; in the gmapping gui, they use
/// llsamplestep and llsamplerange intead of lasamplestep and
/// lasamplerange. It was probably a typo, but who knows.
gsp_->setlasamplerange(lasamplerange_);
gsp_->setlasamplestep(lasamplestep_);
gsp_->setminimumScore(minimum_score_);
// Call the sampling function once to set the seed.
GMapping::sampleGaussian(1,seed_);
ROS_INFO("Initialization complete");
return true;
} /tf::Stamped 对上述数据类型做模板化(除了tf::Transform),并附带元素frame_id_和stamp_ 。
identity matrix 单位矩阵,
我们定义tf::Transform transform 我们定义设置数据类型用来存放转换信息的(简单来说 平移和旋转的向量)
transform.setOrigin( tf::Vector3(msg->x, msg->y, 0.0) );我懂了,这个地方是设置激光雷达饿起始位置,这个还是不错的
参考博客:
http://blog.csdn.net/start_from_scratch/article/details/50762293
当然你也可以定义旋转
tf::Quaternion q;
q.setRPY(0, 0, msg->theta);
transform.setRotation(q);然后在将这个tf广播出去
br.sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(transform, ros::Time::now(), "world", turtle_name));同样定义一个监听器
tf::TransformListener listener定义存放一个关系变量
tf::StampedTransform transform; listener.lookupTransform("/turtle2", "/turtle1",
ros::Time(0), transform);然后通过这个函数lookupTransform用来监听两个TF之间的关系。
设置激光的角度,

通过resize这种方式,传递参数
将所有的激光累的数据进行累加,
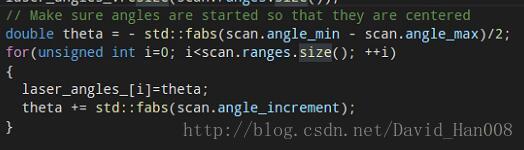
这里就是实现的将所有的激光累的数据进行的累计的叠加。
然后这就是输出激光雷达的一些增量。
设置最大的R(也就是半径的范围)以及设置最大的U的范围
这个激光雷达的名字必须被叫做FLASER,我们通过一些绝对值来计算增量。gmapping需要计算一些正向的角度增量。如果这个角度增量式一个复制,我们需要交换角度的顺序才能将激光雷达的进行填充。
这里需要实例化一个对象
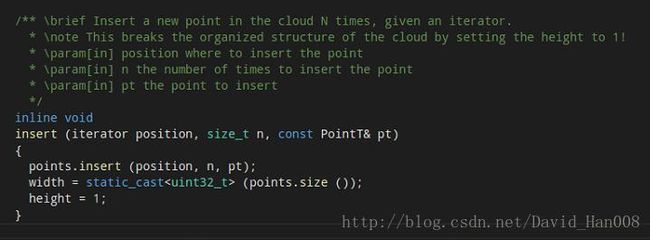
position在哪里插入点。插入点的数量n。pt 插入的点。
GMapping::SensorMap smap;
smap.insert(make_pair(gsp_laser_->getName(), gsp_laser_));//insert
gsp_->setSensorMap(smap);//将这个地图得到地图make_pai
make_pair(gsp_laser_->getName(), gsp_laser_);//返回的值是一个值,就是将他们的数据结构。
然后在通过,insert将两个数据结合起来。
gsp_->setSensorMap(smap);然后
void GridSlamProcessor::setSensorMap(const SensorMap& smap){
SensorMap::const_iterator laser_it=smap.find(std::string("FLASER"));
if (laser_it==smap.end()){
cerr << "Attempting to load the new carmen log format" << endl;
laser_it=smap.find(std::string("ROBOTLASER1"));
assert(laser_it!=smap.end());
}
const RangeSensor* rangeSensor=dynamic_cast<const RangeSensor*>((laser_it->second));
assert(rangeSensor && rangeSensor->beams().size());
m_beams=static_cast<unsigned int>(rangeSensor->beams().size());
double* angles=new double[rangeSensor->beams().size()];
for (unsigned int i=0; ibeams()[i].pose.theta;
}
m_matcher.setLaserParameters(m_beams, angles, rangeSensor->getPose());
delete [] angles;
} .find(std::string("FLASER")全局寻找FLASER标志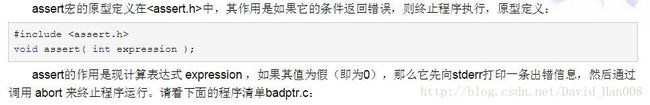
然后将角度进行赋值。,对着将这里匹配到的地图数据,发布到激光雷达的参数当中。

他的输入就是一个map的数据类型。
然后实例化一个里程计的类型。然后里程计信息进行赋值。
下面我们打算设置初始化的位姿。
首先初始化一个位姿。,
这个bool类型,然后在bool类型当中,进行初始化很数据类型
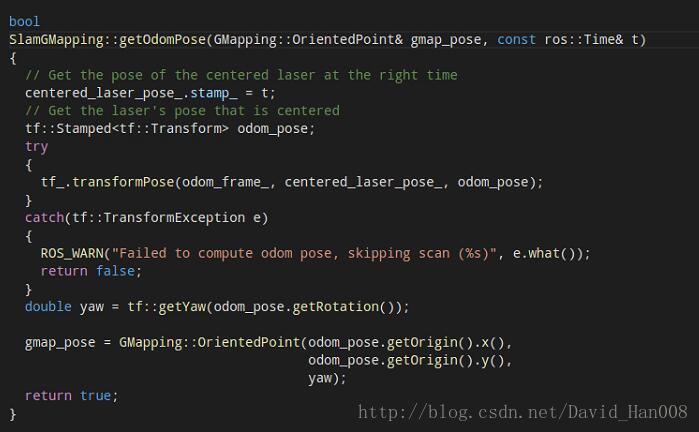
stamp表示的时间戳吧。centered_laser_pose_.stamp_ = t;得到激光雷达的位姿。佳作odom_pose
tf_.transformPose(odom_frame_, centered_laser_pose_, odom_pose);初始化一些他们之间的位姿关系。得到yaw ,然后将这个值,给了传入的参数的数值。
gmap_pose = GMapping::OrientedPoint(odom_pose.getOrigin().x(),
odom_pose.getOrigin().y(),
yaw);然后做出了一些判断,就是判断,其实就是判断有没有得到位姿。
然后进行匹配一些参数

第一步就是匹配激光雷达的参数,然后设置运动模型的参数,第三步,更新距离的参数,第四步,设置更新的时间,第五步 设置更新的地图。 第六步,进行初始化粒子的大小,第七步,设置采样的范围。第八步,设置激光雷达的步长 第九步,设置最小化得分。
第一步:
 设置激光雷达的参数。
设置激光雷达的参数。
第二步:

设置运动模型,本质上还是传递参数。
第三步:
同样将传递的参数进行赋值。
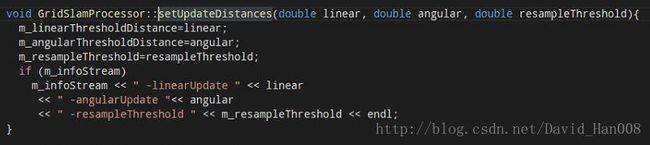
第四步:同样传递参数。
第五步:设置丢他
回到lasercallback线程当中,然后将scan和odom_pose结合起来。一般bool类型,就是用来if语句来进行判断。首先我得到getOdompose函数,这是一种bool类型。将num_ranges理逻辑。就是这两个for类型。然后读取reading函数,将ranges_double,然后设置位姿 其实就是一个传参。将reading这个数值,给的数据传递给processscan
这里返回的是一个bool类型。这个bool类型。bool GridSlamProcessor::processScan(const RangeReading & reading, int adaptParticles)
从reading当中,获得位姿,同时计算里程计。首先我们初始化,然后获得位姿。将上一个帧的位姿进行传参。使用运动模型来更新例子。初始化一个参数,画出运动模型,
OrientedPoint
MotionModel::drawFromMotion(const OrientedPoint& p, const OrientedPoint& pnew, const OrientedPoint& pold) const{
double sxy=0.3*srr;
OrientedPoint delta=absoluteDifference(pnew, pold);
OrientedPoint noisypoint(delta);
noisypoint.x+=sampleGaussian(srr*fabs(delta.x)+str*fabs(delta.theta)+sxy*fabs(delta.y));
noisypoint.y+=sampleGaussian(srr*fabs(delta.y)+str*fabs(delta.theta)+sxy*fabs(delta.x));
noisypoint.theta+=sampleGaussian(stt*fabs(delta.theta)+srt*sqrt(delta.x*delta.x+delta.y*delta.y));
noisypoint.theta=fmod(noisypoint.theta, 2*M_PI);
if (noisypoint.theta>M_PI)
noisypoint.theta-=2*M_PI;
return absoluteSum(p,noisypoint);
}就是当前时刻的位姿,前一个时刻的位姿,
计算新旧帧的绝对误差
absoluteDifference(pnew, pold);从这里看的话,我觉得是进行添加了一下高斯的扰动模型
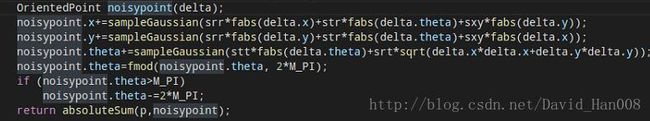
最后输出值,我估计是P
pose=m_motionModel.drawFromMotion(it->pose, relPose, m_odoPose);将这些的更新的状态给了pose
然后更新输出的文件,判断是不是打开了这个文件,然后设置了了一下精度。将当前的位置状态的信息,进行了了输出。然后将一些粒子的更新进行了输出。以及读取的时间。
最后生成一个回调函数,这个函数是空的。
接下来计算机器人的平移和旋转。
计算机器人的旋转和平移
计算角度的角度的变化 通过使用move将前一时刻机器人的位姿和当前时刻机器人的位姿进行做差。然后就是知道move.theta=atan2(sin(move.theta), cos(move.theta));就是线速度的变换和加速度的变换。
随后进行一次将来原来的pose信息给了当前的位置信息。进行了一次迭代。处理了一次迭代。更新当前帧
其实本质上就是次scan-matcher,然后就是一写赋值。如果计数是大于0的话,然后就进行的扫描的匹配。
使用这个scanMatch来匹配每一帧的粒子。
inline void GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch(const double* plainReading){
// 从每一帧scan进行采样
double sumScore=0;
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
OrientedPoint corrected;
double score, l, s;
score=m_matcher.optimize(corrected, it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
// it->pose=corrected;
if (score>m_minimumScore){
it->pose=corrected;
} else {
if (m_infoStream){
m_infoStream << "Scan Matching Failed, using odometry. Likelihood=" << l <<std::endl;
m_infoStream << "lp:" << m_lastPartPose.x << " " << m_lastPartPose.y << " "<< m_lastPartPose.theta <<std::endl;
m_infoStream << "op:" << m_odoPose.x << " " << m_odoPose.y << " "<< m_odoPose.theta <<std::endl;
}
}
m_matcher.likelihoodAndScore(s, l, it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
sumScore+=score;
it->weight+=l;
it->weightSum+=l;
//set up the selective copy of the active area
//by detaching the areas that will be updated
m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();
m_matcher.computeActiveArea(it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
}
if (m_infoStream)
m_infoStream << "Average Scan Matching Score=" << sumScore/m_particles.size() << std::endl;
}
inline void GridSlamProcessor::normalize(){
//normalize the log m_weights
double gain=1./(m_obsSigmaGain*m_particles.size());
double lmax= -std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
lmax=it->weight>lmax?it->weight:lmax;
}
//cout << "!!!!!!!!!!! maxwaight= "<< lmax << endl;
m_weights.clear();
double wcum=0;
m_neff=0;
for (std::vector首先实例化得了一个纠错的;然后for()循环了一下粒子,将所有的粒子,进行了一次遍历。在遍历的第一步是对这里的优化器进行优化,
double ScanMatcher::optimize(OrientedPoint& pnew, const ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& init, const double* readings) const{
double bestScore=-1;初始化一个对家得分
OrientedPoint currentPose=init;将这个输出话的位置传入
double currentScore=score(map, currentPose, readings); 将现在东西进行得分
double adelta=m_optAngularDelta, ldelta=m_optLinearDelta; 将当前的数值进行赋值
unsigned int refinement=0; 设置精度
enum Move{Front, Back, Left, Right, TurnLeft, TurnRight, Done}; 定义一个枚举类型
int c_iterations=0;定义了迭代
do{
if (bestScore>=currentScore){
refinement++;如果最佳的得分大院当前的得分,那么将就这个精度进行++并且将 将两个参数,进行减半
adelta*=.5;
ldelta*=.5;
}
bestScore=currentScore;然后将当前的得分赋值贵最佳的得分。
// cout <<"score="<< currentScore << " refinement=" << refinement; 我们输出当前的得分和以及提纯 的精度。
// cout << "pose=" << currentPose.x << " " << currentPose.y << " " << currentPose.theta << endl;
OrientedPoint bestLocalPose=currentPose; 将当前的位置为信息,给了最佳的位置信息。
OrientedPoint localPose=currentPose; 将当前的的位置赋值给局部的位置。
Move move=Front;
do {
localPose=currentPose;
switch(move){
case Front:
localPose.x+=ldelta;将当前的位置,
move=Back;
break;
case Back:
localPose.x-=ldelta;
move=Left;
break;
case Left:
localPose.y-=ldelta;
move=Right;
break;
case Right:
localPose.y+=ldelta;
move=TurnLeft;
break;
case TurnLeft:
localPose.theta+=adelta;
move=TurnRight;
break;
case TurnRight:
localPose.theta-=adelta;
move=Done;
break;
default:;
}
double localScore=score(map, localPose, readings);局部
if (localScore>currentScore){
currentScore=localScore;
bestLocalPose=localPose;
}
c_iterations++;
} while(move!=Done);
currentPose=bestLocalPose;
//cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "currentScore=" << currentScore<< endl;
//here we look for the best move;
}while (currentScore>bestScore || refinement//cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "bestScore=" << bestScore<< endl;
//cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "iterations=" << c_iterations<< endl;
pnew=currentPose;
return bestScore;
} 然后我们看看,如何计算这里的得分的。
inline double ScanMatcher::score(const ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& p, const double* readings) const{
double s=0; 我要输入的就map 当前的位置点, 和reading
const double * angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip;当前的角度=激光雷达的角度+初始化光束
OrientedPoint lp=p;将位置信息进行赋值
lp.x+=cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x-sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; 计算激光雷达的位置x,y,z
lp.y+=sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x+cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y;
lp.theta+=m_laserPose.theta;
unsigned int skip=0;设置一个阈值
double freeDelta=map.getDelta()*m_freeCellRatio; 设置一个freedata从地图当中得到数据,乘以这个数据的比例。
for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; rm_likelihoodSkip?0:skip; 其实就是进行了一些判断
if (skip||*r>m_usableRange||*r==0.0) continue;,然后对这割方面进行了判断。
Point phit=lp;初始化
phit.x+=*r*cos(lp.theta+*angle); *r表示的是个数字,
phit.y+=*r*sin(lp.theta+*angle);
IntPoint iphit=map.world2map(phit);
Point pfree=lp;
pfree.x+=(*r-map.getDelta()*freeDelta)*cos(lp.theta+*angle);
pfree.y+=(*r-map.getDelta()*freeDelta)*sin(lp.theta+*angle);
pfree=pfree-phit;
IntPoint ipfree=map.world2map(pfree);实例化
bool found=false;
Point bestMu(0.,0.)
for (int xx=-m_kernelSize; xx<=m_kernelSize; xx++)
for (int yy=-m_kernelSize; yy<=m_kernelSize; yy++){对所有的进行赋值
IntPoint pr=iphit+IntPoint(xx,yy);
IntPoint pf=pr+ipfree;
//AccessibilityState s=map.storage().cellState(pr);
//if (s&Inside && s&Allocated){
const PointAccumulator& cell=map.cell(pr);
const PointAccumulator& fcell=map.cell(pf);
if (((double)cell )> m_fullnessThreshold && ((double)fcell )if (!found){
bestMu=mu;
found=true;
}else
bestMu=(mu*mu)<(bestMu*bestMu)?mu:bestMu;
}
//}
}
if (found)
s+=exp(-1./m_gaussianSigma*bestMu*bestMu);然后就是一堆乘法,鬼才知道是怎么乘的,
}
return s;
} 随后进行优化,设置标志位和设置精度,然后得到当前的位姿。将当前的角度x和y的数值和当前的时刻进行输出。随后输出粒子的数量
![]() 然后就是设置位置的更新时刻,然后对这个地方进行更新,然后对数据进行重新采样,
然后就是设置位置的更新时刻,然后对这个地方进行更新,然后对数据进行重新采样,resample(plainReading, adaptParticles, reading_copy); 然后就是,设置更新于都,更新粒子数

首先计算累计的权重,计算在重采样粒子的权重,计算间隔,计算初始化目标的权重 计算重采样目标的索引 返回的是一个容器,容器的数据类型particle
然后对当中的每个粒子数,进行无效的激活,那么就放回的false
计算激活的面积区域
void ScanMatcher::computeActiveArea(ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& p, const double* readings){
if (m_activeAreaComputed)
return;
OrientedPoint lp=p;
lp.x+=cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x-sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y;
lp.y+=sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x+cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y;
lp.theta+=m_laserPose.theta;
IntPoint p0=map.world2map(lp);
Point min(map.map2world(0,0));
Point max(map.map2world(map.getMapSizeX()-1,map.getMapSizeY()-1));
if (lp.x.x) min.x=lp.x;
if (lp.y.y) min.y=lp.y;
if (lp.x>max.x) max.x=lp.x;
if (lp.y>max.y) max.y=lp.y;
/*determine the size of the area*/ 计算这个地图当中空白区域的面积。
const double * angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip; 其实想这样东西就是为了能够平移位置
for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r
if (*r>m_laserMaxRange||*r==0.0||isnan(*r)) continue;
double d=*r>m_usableRange?m_usableRange:*r;
Point phit=lp;
phit.x+=d*cos(lp.theta+*angle);
phit.y+=d*sin(lp.theta+*angle);
if (phit.x.x ) min.x=phit.x; 进行一系列的赋值
if (phit.y.y) min.y=phit.y;
if (phit.x>max.x) max.x=phit.x;
if (phit.y>max.y) max.y=phit.y;
}
if ( !map.isInside(min) || !map.isInside(max)){
Point lmin(map.map2world(0,0));
Point lmax(map.map2world(map.getMapSizeX()-1,map.getMapSizeY()-1));
min.x=( min.x >= lmin.x )? lmin.x: min.x-m_enlargeStep;将最小的数值,进行判断
max.x=( max.x <= lmax.x )? lmax.x: max.x+m_enlargeStep;
min.y=( min.y >= lmin.y )? lmin.y: min.y-m_enlargeStep;
max.y=( max.y <= lmax.y )? lmax.y: max.y+m_enlargeStep;
map.resize(min.x, min.y, max.x, max.y);
}
HierarchicalArray2D::PointSet activeArea;
angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip;
for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r
if (m_generateMap){
double d=*r;
if (d>m_laserMaxRange||d==0.0||isnan(d))
continue;
if (d>m_usableRange)
d=m_usableRange;
Point phit=lp+Point(d*cos(lp.theta+*angle),d*sin(lp.theta+*angle));
IntPoint p0=map.world2map(lp);
IntPoint p1=map.world2map(phit);
GridLineTraversalLine line;
line.points=m_linePoints;
GridLineTraversal::gridLine(p0, p1, &line);
for (int i=0; i
assert(map.isInside(m_linePoints[i]));
activeArea.insert(map.storage().patchIndexes(m_linePoints[i]));
assert(m_linePoints[i].x>=0 && m_linePoints[i].y>=0);
}
if (dcp =map.storage().patchIndexes(p1);
assert(cp.x>=0 && cp.y>=0);
activeArea.insert(cp);
}
} else {
if (*r>m_laserMaxRange||*r>m_usableRange||*r==0.0||isnan(*r)) continue;
Point phit=lp;
phit.x+=*r*cos(lp.theta+*angle);
phit.y+=*r*sin(lp.theta+*angle);
IntPoint p1=map.world2map(phit);
assert(p1.x>=0 && p1.y>=0);
IntPoint cp=map.storage().patchIndexes(p1);
assert(cp.x>=0 && cp.y>=0);
activeArea.insert(cp);
}
map.storage().setActiveArea(activeArea, true);
m_activeAreaComputed=true;
} 返回

ceil函数 返回的大于这个数据的整数。
更新t时刻的粒子群,模型中加入了高斯噪声。
到现在为止,整个gmapping的基本上都主线程都跑了一遍了,可能我自己也没有研究的很透彻。第一次分析源码。到时候。