【算法编程】单链表公共部分、回文、划分、复制、相交、环相关问题
一、打印两个有序链表的公共部分
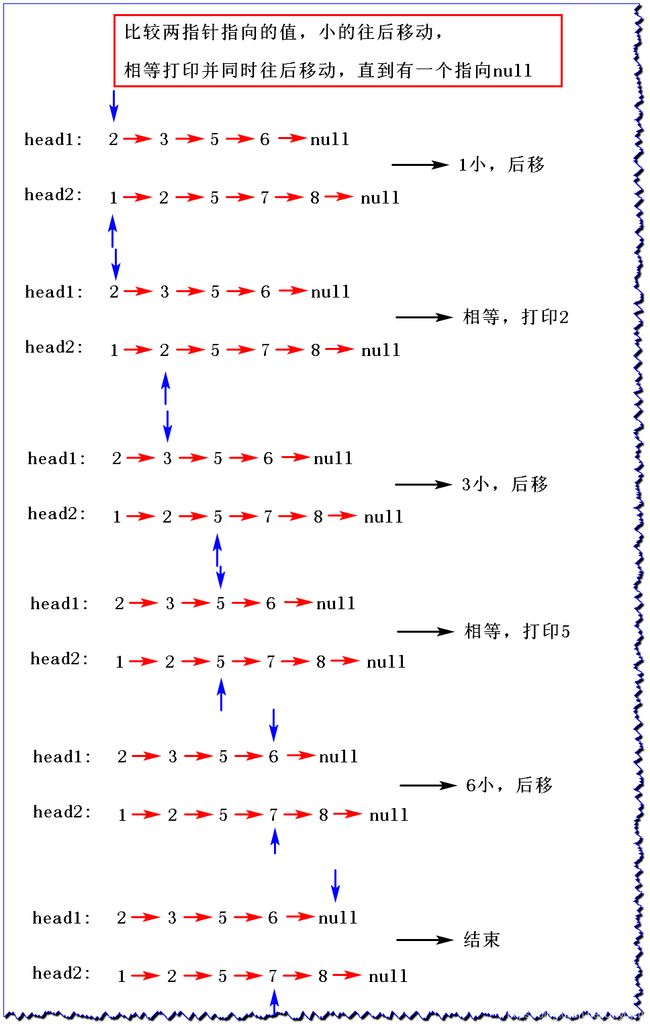
1、题目描述
给定两个有序链表的头指针 head1 和 head2 ,打印两个链表的公共部分
2、图解
3、Java代码
package day02;
/**
* 打印两个有序链表的公共部分
* @author Danycym
*
*/
public class Code11_PrintCommonPart {
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static void printCommonPart(Node head1, Node head2) {
while(head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if(head1.value < head2.value) {
head1 = head1.next;
}else if(head1.value > head2.value) {
head2 = head2.next;
}else {
System.out.print(head1.value + " ");
head1 = head1.next;
head2 = head2.next;
}
}
}
public static void printLinkedList(Node node) {
while(node != null) {
System.out.print(node.value + "->");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print("null\n");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node node1 = new Node(2);
node1.next = new Node(3);
node1.next.next = new Node(5);
node1.next.next.next = new Node(6);
Node node2 = new Node(1);
node2.next = new Node(2);
node2.next.next = new Node(5);
node2.next.next.next = new Node(7);
node2.next.next.next.next = new Node(8);
System.out.print("链表1为:");
printLinkedList(node1);
System.out.print("链表2为:");
printLinkedList(node2);
System.out.print("公共部分为:");
printCommonPart(node1, node2);
}
}
二、判断一个链表是否为回文结构
1、题目描述
给定一个链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构。
例如:
- 1->2->1,返回true
- 1->2->2->1,返回true
- 15->6->15,返回true
- 1->2->3,返回false
进阶:链表长度为N,时间复杂度达到O(N),额外空间复杂度达到O(1)
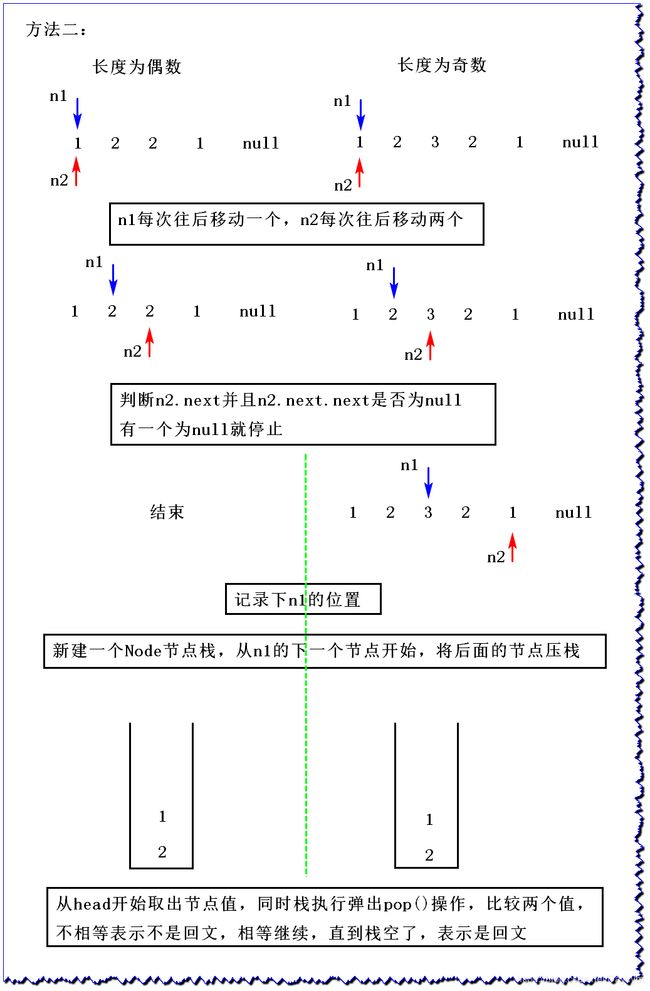
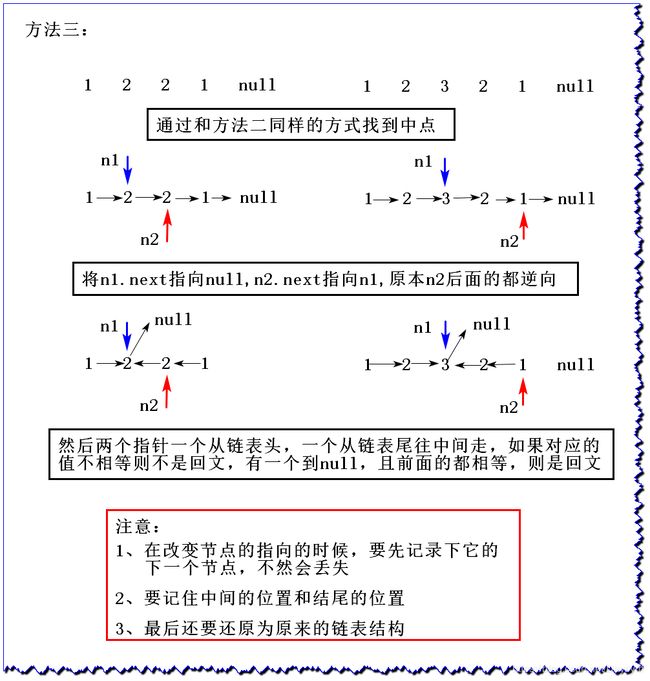
2、图解
3、Java代码
三、将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
1、题目描述
给定一个单向链表的头节点head,节点的值类型是整型,再给定一个整数 pivot。实现一个调整链表的函数,将链表调整为左部分都是值小于 pivot 的节点,中间部分都是值等于 pivot 的节点,右部分都是值大于 pivot 的节点。除这个要求外,对调整后的节点顺序没有更多的要求。
例如:
- 链表
9->0->4->5->1,pivot=3,调整后链表可以是1->0->4->9->5,也可以是0->1->9->5->4 - 总之,满 足左部分都是小于3的节点,中间部分都是等于3的节点(本例中这个部分为空),右部分都是大于3的节点即可。对某部分内部的节点顺序不做要求。
进阶:在原问题的要求之上再增加如下两个要求
- 在左、中、右三个部分的内部也做顺序要求,要求每部分里的节点从左到右的顺序与原链表中节点的先后次序一致
- 如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)
2、图解
需要N的额外空间
需要N/2的额外空间
时间复杂度达到O(N),额外空间复杂度达到O(1)
3、Java代码
package day02;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 判断链表是否为回文
* @author Danycym
*
*/
public class Code12_IsPalindromeList {
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
//方法一
public static boolean isPalindrome1(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
while(head != null) {
if(head.value != stack.pop().value) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
//方法二
public static boolean isPalindrome2(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
Node node1 = head;
Node node2 = head;
while(node2.next != null && node2.next.next != null) {
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next.next;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
node1 = node1.next;
while(node1 != null) {
stack.push(node1);
node1 = node1.next;
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
if(head.value != stack.pop().value) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
//方法三
public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
Node node1 = head;
Node node2 = head;
while(node2.next != null && node2.next.next != null) {
node1 = node1.next; //中点
node2 = node2.next.next;
}
node2 = node1.next; //将node1.next赋给node2
node1.next = null; //node1指向null
Node node3 = null; //空链表
//将后一半指向颠倒
while(node2 != null) {
node3 = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
node1 = node2;
node2 = node3;
}
node3 = node1; //先记录node1和head,避免下面操作后找不到开始位置和中点位置
node2 = head;
boolean res = true;
while(node1 != null && node2 != null) {
if(node1.value != node2.value) { //值不等,说明不是回文
res = false;
break;
}
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next;
}
//将修改的链表还原
node1 = node3.next;
node3.next = null;
while(node1 != null) {
node2 = node1.next;
node1.next = node3;
node3 = node1;
node1 = node2;
}
return res;
}
//打印链表
public static void printLinkedList(Node node) {
System.out.print("链表为:");
while(node != null) {
System.out.print(node.value + "->");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print("null\n");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println(isPalindrome1(head));
System.out.println(isPalindrome2(head));
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head));
Node head1 = null;
head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(1);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head1);
System.out.println(isPalindrome1(head1));
System.out.println(isPalindrome2(head1));
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head1));
}
}
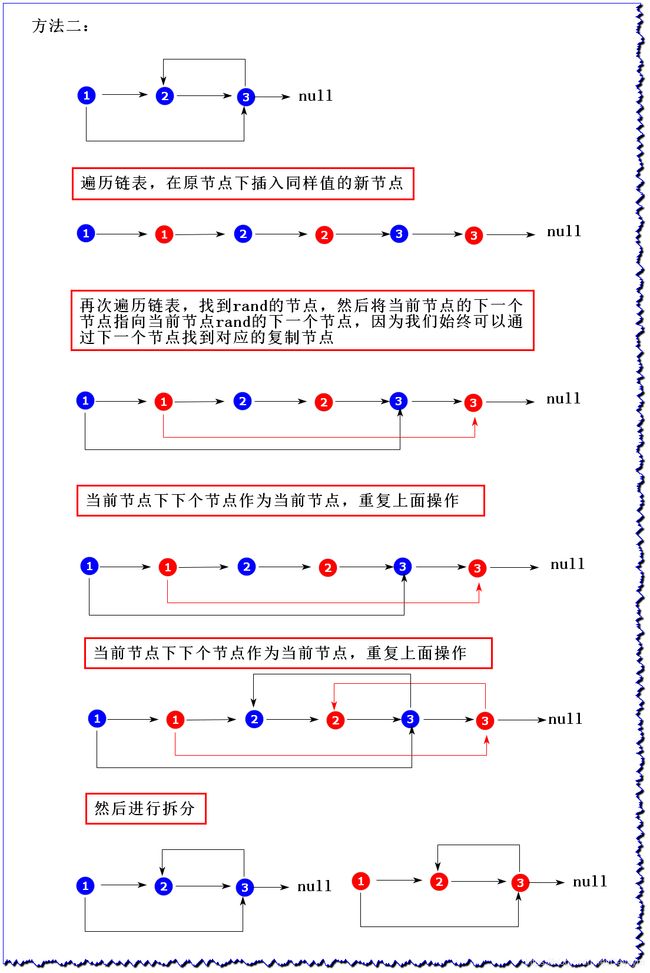
四、复制含有随机指针节点的链表
1、题目描述
一种特殊的链表节点类描述如下:
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node rand;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
Node类中的value是节点值,next指针和正常单链表中next指针的意义一 样,都指向下一个节点,rand指针是Node类中新增的指针,这个指针可 能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null。 给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表中所有结构的复制,并返回复制的新链表的头节点。
进阶:不使用额外的数据结构,只用有限几个变量,且在时间复杂度为 O(N)内完成原问题要实现的函数
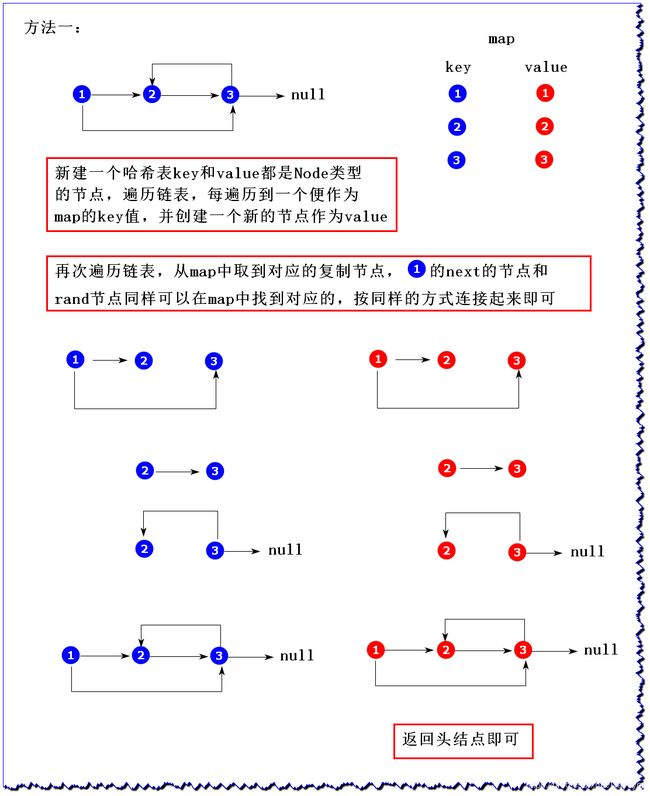
2、图解
该方法只是有限的几个变量就可以实现
3、Java代码
package day02;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* 复制含有随机指针节点的链表
* @author Danycym
*
*/
public class Code14_CopyListWithRandom {
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node rand;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static Node copyListWithRand1(Node head) {
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.value));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
public static Node copyListWithRand2(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
Node next = null;
while(cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = new Node(cur.value);
cur.next.next = next;
cur = next;
}
cur = head;
Node curCopy = null;
while(cur != null) {
next = cur.next.next;
curCopy = cur.next;
curCopy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null;
cur = next;
}
Node res = head.next;
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
next = cur.next.next;
curCopy = cur.next;
curCopy.next = next != null ? next.next : null;
cur = next;
}
return res;
}
public static void printRandLinkedList(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
System.out.print("next: ");
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
cur = head;
System.out.print("rand: ");
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.rand == null ? "- " : cur.rand.value + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 1 -> 6
head.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 2 -> 6
head.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next; // 3 -> 5
head.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next; // 4 -> 3
head.next.next.next.next.rand = null; // 5 -> null
head.next.next.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next; // 6 -> 4
printRandLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
Node res1 = copyListWithRand1(head);
printRandLinkedList(res1);
System.out.println("=========================");
Node res2 = copyListWithRand2(head);
printRandLinkedList(res2);
}
}
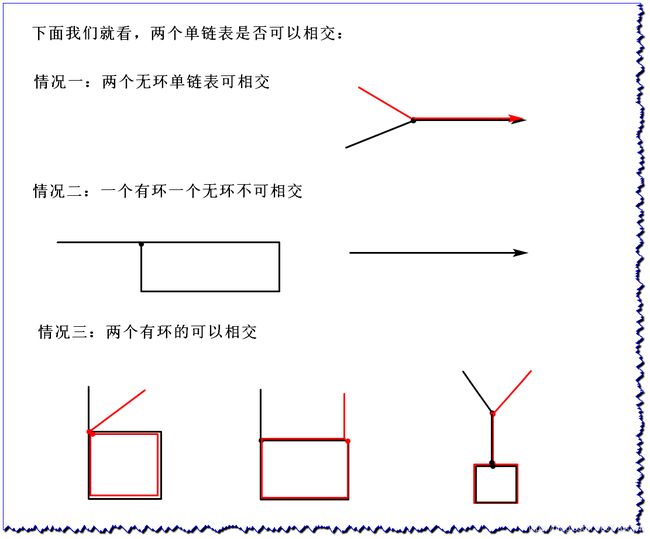
五、两个单链表相交的一系列问题
1、题目描述
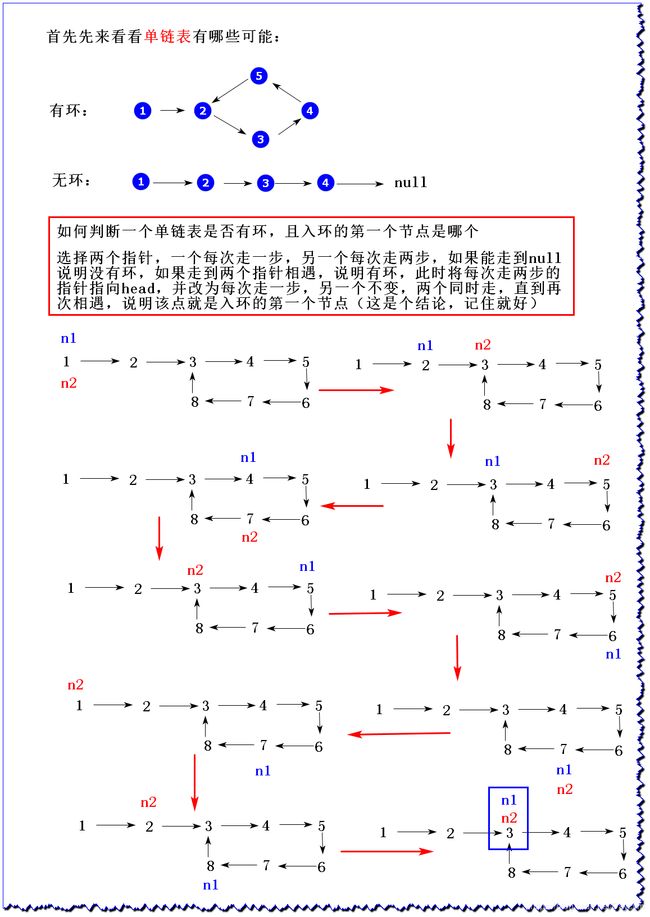
在本题中,单链表可能有环,也可能无环。给定两个单链表的头节点 head1和head2,这两个链表可能相交,也可能不相交。请实现一个函数, 如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的第一个节点;如果不相交,返回null 即可。
要求:如果链表1的长度为N,链表2的长度为M,时间复杂度请达到 O(N+M),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)
2、图解
3、Java代码
package day02;
/**
* 两个单链表相交的一系列问题
* @author Danycym
*
*/
public class Code15_FindFirstIntersectNode {
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
//获取相交的第一个节点
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) {
if(head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
//获取每个链表入环的点(存在返回节点,不存在返回null)
Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1);
Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2);
if(loop1 == null && loop2 == null) {
return noLoop(head1, head2); //两个无环链表求相交点
}
if(loop1 != null && loop2 != null) {
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2); //两个有环链表求相交点
}
return null; //单个有环情况
}
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head) {
//至少三个节点才能围成环
if(head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node n1 = head.next; //慢
Node n2 = head.next.next; //快
while(n1 != n2) { //直到n1和n2相遇
if(n2.next == null || n2.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
n2 = n2.next.next;
n1 = n1.next;
}
n2 = head; //n2从头开始
while(n1 != n2) { //n1和n2相遇于相交点
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
return n1;
}
//两个无环单链表
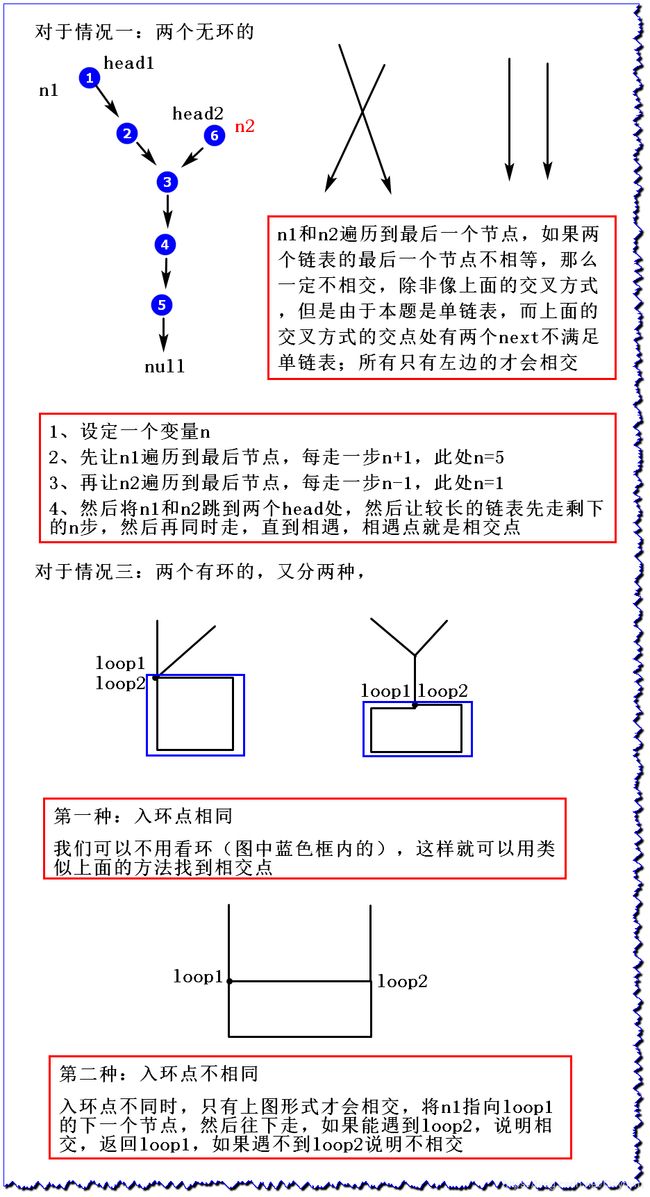
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {
if(head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
//遍历链表1,n++
while(cur1.next != null) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
//遍历链表2,n--
while(cur2.next != null) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
//如果最后一个节点不是同一个节点,不可能相交
if(cur1 != cur2) {
return null;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while(n != 0) { //长的先走n步
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
//共同走,直到相遇,即相交点
while(cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
//两个有环单链表
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) {
Node cur1 = null;
Node cur2 = null;
if(loop1 == loop2) { //共同的入环点,忽略环
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while(cur1 != loop1) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur2 != loop2) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while(n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}else { //不同的入环点
cur1 = loop1.next;
while(cur1 != loop1) {
if(cur1 == loop2) {
return loop1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->null
Node head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
// 0->9->8->6->7->null
Node head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4...
head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4
// 0->9->8->2...
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 0->9->8->6->4->5->6..
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
}
}