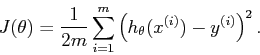基于tensorflow的线性回归
一、问题描述
我们使用俄勒冈州波特兰市的房价,其中X是房屋大小,Y是房价。该数据集包含47个示例。需要拟合Y与X的方程。
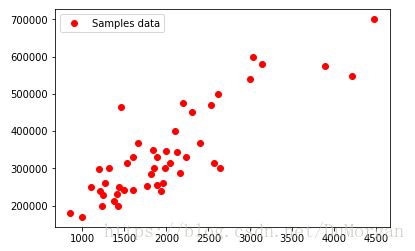
二、数据可视化
由图像可知,Y与X关系为一次线性方程。
三、算法实现
1、数据集预处理
规范化数据有助于提高梯度下降的性能,特别是在多元线性回归的情况下。
我们可以用下面的公式来做到这一点:
其中![]() 是变量的平均值,
是变量的平均值,![]() 是标准偏差。
是标准偏差。
实现代码:
def normalize(array):
return (array - array.mean()) / array.std()2、选择学习率
通常情况下,学习率是在如下范围内进行选择的:
![]()
对于这个任务,我们选择学习率为0.1。
3、实现成本函数并将梯度下降方法应用于最小化平方误差。
成本函数(cost_function)公式:
源代码中的实现:
cost_function = tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(model - Y, 2))/(2 * samples_number)
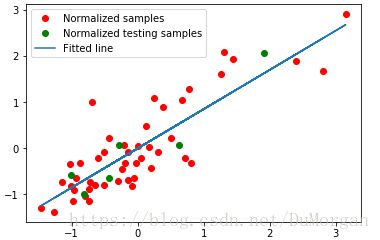
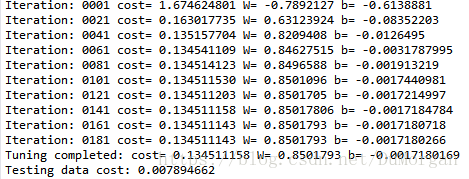
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost_function)四、运行结果
拟合出的直线比较精确,且成本函数值(cost)较小。
五、源代码
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Train a data set
size_data = numpy.asarray([ 2104, 1600, 2400, 1416, 3000, 1985, 1534, 1427,
1380, 1494, 1940, 2000, 1890, 4478, 1268, 2300,
1320, 1236, 2609, 3031, 1767, 1888, 1604, 1962,
3890, 1100, 1458, 2526, 2200, 2637, 1839, 1000,
2040, 3137, 1811, 1437, 1239, 2132, 4215, 2162,
1664, 2238, 2567, 1200, 852, 1852, 1203 ])
price_data = numpy.asarray([ 399900, 329900, 369000, 232000, 539900, 299900, 314900, 198999,
212000, 242500, 239999, 347000, 329999, 699900, 259900, 449900,
299900, 199900, 499998, 599000, 252900, 255000, 242900, 259900,
573900, 249900, 464500, 469000, 475000, 299900, 349900, 169900,
314900, 579900, 285900, 249900, 229900, 345000, 549000, 287000,
368500, 329900, 314000, 299000, 179900, 299900, 239500 ])
size_data_test = numpy.asarray([ 1600, 1494, 1236, 1100, 3137, 2238 ])
price_data_test = numpy.asarray([ 329900, 242500, 199900, 249900, 579900, 329900 ])
def normalize(array):
return (array - array.mean()) / array.std()
size_data_n = normalize(size_data)
price_data_n = normalize(price_data)
size_data_test_n = normalize(size_data_test)
price_data_test_n = normalize(price_data_test)
plt.plot(size_data, price_data, 'ro', label='Samples data')
plt.legend()
plt.draw()
samples_number = price_data_n.size
X = tf.placeholder("float")
Y = tf.placeholder("float")
# Create a model
# Set model weights
W = tf.Variable(numpy.random.randn(), name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(numpy.random.randn(), name="bias")
learning_rate = 0.1
training_iteration = 200
model = tf.add(tf.multiply(X, W), b)
cost_function = tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(model - Y, 2))/(2 * samples_number)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost_function)
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
display_step = 20
# Fit all training data
for iteration in range(training_iteration):
for (x, y) in zip(size_data_n, price_data_n):
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
# Display logs per iteration step
if iteration % display_step == 0:
print( "Iteration:", '%04d' % (iteration + 1), "cost=", "{:.9f}".format(sess.run(cost_function, feed_dict={X:size_data_n, Y:price_data_n})),"W=", sess.run(W), "b=", sess.run(b))
tuning_cost = sess.run(cost_function, feed_dict={X: normalize(size_data_n), Y: normalize(price_data_n)})
print ("Tuning completed:", "cost=", "{:.9f}".format(tuning_cost), "W=", sess.run(W), "b=", sess.run(b))
testing_cost = sess.run(cost_function, feed_dict={X: size_data_test_n, Y: price_data_test_n})
print ("Testing data cost:" , testing_cost)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(size_data_n, price_data_n, 'ro', label='Normalized samples')
plt.plot(size_data_test_n, price_data_test_n, 'go', label='Normalized testing samples')
plt.plot(size_data_n, sess.run(W) * size_data_n + sess.run(b), label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()