APK安装流程系列文章整体内容如下:
- APK安装流程详解0——前言
- APK安装流程详解1——有关"安装ing"的实体类概述
- APK安装流程详解2——PackageManager简介
- APK安装流程详解3——PackageManager与PackageManagerService
- APK安装流程详解4——安装中关于so库的那些事
- APK安装流程详解5——PackageInstallerService和Installer
- APK安装流程详解6——PackageManagerService启动前奏
- APK安装流程详解7——PackageManagerService的启动流程(上)
- APK安装流程详解8——PackageManagerService的启动流程(下)
- APK安装流程详解9——PackageParser解析APK(上)
- APK安装流程详解10——PackageParser解析APK(下)
- APK安装流程详解11——普通应用安装简介
- APK安装流程详解12——PackageManagerService中的新安装流程上(拷贝)
- APK安装流程详解13——PackageManagerService中的新安装流程下(装载)
- APK安装流程详解14——PMS中的新安装流程上(拷贝)补充
- APK安装流程详解15——PMS中的新安装流程下(装载)补充
- APK安装流程详解16——Android包管理总结
本片文章的主要内容如下:
- 1、ABI简介
- 2、PackageManagerService#derivePackageAbi(PackageParser.Package, File,String, boolean)方法解析
- 3、PackageManagerService#setNativeLibraryPaths(PackageParser.Package)方法分析
一、ABI简介
ABI全程是:Application binary interface,即:应用程序二进制接口,它定义了一套规则,允许编译好的二进制目标代码在所兼容该ABI的操作系统和硬件平台中无需改动就能运行。
不同的Android手机使用不同的CPU,因此支持不同的指令集。CPU与指令集的每种组合都有其自己的应用二进制接口(或ABI)。"ABI"精确定义了"运行时,应用的机器码和系统的交互方式"。你必须为应用要使用每个CPU架构指定ABI。
典型的ABI包含以下信息:
- 1、机器代码应使用的CPU指令集
- 2、运行时内存存储和加载的字节顺序
- 3、可执行二进制文件(例如程序和共享库)的格式,以及它们支持的内容类型
- 4、用于解析内容与系统之间的数据的各种约定。这些约定包括对齐限制,以及系统如何使用堆栈和在调用函数时注册。
- 5、运行时可用于机器代码的函数符号列表 - 通常来自非常具体的库集。
由上述定义可以判断:
ABI定义了规则,而具体的实现是由编译器、CPU、操作系统共同来完成的。不同的CPU芯片(如:ARM、Intel x86、MIPS)支持不同的ABI架构,常见的ABI类型包含:armabi、armabi-v7a、x86、x86_64、mips、mips64、arm64-v8a等。
这也就是为什么我们编译出的运行于windows的二进制程序不能运行于Mac OS/Linux/Android平台了,因此CPU芯片和操作系统均不相同,支持的ABI类型也不一样,因此无法识别对方的二进制程序。
而我们说的"交叉编译"的核心原理也跟这些密切相关,交叉编译,就是使用交叉编译工具,在平台上编译生成另一个平台的二进制可执行程序,为什么可以做到?因为交叉编译工具实现了另一个平台所定义的ABI规则。我们在Window/Linux平台使用Android NDK交叉编译工具来编译出Android平台的库也是这个道理。
(一)、.so文件与ABI
如果你的项目中使用了NDK,它就生成了.so文件。如果你的项目只使用了Java语言进行编程,可能就不太关注so文件了。因为Java是跨平台的。但是其实项目中的依赖函数库或者引擎库已经嵌入了so文件。并依赖不同的ABI,比如项目中使用了百度地图,里面就会涉及相应的so文件。
Android应用支持的ABI取决于APK中位于lib/ABI目录中的so文件,其中
ABI可能是上面说过的其中ABI的一种
(二)、关于so文件的一些补充
1、so文件的重要法则
处理so文件时有一条简单但却很重的法则:
应该尽最大可能为每个ABI提供经过优化过的.so文件,且最好不要混合着使用。即你应该为每个ABI目录提供对应的so文件。
2、NDK兼容性
使用NDK时,一般人会倾向于使用最新的编译凭条,但实际上这样做是有问题的。因为NDK平台是不向后兼容的,而是向前兼容的。所以推荐使用APP的minSdkVersion对应的编译平台。这也意味着当你引入一个预编译好的.so文件时,你需要检查它被编译所用的平台版本。
3、混合使用不同的编译的so文件
so文件可以依赖于不同的C++运行时,静态编译或者动态加载,混合使用不同版本的C++运行时可能会导致很多奇怪的crash。最好避免这种情况。
PS:当只有一个so文件时,静态编译C++运行时是没有问题的。但是当存在多个so文件时,应该让所有so文件都动态链接相同的C++运行时。这意味着当引入一个新的预编译so文件,而且项目中还存在其他so文件时,我们需要首先确认新引入的so文件使用的C++运行时是否已经存在的so文件一致。
(三)、ABI和CPU的关系
1、Android CPU的基础知识
C++代码必须根据Android 设备的CPU类型(通常称为"ABIs")进行编译,常用的五种 ABI:
- armeabiv-v7a:第七代及以上ARM处理器。2011年以后的生产的大部分Android设备都是用它。
- arm64-v8a:第8代、64位ARM处理器,设备不多,比如三星Galaxy S6
- armeabi:第5代、第6代ARM处理器,早期的手机用的比较多。
- x86:平台、模拟器用得比较多。
- x86_64:64位的平板。
2、 ABI支持CPU列表
ABI支持CPU列表,如下:
举例说明:
在x86设备上,选择ABI的先后顺序
- 第一步:在libs/x86目录中如果存在.so文件的话,会被安装,如果没有走第二步。
- 第二步:会在armeabi-v7a中的.so文件,如果有,会被安装,如果没有会走第三步。
- 第三步:会在armeabi目录中的.so文件寻找
PS:x86设备能够很好的运行ARM类型函数库,但并不保证100% 发生crash,特别是对旧设备,因为是运行在x86设备上模拟ARM的虚拟层上。
3、 ABI支持CPU的知识点
- 1、大部分CPU都支持多余一种的ABI
- 2、 当一个应用安装在设备上,只有设备支持的CPU架构对应的.so文件会被安装。
- 3、64位设备(arm64-v8a、x86_64、mips64)能够运行32位的函数库,但是以32位版本的ART和Android组件,将丢失64位优化过的性能(ART、webview、media等等)。
- 4、最好针对特定平台提供相应平台的二进制包,这种情况下运行时就少了一个模拟层(例如x86设备上模拟arm模拟层),从而得到更好的性能(归功与最近的架构更新,例如硬件fpu,更多的寄存器,更好的向量化)。
- 5、会优先安装优先级较高的ABI目录,则其他优先级较低的ABI目录(包括其他module中的ABI目录),都无法安装。例如:在cpu是ARMv7架构的手机上,如果检测到armeabi-v7a,就会选择安装armeabi-v7a,则armeabi下的文件,就无法安装了。
- 6、相应的ABI二进制文件,要放进相应的ABI目录中
- 7、一般情况下不要随便修改架构目录名
(四)、常见问题:
1、so文件 放进了优先级低的ABI目录
问题:
如果你的项目中,有其他优先级更好的ABI目录,但是你把ABI文件方法放到了优先级低的目录,最后导致你的ABI文件无法被加载
举例:
某手机CPU架构是ARMv7,ABI文件是armeabi-v7a,但是放进了armeabi目录中:
导致结果
项目中有armeabi-v7a的目录,armeabi目录的文件,无法被加载,然后运行报错,出现类似于如下log信息。
Caused by: java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: dalvik.system.PathClassLoader[DexPathList[[zip file "/data/app/.xx../base.apk"],nativeLibraryDirectories=[/data/app/.xx../lib/arm, /vendor/lib, /system/lib]]] couldn't find "lib..xx...so"
解决方案:建议armeabi-v7a的目录下的文件和armeabi目录的文件保持一致。
2、两个第三方SDK中的ABI文件优先级不一样
问题:
两个第三方的SDK中ABI文件优先级不一样,手机加载运行时,会导致优先级低的库,无法被加载。
例子:
某手机CPU架构是ARMv7,项目中使用了两个第三方SDK:假设是"支付宝"和"银联".
- 支付宝:ABI文件是armeabi-v7a,所以放到armeabi-v7a目录中。
- 银联:ABI文件是armeabi,所以放到armeabi目录中。
导致结果:
在运行时,会发现运行后crash,出现如下日志:
Caused by: java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: dalvik.system.PathClassLoader[DexPathList[[zip file "/data/app/.xx../base.apk"],nativeLibraryDirectories=[/data/app/.xx../lib/arm, /vendor/lib, /system/lib]]] couldn't find "lib..xx...so"
解决方案:
解决方案1:
使用同一优先级的ABI文件,ABI文件放入到优先级相同的ABI目录
比如:
- 支付宝:ABI文件是armeabi-v7a,放到armeabi-v7a目录中。
- 银联:ABI文件是armeabi-v7a,放到armeabi-v7a目录中。
或 - 支付宝:ABI文件是armeabi,放到armeabi目录中。
- 银联:ABI文件是armeabi,放到armeabi目录中。
解决方案2:
如果两个第三方提供的是不同优先级的ABI文件,则将ABI文件放入到优先级相同的ABI。
比如:
- 支付宝:ABI文件是armeabi-v7a,放到armeabi目录中。
- 银联:ABI文件是armeabi,放到armeabi目录中。
二、 PackageManagerService#derivePackageAbi(PackageParser.Package, File,String, boolean)方法解析
这个方法在PackageManagerService的installPackageLI方法里面被调用。代码在代码在PackageManagerService.java 12442行
private void installPackageLI(InstallArgs args, PackageInstalledInfo res) {
...
derivePackageAbi(pkg, new File(pkg.codePath), args.abiOverride,true /* extract libs */);
...
}
在讲解这个方法的时候我们先来了解一个概念是"primaryCpuAbi",关于ABI的概念可以参考我的文章Android ABI简介 ,那"primaryCpuAbi"又是什么?
因为一个系统支持的ABI有很多,不止一个,比如一个64位的机器上它的supportAbiList,可能如下所示:
public static final String[] SUPPORTED_ABIS = getStringList("ro.product.cpu.abilist", ",");
root@:/ # getprop ro.product.cpu.abilist
arm64-v8a,armeabi-v7a,armeabi
所以它能支持的abi有如上的3个,这个primaryCpuAbi就是要知道当前程序的abi在他支持的abi中最靠前的的哪一个。同时依靠这个primaryCpuAbi的值可以决定我们的程序是运行在32位还是64位的。
那我们来看下derivePackageAbi这个方法的内部实现
代码在PackageManagerService.java 7553行
/**
* Derive the ABI of a non-system package located at {@code scanFile}. This information
* is derived purely on the basis of the contents of {@code scanFile} and
* {@code cpuAbiOverride}.
*
* If {@code extractLibs} is true, native libraries are extracted from the app if required.
*/
public void derivePackageAbi(PackageParser.Package pkg, File scanFile,
String cpuAbiOverride, boolean extractLibs)
throws PackageManagerException {
// TODO: We can probably be smarter about this stuff. For installed apps,
// we can calculate this information at install time once and for all. For
// system apps, we can probably assume that this information doesn't change
// after the first boot scan. As things stand, we do lots of unnecessary work.
// Give ourselves some initial paths; we'll come back for another
// pass once we've determined ABI below.
// *********** 第一步 ***********
// 设置so库的安装路径
setNativeLibraryPaths(pkg);
// We would never need to extract libs for forward-locked and external packages,
// since the container service will do it for us. We shouldn't attempt to
// extract libs from system app when it was not updated.
// 如果是系统级别的APP则不用每次都提取
if (pkg.isForwardLocked() || pkg.applicationInfo.isExternalAsec() ||
(isSystemApp(pkg) && !pkg.isUpdatedSystemApp())) {
extractLibs = false;
}
// 本地库目录
final String nativeLibraryRootStr = pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryRootDir;
// 是否有设置过nativeLibraryRootRequiresIsa
final boolean useIsaSpecificSubdirs = pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryRootRequiresIsa;
NativeLibraryHelper.Handle handle = null;
try {
handle = NativeLibraryHelper.Handle.create(scanFile);
// TODO(multiArch): This can be null for apps that didn't go through the
// usual installation process. We can calculate it again, like we
// do during install time.
//
// TODO(multiArch): Why do we need to rescan ASEC apps again ? It seems totally
// unnecessary.
// 获取本地库 的File
final File nativeLibraryRoot = new File(nativeLibraryRootStr);
// Null out the abis so that they can be recalculated.
// 第一顺位的支持的abi
pkg.applicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi = null;
// 第二 顺位的支持的abi
pkg.applicationInfo.secondaryCpuAbi = null;
// 是否支持多架构的APK,这种APK的AndroidManifest.xml里面会设置android:multiarch=true
// *********** 第二步 ***********
if (isMultiArch(pkg.applicationInfo)) {
// 如果支持多平台
// Warn if we've set an abiOverride for multi-lib packages..
// By definition, we need to copy both 32 and 64 bit libraries for
// such packages.
if (pkg.cpuAbiOverride != null
&& !NativeLibraryHelper.CLEAR_ABI_OVERRIDE.equals(pkg.cpuAbiOverride)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Ignoring abiOverride for multi arch application.");
}
// 初始化 32位的abi和64位的abi
int abi32 = PackageManager.NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES;
int abi64 = PackageManager.NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES;
// 如果有 设备支持的32位abi
if (Build.SUPPORTED_32_BIT_ABIS.length > 0) {
// 如果需要导出
if (extractLibs) {
//调用 NativeLibraryHelper的copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi方法进行so库拷贝
abi32 = NativeLibraryHelper.copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi(handle,
nativeLibraryRoot, Build.SUPPORTED_32_BIT_ABIS,
useIsaSpecificSubdirs);
} else {
//调用 NativeLibraryHelper的findSupportedAbi方法读取CPU支持的架构类型
abi32 = NativeLibraryHelper.findSupportedAbi(handle, Build.SUPPORTED_32_BIT_ABIS);
}
}
// 检查是否有异常
maybeThrowExceptionForMultiArchCopy(
"Error unpackaging 32 bit native libs for multiarch app.", abi32);
// 如果有 设备支持的64位abi
if (Build.SUPPORTED_64_BIT_ABIS.length > 0) {
if (extractLibs) {
//调用 NativeLibraryHelper的copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi方法进行so库拷贝
abi64 = NativeLibraryHelper.copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi(handle,
nativeLibraryRoot, Build.SUPPORTED_64_BIT_ABIS,
useIsaSpecificSubdirs);
} else {
//调用 NativeLibraryHelper的findSupportedAbi方法获取CPU支持的架构类型
abi64 = NativeLibraryHelper.findSupportedAbi(handle, Build.SUPPORTED_64_BIT_ABIS);
}
}
// 检查是否有异常
maybeThrowExceptionForMultiArchCopy(
"Error unpackaging 64 bit native libs for multiarch app.", abi64);
// 如果abi64有值,则说明有支持的64位库
if (abi64 >= 0) {
// 设置 第一顺位的abi即primaryCpuAbi为支持的64位ABI
pkg.applicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi = Build.SUPPORTED_64_BIT_ABIS[abi64];
}
// 如果abi32有值,则说明有支持的32位库
if (abi32 >= 0) {
final String abi = Build.SUPPORTED_32_BIT_ABIS[abi32];
if (abi64 >= 0) {
// 如果同时还支持64位, 设置第二顺位的abi为32位的abi
pkg.applicationInfo.secondaryCpuAbi = abi;
} else {
// 如果只支持32位, 设置第一顺位的abi位32的abi
pkg.applicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi = abi;
}
}
} else {
// 不支持多平台
// 获取设备中支持的CPU架构
String[] abiList = (cpuAbiOverride != null) ?
new String[] { cpuAbiOverride } : Build.SUPPORTED_ABIS;
// Enable gross and lame hacks for apps that are built with old
// SDK tools. We must scan their APKs for renderscript bitcode and
// not launch them if it's present. Don't bother checking on devices
// that don't have 64 bit support.
// 是否需要RenderScript重写,RenderScript是Android平台的一种类C脚本语言,咱们暂时不考虑
boolean needsRenderScriptOverride = false;
if (Build.SUPPORTED_64_BIT_ABIS.length > 0 && cpuAbiOverride == null &&
NativeLibraryHelper.hasRenderscriptBitcode(handle)) {
abiList = Build.SUPPORTED_32_BIT_ABIS;
needsRenderScriptOverride = true;
}
final int copyRet;
//如果需要导出
if (extractLibs) {
//调用NativeLibraryHelper的copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi方法进行so拷贝
copyRet = NativeLibraryHelper.copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi(handle,
nativeLibraryRoot, abiList, useIsaSpecificSubdirs);
} else {
//如果不需要导出
//调用NativeLibraryHelper的findSupportedAbi方法读取CPU支持的架构类
copyRet = NativeLibraryHelper.findSupportedAbi(handle, abiList);
}
// 判断是否出现异常
if (copyRet < 0 && copyRet != PackageManager.NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES) {
throw new PackageManagerException(INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR,
"Error unpackaging native libs for app, errorCode=" + copyRet);
}
// 根据copyRet的值,确定当前APP的primaryCpuAbi的值
if (copyRet >= 0) {
// 设置应用包信息中的主要CPU架构类型,后续启动DVM需要用到
pkg.applicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi = abiList[copyRet];
} else if (copyRet == PackageManager.NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES && cpuAbiOverride != null) {
// 没有本地库
pkg.applicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi = cpuAbiOverride;
} else if (needsRenderScriptOverride) {
pkg.applicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi = abiList[0];
}
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to get canonical file " + ioe.toString());
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(handle);
}
// *********** 第三步 ***********
// Now that we've calculated the ABIs and determined if it's an internal app,
// we will go ahead and populate the nativeLibraryPath.
//更新so库的安装位置
setNativeLibraryPaths(pkg);
}
先来看下方法的注释
导出位于scanFile的的ABI包,这个ABI信息是基于scanFile和cpuAbiOverride
如果extractLibs为真,则本地库将会从应用程序中提取出来
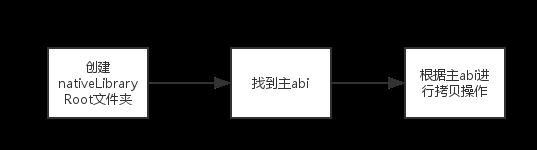
方法内部注释已经很清楚了,我将这个方法分为3部分
- 第一步:设置so的安装路径
- 第二步:对so进行具体的操作,这里面分为两种情况:
- 情况A:其支持多平台
- 情况B:不支持多平台
- 第三步:更新so的安装路径
流程图如下:
这个方法进行so拷贝的是 NativeLibraryHelper.copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi方法,读取CPU支持的类型为NativeLibraryHelper的findSupportedAbi方法,下面我们就来了解下这两个方法
(一)、NativeLibraryHelper的静态方法findSupportedAbi
代码在NativeLibraryHelper.java 191行
/**
* Checks if a given APK contains native code for any of the provided
* {@code supportedAbis}. Returns an index into {@code supportedAbis} if a matching
* ABI is found, {@link PackageManager#NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES} if the
* APK doesn't contain any native code, and
* {@link PackageManager#INSTALL_FAILED_NO_MATCHING_ABIS} if none of the ABIs match.
*/
public static int findSupportedAbi(Handle handle, String[] supportedAbis) {
int finalRes = NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES;
// 遍历handle的apkHandles
for (long apkHandle : handle.apkHandles) {
// 调用nativeFindSupportedAbi进行查找
final int res = nativeFindSupportedAbi(apkHandle, supportedAbis);
if (res == NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES) {
// No native code, keep looking through all APKs.
} else if (res == INSTALL_FAILED_NO_MATCHING_ABIS) {
// Found some native code, but no ABI match; update our final
// result if we haven't found other valid code.
if (finalRes < 0) {
finalRes = INSTALL_FAILED_NO_MATCHING_ABIS;
}
} else if (res >= 0) {
// Found valid native code, track the best ABI match
if (finalRes < 0 || res < finalRes) {
finalRes = res;
}
} else {
// Unexpected error; bail
return res;
}
}
return finalRes;
}
有注释,先看一下注释
- 检查指定的APK是否包含指定的supportedAbis的Native代码。如果匹配则返回一个对应supportedAbis的索引,如果没有Native的代码则返回PackageManager#NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES,如果APK不包含对应的Native代码,则返回ackageManager#INSTALL_FAILED_NO_MATCHING_ABIS
方法内部简单,主要是调用了nativeFindSupportedAbi方法,通过我前面的文章Android跨进程通信IPC之3——关于"JNI"的那些事 我们知道它对应的文件是com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp
那我们就来在com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp文件中找下
代码在577行,如下:
static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
{"nativeOpenApk",
"(Ljava/lang/String;)J",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_openApk},
{"nativeClose",
"(J)V",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_close},
{"nativeCopyNativeBinaries",
"(JLjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;ZZ)I",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_copyNativeBinaries},
{"nativeSumNativeBinaries",
"(JLjava/lang/String;)J",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_sumNativeBinaries},
{"nativeFindSupportedAbi",
"(J[Ljava/lang/String;)I",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_findSupportedAbi},
{"hasRenderscriptBitcode", "(J)I",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_hasRenderscriptBitcode},
};
我们看到nativeCopyNativeBinaries方法对应的是com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_findSupportedAbi方法,那我们再来找下com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_findSupportedAbi方法
那我们就来看下com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_findSupportedAbi方法
代码在com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp 510行
static jint
com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_findSupportedAbi(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz,
jlong apkHandle, jobjectArray javaCpuAbisToSearch)
{
return (jint) findSupportedAbi(env, apkHandle, javaCpuAbisToSearch);
}
我们看到com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_findSupportedAbi方法里面调用了findSupportedAbi方法
那我们再来看下findSupportedAbi方法
代码在com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp 435行
static int findSupportedAbi(JNIEnv *env, jlong apkHandle, jobjectArray supportedAbisArray) {
const int numAbis = env->GetArrayLength(supportedAbisArray);
Vector supportedAbis;
for (int i = 0; i < numAbis; ++i) {
supportedAbis.add(new ScopedUtfChars(env,
(jstring) env->GetObjectArrayElement(supportedAbisArray, i)));
}
// 读取apk文件
ZipFileRO* zipFile = reinterpret_cast(apkHandle);
if (zipFile == NULL) {
return INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
UniquePtr it(NativeLibrariesIterator::create(zipFile));
if (it.get() == NULL) {
return INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
ZipEntryRO entry = NULL;
int status = NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES;
// 开始遍历apk中的每一个文件
while ((entry = it->next()) != NULL) {
// We're currently in the lib/ directory of the APK, so it does have some native
// code. We should return INSTALL_FAILED_NO_MATCHING_ABIS if none of the
// libraries match.
if (status == NO_NATIVE_LIBRARIES) {
status = INSTALL_FAILED_NO_MATCHING_ABIS;
}
const char* fileName = it->currentEntry();
const char* lastSlash = it->lastSlash();
// Check to see if this CPU ABI matches what we are looking for.
const char* abiOffset = fileName + APK_LIB_LEN;
const size_t abiSize = lastSlash - abiOffset;
// 开始遍历apk的子文件,获取so文件的全路径,如果这个路径包含了cpu架构值,就记录并返回索引值
for (int i = 0; i < numAbis; i++) {
const ScopedUtfChars* abi = supportedAbis[i];
if (abi->size() == abiSize && !strncmp(abiOffset, abi->c_str(), abiSize)) {
// The entry that comes in first (i.e. with a lower index) has the higher priority.
if (((i < status) && (status >= 0)) || (status < 0) ) {
status = i;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < numAbis; ++i) {
delete supportedAbis[i];
}
return status;
}
这里看到了先读取apk文件,然后遍历apk文件中的so文件,得到全路径后再和传递捡来的abiList进行比较,得到合适的索引值。假设我们刚才拿到的abiList为:x86,然后就开始比较apk中有没有这些架构平台的so文件,如果有,就直接返回abiList的索引值。比如apk的libs结构如下:
- 如果这时候只有一种架构,libs文件下也有相关的ABI类型,就只能返回0了。
- 假设我们的abiList为:arm64-v8a,armeabi-v7a,armeabi。那么这时候返回的索引值是0,代表的是arm64-v8a架构。如果APK文件中没有arm64-v8a目录的话,那么就返回1。代表的是armeabi-v7a架构的架构。以此类推。得到引用支持的架构索引之后就可以获取so释放到设备中的目录了。
(二)、NativeLibraryHelper的静态方法copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi
代码在NativeLibraryHelper.java 292行
public static int copyNativeBinariesForSupportedAbi(Handle handle, File libraryRoot,
String[] abiList, boolean useIsaSubdir) throws IOException {
// 创建so 目录
createNativeLibrarySubdir(libraryRoot);
/*
* If this is an internal application or our nativeLibraryPath points to
* the app-lib directory, unpack the libraries if necessary.
*/
// 获取应用支持的架构类型
int abi = findSupportedAbi(handle, abiList);
if (abi >= 0) {
/*
* If we have a matching instruction set, construct a subdir under the native
* library root that corresponds to this instruction set.
*/
// 根据不同的架构获取不同的目录
final String instructionSet = VMRuntime.getInstructionSet(abiList[abi]);
final File subDir;
// 是否有父目录
if (useIsaSubdir) {
// 如果有父目录,则设置父目录
final File isaSubdir = new File(libraryRoot, instructionSet);
createNativeLibrarySubdir(isaSubdir);
subDir = isaSubdir;
} else {
// 没有父目录
subDir = libraryRoot;
}
// 进行真正的so拷贝
int copyRet = copyNativeBinaries(handle, subDir, abiList[abi]);
// 如果拷贝没有成功
if (copyRet != PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
return copyRet;
}
}
return abi;
}
他的核心业务代码都在 native 层,它主要做了如下的工作:
这个方法里面的核心调用是** copyNativeBinaries**方法,下面我们就来看下这个方法
NativeLibraryHelper的静态方法copyNativeBinaries
/**
* Copies native binaries to a shared library directory.
*
* @param handle APK file to scan for native libraries
* @param sharedLibraryDir directory for libraries to be copied to
* @return {@link PackageManager#INSTALL_SUCCEEDED} if successful or another
* error code from that class if not
*/
public static int copyNativeBinaries(Handle handle, File sharedLibraryDir, String abi) {
// 遍历handle的apkHandles数组
for (long apkHandle : handle.apkHandles) {
// 调用nativeCopyNativeBinaries方法,因为它是natvie开头,所以它是native的
int res = nativeCopyNativeBinaries(apkHandle, sharedLibraryDir.getPath(), abi,
handle.extractNativeLibs, HAS_NATIVE_BRIDGE);
if (res != INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
return res;
}
}
return INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
}
先来翻译一下注释:
将Native的二进制文件复制到共享库中
- 入参 handle:扫描出来的APK的Native库
- 入参 sharedLibraryDir:要被复制到的目标目录
- 出参 :如果复制成功则返回PackageManager#INSTALL_SUCCEEDED,或者其他错误码
方法内部简单,主要是调用了nativeCopyNativeBinaries方法,通过我前面的文章Android跨进程通信IPC之3——关于"JNI"的那些事 我们知道它对应的文件是com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp
那我们就来在com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp文件中找下
代码在571行,如下:
static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
{"nativeOpenApk",
"(Ljava/lang/String;)J",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_openApk},
{"nativeClose",
"(J)V",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_close},
{"nativeCopyNativeBinaries",
"(JLjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;ZZ)I",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_copyNativeBinaries},
{"nativeSumNativeBinaries",
"(JLjava/lang/String;)J",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_sumNativeBinaries},
{"nativeFindSupportedAbi",
"(J[Ljava/lang/String;)I",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_findSupportedAbi},
{"hasRenderscriptBitcode", "(J)I",
(void *)com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_hasRenderscriptBitcode},
};
我们看到nativeCopyNativeBinaries方法对应的是com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_copyNativeBinaries方法,那我们再来找下com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_copyNativeBinaries方法
代码在com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp 489行
com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper_copyNativeBinaries(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz,
jlong apkHandle, jstring javaNativeLibPath, jstring javaCpuAbi,
jboolean extractNativeLibs, jboolean hasNativeBridge)
{
void* args[] = { &javaNativeLibPath, &extractNativeLibs, &hasNativeBridge };
return (jint) iterateOverNativeFiles(env, apkHandle, javaCpuAbi,
copyFileIfChanged, reinterpret_cast(args));
}
这个方法里面接着调用了iterateOverNativeFiles方法,那我们来看下iterateOverNativeFiles方法的内部实现
PS:这里面的copyFileIfChanged是个函数指针。
代码在com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp 394行
static install_status_t
iterateOverNativeFiles(JNIEnv *env, jlong apkHandle, jstring javaCpuAbi,
iterFunc callFunc, void* callArg) {
// 读取apk文件
ZipFileRO* zipFile = reinterpret_cast(apkHandle);
if (zipFile == NULL) {
return INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
UniquePtr it(NativeLibrariesIterator::create(zipFile));
if (it.get() == NULL) {
return INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
const ScopedUtfChars cpuAbi(env, javaCpuAbi);
if (cpuAbi.c_str() == NULL) {
// This would've thrown, so this return code isn't observable by
// Java.
return INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
ZipEntryRO entry = NULL;
// 开始遍历apk中的每一个文件
while ((entry = it->next()) != NULL) {
const char* fileName = it->currentEntry();
const char* lastSlash = it->lastSlash();
// Check to make sure the CPU ABI of this file is one we support.
const char* cpuAbiOffset = fileName + APK_LIB_LEN;
const size_t cpuAbiRegionSize = lastSlash - cpuAbiOffset;
if (cpuAbi.size() == cpuAbiRegionSize && !strncmp(cpuAbiOffset, cpuAbi.c_str(), cpuAbiRegionSize)) {
// 拷贝so,这一句才是关键。copyFileIfChanged完成释放
install_status_t ret = callFunc(env, callArg, zipFile, entry, lastSlash + 1);
if (ret != INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
ALOGV("Failure for entry %s", lastSlash + 1);
return ret;
}
}
}
return INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
}
我们看到释放工作是在copyFileIfChanged函数里面,下面我们来下这个函数
PS:ZipFileRO的遍历顺序,它是根据文件对应的ZipEntryRO中的hash值而定,而对弈已经hasPrimaryAbi的情况下,非PrimaryAbi是直接跳过copy操作的,所以这里可能会出现很多拷贝so失败的情况。
代码在com_android_internal_content_NativeLibraryHelper.cpp 175行
/*
* Copy the native library if needed.
*
* This function assumes the library and path names passed in are considered safe.
*/
static install_status_t
copyFileIfChanged(JNIEnv *env, void* arg, ZipFileRO* zipFile, ZipEntryRO zipEntry, const char* fileName)
{
void** args = reinterpret_cast(arg);
jstring* javaNativeLibPath = (jstring*) args[0];
jboolean extractNativeLibs = *(jboolean*) args[1];
jboolean hasNativeBridge = *(jboolean*) args[2];
ScopedUtfChars nativeLibPath(env, *javaNativeLibPath);
uint32_t uncompLen;
uint32_t when;
uint32_t crc;
uint16_t method;
off64_t offset;
if (!zipFile->getEntryInfo(zipEntry, &method, &uncompLen, NULL, &offset, &when, &crc)) {
ALOGD("Couldn't read zip entry info\n");
return INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
if (!extractNativeLibs) {
// check if library is uncompressed and page-aligned
if (method != ZipFileRO::kCompressStored) {
ALOGD("Library '%s' is compressed - will not be able to open it directly from apk.\n",
fileName);
return INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
if (offset % PAGE_SIZE != 0) {
ALOGD("Library '%s' is not page-aligned - will not be able to open it directly from"
" apk.\n", fileName);
return INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
if (!hasNativeBridge) {
return INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
}
}
// Build local file path
const size_t fileNameLen = strlen(fileName);
char localFileName[nativeLibPath.size() + fileNameLen + 2];
if (strlcpy(localFileName, nativeLibPath.c_str(), sizeof(localFileName)) != nativeLibPath.size()) {
ALOGD("Couldn't allocate local file name for library");
return INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR;
}
*(localFileName + nativeLibPath.size()) = '/';
if (strlcpy(localFileName + nativeLibPath.size() + 1, fileName, sizeof(localFileName)
- nativeLibPath.size() - 1) != fileNameLen) {
ALOGD("Couldn't allocate local file name for library");
return INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR;
}
// Only copy out the native file if it's different.
// 只有so本地文件改变了才能拷贝
struct tm t;
ZipUtils::zipTimeToTimespec(when, &t);
const time_t modTime = mktime(&t);
struct stat64 st;
if (!isFileDifferent(localFileName, uncompLen, modTime, crc, &st)) {
return INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
}
char localTmpFileName[nativeLibPath.size() + TMP_FILE_PATTERN_LEN + 2];
if (strlcpy(localTmpFileName, nativeLibPath.c_str(), sizeof(localTmpFileName))
!= nativeLibPath.size()) {
ALOGD("Couldn't allocate local file name for library");
return INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR;
}
*(localFileName + nativeLibPath.size()) = '/';
if (strlcpy(localTmpFileName + nativeLibPath.size(), TMP_FILE_PATTERN,
TMP_FILE_PATTERN_LEN - nativeLibPath.size()) != TMP_FILE_PATTERN_LEN) {
ALOGI("Couldn't allocate temporary file name for library");
return INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR;
}
// 生成了一个临时文件,用于拷贝
int fd = mkstemp(localTmpFileName);
if (fd < 0) {
ALOGI("Couldn't open temporary file name: %s: %s\n", localTmpFileName, strerror(errno));
return INSTALL_FAILED_CONTAINER_ERROR;
}
// 解压缩so文件
if (!zipFile->uncompressEntry(zipEntry, fd)) {
ALOGI("Failed uncompressing %s to %s\n", fileName, localTmpFileName);
close(fd);
unlink(localTmpFileName);
return INSTALL_FAILED_CONTAINER_ERROR;
}
close(fd);
// Set the modification time for this file to the ZIP's mod time.
struct timeval times[2];
times[0].tv_sec = st.st_atime;
times[1].tv_sec = modTime;
times[0].tv_usec = times[1].tv_usec = 0;
if (utimes(localTmpFileName, times) < 0) {
ALOGI("Couldn't change modification time on %s: %s\n", localTmpFileName, strerror(errno));
unlink(localTmpFileName);
return INSTALL_FAILED_CONTAINER_ERROR;
}
// Set the mode to 755
static const mode_t mode = S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IXUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IXGRP | S_IROTH | S_IXOTH;
if (chmod(localTmpFileName, mode) < 0) {
ALOGI("Couldn't change permissions on %s: %s\n", localTmpFileName, strerror(errno));
unlink(localTmpFileName);
return INSTALL_FAILED_CONTAINER_ERROR;
}
// Finally, rename it to the final name.
if (rename(localTmpFileName, localFileName) < 0) {
ALOGI("Couldn't rename %s to %s: %s\n", localTmpFileName, localFileName, strerror(errno));
unlink(localTmpFileName);
return INSTALL_FAILED_CONTAINER_ERROR;
}
ALOGV("Successfully moved %s to %s\n", localTmpFileName, localFileName);
return INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
}
上述就是解压缩so文件的实现。先判断so名字和不合法,然后判断是不是文件改变了, 然后创建一个临时文件,最后解压缩,用临时文件拷贝so到指定目录,结尾关闭一些链接。
至此 derivePackageAbi方法分析完毕
三、PackageManagerService#setNativeLibraryPaths(PackageParser.Package)方法分析
上面在derivePackageAbi方面会调用setNativeLibraryPaths方法,我们就简单的分析下这个方法
代码在PackageManagerService.java 7841 行
/**
* Derive and set the location of native libraries for the given package,
* which varies depending on where and how the package was installed.
*/
private void setNativeLibraryPaths(PackageParser.Package pkg) {
final ApplicationInfo info = pkg.applicationInfo;
final String codePath = pkg.codePath;
final File codeFile = new File(codePath);
final boolean bundledApp = info.isSystemApp() && !info.isUpdatedSystemApp();
final boolean asecApp = info.isForwardLocked() || info.isExternalAsec();
info.nativeLibraryRootDir = null;
info.nativeLibraryRootRequiresIsa = false;
info.nativeLibraryDir = null;
info.secondaryNativeLibraryDir = null;
// 判断是不是apk文件,其实就是判断文件是不是以.apk结尾
if (isApkFile(codeFile)) {
// Monolithic install
// 如果是系统相关的应用
if (bundledApp) {
// If "/system/lib64/apkname" exists, assume that is the per-package
// native library directory to use; otherwise use "/system/lib/apkname".
// 获取apk系统根目录的路径
final String apkRoot = calculateBundledApkRoot(info.sourceDir);
final boolean is64Bit = VMRuntime.is64BitInstructionSet(
getPrimaryInstructionSet(info));
// This is a bundled system app so choose the path based on the ABI.
// if it's a 64 bit abi, use lib64 otherwise use lib32. Note that this
// is just the default path.
final String apkName = deriveCodePathName(codePath);
final String libDir = is64Bit ? LIB64_DIR_NAME : LIB_DIR_NAME;
info.nativeLibraryRootDir = Environment.buildPath(new File(apkRoot), libDir,
apkName).getAbsolutePath();
if (info.secondaryCpuAbi != null) {
final String secondaryLibDir = is64Bit ? LIB_DIR_NAME : LIB64_DIR_NAME;
info.secondaryNativeLibraryDir = Environment.buildPath(new File(apkRoot),
secondaryLibDir, apkName).getAbsolutePath();
}
} else if (asecApp) {
// 如果是asec的App
info.nativeLibraryRootDir = new File(codeFile.getParentFile(), LIB_DIR_NAME)
.getAbsolutePath();
} else {
// 普通的App
final String apkName = deriveCodePathName(codePath);
// 在data/app-lib下简历一个apk目录
info.nativeLibraryRootDir = new File(mAppLib32InstallDir, apkName)
.getAbsolutePath();
}
info.nativeLibraryRootRequiresIsa = false;
info.nativeLibraryDir = info.nativeLibraryRootDir;
} else {
// Cluster install
// 如果是目录
info.nativeLibraryRootDir = new File(codeFile, LIB_DIR_NAME).getAbsolutePath();
info.nativeLibraryRootRequiresIsa = true;
// 目录下直接创建一个lib目录
info.nativeLibraryDir = new File(info.nativeLibraryRootDir,
getPrimaryInstructionSet(info)).getAbsolutePath();
if (info.secondaryCpuAbi != null) {
info.secondaryNativeLibraryDir = new File(info.nativeLibraryRootDir,
VMRuntime.getInstructionSet(info.secondaryCpuAbi)).getAbsolutePath();
}
}
}
这个方法就是确定lib库最终的目录,我们看下逻辑,这里分几种情况
- 是APK文件
- 系统相关应用,先判断是不是64位
- 是64位:/system/lib64/apkname
- 不是64位:/system/lib/apkname- ASEC应用:父目录/lib/apkname
- 普通应用:在data/app-lib目录下创建apk目录
- 不是APK文件:直接在当前目录下创建一个lib目录
这个方法里面有一个比较重要的方法calculateBundledApkRoot获取系统应用的根目录
1、calculateBundledApkRoot(String) 方法解析
代码在PackageManagerService.java 7805 行
private static String calculateBundledApkRoot(final String codePathString) {
final File codePath = new File(codePathString);
final File codeRoot;
if (FileUtils.contains(Environment.getRootDirectory(), codePath)) {
codeRoot = Environment.getRootDirectory();
} else if (FileUtils.contains(Environment.getOemDirectory(), codePath)) {
codeRoot = Environment.getOemDirectory();
} else if (FileUtils.contains(Environment.getVendorDirectory(), codePath)) {
codeRoot = Environment.getVendorDirectory();
} else {
// Unrecognized code path; take its top real segment as the apk root:
// e.g. /something/app/blah.apk => /something
try {
File f = codePath.getCanonicalFile();
File parent = f.getParentFile(); // non-null because codePath is a file
File tmp;
while ((tmp = parent.getParentFile()) != null) {
f = parent;
parent = tmp;
}
codeRoot = f;
Slog.w(TAG, "Unrecognized code path "
+ codePath + " - using " + codeRoot);
} catch (IOException e) {
// Can't canonicalize the code path -- shenanigans?
Slog.w(TAG, "Can't canonicalize code path " + codePath);
return Environment.getRootDirectory().getPath();
}
}
return codeRoot.getPath();
}
这个方法其实就是获取相应的目录,主要分为4种情况
- 1、如果是system目录,则返回system目录
- 2、如果是oem目录,则返回oem目录
- 3、如果是vendor目录,则返回vendor
- 4、无法识别的目录则获取其根目录
上一篇文章 APK安装流程详解3——PackageManager与PackageManagerService
下一篇文章 APK安装流程详解5——PackageInstallerService和Installer