场景
在某些场合使用ScrollView去嵌套ListView的时候,ListView会只显示第一个item。
解决办法网上有很多,这篇文章主要从源码角度分析下这个现象产生的原因和解决办法的原理。
分析
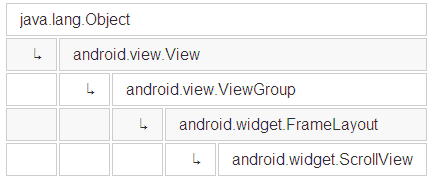
先看下ScrollView关系图:
ScrollView继承自FrameLayout且在onMeasure()调用了父类的onMeasure方法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
//调用父类FrameLayout的onMeasure方法
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//mFillViewport的默认值为false,所以默认以下方法会return
if (!mFillViewport) {
return;
}
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
return;
}
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
final View child = getChildAt(0);
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
if (child.getMeasuredHeight() < height) {
final FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
height -= mPaddingTop;
height -= mPaddingBottom;
int childHeightMeasureSpec =
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
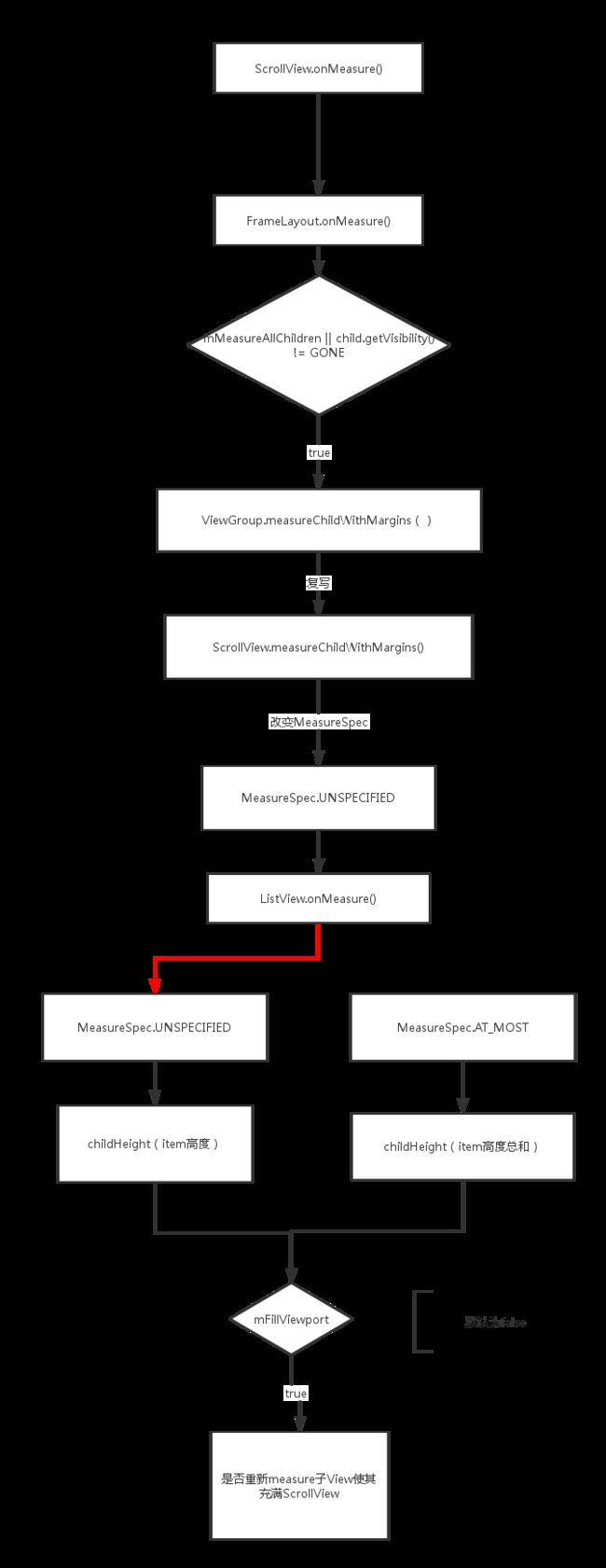
ScrollView首先会调用FrameLayout的onMeasure()方法,当为mFillViewport为true时后续代码才会继续执行,会根据子View的高度和ScrollView本身的高度决定是否重新measure子View使其充满ScrollView。而ScrollView的mFillViewport默认值为false,所以默认情况下ScrollView的onMeasure()基本类似于父类的FrameLayout。
再来追踪下FrameLayout的onMeasure方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(getMeasuredWidth() -
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground() -
lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(getMeasuredHeight() -
getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground() -
lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
FrameLayout的onMeasure()方法有点长,影响ListView的measure的代码主要在for循环内的代码。
//measure Child的Margins
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
继续追踪下measureChildWithMargins()方法:
/**
* Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into
* account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding
* and margins. The child must have MarginLayoutParams The heavy lifting is
* done in getChildMeasureSpec.
*
* @param child The child to measure
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view
* @param widthUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* horizontally (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view
* @param heightUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* vertically (possibly by other children of the parent)
*/
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
在对childView进行measure时会根据childView的child的margin值和heightUsed重新计算childHeightMeasureSpec ,来完成对child的measure。这个就是ViewGroup对childView的measure。而在ScrollView中重写了measureChildWithMargins()方法,measure方法有点不同。
@Override
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin+ widthUsed, lp.width);
//改变childView的measureMode
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
从代码中可以清晰的看到,不管childView是什么模式的measureMode,都会被外层包裹的ScrollView改变成MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED。而这就是导致我们嵌套的ListView为什么只能展示1个item的源头。
接着分析下ListView的onMeasure()方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// Sets up mListPadding
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int childWidth = 0;
int childHeight = 0;
int childState = 0;
mItemCount = mAdapter == null ? 0 : mAdapter.getCount();
if (mItemCount > 0 && (widthMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED ||
heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)) {
final View child = obtainView(0, mIsScrap);
measureScrapChild(child, 0, widthMeasureSpec);
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (recycleOnMeasure() && mRecycler.shouldRecycleViewType(
((LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).viewType)) {
mRecycler.addScrapView(child, 0);
}
}
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
widthSize = mListPadding.left + mListPadding.right + childWidth +
getVerticalScrollbarWidth();
} else {
widthSize |= (childState&MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
heightSize = mListPadding.top + mListPadding.bottom + childHeight +
getVerticalFadingEdgeLength() * 2;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// TODO: after first layout we should maybe start at the first visible position, not 0
heightSize = measureHeightOfChildren(widthMeasureSpec, 0, NO_POSITION, heightSize, -1);
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize , heightSize);
mWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
}
从上述的分析得知这里的heightMeasureSpec里面的measureMode 已经被ScrollView强制改为了MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED,
所以这里的heightMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED。
就会这些下面这个if语句
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
heightSize = mListPadding.top + mListPadding.bottom + childHeight +
getVerticalFadingEdgeLength() * 2;
}
所以我们的嵌套ListView的height就是ListView在垂直高度上的padding和child(也就是我们的item)的高度。
大致流程如下:
解决办法
1.自定义ListView填充全部的item
网上一种解决办法是自定义一个ListView去继承原生的ListView,并复写onMeasure()方法。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int expandSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Integer.MAX_VALUE >> 2,
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, expandSpec);
}
从代码中可以看出,主要是手动改变ListView的heightMeasureSpec。从上面ListView的onMeasure()源码中,可以看到ListView除了对 MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED 这种情况外还对 MeasureSpec.AT_MOST 做了特殊处理。而这个自定义的ListView便是将ListView的heightMeasureSpecMode强制改为 MeasureSpec.AT_MOST ,并把 int 的最大值作为heightMeasureSpecSize。
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// TODO: after first layout we should maybe start at the first visible position, not 0
heightSize = measureHeightOfChildren(widthMeasureSpec, 0, NO_POSITION, heightSize, -1);
}
再来跟进下ListView中的measureHeightOfChildren()方法。截取其中一段代码
for (i = startPosition; i <= endPosition; ++i) {
child = obtainView(i, isScrap);
measureScrapChild(child, i, widthMeasureSpec);
if (i > 0) {
// Count the divider for all but one child
returnedHeight += dividerHeight;
}
// Recycle the view before we possibly return from the method
if (recyle && recycleBin.shouldRecycleViewType(
((LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).viewType)) {
recycleBin.addScrapView(child, -1);
}
returnedHeight += child.getMeasuredHeight();
if (returnedHeight >= maxHeight) {
// We went over, figure out which height to return. If returnedHeight > maxHeight,
// then the i'th position did not fit completely.
return (disallowPartialChildPosition >= 0) // Disallowing is enabled (> -1)
&& (i > disallowPartialChildPosition) // We've past the min pos
&& (prevHeightWithoutPartialChild > 0) // We have a prev height
&& (returnedHeight != maxHeight) // i'th child did not fit completely
? prevHeightWithoutPartialChild
: maxHeight;
}
ListView会遍历所有的item,returnedHeight 会累加所有的 dividerHeight 和 child(也就是item)的高度。如果 returnedHeight >= maxHeight 就会跳出循环,而这个 maxHeight 就是我们自定义ListView中的onMeasure()方法中传入的 heightMeasureSpec的heightMeasureSpecSize(int的最大值)。所以这个for循环就能顺利遍历完全部的item。运行效果就如下:
2.添加ScrollView属性
在本文最前面曾提到过,ScrollView中有个mFillViewpor的变量。当为true时才会继续执行ScrollView自己的measure方法,会根据子View的高度和ScrollView本身的高度决定是否重新measure子View使其充满ScrollView。有以下几种方法可以设置该值。
/**
* Indicates this ScrollView whether it should stretch its content height to fill
* the viewport or not.
*
* @param fillViewport True to stretch the content's height to the viewport's
* boundaries, false otherwise.
*
* @attr ref android.R.styleable#ScrollView_fillViewport
*/
public void setFillViewport(boolean fillViewport) {
if (fillViewport != mFillViewport) {
mFillViewport = fillViewport;
requestLayout();
}
}
以及在layout文件中设置属性
/**
* When set to true, the scroll view measure its child to make it fill the currently
* visible area.
*/
@ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(category = "layout")
private boolean mFillViewport;
只需要给ScrillView在Layout文件中添加属性 android:fillViewport="true" ,或者在java文件中设置 mScrollView.setFillViewport(true); 。
3.事件分发
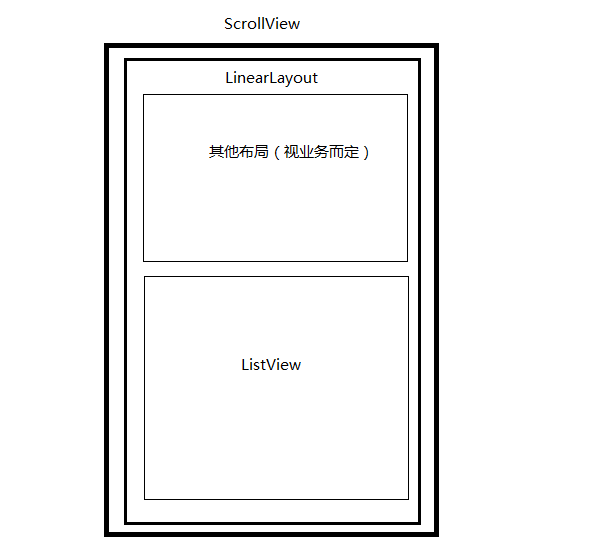
一般情况下不会在ScrollView中直接去嵌套一个ListView。如果在ScrollView中嵌套一个LinearLayout去实现一些业务布局,LinearLayout里面再去嵌套一个ListView,我们可以去手动处理其中的事件分发了。如果是类似于一下布局形式的需要注意一些设置了。
这里分2种情况:1是ListView扩充全部item,2是ListView显示一定的高度,仍然处于平时的滑动状态。
第一种情况的做法已经在上述说明过了,这里讲解下第二种情况。
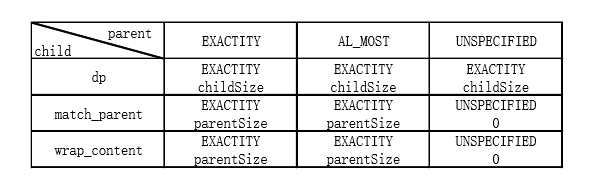
在这里需要注意的是ListView的高度不能使用match_parent属性来填充LinearLayout的剩余高度。ScrollView会将LinearLayout的heightMeasureSpecMode改变为MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED。如果ListView没有设置精确的dp的话,heightMeasureSpecMode会遵循parentSize也就是MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED。
遵循规则如下