一,HTTP请求、响应报文格式
要弄明白网络框架,首先需要先掌握Http请求的,响应的报文格式。
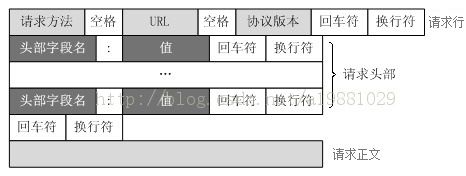
HTTP请求报文格式:
HTTP请求报文主要由请求行、请求头部、请求正文3部分组成.
- 请求行:由请求方法,URL,协议版本三部分构成,之间用空格隔开
请求方法包括:POST、GET、HEAD、PUT、POST、TRACE、OPTIONS、DELETE等
协议版本:HTTP/主版本号.次版本号,常用的有HTTP/1.0和HTTP/1.1
- 请求头部:
请求头部为请求报文添加了一些附加信息,由“名/值”对组成,每行一对,名和值之间使用冒号分隔
常见请求头如下:
Host ----接受请求的服务器地址,可以是IP:端口号,也可以是域名
User-Agent ----发送请求的应用程序名称
Connection ---- 指定与连接相关的属性,如Connection:Keep-Alive
Accept-Charset ---- 通知服务端可以发送的编码格式
Accept-Encoding ---- 通知服务端可以发送的数据压缩格式
Accept-Language ---- 通知服务端可以发送的语言 - 请求正文
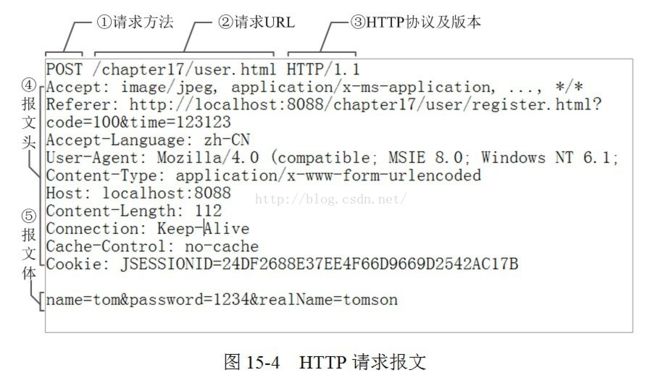
可选部分,比如GET请求就没有请求正文 - 请求示例:
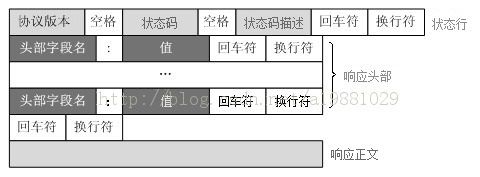
HTTP响应报文格式:
HTTP响应报文主要由状态行、响应头部、响应正文3部分组成
-
状态行:
由3部分组成,分别为:协议版本,状态码,状态码描述,之间由空格分隔
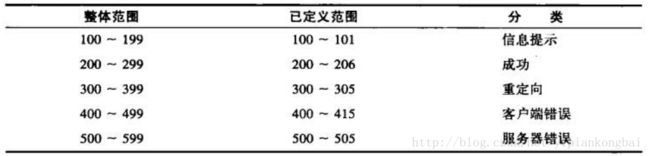
状态码:为3位数字,200-299的状态码表示成功,300-399的状态码指资源重定向,400-499的状态码指客户端请求出错,500-599的状态码指服务端出错(HTTP/1.1向协议中引入了信息性状态码,范围为100-199)
常见的:
200:响应成功
302:重定向跳转,跳转地址通过响应头中的Location属性指定
400:客户端请求有语法错误,参数错误,不能被服务器识别
403:服务器接收到请求,但是拒绝提供服务(认证失败)
404:请求资源不存在
500:服务器内部错误
响应头部 :
与请求头部类似,为响应报文添加了一些附加信息
Server - 服务器应用程序软件的名称和版本
Content-Type - 响应正文的类型(是图片还是二进制字符串)
Content-Length - 响应正文长度
Content-Charset - 响应正文使用的编码
Content-Encoding - 响应正文使用的数据压缩格式
Content-Language - 响应正文使用的语言
Server: bfe/1.0.8.1
Date: Sat, 04 Apr 2015 02:49:41 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Vary: Accept-Encoding
Cache-Control: private
cxy_all: baidu+8ee3da625d74d1aa1ac9a7c34a2191dc
Expires: Sat, 04 Apr 2015 02:49:38 GMT
X-Powered-By: HPHP
bdpagetype: 1
bdqid: 0xb4eababa0002db6e
bduserid: 0
Set-Cookie: BDSVRTM=0; path=/
BD_HOME=0; path=/
H_PS_PSSID=13165_12942_1430_13075_12867_13322_12691_13348_12723_12797_13309_13325_13203_13161_13256_8498; path=/; domain=.baidu.com
__bsi=18221750326646863206_31_0_I_R_2_0303_C02F_N_I_I; expires=Sat, 04-Apr-15 02:49:46 GMT; domain=www.baidu.com; path=/
Content-Encoding: gzip
X-Firefox-Spdy: 3.1
- 响应正文
是请求响应的最终结果,都在响应体里。
报文可以承载很多类型的数字数据:图片、视频、HTML文档、软件应用程序等 - 响应示例
二,HTTP请求和响应的基本使用
主要包含:
- 一般的get请求
- 一般的post请求
- 基于Http的文件上传
- 文件下载
- 加载图片
- 支持请求回调,直接返回对象、对象集合
- 支持session的保持
- 添加网络访问权限并添加库依赖
- HTTP的GET请求
//1,创建okHttpClient对象
OkHttpClient mOkHttpClient = new OkHttpClient();
//2,创建一个Request
final Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://www.baidu.com")
.build();
//3,新建一个call对象
Call call = mOkHttpClient.newCall(request);
//4,请求加入调度,这里是异步Get请求回调
call.enqueue(new Callback()
{
@Override
public void onFailure(Request request, IOException e)
{
}
@Override
public void onResponse(final Response response) throws IOException
{
//String htmlStr = response.body().string();
}
});
对以上的简单请求的构成:
- 发送一个GET请求的步骤,首先构造一个Request对象,参数最起码有个URL,当然也可以通过Request.Builder设置更多的参数比如:header、method等。
//URL带的参数
HashMap params = new HashMap<>();
//GET 请求带的Header
HashMap headers= new HashMap<>();
//HttpUrl.Builder构造带参数url
HttpUrl.Builder urlBuilder = HttpUrl.parse(url).newBuilder();
if (params != null) {
for (String key : params.keySet()) {
urlBuilder.setQueryParameter(key, params.get(key));
}
}
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(urlBuilder.build())
.headers(headers == null ? new Headers.Builder().build() : Headers.of(headers))
.get()
.build();
- 通过Request的对象去构造得到一个Call对象,类似于将你的请求封装成了任务,既然是任务,就会有execute(),enqueue()和cancel()等方法。
execute():同步GET请求
//同步
Response response = call.execute()
if(response.isSuccessful()){
//响应成功
}
enqueue():异步GET请求,将call加入调度队列,然后等待任务执行完成,我们在Callback中即可得到结果。
cancel():Call请求的取消,okHttp支持请求取消功能,当调用请求的cancel()时,请求就会被取消,抛出异常。又是需要监控许多Http请求的执行情况,可以把这些请求的Call搜集起来,执行完毕自动剔除,如果在请求执行过程中(如下载),想取消执行,可使用call.cancel()取消。
- 请求的响应Response
对于同步GET请求,Response对象是直接返回的。异步GET请求,通过onResponse回调方法传参数,需要注意的是这个onResponse回调方法不是在主线程回调,可以使用runInUIThread(new Runnable(){})。
我们希望获得返回的字符串,可以通过response.body().string()获取;
如果希望获得返回的二进制字节数组,则调用response.body().bytes();
如果你想拿到返回的inputStream,则调用response.body().byteStream()
3. HTTP的POST请求
看来上面的简单的get请求,基本上整个的用法也就掌握了,比如post携带参数,也仅仅是Request的构造的不同。
//POST参数构造MultipartBody.Builder,表单提交
HashMap params = new HashMap<>();
MultipartBody.Builder urlBuilder = new MultipartBody.Builder()
.setType(MultipartBody.FORM);
if (params != null) {
for (String key : params.keySet()) {
if (params.get(key)!=null){
urlBuilder.addFormDataPart(key, params.get(key));
}
//urlBuilder.addFormDataPart(key, params.get(key));
}
}
// 构造Request->call->执行
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.headers(extraHeaders == null ? new Headers.Builder().build() : Headers.of(extraHeaders))//extraHeaders 是用户添加头
.url(url)
.post(urlBuilder.build())//参数放在body体里
.build();
Call call = httpClient.newCall(request);
try (Response response = call.execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful()){
//响应成功
}
}
Post的时候,参数是包含在请求体中的,所以我们通过MultipartBody.Builder 添加多个String键值对,然后去构造RequestBody,最后完成我们Request的构造。
4. OKHTTP的上传文件
上传文件本身也是一个POST请求。在上面的POST请求中可以知道,POST请求的所有参数都是在BODY体中的,我们看看请求体的源码RequestBody:请求体=contentType + BufferedSink
RequestBody
//抽象类请求体,**请求体=contentType + BufferedSink**
public abstract class RequestBody {
/** Returns the Content-Type header for this body. */
//返回Body体的内容类型
public abstract @Nullable MediaType contentType();
/**
* Returns the number of bytes that will be written to {@code sink} in a call to {@link #writeTo},
* or -1 if that count is unknown.
*/
//返回写入sink的字节长度
public long contentLength() throws IOException {
return -1;
}
/** Writes the content of this request to {@code sink}. */
//写入缓存sink
public abstract void writeTo(BufferedSink sink) throws IOException;
/**
* Returns a new request body that transmits {@code content}. If {@code contentType} is non-null
* and lacks a charset, this will use UTF-8.
*/
//创建一个请求体,如果contentType不等于null且缺少字符集,将使用UTF-8
public static RequestBody create(@Nullable MediaType contentType, String content) {
Charset charset = Util.UTF_8;
if (contentType != null) {
//contentType里面的字符集
charset = contentType.charset();
if (charset == null) {
charset = Util.UTF_8;
//contentType 里面加入字符集
contentType = MediaType.parse(contentType + "; charset=utf-8");
}
}
//按字符集变成字节
byte[] bytes = content.getBytes(charset);
return create(contentType, bytes);
}
/** Returns a new request body that transmits {@code content}. */
//创建新的请求体,传输字节
public static RequestBody create(
final @Nullable MediaType contentType, final ByteString content) {
return new RequestBody() {
@Override public @Nullable MediaType contentType() {
//请求体需要的内容类型
return contentType;
}
@Override public long contentLength() throws IOException {
//写入BufferedSink 的长度
return content.size();
}
@Override public void writeTo(BufferedSink sink) throws IOException {
//将需要传输的字节,写入缓存BufferedSink 中
sink.write(content);
}
};
}
/** Returns a new request body that transmits {@code content}. */
public static RequestBody create(final @Nullable MediaType contentType, final byte[] content) {
return create(contentType, content, 0, content.length);
}
/** Returns a new request body that transmits {@code content}. */
public static RequestBody create(final @Nullable MediaType contentType, final byte[] content,
final int offset, final int byteCount) {
if (content == null) throw new NullPointerException("content == null");
Util.checkOffsetAndCount(content.length, offset, byteCount);
return new RequestBody() {
@Override public @Nullable MediaType contentType() {
return contentType;
}
@Override public long contentLength() {
return byteCount;
}
@Override public void writeTo(BufferedSink sink) throws IOException {
sink.write(content, offset, byteCount);
}
};
}
/** Returns a new request body that transmits the content of {@code file}. */
//创建一个请求体,传输文件file内容,其实就是file写入bufferedSink
public static RequestBody create(final @Nullable MediaType contentType, final File file) {
if (file == null) throw new NullPointerException("content == null");
return new RequestBody() {
@Override public @Nullable MediaType contentType() {
return contentType;
}
@Override public long contentLength() {
return file.length();
}
@Override public void writeTo(BufferedSink sink) throws IOException {
Source source = null;
try {
//文件写入BufferedSink
source = Okio.source(file);
sink.writeAll(source);
} finally {
Util.closeQuietly(source);
}
}
};
}
}
Http请求中Content-Type
客户端在进行http请求服务器的时候,需要告诉服务器请求的类型,服务器在返回给客户端的数据的时候,也需要告诉客户端返回数据的类型
默认的ContentType为 text/html 也就是网页格式. 常用的内容类型
- text/plain :纯文本格式 .txt
- text/xml : XML格式 .xml
- image/gif :gif图片格式 .gif
- image/jpeg :jpg图片格式 .jpg
- image/png:png图片格式 .png
- audio/mp3 : 音频mp3格式 .mp3
- audio/rn-mpeg :音频mpga格式 .mpga
- video/mpeg4 : 视频mp4格式 .mp4
- video/x-mpg : 视频mpa格式 .mpg
- video/x-mpeg :视频mpeg格式 .mpeg
- video/mpg : 视频mpg格式 .mpg
以application开头的媒体格式类型: - application/xhtml+xml :XHTML格式
- application/xml : XML数据格式
- application/atom+xml :Atom XML聚合格式
- application/json : JSON数据格式
- application/pdf :pdf格式
- application/msword : Word文档格式
- application/octet-stream : 二进制流数据(如常见的文件下载)
MultipartBody.Builder 添加多个String键值对
//MultipartBody源码,MultipartBody其实也是RequestBody ,需要在此RequestBody 体内,添加多个Part
/** An RFC 2387-compliant request body. */
public final class MultipartBody extends RequestBody {
/**
* The "mixed" subtype of "multipart" is intended for use when the body parts are independent and
* need to be bundled in a particular order. Any "multipart" subtypes that an implementation does
* not recognize must be treated as being of subtype "mixed".
*/
//混合的内容类型
public static final MediaType MIXED = MediaType.parse("multipart/mixed");
/**
* The "multipart/alternative" type is syntactically identical to "multipart/mixed", but the
* semantics are different. In particular, each of the body parts is an "alternative" version of
* the same information.
*/
public static final MediaType ALTERNATIVE = MediaType.parse("multipart/alternative");
/**
* This type is syntactically identical to "multipart/mixed", but the semantics are different. In
* particular, in a digest, the default {@code Content-Type} value for a body part is changed from
* "text/plain" to "message/rfc822".
*/
public static final MediaType DIGEST = MediaType.parse("multipart/digest");
/**
* This type is syntactically identical to "multipart/mixed", but the semantics are different. In
* particular, in a parallel entity, the order of body parts is not significant.
*/
public static final MediaType PARALLEL = MediaType.parse("multipart/parallel");
/**
* The media-type multipart/form-data follows the rules of all multipart MIME data streams as
* outlined in RFC 2046. In forms, there are a series of fields to be supplied by the user who
* fills out the form. Each field has a name. Within a given form, the names are unique.
*/
public static final MediaType FORM = MediaType.parse("multipart/form-data");
private static final byte[] COLONSPACE = {':', ' '};
private static final byte[] CRLF = {'\r', '\n'};
private static final byte[] DASHDASH = {'-', '-'};
private final ByteString boundary;
private final MediaType originalType;
//请求体的内容类型
private final MediaType contentType;
//MultiPartBody需要添加多个Part对象,一起请求
private final List parts;
private long contentLength = -1L;
//构造函数
MultipartBody(ByteString boundary, MediaType type, List parts) {
this.boundary = boundary;
this.originalType = type;
this.contentType = MediaType.parse(type + "; boundary=" + boundary.utf8());
this.parts = Util.immutableList(parts);
}
public MediaType type() {
return originalType;
}
public String boundary() {
return boundary.utf8();
}
/** The number of parts in this multipart body. */
//multipart 的数量
public int size() {
return parts.size();
}
//多个parts
public List parts() {
return parts;
}
public Part part(int index) {
return parts.get(index);
}
/** A combination of {@link #type()} and {@link #boundary()}. */
//MultiPart的内容类型
@Override public MediaType contentType() {
return contentType;
}
@Override public long contentLength() throws IOException {
long result = contentLength;
if (result != -1L) return result;
return contentLength = writeOrCountBytes(null, true);
}
//将每个part写入BufferedSink中,传输
@Override public void writeTo(BufferedSink sink) throws IOException {
writeOrCountBytes(sink, false);
}
/**
* Either writes this request to {@code sink} or measures its content length. We have one method
* do double-duty to make sure the counting and content are consistent, particularly when it comes
* to awkward operations like measuring the encoded length of header strings, or the
* length-in-digits of an encoded integer.
*/
//将每个Part的内容都写入,MultiPartBody的BufferedSink 中
private long writeOrCountBytes(@Nullable BufferedSink sink, boolean countBytes) throws IOException {
long byteCount = 0L;
Buffer byteCountBuffer = null;
if (countBytes) {
sink = byteCountBuffer = new Buffer();
}
//写每个part
for (int p = 0, partCount = parts.size(); p < partCount; p++) {
Part part = parts.get(p);
//Part的Headers和RequestBody
Headers headers = part.headers;
RequestBody body = part.body;
sink.write(DASHDASH);
sink.write(boundary);
sink.write(CRLF);
//Part的Headers写入sink
if (headers != null) {
for (int h = 0, headerCount = headers.size(); h < headerCount; h++) {
sink.writeUtf8(headers.name(h))
.write(COLONSPACE)
.writeUtf8(headers.value(h))
.write(CRLF);
}
}
//Part的RequestBody写入Part
//1,写contentType
MediaType contentType = body.contentType();
if (contentType != null) {
sink.writeUtf8("Content-Type: ")
.writeUtf8(contentType.toString())
.write(CRLF);
}
//2,写contentLength
long contentLength = body.contentLength();
if (contentLength != -1) {
sink.writeUtf8("Content-Length: ")
.writeDecimalLong(contentLength)
.write(CRLF);
} else if (countBytes) {
// We can't measure the body's size without the sizes of its components.
byteCountBuffer.clear();
return -1L;
}
sink.write(CRLF);
//3,写body体
if (countBytes) {
byteCount += contentLength;
} else {
body.writeTo(sink);
}
sink.write(CRLF);
}
sink.write(DASHDASH);
sink.write(boundary);
sink.write(DASHDASH);
sink.write(CRLF);
if (countBytes) {
byteCount += byteCountBuffer.size();
byteCountBuffer.clear();
}
return byteCount;
}
/**
* Appends a quoted-string to a StringBuilder.
*
* RFC 2388 is rather vague about how one should escape special characters in form-data
* parameters, and as it turns out Firefox and Chrome actually do rather different things, and
* both say in their comments that they're not really sure what the right approach is. We go with
* Chrome's behavior (which also experimentally seems to match what IE does), but if you actually
* want to have a good chance of things working, please avoid double-quotes, newlines, percent
* signs, and the like in your field names.
*/
//装换换行符,tab符号,引号
static StringBuilder appendQuotedString(StringBuilder target, String key) {
target.append('"');
for (int i = 0, len = key.length(); i < len; i++) {
char ch = key.charAt(i);
switch (ch) {
case '\n':
target.append("%0A");
break;
case '\r':
target.append("%0D");
break;
case '"':
target.append("%22");
break;
default:
target.append(ch);
break;
}
}
target.append('"');
return target;
}
//Part 的定义,Part 是由Headers+RequestBody组成
public static final class Part {
public static Part create(RequestBody body) {
return create(null, body);
}
public static Part create(@Nullable Headers headers, RequestBody body) {
if (body == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("body == null");
}
//Part的headers不能存在Content-Type和Content-Length字段
if (headers != null && headers.get("Content-Type") != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unexpected header: Content-Type");
}
if (headers != null && headers.get("Content-Length") != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unexpected header: Content-Length");
}
return new Part(headers, body);
}
//创建key-value的Part,name其实就是key
public static Part createFormData(String name, String value) {
return createFormData(name, null, RequestBody.create(null, value));
}
//创建key-value的Part
public static Part createFormData(String name, @Nullable String filename, RequestBody body) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name == null");
}
StringBuilder disposition = new StringBuilder("form-data; name=");
// disposition = form-data; name=name;
appendQuotedString(disposition, name);//对name中的特殊符号转换
if (filename != null) {
disposition.append("; filename=");
// disposition = form-data; name=name; filename=filename;
appendQuotedString(disposition, filename);//对filename中的特殊符号转换
}
//创建Part 体,Headers(Content-Disposition- form-data; name=name; filename=filename)+body
return create(Headers.of("Content-Disposition", disposition.toString()), body);
}
//headers
final @Nullable Headers headers;
//body
final RequestBody body;
private Part(@Nullable Headers headers, RequestBody body) {
this.headers = headers;
this.body = body;
}
//Part的headers
public @Nullable Headers headers() {
return headers;
}
//Part的body体
public RequestBody body() {
return body;
}
}
public static final class Builder {
private final ByteString boundary;
private MediaType type = MIXED;
private final List parts = new ArrayList<>();
public Builder() {
this(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
public Builder(String boundary) {
this.boundary = ByteString.encodeUtf8(boundary);
}
/**
* Set the MIME type. Expected values for {@code type} are {@link #MIXED} (the default), {@link
* #ALTERNATIVE}, {@link #DIGEST}, {@link #PARALLEL} and {@link #FORM}.
*/
public Builder setType(MediaType type) {
if (type == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("type == null");
}
if (!type.type().equals("multipart")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("multipart != " + type);
}
this.type = type;
return this;
}
/** Add a part to the body. */
//添加Part
public Builder addPart(RequestBody body) {
return addPart(Part.create(body));
}
/** Add a part to the body. */
//添加Part
public Builder addPart(@Nullable Headers headers, RequestBody body) {
return addPart(Part.create(headers, body));
}
/** Add a form data part to the body. */
//添加表单数据Part
public Builder addFormDataPart(String name, String value) {
return addPart(Part.createFormData(name, value));
}
/** Add a form data part to the body. */
//添加表单数据Part
public Builder addFormDataPart(String name, @Nullable String filename, RequestBody body) {
return addPart(Part.createFormData(name, filename, body));
}
/** Add a part to the body. */
public Builder addPart(Part part) {
if (part == null) throw new NullPointerException("part == null");
parts.add(part);
return this;
}
/** Assemble the specified parts into a request body. */
public MultipartBody build() {
if (parts.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Multipart body must have at least one part.");
}
//构建MultipartBody对象
return new MultipartBody(boundary, type, parts);
}
}
}
总结一下MultipartBody:
- MultipartBody本质一个是一个RequestBody,具有自己的contentType+BufferedSink,是POST请求的最外层封装,需要添加多个Part
- Part对象组成:Headers+RequestBody。是MultipartBody的成员变量,需要写入MultipartBody的BufferedSink中。
HTTP真正的上传文件
- 最基本的上传文件:
重点:RequestBody create(MediaType contentType, final File file)构造文件请求体RequestBody ,并且添加到MultiPartBody中
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
// form 表单形式上传,MultipartBody的内容类型是表单格式,multipart/form-data
MultipartBody.Builder urlBuilder= new MultipartBody.Builder().setType(MultipartBody.FORM);
//参数
HashMap params = new HashMap<>();
if (params != null) {
for (String key : params.keySet()) {
if (params.get(key)!=null){
urlBuilder.addFormDataPart(key, params.get(key));
}
}
}
//需要上传的文件,需要携带上传的文件(小型文件 不建议超过500K)
HashMap files= new HashMap<>();
if (files != null) {
for (String key : files.keySet()) {
//重点:RequestBody create(MediaType contentType, final File file)构造文件请求体RequestBody
urlBuilder.addFormDataPart(key, files.get(key).getName(), RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("multipart/form-data"), files.get(key)));
}
}
//构造请求request
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.headers(extraHeaders == null ? new Headers.Builder().build() : Headers.of(extraHeaders))
.url(url)
.post(urlBuilder.build())
.build();
//异步执行请求
newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
Log.i("lfq" ,"onFailure");
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
//非主线程
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
String str = response.body().string();
Log.i("tk", response.message() + " , body " + str);
} else {
Log.i("tk" ,response.message() + " error : body " + response.body().string());
}
}
});
2. 大文件分块异步上传
我们知道Post上传文件,简单的说就是将文件file封装成RequestBody体,然后添加到MultiPartBody的addPart中构造MultiPartBody所需要的Part对象(Headers+body),RequestBody是个抽象类,里面的所有create方法如下:
可以看出,基本都是重写了抽象类的RequestBody的三种方法,所以我们也可以继承实现自己的Body体:
EG:已上传相机图片(5M)为例, 分块多线程异步同时上传,但是这种方法需要服务端接口才行。
//文件路径
String path = "xxx.jpg";
1,文件块对象
public static final int FILE_BLOCK_SIZE = 500 * 1024;//500k
/*文件块描述*/
public static class FileBlock {
public long start;//起始字节位置
public long end;//结束字节位置
public int index;//文件分块索引
}
2,文件切块
//计算切块,存储在数组
final SparseArray blockArray = splitFile(path, FILE_BLOCK_SIZE);
/**
* 文件分块
*
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @param blockSize 块大小
*
* @return 分块描述集合 文件不存在时返回空
*/
public static SparseArray splitFile(String filePath, long blockSize) {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
return null;
}
SparseArray blockArray = new SparseArray<>();
int i = 0;
int start = 0;
while (start < file.length()) {
i++;
FileBlock fileBlock = new FileBlock();
fileBlock.index = i;
fileBlock.start = start;
start += blockSize;
fileBlock.end = start;
blockArray.put(i, fileBlock);
}
blockArray.get(i).end = file.length();
return blockArray;
}
3,对文件块分块多线程异步上传
服务端的接口:
url:domain/sync/img/upload
method: POST
//请求参数
data = {
'img_md5': 'dddddsds',
'total': 10, #总的分片数
'index': 5, #该分片所在的位置, start by 1
}
请求返回值json:
{
'status': 206/205/400/409/500,
'msg': '分片上传成功/上传图片成功/参数错误/上传数据重复/上传失败'
'data': { # 205时有此字段
'img_url': 'https://foo.jpg',
}
}
只需要图片的md5,总的分片数,该分片的位置,当一块传输成功时返回206,当全部块传完成是返回206,并返回该图片在服务器的url
服务端接口返回解析类:
/**
* 分片上传部分的接口返回
*
* @link {http://10.16.69.11:5000/iSync/iSync%E6%9C%8D%E5%8A%A1%E7%AB%AFv4%E6%96%87%E6%A1%A3/index.html#4_1}
*/
public static class ChuckUploadData implements Serializable {
public ChuckUploadBean data;
public static class ChuckUploadBean implements Serializable{
public String img_url;
}
/** 此块是否上传成功 */
public boolean isPicSuccess() {
return status == 206 || status == 409;
}
/** 全部原图是否上传成功 */
public boolean isAllPicSuccess() {
return status == 205;
}
public boolean isRepitition(){
return status == 409;
}
}
//上传图片的线程池
ExcutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//上传函数
/**
* 上传原图,异步上传
*
* @param httpCallback 回调接口
* @param md5 文件md5
* @param path 图片路径
* @param total 总块数
* @param index 分块索引
* @param start 分块开始位置
* @param end 分块结束位置
*/
public static void uploadBigImage(String userId, final HttpListenerAdapter httpCallback, String md5, String path, int total, int index, long start, long end) {
HashMap params = new HashMap();
params.put("img_uuid", uuid);//完整文件的md5
params.put("total", String.valueOf(total));//总的分片数
params.put("index", String.valueOf(index));//当前分片位置,从1开始
//全局单例OKHttpClient
OkHttpClient httpClient = DataProvider.getInstance().inkApi.getLongWaitHttpClient();
Runnable httpUploadRunnable = HttpRunnableFactory.newPostFileBlockRunnable(
httpClient,
upload_url,//上传url,自定义
null,
params,//上传参数
"image",
new File(path),//图片文件
start,//index块开始的位置
end,//index块结束的位置
ChuckUploadData.class,
httpCallback);//回调函数
threadManager.submit httpUploadRunnable );
}
/**
* 异步post请求 表单方式拆块上传大型文件用,构造Runnable
*
* @param httpClient okhttp客户端
* @param url 请求地址
* @param headers 额外添加的header(通用header由中断器统一添加)
* @param params 请求参数
* @param fileKey 文件的接收用key
* @param file 大型文件对象
* @param seekStart 起始字节
* @param seekEnd 结束字节
* @param cls 返回结果需要序列化的类型
* @param listener 异步回调
* @param 返回结果需要序列化的类型声明
*
* @return 异步post请求用的默认Runnable
*/
public static Runnable newPostFileBlockRunnable(final OkHttpClient httpClient, final String url, final Map headers, final Map params, final String fileKey, final File file, final long seekStart, final long seekEnd, final Class cls, final HttpListenerAdapter listener) {
return new Runnable () {
@Override
public void run() {
Log.e("http", "---postfile---");
Log.e("http", "url: " + url);
Log.e("http", "extraHeaders: " + headers);
Log.e("http", "params: " + params);
Log.e("http", "filepath: " + file.getPath());
Log.e("http", "seekStart: " + seekStart);
Log.e("http", "seekEnd: " + seekEnd);
Call call = null;
if (listener != null) {
listener.onStart(call);
}
try {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(url)) {
throw new InterruptedException("url is null exception");
}
//构造path文件的index块的seekStart到seekEnd的请求体requestBody ,添加到MultiPartBody中
RequestBody requestBody = new RequestBody() {
@Override
public MediaType contentType() {
//请求体的内容类型
return MediaType.parse("multipart/form-data");
}
@Override
public void writeTo(BufferedSink sink) throws IOException {
//切块上传
long nowSeek = seekStart;
long seekEndWrite = seekEnd;
if (seekEndWrite == 0) {
seekEndWrite = file.length();
}
//跳到开始位置
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
if (seekStart > 0) {
long amt = in.skip(seekStart);
if (amt == -1) {
nowSeek = 0;
}
}
//将该块的字节内容写入body的BufferedSink 中
int len;
byte[] buf = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE_DEFAULT];
while ((len = in.read(buf)) >= 0 && nowSeek < seekEndWrite) {
sink.write(buf, 0, len);
nowSeek += len;
if (nowSeek + BUFFER_SIZE_DEFAULT > seekEndWrite) {
buf = new byte[Integer.valueOf((seekEndWrite - nowSeek) + "")];
}
}
closeStream(in);
}
};
//组装其它参数
MultipartBody.Builder urlBuilder = new MultipartBody.Builder()
.setType(MultipartBody.FORM);
if (params != null) {
for (String key : params.keySet()) {
//urlBuilder.addFormDataPart(key, params.get(key));
if (params.get(key)!=null){
urlBuilder.addFormDataPart(key, params.get(key));
}
}
}
//把文件块的请求体添加到MultiPartBody中
urlBuilder.addFormDataPart(fileKey, file.getName(), requestBody);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.headers(headers == null ? new Headers.Builder().build() : Headers.of(headers))
.url(url)
.post(urlBuilder.build())
.build();
call = httpClient.newCall(request);
//虽说是同步调用call.execute(),但是此Http请求过程是在线程池中的,相当于异步调用
try (Response response = call.execute()) {
if (!response.isSuccessful()){
throw new IOException("Unexpected code " + response.code());
}
/*打印json串,json样式的*/
String json = response.body().string();
//解析返回的响应json
T result = JsonUtils.getObjFromStr(cls, json);
if (listener != null) {
//防止回调内的业务逻辑引起二次onFailure回调
try {
listener.onResponse(call, result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} finally {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (listener != null) {
//中途取消导致的中断
if (call != null && call.isCanceled()) {
listener.onCancel(call);
} else {
//其它意义上的请求失败
listener.onFailure(call, e);
}
}
} finally {
if (listener != null) {
listener.onEnd(call);
}
}
}
};
}
//循环遍历所有的文章块,多线程上传
for (int i = 0; i < blockArray.size(); i++) {
//异步分块上传
final FileUtil.FileBlock block = blockArray.get(i + 1);
//提交线程池,异步上传单块
uploadBigImage(userId, new HttpListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, SyncBeans.ChuckUploadData bean) {
try {
//单块上传
if (bean != null ) {
if (bean.isPicSuccess()) {
//205,单块成功不做处理
} else if (bean.isAllPicSuccess()) {
//206,全部成功
}
}
}catch(Exception e){}
},uuid, mediaBean.imageNativeUrl, blockArray.size(), block.index, block.start, block.end);
}
5. OKHttp下载文件,并通知进度
下载文件的原理其实很简单,下载过程其实就是一个GET过程(上传文件是POST过程相对应),下载文件需要在异步线程中执行(方法有二,1,使用okhttp的call.enquene()方法异步执行,2,使用call.excute()同步方法,但是在线程次中执行整个请求过程),在成功响应之后,获得网络文件输入流InputStream,然后循环读取输入流上的文件,写入文件输出流。
/**
* @param url 下载连接
* @param saveDir 储存下载文件的SDCard目录
* @param params url携带参数
* @param extraHeaders 请求携带其他的要求的headers
* @param listener 下载监听
*/
public void download(final String url, final String saveDir,HashMap params, HashMap extraHeaders,final OnDownloadListener listener) {
//构造请求Url
HttpUrl.Builder urlBuilder = HttpUrl.parse(url).newBuilder();
if (params != null) {
for (String key : params.keySet()) {
if (params.get(key)!=null){
urlBuilder.setQueryParameter(key, params.get(key));//非必须
}
}
}
//构造请求request
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(urlBuilder.build())
.headers(extraHeaders == null ? new Headers.Builder().build() : Headers.of(extraHeaders))//headers非必须
.get()
.build();
//异步执行请求
okHttpClient.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
// 下载失败
listener.onDownloadFailed();
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
//非主线程
InputStream is = null;
byte[] buf = new byte[2048];
int len = 0;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// 储存下载文件的目录
String savePath = isExistDir(saveDir);
try {
//获取响应的字节流
is = response.body().byteStream();
//文件的总大小
long total = response.body().contentLength();
File file = new File(savePath);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
long sum = 0;
//循环读取输入流
while ((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
sum += len;
int progress = (int) (sum * 1.0f / total * 100);
// 下载中
if(listener != null){
listener.onDownloading(progress);
}
}
fos.flush();
// 下载完成
if(listener != null){
listener.onDownloadSuccess();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if(listener != null){
listener.onDownloadFailed();
}
} finally {
try {
if (is != null)
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
try {
if (fos != null)
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
});
}
至此,OKHTTP3的基本网络请求访问,发送GET请求,发送POST请求,基本上传文件,切块多线程异步上传文件,下载文件就到这里了,其实下载文件还可以做成断点续传,获取每次的seek点