在看一些大神写的开源框架时, 遇到了一个用于记录进度的类 - NSProgress, 然后通过看官方文档和网上找资料的方式, 来学习这个类的用法, 并在此记录此类的用法, 如果有什么地方错误请留言, 我会抽空修改。
简介
- 在iOS7中, 苹果官方添加了新的类NSProgress。用来报告当前某个任务的进度, 或者多个任务的进度和这些任务的总进度等
- NSProgress可以是一个树状结构, 一个节点进度可以有多个子节点, 每一个子节点只有一个父节点, 每一个子节点都有自己独立的进度体系, 并且子节点完成任务后, 会将完成的数量反馈给父节点
基本属性
- totalUnitCount: 总单元, 用来记载某个任务的总单元数 (可以理解为某个任务正常结束时,
需要完成的任务总量) - completedUnitCount: 已完成单元数量, 记载某个任务执行过程中已经完成的单元数量 (可以理解为, 某一个任务在执行过程中
已经完成的任务量) - fractionCompleted: 某个任务
已完成单元量占总单元量的比例 - localizedDescription: 通过
字符串的形式描述当前任务完成度- 格式:
100% completed
- 格式:
- localizedAdditionalDescription: 同localizedDescription一样, 用来描述
当前任务的完成度- 格式:
9 of 10(总任务量为10, 已完成任务量为9, 即 完成量/总量)
- 格式:
通过基本属性和KVO, 创建简单的单进度报告操作
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface ViewController ()
/** 进度 */
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSProgress *progress;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 初始化进度对象, 并设置进度总量
self.progress = [NSProgress progressWithTotalUnitCount:10];
//使用KVO观察fractionCompleted的改变
[self.progress addObserver:self forKeyPath:@"fractionCompleted" options:(NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew) context:nil];
}
/**
当点击根视图时触发
*/
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
//定时器
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1 target:self selector:@selector(task:) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
//加到当前运行循环
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
}
/**
定时器调用的方法
*/
- (void)task:(NSTimer *)timer
{
if (self.progress.completedUnitCount >= self.progress.totalUnitCount) {
[timer invalidate];
return;
}
self.progress.completedUnitCount += 1;
}
/**
KVO回调方法
*/
- (void)observeValueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath ofObject:(id)object change:(NSDictionary *)change context:(void *)context
{
//获取观察的新值
CGFloat value = [change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey] doubleValue];
//打印
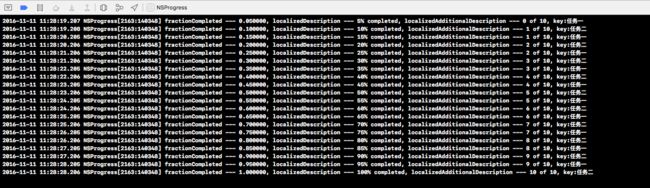
NSLog(@"fractionCompleted --- %f, localizedDescription --- %@, localizedAdditionalDescription --- %@", value, self.progress.localizedDescription, self.progress.localizedAdditionalDescription);
}
@end
- 当点击控制器view的时候, 会有如下打印
添加子节点的方法 (IOS9之前)
- - (void)becomeCurrentWithPendingUnitCount:(int64_t)unitCount;
- 该方法是用来在当前节点中分出一个子节点, 当子节点完成时, 总的进度完成量自动加上unitCount
- unitCount: 子节点完成时, 总任务完成的量
- - (void)resignCurrent;
- 与
- (void)becomeCurrentWithPendingUnitCount:(int64_t)unitCount;配套使用, 在这两个方法中间需要设置至少一个子节点, 当子节点完成后, 总完成量会自动增加unitCount量, 如果不设置子节点, 那么总任务完成量直接增加unitCount - 注意点: 这两个方法成对出现, 并且必须在同一个队列中调用
- 与
- 多节点示例代码:
#import "ViewController.h"
//继承自NSProgress的类, 添加一个唯一标识key
@interface LTProgress : NSProgress
/** 唯一标识 */
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *key;
@end
@implementation LTProgress
@end
@interface ViewController ()
/** 进度 */
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSProgress *progress;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 初始化进度对象, 并设置进度总量
self.progress = [NSProgress progressWithTotalUnitCount:10];
// 分出5个任务量给任务一
[self.progress becomeCurrentWithPendingUnitCount:5];
[self subTask:@"任务一"];
[self.progress resignCurrent];
// 分出5个任务量给任务二
[self.progress becomeCurrentWithPendingUnitCount:5];
[self subTask: @"任务二"];
[self.progress resignCurrent];
}
- (void)subTask:(NSString *)key
{
// 每个子任务的任务量分为10个单元, 每完成一个任务单元, 总任务完成量加上 5.0 / 10.0 = 0.5的任务单元
LTProgress *subProgress = (LTProgress *)[LTProgress progressWithTotalUnitCount:10];
subProgress.key = key;
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1 target:self selector:@selector(task:) userInfo:@{@"subProgress" : subProgress} repeats:YES];
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
}
- (void)task:(NSTimer *)timer
{
//获取当前的进度
NSDictionary *userInfo = timer.userInfo;
LTProgress *subProgress = userInfo[@"subProgress"];
//当完成量达到总量时停止任务
if (subProgress.completedUnitCount >= subProgress.totalUnitCount) {
[timer invalidate];
return;
}
//模仿完成1份
subProgress.completedUnitCount += 1;
//打印
NSLog(@"fractionCompleted --- %f, localizedDescription --- %@, localizedAdditionalDescription --- %@, key:%@", self.progress.fractionCompleted, self.progress.localizedDescription, self.progress.localizedAdditionalDescription, subProgress.key);
}
@end
- 具体打印如下:
- 当一个节点分出两个子节点时, 给每个子节点分配了需要完成的单元量, 只要子节点完成, 总节点的进度就会自动增加对应的节点单元量, 而子节点又可以将这些分配到的单元量重新进行分配
iOS9中的优化
- 在IOS9中新增了以下方法, 用来给节点添加子节点, 不用再使用上述两个方法
+ (NSProgress *)progressWithTotalUnitCount:(int64_t)unitCount parent:(NSProgress *)parent pendingUnitCount:(int64_t)portionOfParentTotalUnitCount- (void)addChild:(NSProgress *)child withPendingUnitCount:(int64_t)inUnitCount- 可以通过这两个方法直接分出子任务进度
- 示例代码:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 初始化进度对象, 并设置进度总量
self.progress = [NSProgress progressWithTotalUnitCount:10];
NSProgress *sub1 = [NSProgress progressWithTotalUnitCount:10 parent:self.progress pendingUnitCount:5];
NSProgress *sub2 = [NSProgress progressWithTotalUnitCount:10 parent:self.progress pendingUnitCount:5];
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1 target:self selector:@selector(task:) userInfo:@{@"sub1" : sub1, @"sub2" : sub2} repeats:YES];
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
}
- (void)task:(NSTimer *)timer
{
//获取当前的进度
NSDictionary *userInfo = timer.userInfo;
NSProgress *sub1 = userInfo[@"sub1"];
NSProgress *sub2 = userInfo[@"sub2"];
//当完成量达到总量时停止任务
if (sub1.completedUnitCount >= sub1.totalUnitCount && sub2.completedUnitCount >= sub2.totalUnitCount) {
[timer invalidate];
return;
}
//模仿完成1份
sub1.completedUnitCount += 1;
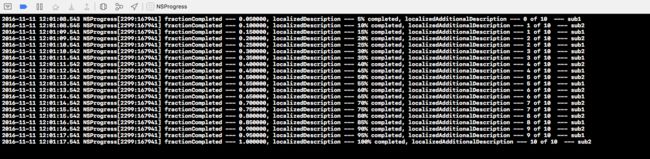
NSLog(@"fractionCompleted --- %f, localizedDescription --- %@, localizedAdditionalDescription --- %@ --- sub1", self.progress.fractionCompleted, self.progress.localizedDescription, self.progress.localizedAdditionalDescription);
sub2.completedUnitCount += 1;
//打印
NSLog(@"fractionCompleted --- %f, localizedDescription --- %@, localizedAdditionalDescription --- %@ --- sub2", self.progress.fractionCompleted, self.progress.localizedDescription, self.progress.localizedAdditionalDescription);
}
- 控制台打印:
- 属性 and 方法
// 获取当前线程的进度管理对象根节点
// 注意:当有NSProgress对象调用了becomeCurrentWithPendingUnitCount:方法后,这个方法才能获取到
+ (nullable NSProgress *)currentProgress;
// 创建NSProgress对象, 并设置进度单元的总数
+ (NSProgress *)progressWithTotalUnitCount:(int64_t)unitCount;
// iOS9后使用 创建NSProgress对象, 并设置进度单元的总数
+ (NSProgress *)discreteProgressWithTotalUnitCount:(int64_t)unitCount NS_AVAILABLE(10_11, 9_0);
/**
iOS9后使用, 创建一个NSProgress对象, 并指定父节点, 当完成时父节点完成单元数量 + portionOfParentTotalUnitCount
@param unitCount 任务进度的单元数量
@param parent 父节点, 可传入nil
@param portionOfParentTotalUnitCount 自身完成时, 父节点进度总量增加的值, 即父节点分配的任务量
@return NSProgress对象, 是parent的子节点
*/
+ (NSProgress *)progressWithTotalUnitCount:(int64_t)unitCount parent:(NSProgress *)parent pendingUnitCount:(int64_t)portionOfParentTotalUnitCount NS_AVAILABLE(10_11, 9_0);
// iOS9后使用, 同上
- (instancetype)initWithParent:(nullable NSProgress *)parentProgressOrNil userInfo:(nullable NSDictionary *)userInfoOrNil NS_DESIGNATED_INITIALIZER;
// 注册为当前线程根节点, 并分配子节点的任务量
- (void)becomeCurrentWithPendingUnitCount:(int64_t)unitCount;
// 取消注册 与注册方法必须同步出现, 必须在同一个线程内
- (void)resignCurrent;
// iOS9后使用, 向一个节点中添加一个子节点
- (void)addChild:(NSProgress *)child withPendingUnitCount:(int64_t)inUnitCount NS_AVAILABLE(10_11, 9_0);
#pragma mark *** Reporting Progress ***
// 进度单元总数
@property int64_t totalUnitCount;
// 进度单元已完成数
@property int64_t completedUnitCount;
// 描述进度 例如: 80% completed
@property (null_resettable, copy) NSString *localizedDescription;
// 描述进度 例如: 2 of 10 (2为已完成单元数量, 10为总单元数量)
@property (null_resettable, copy) NSString *localizedAdditionalDescription;
// 是否可以取消
@property (getter=isCancellable) BOOL cancellable;
// 是否可以暂停
@property (getter=isPausable) BOOL pausable;
// 是否已经取消
@property (readonly, getter=isCancelled) BOOL cancelled;
// 是否已经暂停
@property (readonly, getter=isPaused) BOOL paused;
// 进度取消回调
@property (nullable, copy) void (^cancellationHandler)(void);
// 进度暂停回调
@property (nullable, copy) void (^pausingHandler)(void);
// 进度恢复回调
@property (nullable, copy) void (^resumingHandler)(void) NS_AVAILABLE(10_11, 9_0);
#pragma mark *** Observing and Controlling Progress ***
@property (readonly, getter=isIndeterminate) BOOL indeterminate;
// 进度比例 0 - 1之间
@property (readonly) double fractionCompleted;
// 取消
- (void)cancel;
// 暂停
- (void)pause;
// 恢复
- (void)resume NS_AVAILABLE(10_11, 9_0);