本文基于objc4-709源码进行分析。
1.数据结构
在 objc-private.h 文件中,可以看到 category 是 category_t 结构体的指针。
typedef struct category_t *Category;
struct category_t {
const char *name;//类的名字
classref_t cls;//要扩展的类对象
struct method_list_t *instanceMethods;//实例方法
struct method_list_t *classMethods;//类方法
struct protocol_list_t *protocols;//协议
struct property_list_t *instanceProperties;//实例属性
// Fields below this point are not always present on disk.
struct property_list_t *_classProperties;//类属性
//根据当前类是否元类返回实例方法或者类方法
method_list_t *methodsForMeta(bool isMeta) {
if (isMeta) return classMethods;
else return instanceMethods;
}
//根据当前类是否元类返回实例属性或者类属性
property_list_t *propertiesForMeta(bool isMeta, struct header_info *hi);
};
可以看到,其中存储了可以扩展的实例方法、类方法、协议、实例属性、类属性。其中类属性是2016年Xcode8后开始新增的特性,为了与swift中的 type property 相互操作而引入的,类属性如何创建、使用这里不做展开。
category_list结构体用于存储所有的category。
typedef locstamped_category_list_t category_list;
struct locstamped_category_list_t {
uint32_t count;//category的数量
#if __LP64__
uint32_t reserved;
#endif
locstamped_category_t list[0]; //动态申请内存的写法
};
struct locstamped_category_t {
category_t *cat;
struct header_info *hi;
};
locstamped_category_t 存储 category_t 以及对应的 header_info。header_info 存储了实体在镜像中的加载和初始化状态,以及一些偏移量,在加载 Mach-O 文件相关函数中经常用到。
2.category 的加载
找到runtime的加载入口函数:
void _objc_init(void)
{
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
initialized = true;
// fixme defer initialization until an objc-using image is found?
environ_init();
tls_init();
static_init();
lock_init();
exception_init();
_dyld_objc_notify_register(&map_images, load_images, unmap_image);
}
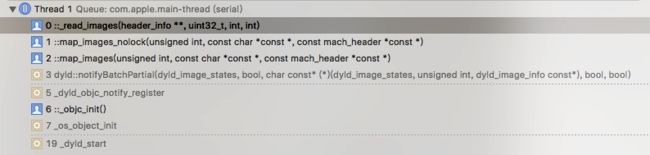
在方法的最后一行,runtime 通过 dyld 动态加载,调用栈如下:
加载镜像文件时map_images函数最终会调用_read_images函数, _read_images函数间接调用到attachCategories函数,完成向类中添加 category 的工作。
节选 _read_images 函数中加载 Category 的代码段(删掉部分不太重要的代码和注释):
// Discover categories. 查找category
for (EACH_HEADER) {
//获取category列表,但怎么得到的没看懂
category_t **catlist = _getObjc2CategoryList(hi, &count);
//是否有类属性
bool hasClassProperties = hi->info()->hasCategoryClassProperties();
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
category_t *cat = catlist[i];
Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
//处理这个category。 首先,将category注册到目标类。 然后,如果类实现了,重建类的方法列表(等)。
bool classExists = NO;
if (cat->instanceMethods || cat->protocols
|| cat->instanceProperties)
{
//把category的实例方法、协议、实例属性添加到类上
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls, hi);
if (cls->isRealized()) {
remethodizeClass(cls);
classExists = YES;
}
}
if (cat->classMethods || cat->protocols
|| (hasClassProperties && cat->_classProperties))
{
//把category的类方法、协议、类属性添加到元类上
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls->ISA(), hi);//注意这里是cls->ISA()
if (cls->ISA()->isRealized()) {
remethodizeClass(cls->ISA());
}
}
}
}
这里主要做了几个事情:
获取category列表
将category及其类(或元类)建立映射
如果类、元类已经实现,重建它的方法、协议、属性列表
把实例对象相关的category实例方法、协议、实例属性添加到类上
把类相关的category类方法、协议、类属性添加到元类上
对协议的处理:同时附加到类、元类中
addUnattachedCategoryForClass函数实际上把类(元类)和category做一个关联映射,把category及其类、元类注册到哈希表中。把category的方法、协议、属性附加到类上交给了 remethodizeClass 函数去做。
static void remethodizeClass(Class cls)
{
category_list *cats;
bool isMeta;
runtimeLock.assertWriting();
isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();
// Re-methodizing: check for more categories
//unattachedCategoriesForClass获取类中还未添加的category列表
if ((cats = unattachedCategoriesForClass(cls, false/*not realizing*/))) {
attachCategories(cls, cats, true /*flush caches*/);
free(cats);
}
}
remethodizeClass先找出类中还没添加的category列表,接着交给核心函数 attachCategories 来完成向类中添加category的工作。attachCategories的实现代码有一点点长,这里稍微简化一下单独拿出添加category method 的实现简单讲一下,添加协议、属性的过程其实差不多。
static void
attachCategories(Class cls, category_list *cats, bool flush_caches)
{
if (!cats) return;
bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();
// fixme rearrange to remove these intermediate allocations
//动态分配内存
method_list_t **mlists = (method_list_t **)malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*mlists));
// Count backwards through cats to get newest categories first
int mcount = 0;
int i = cats->count;
bool fromBundle = NO;
while (i--) {
auto& entry = cats->list[i];
//methodsForMeta得到category的类方法或者实例方法,根据是否metaclass来判断
method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta);
if (mlist) {
mlists[mcount++] = mlist;
fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle();
}
}
//获取类的数据字段
auto rw = cls->data();
//通过attachLists把category中的内容添加到类
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle);
rw->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);
free(mlists);
if (flush_caches && mcount > 0) flushCaches(cls);
}
涉及到的一些数据结构:method_array_t 、method_list_t 、 list_array_tt 、 entsize_list_tt 以及函数:attachLists,在
Rumtime源码中的类和对象的class_rw_t、class_ro_t一节中,已经分析过。
分析上面这段代码。while遍历取出所有category_list *cats的category,根据当前类是否是元类,每一个category获取得到它的类方法或者实例方法列表method_list_t *mlist,存入method_list_t **mlists中,也即把category的方法拼接到一个二维数组中。要注意这里是倒序添加的,新生成的category的方法会先于旧的category的方法插入。
接着获取类的数据字段class_rw_t,通过attachLists函数把上述method_list_t *mlist方法列表添加到类的class_rw_t中的method_array_t methods(method_array_t也相当与是一个二维数组)。
新加的方法列表都会添加到method_array_t前面。即原来类的方法列表方法顺序是A、B、C,category的方法列表方法顺序是D、E,插入之后的类方法列表的顺序是D、E、A、B、C。category 的方法被放到了新的方法列表的前面,runtime在查找方法的时候是沿着着方法列表从前往后查找的,一找到目标名字的方法就不会继续往后找了,这也就是为什么category 会“覆盖”类的同名方法,对原方法的调用实际上会调用 category 中的方法。
由于在category_t中只有 property_list_t 没有 ivar_list_t (无法添加实例变量),并且在class_ro_t 中的ivar_list_t又是只读的,在category中的属性是不会生成实例变量。苹果这么做的目的是为了保护class在编译时期确定的内存空间的连续性,防止runtime增加的变量造成内存重叠。
3.Associated Object
在category中可以添加属性但无法添加实例变量。平时我们在类中使用@property,编译器会为我们生成带下划线的实例变量、getter和setter方法,但是在 category 中就不会这样。
@interface HXObject : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name;
@end
@interface HXObject (AssociateOJ)
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *assoProperty;
- (void)hello;
@end
@implementation HXObject (AssociateOJ)
- (void)hello{
self.assoProperty = @"asso";
NSLog(@"%@", self.assoProperty);
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
HXObject * hxoj = [[HXObject alloc] init];
[hxoj hello];
}
return 0;
}
其实 Xcode 已经给了警告:
运行这段代码,控制台报找不到 category 属性的 setter 方法:
Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '-[HXObject setAssoProperty:]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x100b17710'
category 的属性存取方法需要手动实现,又或者用@dynamic实现。@dynamic在这里我们不讨论。
一般情况下,我们会使用关联对象来为已经存在的类添加“属性”。使用关联对象要引入#import 头文件。
@implementation HXObject (AssociateOJ)
- (void)setAssoProperty:(NSString *)assoProperty {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(assoProperty), assoProperty, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSString *)assoProperty {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd);
}
- (void)hello {
self.assoProperty = @"123";
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
HXObject * hxoj = [[HXObject alloc] init];
hxoj.assoProperty = @"asso";
NSLog(@"%@",hxoj.assoProperty);
}
return 0;
}
关于怎么使用关联对象这里也不会详谈。
通过objc_getAssociatedObject和objc_setAssociatedObject,给category实现了看起来像属性的存取方法的接口,还能使用点语法。通过关联对象模拟了实例变量。但仍需要记住的一点是,category不能生成实例变量,也不能给类增添实例变量。
在分类中,因为类的实例变量的布局已经固定,使用@property已经无法向布局中添加新的实例变量(这样做可能会覆盖子类的实例变量),所以我们需要使用关联对象以及两个方法来模拟构成属性的三个要素。
4.关联对象在runtime源码中的实现
主要函数有三个:
//根据key值获取对应的关联对象
id objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key);
//以键值对的形式添加关联对象,参数value传入nil可以删除单个关联对象
void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy);
//移除所有关联对象
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object);
接下来将对这三个方法进行分析,看看关联对象在runtime中是如何实现的。首先从objc_setAssociatedObject函数入手,但在此之前要先介绍四个涉及到的类。
- ObjcAssociation : value 和 policy 保存于此
- ObjectAssociationMap : key 保存于此
- AssociationsManager
- AssociationsHashMap : object 保存于此
ObjcAssociation
ObjcAssociation 这个类保存了关联策略policy以及关联对象value。其余还有构造、析构函数、成员变量的访问函数等等实现都比较简单。
class ObjcAssociation {
uintptr_t _policy;//关联策略
id _value;//关联对象
public:
//构造、析构函数 以及成员变量的访问方法等
ObjcAssociation(uintptr_t policy, id value) : _policy(policy), _value(value) {}
ObjcAssociation() : _policy(0), _value(nil) {}
uintptr_t policy() const { return _policy; }
id value() const { return _value; }
bool hasValue() { return _value != nil; }
};
ObjectAssociationMap
class ObjectAssociationMap : public std::map {
public:
void *operator new(size_t n) { return ::malloc(n); }
void operator delete(void *ptr) { ::free(ptr); }
};
ObjectAssociationMap 维护了从 key (就是那个 void * 参数)到ObjcAssociation的映射。
AssociationsManager
spinlock_t AssociationsManagerLock;
class AssociationsManager {
static AssociationsHashMap *_map;
public:
AssociationsManager() { AssociationsManagerLock.lock(); }
~AssociationsManager() { AssociationsManagerLock.unlock(); }
//获取_map单例
AssociationsHashMap &associations() {
if (_map == NULL)
_map = new AssociationsHashMap();
return *_map;
}
};
初始化、析构时分别对自旋锁 spinlock_t 进行 lock 和 unlock ,以此保证对 AssociationsManager 的操作线程安全。而 associations 函数实际上是获取了_map单例
AssociationsHashMap
class AssociationsHashMap : public unordered_map {
public:
void *operator new(size_t n) { return ::malloc(n); }
void operator delete(void *ptr) { ::free(ptr); }
};
AssociationsHashMap 维护了从 disguised_ptr_t(实际上是个unsigned long) 到 ObjectAssociationMap 的映射。在稍后将会在源码中看到,disguised_ptr_t 来自于待添加 assiciated object 的对象,所以也即这个类维护的是从对象到 ObjectAssociationMap 的映射。
总结以上内容来说,关联对象是存储在单独的哈希表中的。
4.1objc_setAssociatedObject
objc_setAssociatedObject 函数的实现中仅调用了_object_set_associative_reference 函数。配合注释以及上述介绍的四个相关类,这个方法的实现很好理解。
/**
@param object 要绑定到哪个对象上(宿主对象)
@param key key
@param value 关联对象
@param policy 关联策略
*/
void _object_set_associative_reference(id object, void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy) {
//1.理解为一个临时的ObjcAssociation,在之后保存原有的ObjcAssociation
ObjcAssociation old_association(0, nil);
//2.根据策略选择retain 或 copy 这个属性
id new_value = value ? acquireValue(value, policy) : nil;
{
AssociationsManager manager;
//3.得到AssociationsHashMap单例
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations());
//4.得到一个代表对象的obj key(obj key要和key区分开来)
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
//如果传入的关联对象value != nil
if (new_value) {
// 5.在AssociationsHashMap中根据obj key查找对应的ObjectAssociationMap
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
// 6.找得到
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
//6.1在ObjectAssociationMap中根据key查找ObjcAssociation
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
//6.2找得到,把原ObjcAssociation存到临时的old_association,然后更新新的ObjcAssociation
if (j != refs->end()) {
old_association = j->second;
j->second = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
} else {
//6.3找不到,就在ObjectAssociationMap中新增一个'key-ObjcAssociation'映射
(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
}
}
//7.找不到
else {
//7.1新建一个ObjectAssociationMap实例,把'对象-ObjectAssociationMap'的映射填入AssociationsHashMap;把'key-ObjcAssociation'的映射填入ObjectAssociationMap
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = new ObjectAssociationMap;
associations[disguised_object] = refs;
(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
object->setHasAssociatedObjects();//7.2这个方法会标记对象含有关联对象(将isa_t结构体中的标记位has_assoc置为true)
}
}
//8.如果传入的关联对象value == nil
else {
// 在AssociationsHashMap中根据obj key查找对应的ObjectAssociationMap
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
//如果找得到,移除ObjectAssociationMap中key对应的ObjcAssociation
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
old_association = j->second;
refs->erase(j);
}
}
}
}
//9.如果原关联对象有值,就释放该关联对象
if (old_association.hasValue()) ReleaseValue()(old_association);
}
- 创建一个临时的
ObjcAssociation,在之后保存原有的关联对象。 - 根据关联策略选择
retain或copy这个属性。 - 创建一个
AssociationsManager实例,获取AssociationsHashMap单例。 - 用
DISGUISE(object)得到一个代表对象的obj key(obj key要和key区分开来)。 - 如果方法的参数 value != nil。在
AssociationsHashMap中根据obj key查找对应的ObjectAssociationMap。如果方法的参数 value = nil,跳到第8步。 - 找得到
ObjectAssociationMap。接着在ObjectAssociationMap中根据key查找ObjcAssociation。找到,把原ObjcAssociation存到临时的old_association,然后更新新的ObjcAssociation;找不到,就在ObjectAssociationMap中新增一个'key-ObjcAssociation'映射。 - 找不到
ObjectAssociationMap。新建一个ObjectAssociationMap实例,把'对象-ObjectAssociationMap'的映射填入AssociationsHashMap;把'key-ObjcAssociation'的映射填入ObjectAssociationMap。 - 移除
ObjectAssociationMap中key对应的ObjcAssociation。 - 如果原关联对象(
old_association)有值,就释放该关联对象
ps:这里注意一下obj key指的是disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object)得到的disguised_object。而key指的是方法的参数key。
4.2objc_getAssociatedObject
objc_getAssociatedObject 函数的实现中仅调用了_object_get_associative_reference 函数。代码中的查找逻辑和objc_setAssociatedObject中的差不多,有差别的地方我用注释写了一下。
id _object_get_associative_reference(id object, void *key) {
id value = nil;
uintptr_t policy = OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN;//默认值
{
AssociationsManager manager;
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations());
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
ObjcAssociation &entry = j->second;
//获取value和policy
value = entry.value();
policy = entry.policy();
//根据policy调用retain方法
if (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_RETAIN) ((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(value, SEL_retain);
}
}
}
//根据policy调用autorelease方法
if (value && (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_AUTORELEASE)) {
((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(value, SEL_autorelease);
}
return value;
}
在查找到ObjcAssociation后获取其中的value和policy成员,policy的默认值是OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN。根据获取得到的policy值决定对value进行retain或者autorelease.
objc_removeAssociatedObjects
objc_removeAssociatedObjects会先使用hasAssociatedObjects函数来确认对象有没有关联对象,然后才调用_object_remove_assocations进行具体的移除操作。
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object)
{
//hasAssociatedObjects确认对象有没有关联对象
if (object && object->hasAssociatedObjects()) {
_object_remove_assocations(object);
}
}
void _object_remove_assocations(id object) {
vector< ObjcAssociation,ObjcAllocator > elements;
{
AssociationsManager manager;
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations());
if (associations.size() == 0) return;
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
//把ObjectAssociationMap中的所有ObjcAssociation存到一个vector中
for (ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->begin(), end = refs->end(); j != end; ++j) {
elements.push_back(j->second);
}
//释放ObjectAssociationMap,移除AssociationsHashMap的'对象-ObjectAssociationMap'映射
delete refs;
associations.erase(i);
}
}
//对所有ObjcAssociation调用ReleaseValue()进行释放
for_each(elements.begin(), elements.end(), ReleaseValue());
}
唔...查找ObjcAssociation的逻辑一样的。这里把ObjectAssociationMap中的所有ObjcAssociation存到一个vector中,然后释放ObjectAssociationMap、移除AssociationsHashMap的'对象-ObjectAssociationMap'映射,最后对保存在vector中的所有ObjcAssociation调用ReleaseValue()进行释放。
生命周期
对象的销毁函数:
void *objc_destructInstance(id obj)
{
if (obj) {
// Read all of the flags at once for performance.
bool cxx = obj->hasCxxDtor();
bool assoc = obj->hasAssociatedObjects();
// This order is important.
if (cxx) object_cxxDestruct(obj);//调用对象的析构函数
if (assoc) _object_remove_assocations(obj);//移除所有关联对象
obj->clearDeallocating();//清空引用计数和weak表
}
return obj;
}
在这个函数中我们看到,我们无需关心关联对象的生命周期,在销毁对象时,会检查这个对象有没有关联对象,有的话就调用_object_remove_assocations函数把所有关联对象移除掉。
ps:根据Objective-C Associated Objects 的实现原理一文中的分析,
关联对象的释放时机与移除时机并不总是一致,比如用关联策略 OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN 进行关联的对象,很早就已经被释放了(由于autoreleasepool drain而释放),但是并没有被移除,而再使用这个关联对象时就会造成 Crash 。
参考文章:
深入理解Objective-C:Category
结合 category 工作原理分析 OC2.0 中的 runtime
Objective-C Associated Objects 的实现原理