2.2.3 ArrayList
如果要动态地改变数组所占用内存空间的大小,则需以数组为基础进一步抽象,以实现这个功能。以图2.2的学生宿舍为例,为了使A班的所学生住在连续的宿舍内,可以把A班的学生全部搬迁到连续的5间空宿舍内。其效果如图2.6所示:
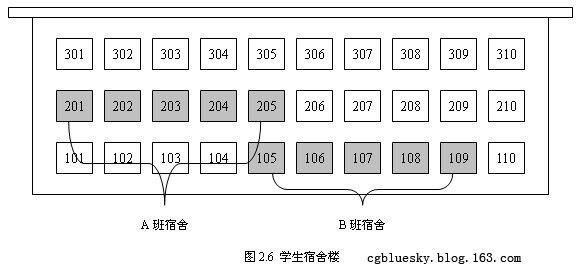
现实中,为了让一个班新加入的10个学生能跟原来的学生住在一起而把班级整体搬迁,这样的做法显示不合适,因为搬迁的成本太高。但在计算机中,内存成片区域间的拷贝成本是非常低的,这样的解决方案是合理可行的。
但是这个解决方案还存在问题,如果一个班级频繁地有新学生加入,为了保证学生能住在连续的宿舍内,整个班级就不得不频繁地搬迁。可以采用以空间换时间的做法来解决这个问题,在学生每次搬迁时,都让班级宿舍的数量是原来的两倍。也就是说,如果原来一个班级有4间宿舍,搬迁后就变为8间,再次搬迁则变为16间。如图2.2所示,A班的宿舍为201~208。206~208这三间宿舍做为本班备用宿舍,不再允许其他班级的学生搬入。
C#中的ArrayList正是采用上述方法来动态改变数组大小的。ArrayList又被称为动态数组,它的存储空间可以被动态改变,同时还拥有添加、删除元素的功能。
下面列出了ArrayList的部分核心代码:
【ArrayList.cs】
namespace LinearList
{
public class ArrayList
{
// 成员变量
private const int _defaultCapacity = 4 ; // 默认初始容量
private object [] _items; // 用于存放元素的数组
private int _size; // 指示当前元素个数
// 当元素个数为零时的数组状态
private static readonly object [] emptyArray = new object [ 0 ];
// 方法
public ArrayList() // 默认构造方法
{ // 这样做可以避免元素个数为零时的访问出错
this ._items = emptyArray;
}
// 指定ArrayList初始容量的构造方法
public ArrayList( int capacity)
{
if (capacity < 0 )
{ // 当容量参数为负数时引发异常
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException( " capacity " ,
" 为ArrayList指定的初始容量不能为负数 " );
}
// 按照capacity参数指定的长度的值初始化数组
this ._items = new object [capacity];
}
// 添加一个方法
public virtual int Add( object value)
{ // 当空间满时
if ( this ._size == this ._items.Length)
{ // 调整空间
this .EnsureCapacity( this ._size + 1 );
}
this ._items[ this ._size] = value; // 添加元素
return this ._size ++ ; // 使长度加1
}
// 动态调整数组空间
private void EnsureCapacity( int min)
{
if ( this ._items.Length < min)
{ // 空间加倍
int num = ( this ._items.Length == 0 ) ?
_defaultCapacity : ( this ._items.Length * 2 );
if (num < min)
{
num = min;
}
// 调用Capacity的set访问器以按照num的值调整数组空间
this .Capacity = num;
}
}
// 在指定索引入插入指定元素
public virtual void Insert( int index, object value)
{
if ((index < 0 ) || (index > this ._size))
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException( " index " , " 索引超出范围 " );
}
if ( this ._size == this ._items.Length)
{ // 当空间满时调整空间
this .EnsureCapacity( this ._size + 1 );
}
if (index < this ._size)
{ // 插入点后面的所有元素向后移动一位
Array.Copy( this ._items, index,
this ._items, index + 1 , this ._size - index);
}
this ._items[index] = value; // 插入元素
this ._size ++ ; // 使长度加1
}
// 移除指定索引的元素
public virtual void RemoveAt( int index)
{
if ((index < 0 ) || (index >= this ._size))
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException( " index " , " 索引超出范围 " );
}
this ._size -- ; // 使长度减1
if (index < this ._size)
{ // 使被删除元素后的所有元素向前移动一位
Array.Copy( this ._items, index + 1 ,
this ._items, index, this ._size - index);
}
this ._items[ this ._size] = null ; // 最后一位空出的元素置空
}
// 裁减空间,使存储空间正好适合元素个数
public virtual void TrimToSize()
{
this .Capacity = this ._size;
}
// 属性
public virtual int Capacity // 指示ArrayList的存储空间
{
get
{
return this ._items.Length;
}
set
{
if (value != this ._items.Length)
{
if (value < this ._size)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException( " value " , " 容量太小 " );
}
if (value > 0 )
{ // 开辟一块新的内存空间存储元素
object [] destinationArray = new object [value];
if ( this ._size > 0 )
{ // 把元素搬迁到新空间内
Array.Copy( this ._items, 0 ,
destinationArray, 0 , this ._size);
}
this ._items = destinationArray;
}
else // 最小空间为_defaultCapacity所指定的数目,这里是4
{
this ._items = new object [_defaultCapacity];
}
}
}
}
public virtual int Count // 只读属性,指示当前元素个数
{
get
{
return this ._size;
}
}
public virtual object this [ int index] // 索引器
{
get // 获取指定索引的元素值
{
if ((index < 0 ) || (index >= this ._size))
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException( " index " , " 索引超出范围 " );
}
return this ._items[index];
}
set // 设置指定索引的元素值
{
if ((index < 0 ) || (index >= this ._size))
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException( " index " , " 索引超出范围 " );
}
this ._items[index] = value;
}
}
}
}
上述代码通过在一个数组(第8行代码的成员变量_items)的基础上做进一步抽象,构建了一个可动态改变空间的顺序表ArrayList,并实现了一些基础操作,下面对之进行一一介绍。
1. 初始化
这里实现了2种初始方法,第一种为13~16行代码,它把顺序表空间初始化为一个0长度数组。这样做的目的是为了调用方便。做为成员变量的object类型数组_items默认会被初始化为null,如果不把它初始化为0长度数组,在使用代码 ArrayList arr = new ArrayList() 来创建ArrayList后试图访问它的Count属性将会导致错误发生。
第二种初始化方法为18~27行代码,它根据capacity参数所指定的值来初始化_items数组的长度,如果初始化一个长度为100的ArrayList数组可以使用如下代码:
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(100)
当可以预见ArrayList所操作的大概元素个数时,使用这种方法可以在一定程序上避免数组重复创建和数据迁移,以提高性能和减少内存垃圾回收的压力。
2. 动态改变存储空间操作
39~52行的EnsureCapacity(int min)方法用于空间不足时使空间加倍,从代码:
int num = (this._items.Length == 0) ? _defaultCapacity : (this._items.Length * 2);
可以得知,当元素个数为0是,空间增长为4,否则将翻倍。改变空间大小的代码是在Capacity属性中的set访问器中实现的(代码99~122行)。代码
object[] destinationArray = new object[value];
创建了一个新的object数组,它在内存中开辟了一个新的空间用于存放元素。代码
Array.Copy(this._items, 0, destinationArray, 0, this._size);
把_items数组中的元素全部拷贝到新数组destinationArray中,可以把它理解为数据搬新家。最后通过
this._items = destinationArray;
使用于存放数据的成员变量_items指向新的数组对象destinationArray。
88~91行的TrimToSize()方法用于裁减多余空间,实际的裁减操作也是在Capacity属性中的set访问器中实现。这个操作也会导致数组的重新创建和数据迁移,建议一般情况下不使用此操作,除非集合中的剩余空间很多。
3. 元素的读写操作
131~149行代码实现了一个索引器,这样就可以使用中括号加索引号来读取和给元素赋值,使ArrayList的使用看上去和数组很相似。
4. 元素的添加和插入操作
29~37行的Add(object value)方法实现了添加元素的功能。元素添加在集合的末尾,成员变量_size用于指示当前元素个数,它总是指向集合中的最后一个元素。
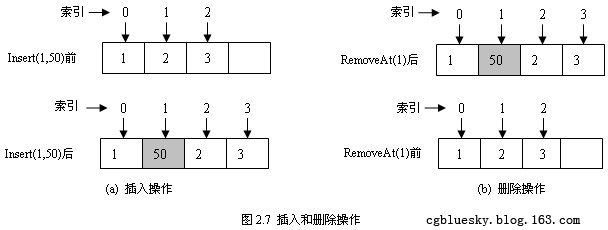
54~71行的Insert(int index, object value)方法用于在指定索引处插入一个元素。为了保证顺序表中的每个元素物理上相邻,插入点后面的所有元素都将后移一位,其效果如图2.7(a)所示。
1. 元素的删除操作
73~86行的RemoveAt(int index)方法用于删除指定索引的元素,删除指定元素后,删除点后的所有元素将向前移动一位其效果如图2.7(b)所示。
下面对ArrayList类进行测试。
【例2-1】ArrayList的使用
新建一个控制台应用程序,并在项目中把上面的ArrayList.cs文件做为一个【现有项】添加进去。在代码窗体前面使用如下语句加入LinearList命名空间:
using LinearList;
并在Main方法中输入如下代码:
using LinearList;
namespace Demo2_1
{
class Program
{
static void Main( string [] args)
{
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList();
Console.WriteLine( " arr现在的容量为: " + arr.Capacity + " 长度为: " + arr.Count);
arr.Add( 1 ); // 添加一个元素
Console.WriteLine( " arr现在的容量为: " + arr.Capacity + " 长度为: " + arr.Count);
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= 5 ; i ++ )
{ // 添加4个元素,完成后元素总数达到5个
arr.Add(i);
}
Console.WriteLine( " arr现在的容量为: " + arr.Capacity + " 长度为: " + arr.Count);
for ( int i = 6 ; i <= 9 ; i ++ )
{ // 添加4个元素,完成后元素总数达到9个
arr.Add(i);
}
Console.WriteLine( " arr现在的容量为: " + arr.Capacity + " 长度为: " + arr.Count);
for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr.Count; i ++ ) // 打印所有元素
{
Console.Write(i + " " );
}
// 删除两个元素
arr.RemoveAt(arr.Count - 1 );
arr.RemoveAt(arr.Count - 1 );
Console.WriteLine(); // 换行
for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr.Count; i ++ ) // 打印所有元素
{
Console.Write(i + " " );
}
Console.WriteLine(); // 换行
Console.WriteLine( " arr现在的容量为: " + arr.Capacity + " 长度为: " + arr.Count);
arr.TrimToSize(); // 载减多余空间
Console.WriteLine( " arr现在的容量为: " + arr.Capacity + " 长度为: " + arr.Count);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
运行结果:如图2.8所示。
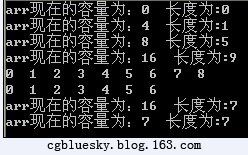
由运行结果可以得知,数组对象arr的容量随着元素的不断增加,从0→4→8→16不断改变,在删除两个元素之后,容量还保持在16不变,在通过调用TrimToSize()裁减空间后,容量最终变为7。
2.2.4 类型安全
数组和ArrayList的本质区别在于前者是类型安全的,而后者不是类型安全的。ArrayList为了兼容所有类型的对象,使用了object数组,这给使用带来了一些的麻烦。如下例所示:
【例2-2】数组和ArrayList的对比
本例使用了C#类库中的ArrayList而不是前面自定义的ArrayList,它存在于System.Collections命名空间中。新建一个控制台应用程序,引入System.Collections命名空间,并在Main()方法中输入如下代码:
using System.Collections;
namespace Demo2_2
{
class Program
{
static void Main( string [] args)
{
int [] arr = new int [ 2 ];
arr[ 0 ] = 5 ;
arr[ 1 ] = 6 ;
int result = arr[ 0 ] * arr[ 1 ];
Console.WriteLine(result);
ArrayList arrL = new ArrayList();
arrL.Add( 5 );
arrL.Add( 6 );
result = ( int )arrL[ 0 ] * ( int )arrL[ 1 ];
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
运行结果:
|
30 30 |
本例使用数组和ArrayList分别做了相同的事情,但使用方法却大相径庭。首先数组在创建时就已经确定只接收int类型数据,并且它的长度是固定的。而ArrayList则可以接收任意object类型,而事实上,C#中的所有类均是object类型的子类。
其次数组没有添加元素的功能,因为在数组创建时,各个元素就已经存在,只是被初始化为0而已,只能通过下标改变各个元素的值。而ArrayList只有把元素添加进去后才可以通过下标访问相应的元素。
最后,在使用集合中的元素时,数组不需要进行强制类型转换,而ArrayList必须要经过强制类型转换才能使用。这是因为ArrayList实际存放的是object对象,要按照这些对象原本的类型来使用就必须要使用强制类型转换。
ArrayList的这个特点带来了类型安全问题,如:
arrL.Add( 5 );
arrL.Add( " Hello World " );
arrL.Add( new Button());
以上代码在集合中存放了各种各样的数据类型,但这样做是被允许的。这种类型的不安全一方面给程序带来了隐患,另一方面如果集合中存放的是值类型还会产生装箱和拆箱操作,降低了程序的性能。
.NET 2.0版本的泛型的出现完美地解决了上述问题,新版本使用System.Collections.Generic命名空间下的List
arrL.Add( 1 );
arrL.Add( 2 );
可以看到,第一行代码在集合创建时就已经把元素类型限定为int,它是类型安全的,同时避免了装箱和拆箱操作。强烈建议在实际编程中使用List