作者: 一字马胡
转载标志 【2018-01-07】
更新日志
| 日期 | 更新内容 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 2018-01-07 | 创建分析文档 | Spring源码分析系列文章(四) |
导入
Spring源码分析系列文章索引:
- Spring源码分析之Bean的解析
- Spring源码分析之Bean的加载
- Spring源码分析之AOP
本文是系列文章的第四篇,内容为Spring WebMVC模块的源码分析。主要分析WebMVC模块的工作流程,依然只分析主干流程,不会涉及太多的细节。MVC是一种将Web层进行解耦的架构模式,MVC即Model、View、Controller,Model即数据模型,View即视图,Controller即处理器,知道了MVC的大概原理,就可以开始进行Spring MVC的源码分析了,Spring MVC是MVC架构的一种优秀实现,能高效的进行Web模块的开发工作。
在进行实际的Spring MVC源码分析之前,大概先来猜测一下整个流程中的关键步骤,然后对照着猜测来分析Spring MVC中的具体实现。
- 首要的一点是如何将bean解析并加载到容器中来。因为在Spring MVC开发中,我们不需要也没有权限写一个main方法,然后使用ApplicationContext来加载xml文件的环节(是否也可以这样呢?但是需要放在什么位置来加载xml呢?使用什么来加载xml呢?),所以在WebMVC中首先要解决的一个问题就是使用一个特殊的组件来触发Spring的bean解析-bean加载这个流程。
- 在把Spring bean加载成功之后,现在,我们可以正常使用我们在Spring配置文件中配置的bean了,对于Web应用来说,使用的协议一般为Http/Https,所以接下来需要考虑的一个问题是,在Spring MVC中是如何处理客户端请求的。客户端的请求应该是一个http请求,而达到Spring MVC之后需要做的事情应该是找到合适的Controller,并且找到Controller中的具体可以处理该请求的Handler,让Handler来处理请求,并且获取到结果之后将结果传递到View解析器,View解析器会根据合适的视图对数据进行渲染,然后返回给客户端去。
第一步看起来比较简单,毕竟我们需要的只是在合适的时候引导Spring来加载xml文件来解析bean并且加载解析的bean,较为复杂和核心的功能应该是第二步,需要做的事情看起来非常多,首先要拦截请求,并且将请求封装成Spring MVC可以处理的bean,然后需要根据请求来选择合适的Controller,并且将合适的Handler交给拦截器进行请求处理,处理完了还需要将数据交付给视图渲染组件来返回合适的试图。
所以就目前来说,在第二步,有几个问题需要得到解决:
- Controller看起来和普通的bean是不一样的,因为普通的bean不涉及Handler,而Controller涉及到Handler,并且可能一个Controller包含了多个Handler,所以看起来Controller需要特殊对待,就解析Controller来说,需要结合Controller代码来进行解析,将所有Controller支持的Handler和对应的Url解析好,然后在请求到达的时候,只需要和解析好的这些Url和Handler进行匹配就可以了。
- Controller的Handler解析好了,那是怎么匹配具体的请求的呢?这是另外一个需要考虑的问题,一个请求肯定会带着一个url,怎么为这个url找到合适的Handler是处理请求的关键一步。
- 匹配好了Handler之后,Handler是怎么处理请求的呢?也就是怎么交给具体的Handler的呢?处理完成的数据会流转到哪里呢?
现在想起来并不会太全面,很容易忽略细节,但是大概就应该是这样,下面就带着这些问题来分析Spring WebMVC的源码。
Spring WebMVC模块解析
首先是第一个问题,怎么触发Spring中的bean的解析-bean的加载那一套流程。在Spring WebMVC项目中都需要配置一个web.xml文件,这个文件配置一些相关Web的配置项,下面是一个关键配置,与触发Spring bean解析密切相关:
contextConfigLocation
classpath*:applicationContext*.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
context-param标签用于进行一些key-value类型的配置项设置,key是param-name,Value就是param-value,上面的配置中配置了一个key为contextConfigLocation的配置项,代表Spring bean解析bean的xml文件来源,从value可以看出,Spring会加载classpath:applicationContext.xml这些文件来进行bean的解析。
接着是一个listener标签,看起来是一个监听器,所谓监听器,就是会监听一些事件,当某些事件发生的时候就会做一些事情的组件,而listener-class标签设定了具体的监听器类。在上面的设置中设置了ContextLoaderListener这个类,看起来就是这个类来触发Spring 进行bean的加载,而上面的context-param配置的就是Spring 加载bean扫描的xml文件,下面来具体分析一下整个流程。
ContextLoaderListener 实现了 ServletContextListener接口,ServletContextListener 有一个关键的方法是contextInitialized,根据注释,这个方法会在web应用初始化的时候调用,所以也就是在Web应用最开始的地方会触发这个方法,具体联系ContextLoaderListener,就是会在这个时候进行bean的加载流程,下面来具体分析一下ContextLoaderListener中contextInitialized这个方法的实现:
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
关键的流程流转到了initWebApplicationContext这个方法中来了,下面来分析一下initWebApplicationContext这个方法中的关键代码:
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
上面的代码截取自initWebApplicationContext方法,这个方法实现的功能就是触发Spring的bean的加载流程,但是这只是触发的开始,来分析一下上面的代码,首先是createWebApplicationContext方法,会根据servletContext来create一个WebApplicationContext,下面是这个方法的具体实现:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
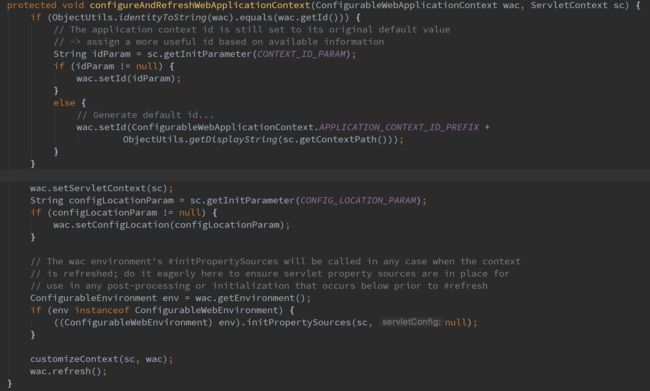
经过上面的步骤之后,就会走到关键的方法configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext,这个方法很关键,它引导web应用开始进行bean的加载操作,下面来看一下这个方法内部的实现:
其中的configLocationParam就是我们在web.xml中配置的那个参数,是Spring扫描bean的路径,配置好路径之后,就和我们自己写加载bean的流程是一样的了,只是这里webMVC会自动进行这些步骤,看到最后的wac.refresh(),就可以确定,Spring要开始进行xml的加载,并且进行bean的解析、加载等流程了,关于这些步骤已经在前面的文章中分析过,在此不再赘述。
DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC中的核心组件,它接收请求,并且为请求找到合适的Handler进行处理,DispatcherServlet也是本文分析的重点内容,下面首先来看一下再Spring MVC应用中web.xml中关于DispatcherServlet的配置:
Spring-MVC-API-Servlet
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath*:springmvc-servlet.xml
2
Spring-MVC-API-Servlet
/api/*
就像上面看起来的一样,每一个servlet都需要配置一个ervlet-mapping,用来将相应的请求交给对应的DispatcherServlet进行处理。在上面的配置中,配置了一个servlet名字叫做Spring-MVC-API-Servlet,指定为org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet这个类,并且配置了加载Controller的xml文件路径为classpath*:springmvc-servlet.xml,除此之外,为该servlet配置了mapping,将所有以/api开头的请求都路由到该DispatcherServlet进行处理。一个Web 应用可以配置多个DispatcherServlet来处理不同的资源类型,视具体情况来使用,只需要记住,每一个DispatcherServlet都需要配置配套的mapping就可以了。
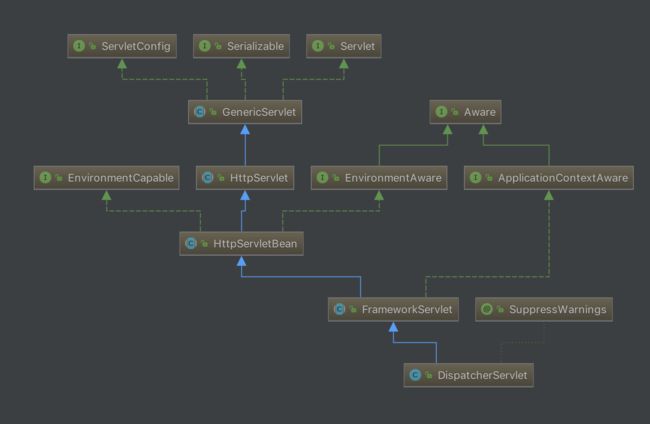
有了DispatcherServlet配置,现在来分析一下DispatcherServlet的具体细节,在第一步触发Spring bean的加载流程哪里,结束之后并不会包含Controller,所以Controller需要特殊解析,因为涉及到Handler的解析问题,所以可以理解需要特殊解析。下面是DispatcherServlet的类图,可以看到DispatcherServlet的实现是比较复杂的:
首先关注DispatcherServlet实现了Servlet接口,Servlet接口有一个重要的方法init,这个方法应该是会在实例化了Servlet之后调用,具体的实现是在HttpServletBean的,下面是它的实现:
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
try {
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
throw ex;
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
其中有一个方法值得注意:initServletBean,具体的实现在FrameworkServlet:
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
这里面初始化的就是我们在web.cml中配置的一个DispatcherServlet,每一个DispatcherServlet都会进行一次,首先需要注意的一个方法是initWebApplicationContext这个方法,然后是initFrameworkServlet这个方法,首先来看一下前面的那个方法的具体实现内容。
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
上面是第一个试图找到一个webApplicationContext的第一个分支,如果webApplicationContext在构造函数中被带赋值,那么就会走到该分支中来,这个分支中需要关注的一个方法是configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext,这个方法做什么的呢?下面是该方法的具体实现:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + "/" + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
最后的wac.refresh()代表需要重新走一次Spring bean加载的流程。下面是第二个试图找到一个webApplicationContext的第二个分支:
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
下面是第三个分支,一般情况下会走到这个分支中来:
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
Class contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
主要是设定了扫描路径,然后就调用了configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法来开始进行bean的加载流程,这个方法在上面已经提及,在此不再赘述。
接着是一个关键的方法onRefresh:
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
//初始化andlerMappings
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
这其中初始化了很多内容,比如MultipartResolver、hemeResolver等,但是目前我比较关心的是HandlerMappings的初始化,下面就主要来分析这个initHandlerMappings这个方法的实现细节。
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
上面这个方法大概的意思就是加载系统设置的HandlerMappings,可以在webMVC模块中的Resources中看到有一个文件叫做DispatcherServlet.properties,可以在其中找到下面的内容:
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
也就是说,如果没有设置自己的HandlerMappings的话,Spring就会去加载这两个HandlerMappings,本文主要分析后者RequestMappingHandlerMapping。
到目前为止,总结一下现在的上下文,首先,我们已经知道了Spring MVC是什么时候以及怎么样触发Bean的加载流程的,这一步貌似和Spring MVC关系不大,但是却很重要,接着,了解了web.xml中关于servlet的配置准则,以及配置的意义,然后对servlet进行了初始化,并且最终触发了一系列的初始化,包括HandlerMappings。至此,貌似可以接受请求了,也就是说Spring WebMVC的分析已经走了一半了,接下来的一半内容就是如何处理请求了,这就得和Servlet的生命周期配合起来理解分析了,并且会涉及到Servlet将请求交给合适的Controller的合适的Handler的过程。下面来逐步分析一下。
DispatcherServlet在实现上继承了HttpServlet,而HttpServlet提高了大量的方法来进行请求的处理,比如doGet、doPut等,而HttpServlet中的service方法就是一个dispatch,会解析请求,然后根据不同的请求方法来调用不同的doXXX方法,我们主要关注doGet和doPut方法即可。需要注意的是,service方法在FrameworkServlet类中被重写了,具体实现如下:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (HttpMethod.PATCH == httpMethod || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
一般情况下会走到else分支中,然后调用了super的service方法,下面是该方法的实现内容:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
可以看到,service方法就是解析请求,然后根据不同的请求类型交给不同的方法来处理,比如GET类型的请求就会交给doGet方法来进行处理,下面主要关注doGet这个方法的接下来的流程,其余的方法分析类似,就不再赘述了。
doGet方法在FrameworkServlet类中重写了,所以会走到FrameworkServlet类中的doGet方法中来,下面是该方法的具体实现:
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
接着走到了processRequest方法内部,下面是该方法的主要代码:
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
doService(request, response);
}
这个方法将对Request和Response做一些修饰,然后就会走到doService这个方法。下面是doService方法的具体细节:
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
看起来这个方法也还没开始真正处理请求,而会继续修饰Request,然后交给doDispatch这个方法来做,下面是doDispatch方法的具体细节:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
看起来这个方法就是真正处理请求的方法了,下面详细分析一下这个方法的实现内容。
首先对request做了一些处理,然后会调用getHandler来获取一个可以处理该请求的Handler,这个方法是关键,需要详细分析一下。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
这个方法内部会进行遍历所有已加载的handlerMappings,而handlerMappings的加载在上文中已经提到过,getHandler方法会询问所有加载的handlerMappings,看看到底哪个handlerMapping可以处理。通过调用HandlerMapping的getHandler方法来进行判断是否这个Handler可以处理当前请求。下面以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例来分析接下来的具体流程。可以在AbstractHandlerMapping类中找到getHandler这个方法:
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
该方法的关键是第一个方法调用getHandlerInternal,下面来分析一下getHandlerInternal这个方法的实现细节。可以在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中找到getHandlerInternal这个方法的具体实现:
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
}
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (handlerMethod != null) {
logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
}
else {
logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
}
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
这里面的第一个需要注意的方法是getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest,该方法会根据请求解析出具体的用于匹配Handler的url,这是一个很关键的步骤,寻找合适的Handler就是根据url来进行的。下面是该方法的具体实现内容:
public String getLookupPathForRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
// Always use full path within current servlet context?
if (this.alwaysUseFullPath) {
return getPathWithinApplication(request);
}
// Else, use path within current servlet mapping if applicable
String rest = getPathWithinServletMapping(request);
if (!"".equals(rest)) {
return rest;
}
else {
return getPathWithinApplication(request);
}
}
这个方法里面需要注意的是getPathWithinServletMapping这个方法的调用,这就是具体的对请求的url的处理。下面是该方法的具体实现细节:
public String getPathWithinServletMapping(HttpServletRequest request) {
String pathWithinApp = getPathWithinApplication(request);
String servletPath = getServletPath(request);
String sanitizedPathWithinApp = getSanitizedPath(pathWithinApp);
String path;
// if the app container sanitized the servletPath, check against the sanitized version
if (servletPath.indexOf(sanitizedPathWithinApp) != -1) {
path = getRemainingPath(sanitizedPathWithinApp, servletPath, false);
}
else {
path = getRemainingPath(pathWithinApp, servletPath, false);
}
if (path != null) {
// Normal case: URI contains servlet path.
return path;
}
else {
// Special case: URI is different from servlet path.
String pathInfo = request.getPathInfo();
if (pathInfo != null) {
// Use path info if available. Indicates index page within a servlet mapping?
// e.g. with index page: URI="/", servletPath="/index.html"
return pathInfo;
}
if (!this.urlDecode) {
// No path info... (not mapped by prefix, nor by extension, nor "/*")
// For the default servlet mapping (i.e. "/"), urlDecode=false can
// cause issues since getServletPath() returns a decoded path.
// If decoding pathWithinApp yields a match just use pathWithinApp.
path = getRemainingPath(decodeInternal(request, pathWithinApp), servletPath, false);
if (path != null) {
return pathWithinApp;
}
}
// Otherwise, use the full servlet path.
return servletPath;
}
}
getPathWithinApplication这个方法会解析好一个请求的url(纯洁的url,比如 /api/user/1310561):
public String getPathWithinApplication(HttpServletRequest request) {
String contextPath = getContextPath(request);
String requestUri = getRequestUri(request);
String path = getRemainingPath(requestUri, contextPath, true);
if (path != null) {
// Normal case: URI contains context path.
return (StringUtils.hasText(path) ? path : "/");
}
else {
return requestUri;
}
}
接着,getServletPath这个方法会返回web.xml中配置的路由路径:
public String getServletPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
String servletPath = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.INCLUDE_SERVLET_PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
if (servletPath == null) {
servletPath = request.getServletPath();
}
if (servletPath.length() > 1 && servletPath.endsWith("/") && shouldRemoveTrailingServletPathSlash(request)) {
// On WebSphere, in non-compliant mode, for a "/foo/" case that would be "/foo"
// on all other servlet containers: removing trailing slash, proceeding with
// that remaining slash as final lookup path...
servletPath = servletPath.substring(0, servletPath.length() - 1);
}
return servletPath;
}
getRemainingPath这个方法大概是将url中的前缀去掉,所谓前缀就是web.xml中配置的路由,这样才能去匹配Controller中的Handler对吧?现在回到getHandlerInternal这个方法,现在可以拿到lookupPath了,那接下来就可以根据lookupPath来匹配Controller的Handler了吧?接着往下分析。接着一个比较关键的方法是lookupHandlerMethod,下面来分析一下这个方法的实现:
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List matches = new ArrayList();
List directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" +
lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
}
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" +
request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
这里面需要关注的一个方法是addMatchingMappings,用于添加匹配的Handler:
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection mappings, List matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
获取到所有匹配的Handler之后需要挑选一个最合适的Handler进行请求的处理,lookupHandlerMethod方法中接下来的代码实现的功能就是这些,下面回到doDispatch方法,接着走接下来的流程,现在,我们已经获取到了合适的Handler,下面,就是进行Handler的访问来处理请求了。
关键代码是:ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()),具体的handle方法实现在AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter类中,具体实现细节如下:
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
handleInternal就是我们希望看到的方法,这个方法做的事情就是执行Controller中根据url挑选出来的Handler,并且将Handler的处理结果进行合适的view渲染的过程,关键的方法是invokeHandlerMethod:
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found concurrent result value [" + result + "]");
}
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
上面的方法的关键是invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle,下面是关键的方法调用代码:
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Invoking [");
sb.append(getBeanType().getSimpleName()).append(".");
sb.append(getMethod().getName()).append("] method with arguments ");
sb.append(Arrays.asList(args));
logger.trace(sb.toString());
}
Object returnValue = doInvoke(args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method [" + getMethod().getName() + "] returned [" + returnValue + "]");
}
return returnValue;
}
doInvoke方法就是实际访问Handler的实现,到此,Controller中的Handler方法已经执行完成了,接着会调用getModelAndView来进行试图渲染,这一部分的内容就不再分析了,未来找机会再进行详细分析。
至此,我们居然已经分析完了一个请求的处理流程,包括请求的解析,url匹配Handler,已经Controller中Handler的执行等内容,但是好像还缺点什么,那就是我们在进行用url来匹配handler的时候,貌似没有解析Controller类的流程,但是可以肯定的是这个流程肯定是存在的,那是否这个流程在处理请求之前就完成了呢?现在来挖掘一下这部分的内容,当我们找到并且分析了这部分的内容之后,整个流程就算是走通了。
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类中有一个方法特别关键,那就是afterPropertiesSet:
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class beanType = null;
try {
beanType = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现了InitializingBean接口,所以在bean进行了初始化之后会调用该afterPropertiesSet做一些事情,下面来具体分析一下initHandlerMethods这个方法的细节,看样子是开始初始化Handler的过程。首先获取了所有的beanName,然后会对每一个bean进行处理,使用etApplicationContext().getType方法来获取bean的类型,然后使用isHandler来判断一个bean是否是Handler类型的bean,如果是的话就会调用detectHandlerMethods,下面是isHandler方法的具体实现:
protected boolean isHandler(Class beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
关于如何快速判断一个类是否具有注解可以参考文章Java如何快速获取类附带的注解,只要注解中有 Controller或者RequestMapping就代表该类含有Handler,所以就得去detect,现在回到initHandlerMethods方法,接着看一下detectHandlerMethods方法的具体实现。
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
Class handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
final Class userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup() {
@Override
public T inspect(Method method) {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
});
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods);
}
for (Map.Entry entry : methods.entrySet()) {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
T mapping = entry.getValue();
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
}
}
主要看registerHandlerMethod这个方法,就是注册Handler的实现:
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + handlerMethod);
}
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
register方法实现了handler的注册,解析好了之后当然要保存起来啊,否则后面怎么取?所以在此注册之后,就可以在用url匹配handler的时候使用了。
至此,整条链路就走通了,从Spring bean加载流程的触发,到web.xml的配置以及准则等细节,再到实际请求的处理流程,最后发现在处理请求的时候使用到的handler还没有分析解析流程,所以最后分析了MVC中Controller的handler解析流程,在这一步保存解析好保存起来之后,后面处理请求的时候就可以用来匹配具体的url以及其他的匹配项了,最终一个请求可以得到处理。当然,本文并没有涉及到view渲染的分析,因为在很多时候,我们直接将model写到了response中去了,而不是返回一个视图,而且渲染视图的流程简单但是较为繁琐,基于这些原因就不再分析了。本文涉及的大部分细节内容会不断进行学习补充,但是主干流程应该就像本文分析的一样,并且这些都是可以猜出来的,只是Spring MVC的实现由他自己的优秀的地方,而正是由于具备优秀的特性,才值得不断学习,发现其中的优秀。