【小家Java】Java第二API之apache的commons-lang3工具包史上最完整的讲解(书写优雅代码必备工具)
相关阅读
【小家java】java5新特性(简述十大新特性) 重要一跃
【小家java】java6新特性(简述十大新特性) 鸡肋升级
【小家java】java7新特性(简述八大新特性) 不温不火
【小家java】java8新特性(简述十大新特性) 饱受赞誉
【小家java】java9新特性(简述十大新特性) 褒贬不一
【小家java】java10新特性(简述十大新特性) 小步迭代
【小家java】java11新特性(简述八大新特性) 首个重磅LTS版本
每篇一句
曹德旺:滴水之恩,涌泉相报。记住每家帮你的。但当你帮助了别人的时候,立马忘掉,记住心上,你会完蛋,会害了你。
前言:
apache提供的众多commons工具包,号称Java第二API,而common里面lang3包更是被我们使用得最多的。因此本文主要详细讲解lang3包里面几乎每个类的使用,希望以后大家使用此工具包,写出优雅的代码
讲解版本为(2018年10月最新版本):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3artifactId>
<version>3.8version>
dependency>
在日常工作中,我们经常要使用到一些开源工具包,比如String,Date等等。有时候我们并不清楚有这些工具类的存在,造成在开发过程中重新实现导致时间浪费,且开发的代码质量不佳。而apache其实已经提供了系列的工具包给我们使用,只是大多数人,平时没有注意到。这个系列我将带领大家熟悉这些常用的工具包,让大家熟悉Apache都给我们提供了那些常用的工具类和方法……
commons-lang3和commons-lang的区别
lang3是Apache Commons 团队发布的工具包,要求jdk版本在1.5以上,相对于lang来说完全支持java5的特性,废除了一些旧的API。该版本无法兼容旧有版本,于是为了避免冲突改名为lang3
lang包可以说是废弃了,以后请不要使用。采用lang3直接代替即可
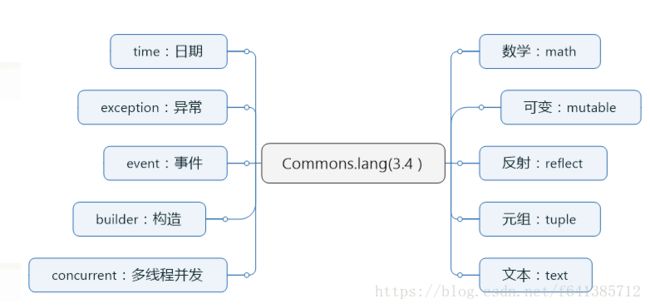
包结构
org.apache.commons.lang3
org.apache.commons.lang3.builder
org.apache.commons.lang3.concurrent
org.apache.commons.lang3.event
org.apache.commons.lang3.exception
org.apache.commons.lang3.math
org.apache.commons.lang3.mutable
org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect
org.apache.commons.lang3.text
org.apache.commons.lang3.text.translate
org.apache.commons.lang3.time
org.apache.commons.lang3.tuple
脑图如下:
类截图如下:
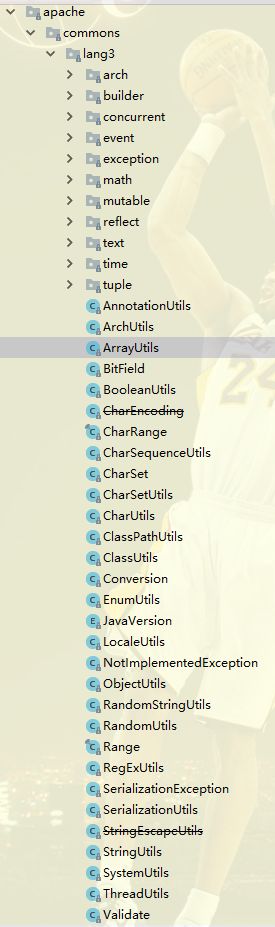
下面进行用得着的情况,从上倒下逐个类讲解。
ArrayUtils:用于对数组的操作,如添加、查找、删除、子数组、倒序、元素类型转换等
- 它提供了8中基本数据类型以及包装类以及各种类型的长度为0的空数组。所以以后需要长度为0的数组,可以不用new了,直接用这个即可
public static final int[] EMPTY_INT_ARRAY = new int[0];
public static final Integer[] EMPTY_INTEGER_OBJECT_ARRAY = new Integer[0];
- toString:功能基本同java自己的Arrays.toString方法
- hashCode:相同个数、相同顺序的数组hashCode会是一样的
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] inArr = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3};
Integer[] inArr2 = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.hashCode(inArr)); //862547
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.hashCode(inArr2)); //862547
inArr = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3};
inArr2 = new Integer[]{1, 3, 3};
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.hashCode(inArr)); //862547
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.hashCode(inArr2)); //862584
}
- isEquals:该方法已经被废弃。取代的为java自己的java.util.Objects.deepEquals(Object, Object)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] inArr = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3};
Integer[] inArr2 = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(Objects.deepEquals(inArr, inArr2)); //true
inArr = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3};
inArr2 = new Integer[]{1, 3, 3};
System.out.println(Objects.deepEquals(inArr, inArr2)); //false
}
- toArray:可以简便的构建一个数组。但是注意下面的区别:
Integer[] integers = ArrayUtils.toArray(1, 2, 3);
Serializable[] serializables = ArrayUtils.toArray(1, 2, "3");
- nullToEmpty:将null转换为空的数组,如果数组不为null,返回原数组,如果数组为null,返回一个空的数组
- toObject/toPrimitive:这两个方法很有用 可以实现比如int[]和Integer[]数组之间的互转
Integer[] inArr = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3};
int[] ints = ArrayUtils.toPrimitive(inArr);
Integer[] integers = ArrayUtils.toObject(ints);
toStringArray:同上。这个方法是将Object数组转换成String数组。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] inArr = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3};
int[] ints = new int[]{1,2,3};
String[] strings = ArrayUtils.toStringArray(inArr);
//ArrayUtils.toStringArray(ints); //编译报错哟
}
需要注意:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] inArr = new Integer[]{1, 2, null};
//String[] strings = ArrayUtils.toStringArray(inArr);
//如果里面有null元素,会报错的,所以我们可以用下面这个方法 把null转成指定的值即可
String[] strings = ArrayUtils.toStringArray(inArr,"");
}
- getLength、isSameLength:有时候建议使用。因为它是对null安全的。null的length为0
CharEncoding:过时。被Java自己的java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets取代
CharUtils – 用于操作char值和Character对象
- toCharacterObjec/toChart:把char或者String转为一个Character对象。互转。Character,valueOf()很多时候也能达到这个效果
- toIntValue:把char和Character转为对应的int值
- isAscii系列:判断该字符是否是Ascii码
ClassPathUtils:处理类路径的一些工具类
- toFullyQualifiedName(Class context, String resourceName) 返回一个由class包名+resourceName拼接的字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fullPath = ClassPathUtils.toFullyQualifiedName(Integer.class, "");
System.out.println(fullPath); //java.lang.
//fullPath = ClassPathUtils.toFullyQualifiedName(Integer.class.getPackage(), "Integer.value");
fullPath = ClassPathUtils.toFullyQualifiedName(Integer.class, "Integer.value");
System.out.println(fullPath); //java.lang.Integer.value
}
- toFullyQualifiedName(Package context, String resourceName) 返回一个由class包名+resourceName拼接的字符串
- toFullyQualifiedPath(Class context, String resourceName) 返回一个由class包名+resourceName拼接的字符串
- toFullyQualifiedPath(Package context, String resourceName) 返回一个由class包名+resourceName拼接的字符串
ClassPathUtils.toFullyQualifiedPath(StringUtils.class, "StringUtils.properties") = "org/apache/commons/lang3/StringUtils.properties"
ClassUtils – 用于对Java类的操作(有很多方法还是挺有用的)
- getShortClassName:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(int[].class.getSimpleName()); //int[]
System.out.println(ClassUtils.getShortClassName(int[].class)); //int[]
System.out.println(ClassUtils.getShortClassName(String.class)); //String
System.out.println(ClassUtils.getShortClassName(ArrayList.class)); //ArrayList
System.out.println(ClassUtils.getShortClassName("List")); //List
}
- getPackageName:获取包名
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(ClassUtils.getPackageName(int[].class)); //""
System.out.println(ClassUtils.getPackageName(String.class)); //java.lang
}
- getAllSuperclasses:获取到该类的所有父类 注意:只是父类 不包含接口
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Class<?>> allSuperclasses = ClassUtils.getAllSuperclasses(ArrayList.class);
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.toString(allSuperclasses)); //[class java.util.AbstractList, class java.util.AbstractCollection, class java.lang.Object]
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Class<?>> allSuperclasses = ClassUtils.getAllSuperclasses(ArrayList.class);
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.toString(allSuperclasses)); //[class java.util.AbstractList, class java.util.AbstractCollection, class java.lang.Object]
allSuperclasses = ClassUtils.getAllSuperclasses(Object.class);
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.toString(allSuperclasses)); //[]
}
- getAllInterfaces:同上。但此方法指的是接口
- convertClassNamesToClasses/convertClassesToClassNames 见名知意
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Class<?>> classes = ClassUtils.convertClassNamesToClasses(Arrays.asList("java.lang.Integer","java.lang.int"));
System.out.println(classes); //[class java.lang.Integer, null]
}
- isPrimitiveOrWrapper、isPrimitiveWrapper 、primitiveToWrapper、primitivesToWrappers、wrapperToPrimitive判断是基本类型还是包装类型
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(Integer.class)); //true
System.out.println(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(int.class)); //true
//检测是否是包装类型
System.out.println(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveWrapper(Object.class)); //false 注意 此处是false
System.out.println(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveWrapper(Integer.class)); //true
System.out.println(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveWrapper(int.class)); //false
//检测是否是基本类型
System.out.println(Object.class.isPrimitive()); //false 注意 此处也是false
System.out.println(Integer.class.isPrimitive()); //false
System.out.println(int.class.isPrimitive()); //true
}
-
isAssignable:是否是相同的class类型 支持class、数组等等 挺实用的
-
isInnerClass:检查一个类是否是内部类或者静态内部类等
-
getClass:加强版的Class.forName() 可以指定值是否要马上初始化该类
-
hierarchy:获取到该类的继承结构
public static void main(String[] args) {
Iterable<Class<?>> hierarchy = ClassUtils.hierarchy(ArrayList.class);
hierarchy.forEach(System.out::println);
//输出了类的层级结构(默认是不包含接口的)
//class java.util.ArrayList
//class java.util.AbstractList
//class java.util.AbstractCollection
//class java.lang.Object
hierarchy = ClassUtils.hierarchy(ArrayList.class,ClassUtils.Interfaces.INCLUDE);
hierarchy.forEach(System.out::println);
//class java.util.ArrayList
//interface java.util.List
//interface java.util.Collection
//interface java.lang.Iterable
//interface java.util.RandomAccess
//interface java.lang.Cloneable
//interface java.io.Serializable
//class java.util.AbstractList
//class java.util.AbstractCollection
//class java.lang.Object
}
EnumUtils:辅助操作枚举的一些工具
- getEnum(Class enumClass, String enumName) 通过类返回一个枚举,可能返回空
- getEnumList(Class enumClass) 通过类返回一个枚举集合
- getEnumMap(Class enumClass) 通过类返回一个枚举map
- isValidEnum(Class enumClass, String enumName) 验证enumName是否在枚举中,返回true false
//枚举类
public enum ImagesTypeEnum {
JPG,JPEG,PNG,GIF;
}
//测试
ImagesTypeEnum imagesTypeEnum = EnumUtils.getEnum(ImagesTypeEnum.class, "JPG");
System.out.println("imagesTypeEnum = " + imagesTypeEnum);
System.out.println("--------------");
List<ImagesTypeEnum> imagesTypeEnumList = EnumUtils.getEnumList(ImagesTypeEnum.class);
imagesTypeEnumList.stream().forEach(
imagesTypeEnum1 -> System.out.println("imagesTypeEnum1 = " + imagesTypeEnum1)
);
System.out.println("--------------");
Map<String, ImagesTypeEnum> imagesTypeEnumMap = EnumUtils.getEnumMap(ImagesTypeEnum.class);
imagesTypeEnumMap.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println("key:" + k + ",value:" + v));
System.out.println("-------------");
boolean result = EnumUtils.isValidEnum(ImagesTypeEnum.class, "JPG");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
boolean result1 = EnumUtils.isValidEnum(ImagesTypeEnum.class, null);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
输出:
imagesTypeEnum = JPG
--------------
imagesTypeEnum1 = JPG
imagesTypeEnum1 = JPEG
imagesTypeEnum1 = PNG
imagesTypeEnum1 = GIF
--------------
key:JPG,value:JPG
key:JPEG,value:JPEG
key:PNG,value:PNG
key:GIF,value:GIF
-------------
result = true
result1 = false
JavaVersion 枚举类,记录了java所有的版本号
RandomStringUtils : 需要随机字符串的时候,它或许能帮上忙
public static void main(String[] args) {
//随便随机一个字 所以有可能是乱码
String random = RandomStringUtils.random(10);
//在指定范围内随机
String randomChars = RandomStringUtils.random(3,'a','b','c','d','e');
//随便随机10个Ascii
String randomAscii = RandomStringUtils.randomAscii(10);
//注意这里不是5到10内随机,而是随机一个长度的数字
String randomNumeric = RandomStringUtils.randomNumeric(5,10);
System.out.println(random); //?ᣒ?⍝?䆃ぬ
System.out.println(randomChars); //dac
System.out.println(randomAscii); //hpCQrtmUvi
System.out.println(randomNumeric); //2580338
}
RandomUtils:这个不解释,如果你需要随机数字,用它吧。int、long、flort都是ok的
RegExUtils:处理字符串用正则替换等
- removeAll
- removeFirst
- removePattern
- replaceAll
- replaceFirst
SerializationUtils:对象的序列化工具。
在Json流行的时代,这个工具使用的几率就较小了。
- clone:采用字节数组ByteArrayInputStream来拷贝一个一模一样的对象
- serialize(final Serializable obj, final OutputStream outputStream) :可以把对象序列化到输出流里
- byte[] serialize(final Serializable obj):直接序列化成字节数组
- deserialize(final InputStream inputStream)、deserialize(final byte[] objectData)
SystemUtils:主要定义了一些系统底层的常量。比如类路径、操作系统、类型、java版本等等
StringUtils的使用:
参考我的另外一篇博文:【小家Java】common-lang3中StringUtils的使用详解
知识交流

若群二维码失效,请加微信号(或者扫描下方二维码):fsx641385712。
并且备注:“java入群” 字样,会手动邀请入群
