verilog 4位16位任意位超前进位加法器
众所周知,1+1=2,对于较小位数的加法,大家都可以在瞬间报出结果,但是如果比较大呢?
13242345609745021+24234123421=?我们就需要一些运算时间来计算出结果。当然如果您是最强大脑选手,可能也能立刻报出答案。对于这种“最强大脑”选手,我们在FPGA中对应的就是性能,我们选择成本更高的fpga比如您一开始使用的是cyclone I,现在换成了cyclone V系列产品,那么运算速度就自然会提高。
我们现在的想法就是想在同一个芯片上,减小运算的延时,从而提高系统的工作频率,而不是通过改变器件。
回想一下我们小学课上学的竖式加法运算
我们想得到第k位的最终结果,就需要知道第k位的加数,被加数,以及是否进位,那么进位又需要上一位的加数,被加数,进位数..以此类推直到第一位。这就是所谓的行波加法器了。
module add_4 (
input [3:0]a,
input [3:0]b,
input c_in,
output [3:0] sum,
output c_out
);
wire [3:0] c_tmp;
full_adder i0 ( a[0], b[0], c_in, sum[0], c_tmp[0]);
full_adder i1 ( a[1], b[1], c_tmp[0], sum[1], c_tmp[1] );
full_adder i2 ( a[2], b[2], c_tmp[1], sum[2], c_tmp[2] );
full_adder i3 ( a[3], b[3], c_tmp[2], sum[3], c_tmp[3] );
assign c_out = c_tmp[3];
endmodule
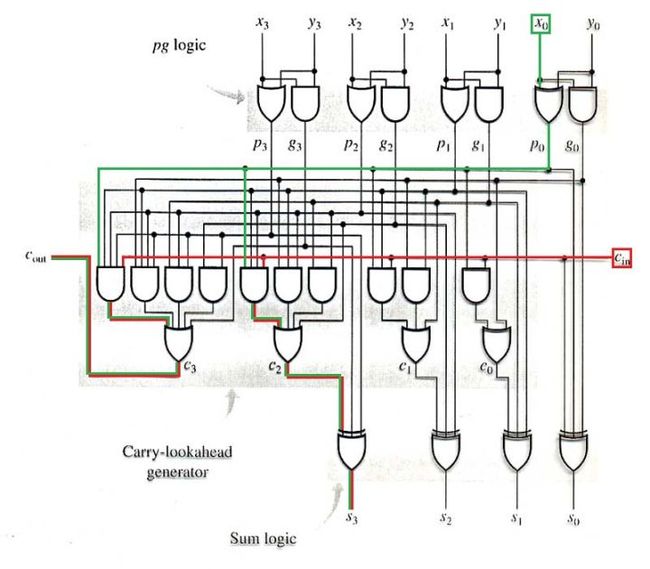
这是我从网上找到的一张图片,大概就是四个全加器级联,怎么个级联方法呢,就是把他们的低位进位输出连接到高位进位输入。关于全加器,如果大家不会的话,还是先翻翻verilog书吧,建议还是先把基础打好,因为这可以说是十分基本的内容了,任何一本verilog的书上肯定都会有的,我在这里主要介绍的是他的加强版超前进位加法器。
事实上,这个加法器需要9个门的传输延时,(第一个加法器需要三个,其他都是两个),于是我们想有没有一种方法可以快一点,让这个传输门的个数少一些呢,当然是可以的。这就是我要介绍的超前进位加法器了。
大家可以先自己想想,对于一个四位加法器来说,我们如何可以立刻知道第k位的进位值呢?因为如果我们知道了该位的进位值,就仅需要一个全加器也就是3个门延时就能得到了结果了,这无疑是令人兴奋的。
对于一个全加器我们知道
Si =Ai ^ Bi^ Ci-1
Ci = AiBi + AiCi-1 + BiCi-1=AiBi + (Ai+Bi)Ci-1
Ci = AiBi + AiCi-1 + BiCi-1=AiBi + (Ai+Bi)Ci-1
令 Gi=Ai*Bi ; Pi=Ai+Bi 代入Ci =AiBi + (Ai+Bi)Ci-1
得 Ci=Gi+Gi*Ci-1
C0 = C_in
C1=G0 + P0·C0
C2=G1 + P1·C1 = G1 + P1·G0 + P1·P0 ▪C0
C3=G2 + P2·C2 = G2 + P2·G1 + P2·P1·G0 + P2·P1·P0·C0
C4=G3 + P3·C3 = G3 + P3·G2 + P3·P2·G1 + P3·P2·P1·G0 + P3·P2·P1·P0·C0
C_out=C4
C1=G0 + P0·C0
C2=G1 + P1·C1 = G1 + P1·G0 + P1·P0 ▪C0
C3=G2 + P2·C2 = G2 + P2·G1 + P2·P1·G0 + P2·P1·P0·C0
C4=G3 + P3·C3 = G3 + P3·G2 + P3·P2·G1 + P3·P2·P1·G0 + P3·P2·P1·P0·C0
C_out=C4
现在我们只需要三个门就可以实现四位加法运算了!
module ahead_adder4
(
input cin,
input [3:0]A,
input [3:0]B,
input [3:0]G,
input [3:0]P,
output [3:0]S,
output cout
);
wire [3:0]C;
assign C[0]= G[0] | (cin&P[0]);
assign C[1]= G[1] | (P[1]&G[0]) | (P[1]&P[0]&cin);
assign C[2]= G[2] | (P[2]&G[1]) | (P[2]&P[1]&G[0]) | (P[2]&P[1]&P[0]&cin);
assign C[3]= G[3] | (P[3]&G[2]) | (P[3]&P[2]&G[1]) | (P[3]&P[2]&P[1]&G[0]) | (P[3]&P[2]&P[1]&P[0]&cin);
assign S[0]=A[0]^B[0]^cin;
assign S[1]=A[1]^B[1]^C[0];
assign S[2]=A[2]^B[2]^C[1];
assign S[3]=A[3]^B[3]^C[2];
assign cout=C[3];
endmodule
那么问题来了,如何实现16位超前进位加法器呢!?
有一种办法是将4个4位超前进位加法器级联,但实际上这是一种超前+行波的方式,并不是最快的组合!
事实上我们可以根据16位加数和被加数直接写出这四个超前进位加法器的进位值,这样即实现了超前进位的超前进位加法器!
代码如下:
module ahead_adder
(
input [15:0]A,
input [15:0]B,
input CIN,
output reg [15:0]S,
output reg cout
);
wire [15:0]G=A&B;
wire [15:0]P=A|B;
reg [3:0]cin;
wire cout1;
task ahead_adder4;
input cin;
input [3:0]A;
input [3:0]B;
input [3:0]G;
input [3:0]P;
output reg [3:0]S;
output reg cout;
reg [3:0]C;
begin
C[0]= G[0] | (cin&P[0]);
C[1]= G[1] | (P[1]&G[0]) | (P[1]&P[0]&cin);
C[2]= G[2] | (P[2]&G[1]) | (P[2]&P[1]&G[0]) | (P[2]&P[1]&P[0]&cin);
C[3]= G[3] | (P[3]&G[2]) | (P[3]&P[2]&G[1]) | (P[3]&P[2]&P[1]&G[0]) | (P[3]&P[2]&P[1]&P[0]&cin);
S[0]=A[0]^B[0]^cin;
S[1]=A[1]^B[1]^C[0];
S[2]=A[2]^B[2]^C[1];
S[3]=A[3]^B[3]^C[2];
cout=C[3];
end
endtask
task ahead_carry;
input cin;
input [15:0]G;
input [15:0]P;
output reg [3:0]cout;
reg [3:0]G2;
reg [3:0]P2;
begin
G2[0]=G[3] | P[3]&G[2] | P[3]&P[2]&G[1] | P[3]&P[2]&P[1]&G[0];
G2[1]=G[7] | P[7]&G[6] | P[7]&P[6]&G[5] | P[7]&P[6]&P[5]&G[4];
G2[2]=G[11] | P[11]&G[10] | P[11]&P[10]&G[9] | P[11]&P[10]&P[9]&G[8];
G2[3]=G[15] | P[15]&G[14] | P[15]&P[14]&G[13] | P[15]&P[14]&P[13]&G[12];
P2[0]=P[3]&P[2]&P[1]&P[0];
P2[1]=P[7]&P[6]&P[5]&P[4];
P2[2]=P[11]&P[10]&P[9]&P[8];
P2[3]=P[15]&P[14]&P[13]&P[12];
cout[0]=G2[0] | (cin&P2[0]);
cout[1]=G2[1] | (P2[1]&G2[0]) | (P2[1]&P2[0]&cin);
cout[2]=G2[2] | (P2[2]&G2[1]) | (P2[2]&P2[1]&G2[0]) | (P2[2]&P2[1]&P2[0]&cin);
cout[3]=G2[3] | (P2[3]&G2[2]) | (P2[3]&P2[2]&G2[1]) | (P2[3]&P2[2]&P2[1]&G2[0]) | (P2[3]&P2[2]&P2[1]&P2[0]&cin);
end
endtask
always@(*)
begin
ahead_carry(CIN,G[15:0],P[15:0],cin[3:0]);
ahead_adder4 (CIN,A[3:0],B[3:0],G[3:0],P[3:0],S[3:0],cout1);//因为进位值实际上已经被算出来了,所以这个cout1就没有实际意义
ahead_adder4 (cin[0],A[7:4],B[7:4],G[7:4],P[7:4],S[7:4],cout1);
ahead_adder4 (cin[1],A[11:8],B[11:8],G[11:8],P[11:8],S[11:8],cout1);
ahead_adder4 (cin[2],A[15:12],B[15:12],G[15:12],P[15:12],S[15:12],cout);//但是这个cout有实际意义,因为超前进位算出的是四个adder的低位进位值,没有算最后一个的高位进位,所以要保留
end
endmodule