TensorFlow实战——RNN(LSTM)——预测sin函数
http://blog.csdn.net/u011239443/article/details/73650806
关于LSTM可以参阅:http://blog.csdn.net/u011239443/article/details/73196473
完整代码:https://github.com/xiaoyesoso/TensorFlowinAction/blob/master/InActionB1/chapter8/sinModel.py
数据
我们先来看下需要产生的数据,我们每隔SAMPLE_GAP采样一个点:
test_start = TRAINING_EXAMPLES * SAMPLE_GAP
test_end = (TRAINING_EXAMPLES + TESTING_EXAMPLES) * SAMPLE_GAPTRAINING_EXAMPLES为训练样本的个数,TESTING_EXAMPLES为测试样本的个数。那么可知训练集的样本点落在 [0,test_start) 上,而测试集的样本落在 [test_start,test_end) 上:
train_X,train_y = generate_data(np.sin(np.linspace(0,test_start,TRAINING_EXAMPLES,dtype=np.float32)))
test_X,test_y = generate_data(np.sin(np.linspace(test_start,test_end,TESTING_EXAMPLES,dtype=np.float32)))使用numpy的linspace的到对应区间上的离散点后,再使用sin求出起sin函数值。然后将该数组传入generate_data函数。我们接下来看看generate_data函数是如何实现的:
def generate_data(seq):
X = []
y = []
for i in range(len(seq) - TIMESTEPS -1):
X.append([seq[i:i+TIMESTEPS]])
y.append([seq[i+TIMESTEPS]])
return np.array(X,dtype=np.float32),np.array(y,dtype=np.float32)我们要做的任务为根据前TIMESTEPS-1个采样点来预测第TIMESTEPS点的值。所以,可以看到X中存的是seq中的子数组,位置为: [0,0+TIMESTEPS],[1,1+TIMESTEPS],[2,2+TIMESTEPS]...[len(seq)−TIMESTEPS−1,len(seq)−1] 。y存的则是上述每个数组的最后一个数。
TFlearn & lstm_model
TFlearn是一个方便我们建模的工具:
learn = tf.contrib.learn调用Estimator来设置模型:
regressor = learn.Estimator(model_fn=lstm_model)调用fit来训练模型:
regressor.fit(train_X,train_y,batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,steps=TRAINING_STEPS)调用predict预测结果:
predicted = [[pred] for pred in regressor.predict(test_X)]接下来我们来看看函数lstm_model:
def lstm_model(X,y):
# 创建深度LSTM,深度为 HIDDEN_SIZE
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(HIDDEN_SIZE, state_is_tuple=True)
# 将 lstm_cell 变为多层RNN,层数为NUM_LAYERS
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([lstm_cell] * NUM_LAYERS)
# 训练rnn,output为输出的结果,_ 返回的是最终的状态
output,_ = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell,X,dtype=tf.float32)
# 将output 重塑成 n×HIDDEN_SIZE 的矩阵,即每行属于同一层
output = tf.reshape(output,[-1, HIDDEN_SIZE])
# 创建一个全连接层,1 表示输出的维度为1,即做的是 n×HIDDEN_SIZE 的矩阵 和 HIDDEN_SIZE×1的矩阵相乘。None指的是不使用激活函数。
predictions = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(output, 1, None)
# 重塑 y 和 predictions
labels = tf.reshape(y, [-1])
predictions = tf.reshape(predictions, [-1])
# 得到均方损失
loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(predictions, labels)
# 得到训练操作
train_op = tf.contrib.layers.optimize_loss(
loss, tf.contrib.framework.get_global_step(),
optimizer="Adagrad", learning_rate=0.1)
return predictions,loss,train_op函数的参数X,y,对应着训练时的train_X,train_y。返回值为(预测结果,损失值,训练操作):predictions,loss,train_op
预测 & 评价
predicted = [[pred] for pred in regressor.predict(test_X)]
rmse = np.sqrt(((predicted - test_y) ** 2 ).mean(axis=0))
print ("rmse : %f" % rmse[0])最后得到的均方根误差为:
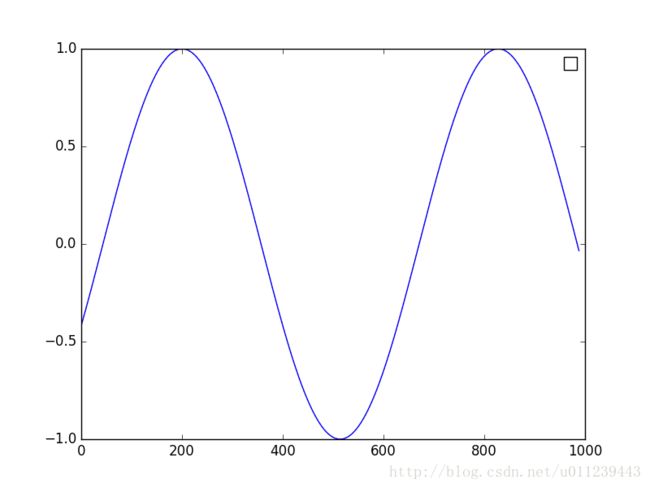
rmse : 0.001724用predicted,test_y描点画图:
fig = plt.figure()
plot_predicted = plt.plot(predicted,label='predicted')
plot_test = plt.plot(test_y,label='real_sin')
plt.legend([plot_predicted,plot_test],['predicted','real_sin'])
fig.savefig('sin.png')