数据集下载地址:http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Adult
在写该算法时遇到一个问题:
构造决策树时,这两段代码虽然都可以成功运行,但是构造的结果却有些不同。
如果用第一种方式遍历每个分支,会导致每次从右侧分支开始遍历,即使把branc_dict调整为{'right':right_split,'left':left_split}
而使用第二种方式,则可以正常遍历(先遍历左分支,再遍历右分支),到目前为止还没发现是什么原因导致的,各位有知道的欢迎留言~
以下为代码过程:
读入数据
import pandas as pd
columns=['age', 'workclass', 'fnlwgt', 'education', 'education_num',
'marital_status', 'occupation', 'relationship', 'race', 'sex',
'capital_gain', 'capital_loss', 'hours_per_week', 'native_country',
'high_income']
data=pd.read_table('./data/income.data',delimiter=',',names=columns)
data.head()
在开始构建决策树之前,我们需要把数据集中的分类型数据转换为数值型,pandas.Categorical方法可以把string型分类的column转换为Categorical Type,转换以后系统就会自动将该column中的类别映射为一个数字。
list=['workclass','education','marital_status', 'occupation',
'relationship', 'race', 'sex', 'native_country','high_income']
for name in list:
col=pd.Categorical.from_array(data[name])
data[name]=col.codes
data.head()
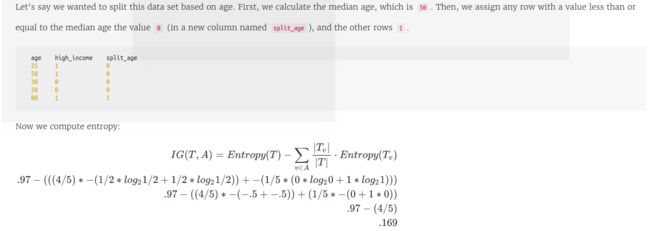
计算熵和信息增益:
熵
信息增益
def calc_entropy(target):
counts=np.bincount(target)
probabilities=counts/len(target)
entropys=probabilities*np.log2(probabilities)
return -sum(entropys)
def calc_information_gain(data,split_name,target):
entropy=calc_entropy(data[target])
median=np.median(data[split_name])
left_split=data[data[split_name]<=median]
right_split=data[data[split_name]>median]
to_subtract=0
for subset in [left_split,right_split]:
prob=subset.shape[0]/data.shape[0]
to_subtract+=prob*calc_entropy(subset[target])
return entropy-to_subtract
#通过计算每一个column的信息增益,获得最佳分裂属性(信息增益最大的)
def find_best_column(data,columns,target):
information_gains=[]
for name in columns:
information_gains.append(calc_information_gain(data,name,'high_income'))
information_index=information_gains.index(max(information_gains))
best_column=columns[information_index]
return best_column
带有存储功能的ID3算法:
为了实现存储功能,可以使用一个含有以下关键字的dictionary存储节点:
- left/right 关键字表示左右结点
- column 最佳分裂属性
- median 分裂属性的中位数
- number 结点编号
- label
如果结点为叶节点,则仅仅含有label(值为0/1)和number关键字
伪代码如下:
def id3(data, target, columns, tree)
1 Create a node for the tree
2 Number the node
3 If all of the values of the target attribute are 1, assign 1 to the label key in tree
4 If all of the values of the target attribute are 0, assign 0 to the label key in tree
5 Using information gain, find A, the column that splits the data best
6 Find the median value in column A
7 Assign the column and median keys in tree
8 Split A into values less than or equal to the median (0), and values above the median (1)
9 For each possible value (0 or 1), vi, of A,
10 Add a new tree branch below Root that corresponds to rows of data where A = vi
11 Let Examples(vi) be the subset of examples that have the value vi for A
12 Create a new key with the name corresponding to the side of the split (0=left, 1=right). The value of this key should be an empty dictionary.
13 Below this new branch, add the subtree id3(data[A==vi], target, columns, tree[split_side])
14 Return Root
实现代码:
tree={}
nodes=[] #重点注意:因为在递归中使用int型不能自增,所以采取使用数组的方法。
def id3(data,columns,target,tree):
nodes.append(len(nodes)+1)
tree['number']=nodes[-1]
unique_targets=pd.unique(data[target])
if len(unique_targets)==1:
tree['label']=unique_targets[0]
return #不要忘记返回
#如unique长度不为1,既包含0又含1,需要分裂:
best_column=find_best_column(data,columns,target)
median=np.median(data[best_column])
tree['column']=best_column #分裂key
tree['median']=median #median key
left_split=data[data[best_column]<=median]
right_split=data[data[best_column]>median]
branch_dict={'left':left_split,'right':right_split}
for branch in branch_dict:
tree[branch]={}
id3(branch_dict[branch],columns,target,tree[branch])
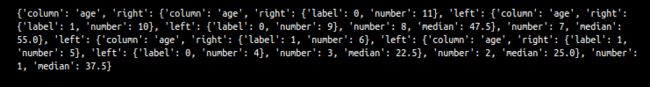
id3(data, ["age", "marital_status"],"high_income", tree)
print(tree)
结果为
为了方便观察决策树的构造结果,我们可以写一个结点输出函数,结构化的输出生成的决策树:
def print_with_depth(string,depth):
prefix=" "*depth
print("{0}{1}".format(prefix,string))
def print_node(tree,depth):
if 'label' in tree:
print_with_depth('Leaf label{0}'.format(tree['label']),depth)
return
print_with_depth('{0}>{1}'.format(tree['column'],tree['median']),depth)
branches = [tree["left"], tree["right"]]
for branch in branches:
print_node(branch,depth+1)
print_node(tree, 0 )
输出
实现预测功能:
#预测函数
def predict(tree,row):
if 'label' in tree:
return tree['label']
column=tree['column']
median=tree['median']
if row['columns']<=median:
return predict(tree['left'],row)
else:
return predict(tree['right'],row)
print(predict(tree, data.iloc[0]))
predictions=data.apply(lambda x:predict(tree,x),axis=1)
完。