PyTorch笔记8-Dropout
本系列笔记为莫烦PyTorch视频教程笔记 github源码
概要
在训练时 loss 已经很小,但是把训练的 NN 放到测试集中跑,loss 突然飙升,这很可能出现了过拟合(overfitting)
减低过拟合,一般可以通过:加大训练集、loss function 加入正则化项、Dropout 等途径,这里演示 Dropout
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(1)
%matplotlib inline准备数据
出现过拟合一般是由于训练数据过少且网络结构较复杂,为了凸显过拟合问题,这里只用 10 个数据集来进行训练
DATA_SIZE = 10
# training set
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, DATA_SIZE), dim=1) # sieze (20,1)
y = x + 0.3*torch.normal(torch.zeros(DATA_SIZE, 1), torch.ones(DATA_SIZE, 1))
x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y)
# test set
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, DATA_SIZE), dim=1)
test_y = test_x + 0.3*torch.normal(torch.zeros(DATA_SIZE,1), torch.ones(DATA_SIZE,1))
test_x, test_y = Variable(test_x), Variable(test_y)
# scatter
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy(), label='train')
plt.scatter(test_x.data.numpy(), test_y.data.numpy(), label='test')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylim((-2.5, 2.5))
plt.show()搭建神经网络
这里准备两个网络,一个是带 Dropout 的,一个是没有 Dropout 的,为了区分这两个网络,不带 Dropout 的容易出现过拟合(overfitting)故命名为 net_overfitting,而含 Dropout 的命名为 net_dropout
- 注1:设置 Dropout 时,torch.nn.Dropout(0.5), 这里的 0.5 是指该层(layer)的神经元在每次迭代训练时会随机有 50% 的可能性被丢弃(失活),不参与训练,一般多神经元的 layer 设置随机失活的可能性比神经元少的高
- 注2:由于要 Dropout,以及凸显过拟合现象,所以 layer 的神经元设置多些,这里为 300
N_HIDDEN = 300
# quick build NN by using Sequential
net_overfitting = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, N_HIDDEN), # first hidden layer
torch.nn.ReLU(), # activation func for first hidden layer
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, N_HIDDEN), # second hidden layer
torch.nn.ReLU(), # activation func for second hidden layer
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, 1)
)
net_dropout = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, N_HIDDEN),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5), # drop 50% neurons
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, N_HIDDEN),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, 1)
)
print('net_overfitting: \n', net_overfitting)
print('\n net_dropout: \n', net_dropout)net_overfitting:
Sequential (
(0): Linear (1 -> 300)
(1): ReLU ()
(2): Linear (300 -> 300)
(3): ReLU ()
(4): Linear (300 -> 1)
)
net_dropout:
Sequential (
(0): Linear (1 -> 300)
(1): Dropout (p = 0.5)
(2): ReLU ()
(3): Linear (300 -> 300)
(4): Dropout (p = 0.5)
(5): ReLU ()
(6): Linear (300 -> 1)
)
训练
为了控制单一变量(网络加不加 Dropout),net_overfitting 和 net_Dropout 的 loss、optimizer、lr等设置一致
optimizer_overfitting = torch.optim.Adam(net_overfitting.parameters(), lr=0.01)
optimizer_dropout = torch.optim.Adam(net_dropout.parameters(), lr=0.01)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for t in range(1000):
# train the NN by training set
prediction_overfitting = net_overfitting(x)
prediction_dropout = net_dropout(x)
loss_overfitting = loss_func(prediction_overfitting, y)
loss_dropout = loss_func(prediction_dropout, y)
optimizer_overfitting.zero_grad()
optimizer_dropout.zero_grad()
loss_overfitting.backward()
loss_dropout.backward()
optimizer_overfitting.step()
optimizer_dropout.step()测试并出图
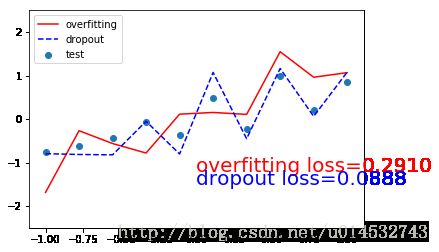
用之前伪造的 test set 进行测试,比较 net_overfitting 和 net_dropout 两个网络的 loss ,并用图形直观显示
- 注1:在测试时,是不需要 Dropout 的,所以在 测试前将网络改成 eval() 形式,net_overfitting 没有加 Dropout,所以不需更改
# test the NN by test set
net_dropout.eval() # test time differ from train time, NOT Dropout as test time
test_prediction_overfitting = net_overfitting(test_x)
test_prediction_dropout = net_dropout(test_y)
# scatter
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy(), label='train')
plt.scatter(test_x.data.numpy(), test_y.data.numpy(), label='test')
# plot
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), test_prediction_overfitting.data.numpy(),'r-', label='overfitting')
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), test_prediction_dropout.data.numpy(), 'b--', label='dropout')
plt.text(0, -1.2, 'overfitting loss=%.4f' % loss_func(test_prediction_overfitting, test_y).data[0], fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.text(0, -1.5, 'dropout loss=%.4f' % loss_func(test_prediction_dropout, test_y).data[0], fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'blue'})
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylim((-2.5, 2.5))
plt.show()从上图可以看出,测试集中,net_overfitting(not dropout)的 loss 比 net_dropout(with dropout)的 loss 大,红色线条(not dropout) 对测试集数据的拟合效果比蓝色线条(with dropout)差