深度有趣 | 04 图像风格迁移
简介
图像风格迁移是指,将一幅内容图的内容,和一幅或多幅风格图的风格融合在一起,从而生成一些有意思的图片
以下是将一些艺术作品的风格,迁移到一张内容图之后的效果
我们使用TensorFlow和Keras分别来实现图像风格迁移,主要用到深度学习中的卷积神经网络,即CNN
准备
安装包
pip install numpy scipy tensorflow keras
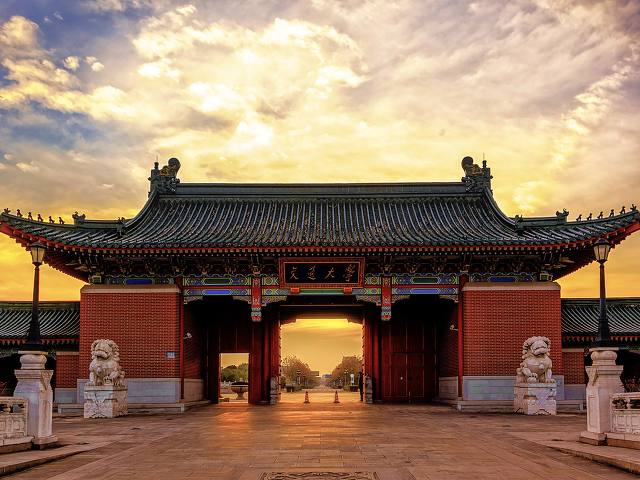
再准备一些风格图片,和一张内容图片
原理
为了将风格图的风格和内容图的内容进行融合,所生成的图片,在内容上应当尽可能接近内容图,在风格上应当尽可能接近风格图
因此需要定义内容损失函数和风格损失函数,经过加权后作为总的损失函数
实现步骤如下
- 随机产生一张图片
- 在每轮迭代中,根据总的损失函数,调整图片的像素值
- 经过多轮迭代,得到优化后的图片
内容损失函数
两张图片在内容上相似,不能仅仅靠简单的纯像素比较
CNN具有抽象和理解图像的能力,因此可以考虑将各个卷积层的输出作为图像的内容
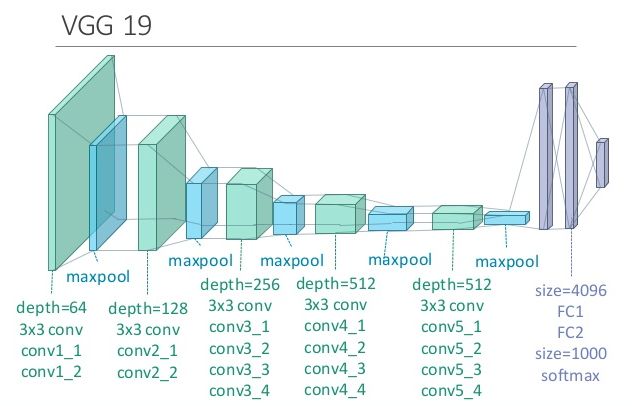
以VGG19为例,其中包括了多个卷积层、池化层,以及最后的全连接层
这里我们使用conv4_2的输出作为图像的内容表示,定义内容损失函数如下
L c o n t e n t ( p ⃗ , x ⃗ , l ) = 1 2 ∑ i , j ( F i j l − P i j l ) 2 L_{content}(\vec{p},\vec{x},l)=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i,j}{(F_{ij}^{l}-P_{ij}^{l})}^2 Lcontent(p,x,l)=21i,j∑(Fijl−Pijl)2
风格损失函数
风格是一个很难说清楚的概念,可能是笔触、纹理、结构、布局、用色等等
这里我们使用卷积层各个特征图之间的互相关作为图像的风格,以conv1_1为例
- 共包含64个特征图即feature map,或者说图像的深度、通道的个数
- 每个特征图都是对上一层输出的一种理解,可以类比成64个人对同一幅画的不同理解
- 这些人可能分别偏好印象派、现代主义、超现实主义、表现主义等不同风格
- 当图像是某一种风格时,可能这一部分人很欣赏,但那一部分人不喜欢
- 当图像是另一种风格时,可能这一部分人不喜欢,但那一部分人很欣赏
- 64个人之间理解的差异,可以用特征图的互相关表示,这里使用
Gram矩阵计算互相关 - 不同的风格会导致差异化的互相关结果
Gram矩阵的计算如下,如果有64个特征图,那么Gram矩阵的大小便是64*64,第i行第j列的值表示第i个特征图和第j个特征图之间的互相关,用内积计算
G i j l = ∑ k F i k l F j k l G_{ij}^l=\sum_k{F_{ik}^l F_{jk}^l} Gijl=k∑FiklFjkl
风格损失函数定义如下,对多个卷积层的风格表示差异进行加权
E l = 1 4 N l 2 M l 2 ∑ i , j ( G i j l − A i j l ) 2 E_l=\frac{1}{4N_l^2 M_l^2}\sum_{i,j}(G_{ij}^l-A_{ij}^l)^2 El=4Nl2Ml21i,j∑(Gijl−Aijl)2
L s t y l e ( a ⃗ , x ⃗ ) = ∑ l = 0 L ω l E l L_{style}(\vec{a},\vec{x})=\sum_{l=0}^{L}\omega_l E_l Lstyle(a,x)=l=0∑LωlEl
这里我们使用conv1_1、conv2_1、conv3_1、conv4_1、conv5_1五个卷积层,进行风格损失函数的计算,不同的权重会导致不同的迁移效果
总的损失函数
总的损失函数即内容损失函数和风格损失函数的加权,不同的权重会导致不同的迁移效果
L t o t a l ( p ⃗ , a ⃗ , x ⃗ ) = α L c o n t e n t ( p ⃗ , x ⃗ ) + β L s t y l e ( a ⃗ , x ⃗ ) L_{total}(\vec{p},\vec{a},\vec{x})=\alpha L_{content}(\vec{p},\vec{x})+\beta L_{style}(\vec{a},\vec{x}) Ltotal(p,a,x)=αLcontent(p,x)+βLstyle(a,x)
TensorFlow实现
加载库
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
import os
import time
def the_current_time():
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime(int(time.time()))))
定义一些变量
CONTENT_IMG = 'content.jpg'
STYLE_IMG = 'style5.jpg'
OUTPUT_DIR = 'neural_style_transfer_tensorflow/'
if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):
os.mkdir(OUTPUT_DIR)
IMAGE_W = 800
IMAGE_H = 600
COLOR_C = 3
NOISE_RATIO = 0.7
BETA = 5
ALPHA = 100
VGG_MODEL = 'imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat'
MEAN_VALUES = np.array([123.68, 116.779, 103.939]).reshape((1, 1, 1, 3))
加载VGG19模型
def load_vgg_model(path):
'''
Details of the VGG19 model:
- 0 is conv1_1 (3, 3, 3, 64)
- 1 is relu
- 2 is conv1_2 (3, 3, 64, 64)
- 3 is relu
- 4 is maxpool
- 5 is conv2_1 (3, 3, 64, 128)
- 6 is relu
- 7 is conv2_2 (3, 3, 128, 128)
- 8 is relu
- 9 is maxpool
- 10 is conv3_1 (3, 3, 128, 256)
- 11 is relu
- 12 is conv3_2 (3, 3, 256, 256)
- 13 is relu
- 14 is conv3_3 (3, 3, 256, 256)
- 15 is relu
- 16 is conv3_4 (3, 3, 256, 256)
- 17 is relu
- 18 is maxpool
- 19 is conv4_1 (3, 3, 256, 512)
- 20 is relu
- 21 is conv4_2 (3, 3, 512, 512)
- 22 is relu
- 23 is conv4_3 (3, 3, 512, 512)
- 24 is relu
- 25 is conv4_4 (3, 3, 512, 512)
- 26 is relu
- 27 is maxpool
- 28 is conv5_1 (3, 3, 512, 512)
- 29 is relu
- 30 is conv5_2 (3, 3, 512, 512)
- 31 is relu
- 32 is conv5_3 (3, 3, 512, 512)
- 33 is relu
- 34 is conv5_4 (3, 3, 512, 512)
- 35 is relu
- 36 is maxpool
- 37 is fullyconnected (7, 7, 512, 4096)
- 38 is relu
- 39 is fullyconnected (1, 1, 4096, 4096)
- 40 is relu
- 41 is fullyconnected (1, 1, 4096, 1000)
- 42 is softmax
'''
vgg = scipy.io.loadmat(path)
vgg_layers = vgg['layers']
def _weights(layer, expected_layer_name):
W = vgg_layers[0][layer][0][0][2][0][0]
b = vgg_layers[0][layer][0][0][2][0][1]
layer_name = vgg_layers[0][layer][0][0][0][0]
assert layer_name == expected_layer_name
return W, b
def _conv2d_relu(prev_layer, layer, layer_name):
W, b = _weights(layer, layer_name)
W = tf.constant(W)
b = tf.constant(np.reshape(b, (b.size)))
return tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(prev_layer, filter=W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') + b)
def _avgpool(prev_layer):
return tf.nn.avg_pool(prev_layer, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
graph = {}
graph['input'] = tf.Variable(np.zeros((1, IMAGE_H, IMAGE_W, COLOR_C)), dtype='float32')
graph['conv1_1'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['input'], 0, 'conv1_1')
graph['conv1_2'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv1_1'], 2, 'conv1_2')
graph['avgpool1'] = _avgpool(graph['conv1_2'])
graph['conv2_1'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['avgpool1'], 5, 'conv2_1')
graph['conv2_2'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv2_1'], 7, 'conv2_2')
graph['avgpool2'] = _avgpool(graph['conv2_2'])
graph['conv3_1'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['avgpool2'], 10, 'conv3_1')
graph['conv3_2'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv3_1'], 12, 'conv3_2')
graph['conv3_3'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv3_2'], 14, 'conv3_3')
graph['conv3_4'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv3_3'], 16, 'conv3_4')
graph['avgpool3'] = _avgpool(graph['conv3_4'])
graph['conv4_1'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['avgpool3'], 19, 'conv4_1')
graph['conv4_2'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv4_1'], 21, 'conv4_2')
graph['conv4_3'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv4_2'], 23, 'conv4_3')
graph['conv4_4'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv4_3'], 25, 'conv4_4')
graph['avgpool4'] = _avgpool(graph['conv4_4'])
graph['conv5_1'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['avgpool4'], 28, 'conv5_1')
graph['conv5_2'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv5_1'], 30, 'conv5_2')
graph['conv5_3'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv5_2'], 32, 'conv5_3')
graph['conv5_4'] = _conv2d_relu(graph['conv5_3'], 34, 'conv5_4')
graph['avgpool5'] = _avgpool(graph['conv5_4'])
return graph
内容损失函数
def content_loss_func(sess, model):
def _content_loss(p, x):
N = p.shape[3]
M = p.shape[1] * p.shape[2]
return (1 / (4 * N * M)) * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(x - p, 2))
return _content_loss(sess.run(model['conv4_2']), model['conv4_2'])
风格损失函数
STYLE_LAYERS = [('conv1_1', 0.5), ('conv2_1', 1.0), ('conv3_1', 1.5), ('conv4_1', 3.0), ('conv5_1', 4.0)]
def style_loss_func(sess, model):
def _gram_matrix(F, N, M):
Ft = tf.reshape(F, (M, N))
return tf.matmul(tf.transpose(Ft), Ft)
def _style_loss(a, x):
N = a.shape[3]
M = a.shape[1] * a.shape[2]
A = _gram_matrix(a, N, M)
G = _gram_matrix(x, N, M)
return (1 / (4 * N ** 2 * M ** 2)) * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(G - A, 2))
return sum([_style_loss(sess.run(model[layer_name]), model[layer_name]) * w for layer_name, w in STYLE_LAYERS])
随机产生一张初始图片
def generate_noise_image(content_image, noise_ratio=NOISE_RATIO):
noise_image = np.random.uniform(-20, 20, (1, IMAGE_H, IMAGE_W, COLOR_C)).astype('float32')
input_image = noise_image * noise_ratio + content_image * (1 - noise_ratio)
return input_image
加载图片
def load_image(path):
image = scipy.misc.imread(path)
image = scipy.misc.imresize(image, (IMAGE_H, IMAGE_W))
image = np.reshape(image, ((1, ) + image.shape))
image = image - MEAN_VALUES
return image
保存图片
def save_image(path, image):
image = image + MEAN_VALUES
image = image[0]
image = np.clip(image, 0, 255).astype('uint8')
scipy.misc.imsave(path, image)
调用以上函数并训练模型
the_current_time()
with tf.Session() as sess:
content_image = load_image(CONTENT_IMG)
style_image = load_image(STYLE_IMG)
model = load_vgg_model(VGG_MODEL)
input_image = generate_noise_image(content_image)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
sess.run(model['input'].assign(content_image))
content_loss = content_loss_func(sess, model)
sess.run(model['input'].assign(style_image))
style_loss = style_loss_func(sess, model)
total_loss = BETA * content_loss + ALPHA * style_loss
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(2.0)
train = optimizer.minimize(total_loss)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
sess.run(model['input'].assign(input_image))
ITERATIONS = 2000
for i in range(ITERATIONS):
sess.run(train)
if i % 100 == 0:
output_image = sess.run(model['input'])
the_current_time()
print('Iteration %d' % i)
print('Cost: ', sess.run(total_loss))
save_image(os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'output_%d.jpg' % i), output_image)
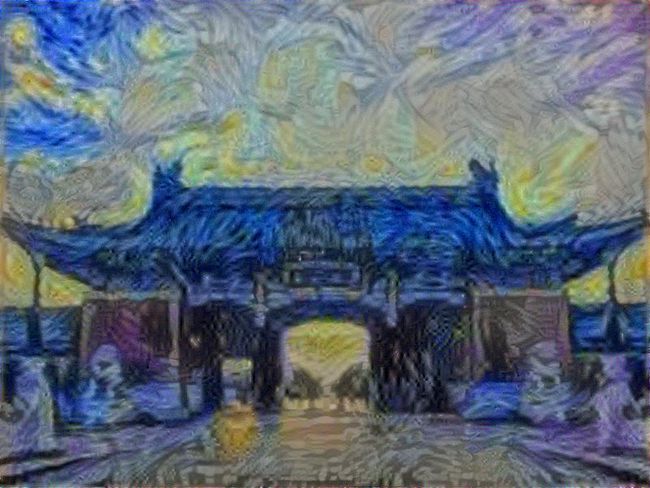
在GPU上跑,花了5分钟左右,2000轮迭代后是这个样子
对比原图
Keras实现
Keras官方提供了图像风格迁移的例子
https://github.com/fchollet/keras/blob/master/examples/neural_style_transfer.py
代码里引入了一个total variation loss,翻译为全变差正则,据说可以让生成的图像更平滑
- Keras相对TensorFlow封装更高,所以实现已有的模块更方便,但需要造轮子时较麻烦
- 增加了全变差正则,以生成的图像作为参数
- 使用
conv5_2计算内容损失 - 将内容图作为一开始的结果,即不使用随机产生的图片
代码使用方法如下
python neural_style_transfer.py path_to_your_base_image.jpg path_to_your_reference.jpg prefix_for_results
--iter:迭代次数,默认为10--content_weight:内容损失权重,默认为0.025--style_weight:风格损失权重,默认为1.0--tv_weight:全变差正则权重,默认为1.0
新建文件夹neural_style_transfer_keras
python main_keras.py content.jpg style5.jpg neural_style_transfer_keras/output
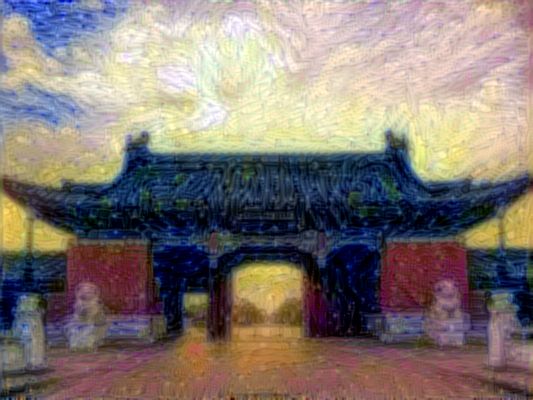
生成的图片长这样,10次迭代,花了1分钟左右
参考
- A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style:https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.06576
- TensorFlow Implementation of “A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style”:http://www.chioka.in/tensorflow-implementation-neural-algorithm-of-artistic-style
- 图像风格迁移简史:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/26746283
- 【啄米日常】图像风格转移:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/23479658
视频讲解课程
深度有趣(一)