Ardupilot飞控姿态角与姿态角速度控制过程
目录
-
- 目录
- 摘要
- 1.自稳模式初始化
- 2.自稳模式更新函数
- 这个代码主要把横滚输入,俯仰输入量转换成目标角度需要的范围,也就是+4500,-4500
- 3.姿态角速度代码控制过程分析
- 4.电机PWM控制运算
摘要
本节主要记录自己学习ardupilot飞控代码的姿态角速度的控制过程
分析过程:主要从ardupilot自稳模式开始,然后到角速度控制,最后到输出PWM控制电机实现无人机的基本运动模式的过程。思考:无人机工作在自稳模式,需要输入的是什么,自稳模式工作后输出了什么,输出的值怎么传到姿态角速度控制,姿态角速度控制最后输出了的PID怎么控制无人机的?
1.自稳模式初始化
从bool Copter::set_mode(control_mode_t mode, mode_reason_t reason)函数开始
寻找自稳模式初始化:
success = stabilize_init(ignore_checks); //姿态自我稳定模式
bool Copter::stabilize_init(bool ignore_checks)
{
// if landed and the mode we're switching from does not have manual throttle and the throttle stick is too high
//如果着陆,我们切换的模式不能是手动控制模式并且油门值不能太高,否则返回。
if (motors->armed() && ap.land_complete && !mode_has_manual_throttle(control_mode) &&
(get_pilot_desired_throttle(channel_throttle->get_control_in()) > get_non_takeoff_throttle()))
{
return false;
}
//将目标高度设置为零以用于报告--------set target altitude to zero for reporting
pos_control->set_alt_target(0);
return true;
}
看下其中一个函数:
void set_alt_target(float alt_cm) //设置目标高度
{
_pos_target.z = alt_cm;
}
这个函数就是设置目标高度的函数,我们是自稳模式,定高不需要设置,自稳模式设置不是特别复杂。下面看下自稳模式运行函数2.自稳模式更新函数
(1)从update_flight_mode()函数开始;
(2) stabilize_run(); //自稳控制
自稳模式作用完一定会把运算的PID数据作为姿态角速度环的目标输入量,我们看下这个函数的实现过程:
void Copter::stabilize_run()
{
float target_roll, target_pitch;
float target_yaw_rate;
float pilot_throttle_scaled;
//如果没有解锁,油门死区没有设置,获取电机安全锁没有开,立即返回---------if not armed set throttle to zero and exit immediately
if (!motors->armed() || ap.throttle_zero || !motors->get_interlock()) //要想解锁,这些条件全部是假的,才可以;_flags.interlock=0,不转
{
motors->set_desired_spool_state(AP_Motors::DESIRED_SPIN_WHEN_ARMED);
attitude_control->set_throttle_out_unstabilized(0,true,g.throttle_filt);
return;
}
//清空着落标志------------------------clear landing flag
set_land_complete(false); //ap.land_complete=0没有着落
motors->set_desired_spool_state(AP_Motors::DESIRED_THROTTLE_UNLIMITED); //设置油门限制不使能
//申请简单的模式到飞行器-----------------------------------------apply SIMPLE mode transform to pilot inputs
update_simple_mode();
//将遥控器输入转换成倾斜角度----------------------------------------convert pilot input to lean angles
//要做的:转换成无人机的倾斜角度作为期望的角度(单位是浮点数据)-----------To-Do: convert get_pilot_desired_lean_angles to return angles as floats
get_pilot_desired_lean_angles(channel_roll->get_control_in(), channel_pitch->get_control_in(), target_roll, target_pitch, aparm.angle_max);
//获取目标偏航角速度-----------------------------------------------get pilot's desired yaw rate
target_yaw_rate = get_pilot_desired_yaw_rate(channel_yaw->get_control_in());
//获取飞行目标所需要的油门值-----------------------------------------get pilot's desired throttle
pilot_throttle_scaled = get_pilot_desired_throttle(channel_throttle->get_control_in());
//调用姿态控制器---------------------------------------------------call attitude controller
attitude_control->input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_euler_rate_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, target_yaw_rate, get_smoothing_gain());
//机体坐标角速率控制器运行周期100hz-----------------------------------body-frame rate controller is run directly from 100hz loop
//输出飞行油门值--------------------------------------------------output pilot's throttle
attitude_control->set_throttle_out(pilot_throttle_scaled, true, g.throttle_filt);
}对这个代码重点分析:
1》基本需要检查
if (!motors->armed() || ap.throttle_zero || !motors->get_interlock()) //要想解锁,这些条件全部是假的,才可以;_flags.interlock=0,不转
{
motors->set_desired_spool_state(AP_Motors::DESIRED_SPIN_WHEN_ARMED); //电机不解锁
attitude_control->set_throttle_out_unstabilized(0,true,g.throttle_filt); //油门输出0
return;
}2》清空着陆标志
set_land_complete(false); //ap.land_complete=0没有着落3》油门限制不使能
motors->set_desired_spool_state(AP_Motors::DESIRED_THROTTLE_UNLIMITED); //设置油门限制不使能4》更新遥控器控制机头飞行模式
update_simple_mode();
void Copter::update_simple_mode(void)
{
float rollx, pitchx;
//如果没有新遥控器数据,再简单模式下立即退出------exit immediately if no new radio frame or not in simple mode
if (ap.simple_mode == 0 || !ap.new_radio_frame) //没有配置简单模式就是直接正常模式
{
return;
}
//标记无线帧消耗---------- mark radio frame as consumed
ap.new_radio_frame = false;
//总结:简单模式就是飞行器起飞时头部对准的方向始终为机体坐标系的pitch轴,
//也就是说启动的时候就定死了机体坐标系,所以遥控器需要传入的 roll 和 pitch
//值需要转到机体坐标系,在转到地球坐标中。
if (ap.simple_mode == 1)//简单模式,头部对准的方向始终为机体方向
{
//旋转滚转,俯仰输入-初始简单航向(即面向北)---------rotate roll, pitch input by -initial simple heading (i.e. north facing)
rollx = channel_roll->get_control_in()*simple_cos_yaw - channel_pitch->get_control_in()*simple_sin_yaw; //机体坐标
pitchx = channel_roll->get_control_in()*simple_sin_yaw + channel_pitch->get_control_in()*simple_cos_yaw;
}else //无头模式
{
//旋转滚转,俯仰输入-超简单航向(倒向回家)---------rotate roll, pitch input by -super simple heading (reverse of heading to home)
rollx = channel_roll->get_control_in()*super_simple_cos_yaw - channel_pitch->get_control_in()*super_simple_sin_yaw;
pitchx = channel_roll->get_control_in()*super_simple_sin_yaw + channel_pitch->get_control_in()*super_simple_cos_yaw;
}
// rotate roll, pitch input from north facing to vehicle's perspective
channel_roll->set_control_in(rollx*ahrs.cos_yaw() + pitchx*ahrs.sin_yaw()); //旋转到地理坐标
channel_pitch->set_control_in(-rollx*ahrs.sin_yaw() + pitchx*ahrs.cos_yaw()); //旋转到地理坐标
}5》从遥控器获取目标自稳控制量(target_roll,target_pitch,target_yaw_rate,pilot_throttle_scaled)
//获取目标横滚,俯仰,偏航自稳控制输入量
get_pilot_desired_lean_angles(channel_roll->get_control_in(), channel_pitch->get_control_in(), target_roll, target_pitch, aparm.angle_max);
target_yaw_rate = get_pilot_desired_yaw_rate(channel_yaw->get_control_in());其中:channel_roll->get_control_in()
channel_pitch->get_control_in()
channel_yaw->get_control_in()
表示遥控器的输入量
RC_Channel *channel_roll;
RC_Channel *channel_pitch;
RC_Channel *channel_throttle;
RC_Channel *channel_yaw;
void Copter::get_pilot_desired_lean_angles(float roll_in, float pitch_in, float &roll_out, float &pitch_out, float angle_max)
{
//安全检查角最大参数------------ sanity check angle max parameter
aparm.angle_max = constrain_int16(aparm.angle_max,1000,8000);
//限制最大倾斜角度-------------limit max lean angle
angle_max = constrain_float(angle_max, 1000, aparm.angle_max);
//求出系数--------------------scale roll_in, pitch_in to ANGLE_MAX parameter range
float scaler = aparm.angle_max/(float)ROLL_PITCH_YAW_INPUT_MAX; ///4500
roll_in *= scaler;
pitch_in *= scaler;
//循环极限--------------------do circular limit
float total_in = norm(pitch_in, roll_in); //横滚和俯仰合成限制
if (total_in > angle_max)
{
float ratio = angle_max / total_in;
roll_in *= ratio;
pitch_in *= ratio;
}
// do lateral tilt to euler roll conversion
roll_in = (18000/M_PI) * atanf(cosf(pitch_in*(M_PI/18000))*tanf(roll_in*(M_PI/18000)));
// return
roll_out = roll_in;
pitch_out = pitch_in;
}这个代码主要把横滚输入,俯仰输入量转换成目标角度需要的范围,也就是+4500,-4500
float Copter::get_pilot_desired_yaw_rate(int16_t stick_angle)
{
float yaw_request;
// calculate yaw rate request
if (g2.acro_y_expo <= 0)
{
yaw_request = stick_angle * g.acro_yaw_p; //g.acro_yaw_p=4.5
} else
{
// expo variables
float y_in, y_in3, y_out;
// range check expo
if (g2.acro_y_expo > 1.0f || g2.acro_y_expo < 0.5f)
{
g2.acro_y_expo = 1.0f;
}
// yaw expo
y_in = float(stick_angle)/ROLL_PITCH_YAW_INPUT_MAX;
y_in3 = y_in*y_in*y_in;
y_out = (g2.acro_y_expo * y_in3) + ((1.0f - g2.acro_y_expo) * y_in);
yaw_request = ROLL_PITCH_YAW_INPUT_MAX * y_out * g.acro_yaw_p;
}
// convert pilot input to the desired yaw rate
return yaw_request;
}
偏航的控制,之间进行比例控制,然后把输出作为内环的控制量,由于偏航通道可以控制无人机顺时针旋转和逆时针旋转,所以这里怎么区分出来的呢?肯定是摇杆中立点是分界线,处理后,往左打是负值,往右是正,区分两个方向。最后得到偏航角速度目标控制量,偏航打杆控制速率,跟横滚,俯仰有所不同。油门函数处理;
pilot_throttle_scaled = get_pilot_desired_throttle(channel_throttle->get_control_in());
float Copter::get_pilot_desired_throttle(int16_t throttle_control, float thr_mid)
{
if (thr_mid <= 0.0f)
{
thr_mid = motors->get_throttle_hover();
}
int16_t mid_stick = channel_throttle->get_control_mid();
// protect against unlikely divide by zero
if (mid_stick <= 0)
{
mid_stick = 500;
}
// ensure reasonable throttle values
throttle_control = constrain_int16(throttle_control,0,1000); //确保数据值在0-1000
// calculate normalised throttle input
float throttle_in;
if (throttle_control < mid_stick)
{
// below the deadband
throttle_in = ((float)throttle_control)*0.5f/(float)mid_stick;
}else if(throttle_control > mid_stick)
{
// above the deadband
throttle_in = 0.5f + ((float)(throttle_control-mid_stick)) * 0.5f / (float)(1000-mid_stick);
}else
{
// must be in the deadband
throttle_in = 0.5f;
}
float expo = constrain_float(-(thr_mid-0.5)/0.375, -0.5f, 1.0f);
// calculate the output throttle using the given expo function
float throttle_out = throttle_in*(1.0f-expo) + expo*throttle_in*throttle_in*throttle_in;
return throttle_out; //0---1
}最后得到的油门值范围是【0-1】
6》最重要的姿态控制器
attitude_control->input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_euler_rate_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, target_yaw_rate, get_smoothing_gain());
void AC_AttitudeControl::input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_euler_rate_yaw(float euler_roll_angle_cd, float euler_pitch_angle_cd, float euler_yaw_rate_cds, float smoothing_gain)
{
//转换为弧度------Convert from centidegrees on public interface to radians
float euler_roll_angle = radians(euler_roll_angle_cd*0.01f); //缩小100倍
float euler_pitch_angle = radians(euler_pitch_angle_cd*0.01f); //缩小100倍
float euler_yaw_rate = radians(euler_yaw_rate_cds*0.01f); //缩小100倍
//计算所需要的目标姿态欧拉角度--------calculate the attitude target euler angles
_attitude_target_quat.to_euler(_attitude_target_euler_angle.x, _attitude_target_euler_angle.y, _attitude_target_euler_angle.z);
//确保平滑增益不会引起过冲------------ensure smoothing gain can not cause overshoot
smoothing_gain = constrain_float(smoothing_gain,1.0f,1/_dt);
//增加辊纵倾以补偿Heli中的尾旋翼推力(将在多旋翼上返回零)----Add roll trim to compensate tail rotor thrust in heli (will return zero on multirotors)
euler_roll_angle += get_roll_trim_rad();
if (_rate_bf_ff_enabled & _use_ff_and_input_shaping)
{
//将横滚,俯仰和偏航加速度极限转换为欧拉轴---- translate the roll pitch and yaw acceleration limits to the euler axis
Vector3f euler_accel = euler_accel_limit(_attitude_target_euler_angle, Vector3f(get_accel_roll_max_radss(), get_accel_pitch_max_radss(), get_accel_yaw_max_radss()));
// When acceleration limiting and feedforward are enabled, the sqrt controller is used to compute an euler
// angular velocity that will cause the euler angle to smoothly stop at the input angle with limited deceleration
// and an exponential decay specified by smoothing_gain at the end.
//当启用加速限制和前馈时,使用Sqt控制器计算欧拉。
//角速度将使欧拉角在有限减速下的输入角平稳停止。
//最后由平滑增益指定的指数衰减。
_attitude_target_euler_rate.x = input_shaping_angle(euler_roll_angle-_attitude_target_euler_angle.x, smoothing_gain, euler_accel.x, _attitude_target_euler_rate.x);
_attitude_target_euler_rate.y = input_shaping_angle(euler_pitch_angle-_attitude_target_euler_angle.y, smoothing_gain, euler_accel.y, _attitude_target_euler_rate.y);
// When yaw acceleration limiting is enabled, the yaw input shaper constrains angular acceleration about the yaw axis, slewing
// the output rate towards the input rate.
//偏航
_attitude_target_euler_rate.z = input_shaping_ang_vel(_attitude_target_euler_rate.z, euler_yaw_rate, euler_accel.z);
// Convert euler angle derivative of desired attitude into a body-frame angular velocity vector for feedforward
//将实际的姿态的欧拉角导数,转化到机体坐标系中速度矢量,作为前馈速度矢量
euler_rate_to_ang_vel(_attitude_target_euler_angle, _attitude_target_euler_rate, _attitude_target_ang_vel);
} else
{
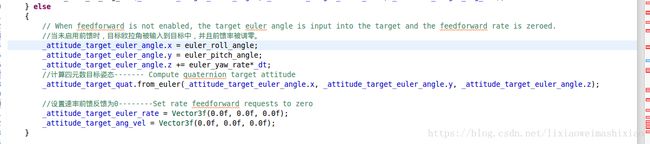
// When feedforward is not enabled, the target euler angle is input into the target and the feedforward rate is zeroed.
_attitude_target_euler_angle.x = euler_roll_angle;
_attitude_target_euler_angle.y = euler_pitch_angle;
_attitude_target_euler_angle.z += euler_yaw_rate*_dt;
// Compute quaternion target attitude
_attitude_target_quat.from_euler(_attitude_target_euler_angle.x, _attitude_target_euler_angle.y, _attitude_target_euler_angle.z);
// Set rate feedforward requests to zero
_attitude_target_euler_rate = Vector3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
_attitude_target_ang_vel = Vector3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
}
//呼叫四元数姿态控制器-------------Call quaternion attitude controller
attitude_controller_run_quat();
}对代码进行分析:
1》》转换得到需要的目标弧度值
float euler_roll_angle = radians(euler_roll_angle_cd*0.01f); //缩小100倍–[-45,45]
float euler_pitch_angle = radians(euler_pitch_angle_cd*0.01f); //缩小100倍
float euler_yaw_rate = radians(euler_yaw_rate_cds*0.01f); //缩小100倍
2》》获取当前无人机实际的姿态角
_attitude_target_quat.to_euler(_attitude_target_euler_angle.x, _attitude_target_euler_angle.y, _attitude_target_euler_angle.z);
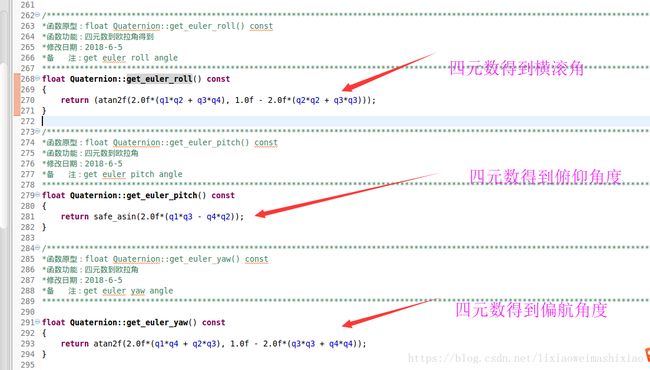
到这里我们得到了无人机的实际姿态角度
_attitude_target_euler_angle.x—–实际横滚角度
_attitude_target_euler_angle.y—-实际的俯仰角度
_attitude_target_euler_angle.z—-实际的偏航角度
3》》油门值处理
smoothing_gain = constrain_float(smoothing_gain,1.0f,1/_dt);
4》》补偿处理: euler_roll_angle += get_roll_trim_rad();
5》》姿态PID运算
f (_rate_bf_ff_enabled & _use_ff_and_input_shaping)
{
//将横滚,俯仰和偏航加速度极限转换为欧拉轴---- translate the roll pitch and yaw acceleration limits to the euler axis
Vector3f euler_accel = euler_accel_limit(_attitude_target_euler_angle, Vector3f(get_accel_roll_max_radss(), get_accel_pitch_max_radss(), get_accel_yaw_max_radss()));
// When acceleration limiting and feedforward are enabled, the sqrt controller is used to compute an euler
// angular velocity that will cause the euler angle to smoothly stop at the input angle with limited deceleration
// and an exponential decay specified by smoothing_gain at the end.
//当启用加速限制和前馈时,使用Sqt控制器计算欧拉。
//角速度将使欧拉角在有限减速下的输入角平稳停止。
//最后由平滑增益指定的指数衰减。
_attitude_target_euler_rate.x = input_shaping_angle(euler_roll_angle-_attitude_target_euler_angle.x, smoothing_gain, euler_accel.x, _attitude_target_euler_rate.x);
_attitude_target_euler_rate.y = input_shaping_angle(euler_pitch_angle-_attitude_target_euler_angle.y, smoothing_gain, euler_accel.y, _attitude_target_euler_rate.y);
// When yaw acceleration limiting is enabled, the yaw input shaper constrains angular acceleration about the yaw axis, slewing
// the output rate towards the input rate.
//偏航
_attitude_target_euler_rate.z = input_shaping_ang_vel(_attitude_target_euler_rate.z, euler_yaw_rate, euler_accel.z);
// Convert euler angle derivative of desired attitude into a body-frame angular velocity vector for feedforward
//将实际的姿态的欧拉角导数,转化到机体坐标系中速度矢量,作为前馈速度矢量
euler_rate_to_ang_vel(_attitude_target_euler_angle, _attitude_target_euler_rate, _attitude_target_ang_vel);
} else
{
// When feedforward is not enabled, the target euler angle is input into the target and the feedforward rate is zeroed.
_attitude_target_euler_angle.x = euler_roll_angle;
_attitude_target_euler_angle.y = euler_pitch_angle;
_attitude_target_euler_angle.z += euler_yaw_rate*_dt;
// Compute quaternion target attitude
_attitude_target_quat.from_euler(_attitude_target_euler_angle.x, _attitude_target_euler_angle.y, _attitude_target_euler_angle.z);
// Set rate feedforward requests to zero
_attitude_target_euler_rate = Vector3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
_attitude_target_ang_vel = Vector3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
}
这里我们先讲解不使用平方根滤波器代码,也就是else代码
目标姿态角: _attitude_target_euler_angle.x = euler_roll_angle;
_attitude_target_euler_angle.y = euler_pitch_angle;
_attitude_target_euler_angle.z += euler_yaw_rate*_dt;
我们看下这个代码
_attitude_target_quat.from_euler(_attitude_target_euler_angle.x, _attitude_target_euler_angle.y, _attitude_target_euler_angle.z);
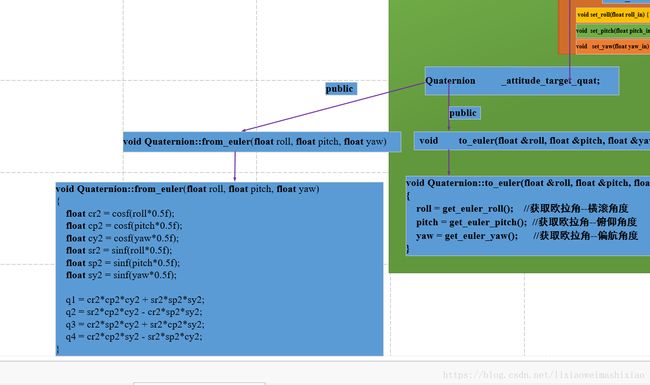
不进行速度前馈:
_attitude_target_euler_rate = Vector3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
_attitude_target_ang_vel = Vector3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
我们看下if(_rate_bf_ff_enabled & _use_ff_and_input_shaping)
1>>> Vector3f euler_accel = euler_accel_limit(_attitude_target_euler_angle, Vector3f(get_accel_roll_max_radss(), get_accel_pitch_max_radss(), get_accel_yaw_max_radss()));
Vector3f AC_AttitudeControl::euler_accel_limit(Vector3f euler_rad, Vector3f euler_accel)
{
float sin_phi = constrain_float(fabsf(sinf(euler_rad.x)), 0.1f, 1.0f);
float cos_phi = constrain_float(fabsf(cosf(euler_rad.x)), 0.1f, 1.0f);
float sin_theta = constrain_float(fabsf(sinf(euler_rad.y)), 0.1f, 1.0f);
Vector3f rot_accel;
if(is_zero(euler_accel.x) || is_zero(euler_accel.y) || is_zero(euler_accel.z) || (euler_accel.x < 0.0f) || (euler_accel.y < 0.0f) || (euler_accel.z < 0.0f))
{
rot_accel.x = euler_accel.x;
rot_accel.y = euler_accel.y;
rot_accel.z = euler_accel.z;
} else
{
rot_accel.x = euler_accel.x;
rot_accel.y = MIN(euler_accel.y/cos_phi, euler_accel.z/sin_phi);
rot_accel.z = MIN(MIN(euler_accel.x/sin_theta, euler_accel.y/sin_phi), euler_accel.z/cos_phi);
}
return rot_accel;
}2>>>获取实际的姿态角速度
_attitude_target_euler_rate.x = input_shaping_angle(euler_roll_angle-_attitude_target_euler_angle.x, smoothing_gain, euler_accel.x, _attitude_target_euler_rate.x);
_attitude_target_euler_rate.y = input_shaping_angle(euler_pitch_angle-_attitude_target_euler_angle.y, smoothing_gain, euler_accel.y, _attitude_target_euler_rate.y);
// When yaw acceleration limiting is enabled, the yaw input shaper constrains angular acceleration about the yaw axis, slewing
// the output rate towards the input rate.
//偏航
_attitude_target_euler_rate.z = input_shaping_ang_vel(_attitude_target_euler_rate.z, euler_yaw_rate, euler_accel.z);
//速率平方根前馈
float AC_AttitudeControl::input_shaping_angle(float error_angle, float smoothing_gain, float accel_max, float target_ang_vel)
{
error_angle = wrap_PI(error_angle);
// Calculate the velocity as error approaches zero with acceleration limited by accel_max_radss
float ang_vel = sqrt_controller(error_angle, smoothing_gain, accel_max);
// Acceleration is limited directly to smooth the beginning of the curve.
if (accel_max > 0)
{
float delta_ang_vel = accel_max * _dt;
return constrain_float(ang_vel, target_ang_vel-delta_ang_vel, target_ang_vel+delta_ang_vel);
} else
{
return ang_vel;
}
}
// limits the acceleration and deceleration of a velocity request
float AC_AttitudeControl::input_shaping_ang_vel(float target_ang_vel, float desired_ang_vel, float accel_max)
{
if (accel_max > 0.0f)
{
float delta_ang_vel = accel_max * _dt;
target_ang_vel += constrain_float(desired_ang_vel - target_ang_vel, -delta_ang_vel, delta_ang_vel);
} else
{
target_ang_vel = desired_ang_vel;
}
return target_ang_vel;
}3>>>将实际的欧拉角转化为机体速度
//将实际的姿态的欧拉角导数,转化到机体坐标系中速度矢量,作为前馈速度矢量
euler_rate_to_ang_vel(_attitude_target_euler_angle, _attitude_target_euler_rate, _attitude_target_ang_vel);
void AC_AttitudeControl::euler_rate_to_ang_vel(const Vector3f& euler_rad, const Vector3f& euler_rate_rads, Vector3f& ang_vel_rads)
{
float sin_theta = sinf(euler_rad.y);
float cos_theta = cosf(euler_rad.y);
float sin_phi = sinf(euler_rad.x);
float cos_phi = cosf(euler_rad.x);
ang_vel_rads.x = euler_rate_rads.x - sin_theta * euler_rate_rads.z;
ang_vel_rads.y = cos_phi * euler_rate_rads.y + sin_phi * cos_theta * euler_rate_rads.z;
ang_vel_rads.z = -sin_phi * euler_rate_rads.y + cos_theta * cos_phi * euler_rate_rads.z;
}7》》调用四元数姿态控制器
attitude_controller_run_quat();
void AC_AttitudeControl::attitude_controller_run_quat()
{
// Retrieve quaternion vehicle attitude
// TODO add _ahrs.get_quaternion()
Quaternion attitude_vehicle_quat;
attitude_vehicle_quat.from_rotation_matrix(_ahrs.get_rotation_body_to_ned());
// Compute attitude error
Vector3f attitude_error_vector;
thrust_heading_rotation_angles(_attitude_target_quat, attitude_vehicle_quat, attitude_error_vector, _thrust_error_angle);
// Compute the angular velocity target from the attitude error
_rate_target_ang_vel = update_ang_vel_target_from_att_error(attitude_error_vector);
// Add feedforward term that attempts to ensure that roll and pitch errors rotate with the body frame rather than the reference frame.
_rate_target_ang_vel.x += attitude_error_vector.y * _ahrs.get_gyro().z;
_rate_target_ang_vel.y += -attitude_error_vector.x * _ahrs.get_gyro().z;
// Add the angular velocity feedforward, rotated into vehicle frame
Quaternion attitude_target_ang_vel_quat = Quaternion(0.0f, _attitude_target_ang_vel.x, _attitude_target_ang_vel.y, _attitude_target_ang_vel.z);
Quaternion attitude_error_quat = attitude_vehicle_quat.inverse() * _attitude_target_quat;
Quaternion target_ang_vel_quat = attitude_error_quat.inverse()*attitude_target_ang_vel_quat*attitude_error_quat;
// Correct the thrust vector and smoothly add feedforward and yaw input
if(_thrust_error_angle > AC_ATTITUDE_THRUST_ERROR_ANGLE*2.0f)
{
_rate_target_ang_vel.z = _ahrs.get_gyro().z;
}else if(_thrust_error_angle > AC_ATTITUDE_THRUST_ERROR_ANGLE)
{
float flip_scalar = (1.0f - (_thrust_error_angle-AC_ATTITUDE_THRUST_ERROR_ANGLE)/AC_ATTITUDE_THRUST_ERROR_ANGLE);
_rate_target_ang_vel.x += target_ang_vel_quat.q2*flip_scalar;
_rate_target_ang_vel.y += target_ang_vel_quat.q3*flip_scalar;
_rate_target_ang_vel.z += target_ang_vel_quat.q4;
_rate_target_ang_vel.z = _ahrs.get_gyro().z*(1.0-flip_scalar) + _rate_target_ang_vel.z*flip_scalar;
} else
{
_rate_target_ang_vel.x += target_ang_vel_quat.q2;
_rate_target_ang_vel.y += target_ang_vel_quat.q3;
_rate_target_ang_vel.z += target_ang_vel_quat.q4;
}
if (_rate_bf_ff_enabled & _use_ff_and_input_shaping)
{
// rotate target and normalize
Quaternion attitude_target_update_quat;
attitude_target_update_quat.from_axis_angle(Vector3f(_attitude_target_ang_vel.x * _dt, _attitude_target_ang_vel.y * _dt, _attitude_target_ang_vel.z * _dt));
_attitude_target_quat = _attitude_target_quat * attitude_target_update_quat;
_attitude_target_quat.normalize();
}
}最后得到姿态PID控制输出量:
_rate_target_ang_vel.x += target_ang_vel_quat.q2;
_rate_target_ang_vel.y += target_ang_vel_quat.q3;
_rate_target_ang_vel.z += target_ang_vel_quat.q4;
具体先不分析,这里面还是很复杂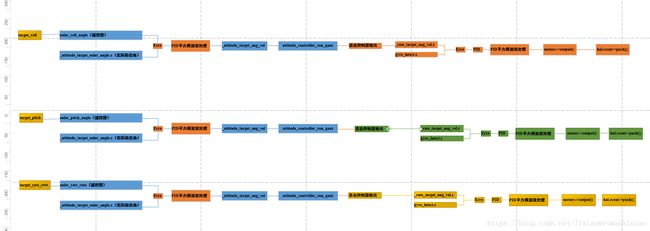
3.姿态角速度代码控制过程分析
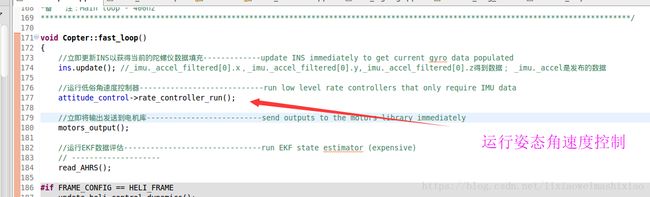
可以看出:AC_AttitudeControl *attitude_control; //指针对象
virtual void rate_controller_run() = 0;是AC_AttitudeControl中的纯虚函数,不同子类去实现,我们以多旋翼为例,那就是AC_AttitudeControl_Multi中实现那个函数的功能
(1)更新油门到电机需要的值
void AC_AttitudeControl_Multi::update_throttle_rpy_mix()
void AC_AttitudeControl_Multi::update_throttle_rpy_mix()
{
// slew _throttle_rpy_mix to _throttle_rpy_mix_desired
if (_throttle_rpy_mix < _throttle_rpy_mix_desired)
{
// increase quickly (i.e. from 0.1 to 0.9 in 0.4 seconds)
_throttle_rpy_mix += MIN(2.0f*_dt, _throttle_rpy_mix_desired-_throttle_rpy_mix);
} else if (_throttle_rpy_mix > _throttle_rpy_mix_desired)
{
// reduce more slowly (from 0.9 to 0.1 in 1.6 seconds)
_throttle_rpy_mix -= MIN(0.5f*_dt, _throttle_rpy_mix-_throttle_rpy_mix_desired);
}
_throttle_rpy_mix = constrain_float(_throttle_rpy_mix, 0.1f, AC_ATTITUDE_CONTROL_MAX);
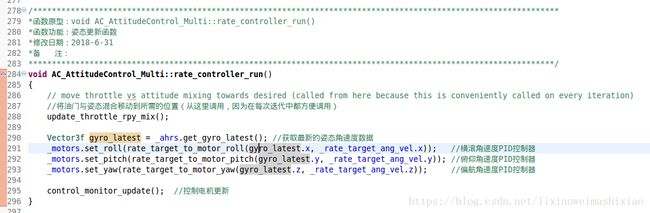
}(2)获取无人机的角速度信息
Vector3f gyro_latest = _ahrs.get_gyro_latest(); //获取最新的姿态角速度数据,
_rate_target_ang_vel.x,
_rate_target_ang_vel.y,
_rate_target_ang_vel.z表示姿态PID的输出量
(3)进行内环角速度环控制
_motors.set_roll(rate_target_to_motor_roll(gyro_latest.x, _rate_target_ang_vel.x)); //横滚角速度PID控制器 _motors.set_pitch(rate_target_to_motor_pitch(gyro_latest.y, _rate_target_ang_vel.y)); //俯仰角速度PID控制器 _motors.set_yaw(rate_target_to_motor_yaw(gyro_latest.z, _rate_target_ang_vel.z)); //偏航角速度PID控制器
我们首先看下:
**rate_target_to_motor_roll()
rate_target_to_motor_pitch()
rate_target_to_motor_yaw()**
--------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------
float AC_AttitudeControl::rate_target_to_motor_roll(float rate_actual_rads, float rate_target_rads)
{
float rate_error_rads = rate_target_rads - rate_actual_rads; //误差=目标-实际的值
// 传递误差到PID控制器---------pass error to PID controller
get_rate_roll_pid().set_input_filter_d(rate_error_rads);//微分控制器
get_rate_roll_pid().set_desired_rate(rate_target_rads); //输入的目标值数据
float integrator = get_rate_roll_pid().get_integrator();
// printf("ABCDE\r\n");
// 确保只有输出饱和时才能减少积分器-----Ensure that integrator can only be reduced if the output is saturated
if (!_motors.limit.roll_pitch || ((integrator > 0 && rate_error_rads < 0) || (integrator < 0 && rate_error_rads > 0)))
{
// printf("ABCD\r\n");
integrator = get_rate_roll_pid().get_i();
}
//计算输出范围是: -1 ~ +1
float output = get_rate_roll_pid().get_p() + integrator + get_rate_roll_pid().get_d() + get_rate_roll_pid().get_ff(rate_target_rads);
//限制输出范围在:-1~+1之间------------Constrain output
return constrain_float(output, -1.0f, 1.0f);
}
--------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------
float AC_AttitudeControl::rate_target_to_motor_pitch(float rate_actual_rads, float rate_target_rads)
{
float rate_error_rads = rate_target_rads - rate_actual_rads;
// 传递误差到PID控制器---------pass error to PID controller
get_rate_pitch_pid().set_input_filter_d(rate_error_rads);
get_rate_pitch_pid().set_desired_rate(rate_target_rads);
float integrator = get_rate_pitch_pid().get_integrator();
// 确保只有输出饱和时才能减少积分器-----Ensure that integrator can only be reduced if the output is saturated
if (!_motors.limit.roll_pitch || ((integrator > 0 && rate_error_rads < 0) || (integrator < 0 && rate_error_rads > 0))) {
integrator = get_rate_pitch_pid().get_i();
}
//计算输出范围是: -1 ~ +1
float output = get_rate_pitch_pid().get_p() + integrator + get_rate_pitch_pid().get_d() + get_rate_pitch_pid().get_ff(rate_target_rads);
//限制输出范围在:-1~+1之间------------Constrain output
return constrain_float(output, -1.0f, 1.0f);
}
--------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------
float AC_AttitudeControl::rate_target_to_motor_yaw(float rate_actual_rads, float rate_target_rads)
{
float rate_error_rads = rate_target_rads - rate_actual_rads;
// 传递误差到PID控制器---------pass error to PID controller
get_rate_yaw_pid().set_input_filter_all(rate_error_rads);
get_rate_yaw_pid().set_desired_rate(rate_target_rads);
float integrator = get_rate_yaw_pid().get_integrator();
// 确保只有输出饱和时才能减少积分器-----Ensure that integrator can only be reduced if the output is saturated
if (!_motors.limit.yaw || ((integrator > 0 && rate_error_rads < 0) || (integrator < 0 && rate_error_rads > 0))) {
integrator = get_rate_yaw_pid().get_i();
}
//计算输出范围是: -1 ~ +1
float output = get_rate_yaw_pid().get_p() + integrator + get_rate_yaw_pid().get_d() + get_rate_yaw_pid().get_ff(rate_target_rads);
//限制输出范围在:-1~+1之间------------Constrain output
return constrain_float(output, -1.0f, 1.0f);
}运算之后,传入:
void set_roll(float roll_in) { _roll_in = roll_in; }; // range -1 ~ +1
void set_pitch(float pitch_in) { _pitch_in = pitch_in; }; // range -1 ~ +1
void set_yaw(float yaw_in) { _yaw_in = yaw_in; }; // range -1 ~ +1**
到这里我们得到陀螺仪角速度与目标角速度的PID控制输出量:
横滚角速度PID=_roll_in
俯仰角速度PID=_pitch_in
偏航角速度PID=_yaw_in
(4)更新控制监视器
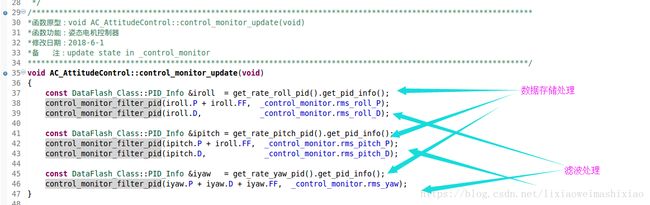
void AC_AttitudeControl::control_monitor_update(void)
void AC_AttitudeControl::control_monitor_update(void)
{
const DataFlash_Class::PID_Info &iroll = get_rate_roll_pid().get_pid_info();
control_monitor_filter_pid(iroll.P + iroll.FF, _control_monitor.rms_roll_P);
control_monitor_filter_pid(iroll.D, _control_monitor.rms_roll_D);
const DataFlash_Class::PID_Info &ipitch = get_rate_pitch_pid().get_pid_info();
control_monitor_filter_pid(ipitch.P + iroll.FF, _control_monitor.rms_pitch_P);
control_monitor_filter_pid(ipitch.D, _control_monitor.rms_pitch_D);
const DataFlash_Class::PID_Info &iyaw = get_rate_yaw_pid().get_pid_info();
control_monitor_filter_pid(iyaw.P + iyaw.D + iyaw.FF, _control_monitor.rms_yaw);
}AC_PID& get_rate_roll_pid() { return _pid_rate_roll; }
AC_PID& get_rate_pitch_pid() { return _pid_rate_pitch; }
AC_PID& get_rate_yaw_pid() { return _pid_rate_yaw; }
void AC_AttitudeControl::control_monitor_filter_pid(float value, float &rms)
{
const float filter_constant = 0.99f;
// we don't do the sqrt() here as it is quite expensive. That is
// done when reporting a result
rms = filter_constant * rms + (1.0f - filter_constant) * sq(value);
}到这里你是否有一个疑惑?就是
_control_monitor.rms_roll_P
_control_monitor.rms_pitch_P
_control_monitor.rms_yaw
与
_pid_rate_roll
_pid_rate_pitch
_pid_rate_yaw
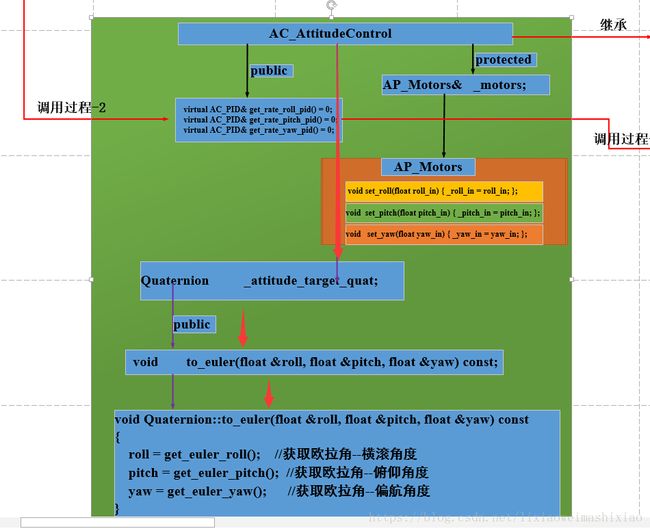
然后怎么连接上面(3)_roll_in,_pitch_in,_yaw_in之间的联系起来的。要想弄明白这个我们必须看各个类之间怎么实现的关系,这里我还是用Visio图画出来,(需要完整图的可以联系我,这里没法上传清晰的)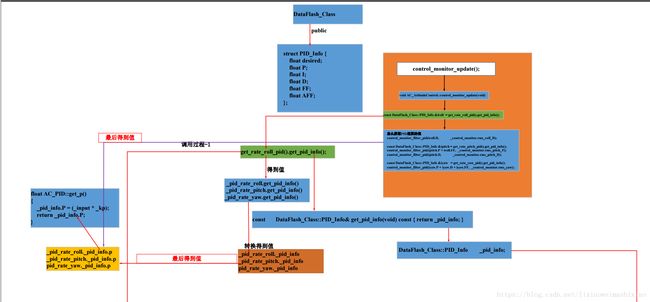
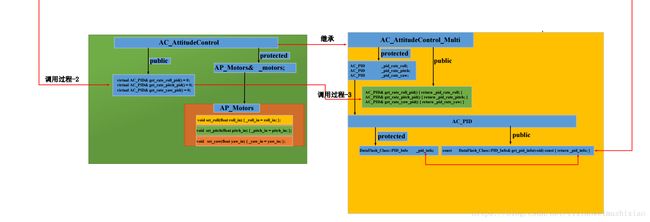
这里有个疑惑就是还没解决?
_motors.set_roll(rate_target_to_motor_roll(gyro_latest.x, _rate_target_ang_vel.x)); //横滚角速度PID控制器
_motors.set_pitch(rate_target_to_motor_pitch(gyro_latest.y, _rate_target_ang_vel.y)); //俯仰角速度PID控制器
_motors.set_yaw(rate_target_to_motor_yaw(gyro_latest.z, _rate_target_ang_vel.z)); //偏航角速度PID控制器与_control_monitor.rms_roll_P, _control_monitor.rms_roll_D, _control_monitor.rms_pitch_P,_control_monitor.rms_pitch_D
_control_monitor.rms_yaw之间怎么联系起来,我个人感觉还是在上面那个流程图,不过看不懂也没事,我们继续看代码,说不定后面会给提示
4.电机PWM控制运算
我们先看下代码,然后对代码进行详细分析;
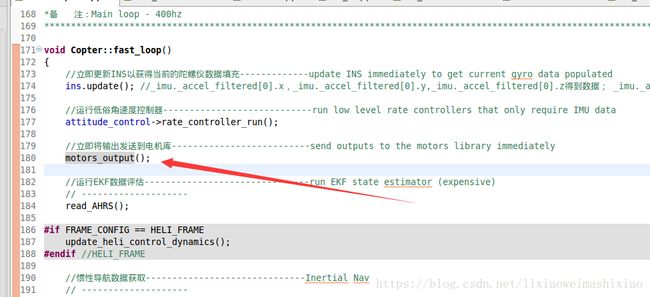
void Copter::motors_output()
{
#if ADVANCED_FAILSAFE == ENABLED
// this is to allow the failsafe module to deliberately crash
// the vehicle. Only used in extreme circumstances to meet the
// OBC rules
if (g2.afs.should_crash_vehicle()) //这是为了允许故障安全模块故意崩溃。车辆。只有在极端情况下才能满足OBC规则
{
g2.afs.terminate_vehicle();
return;
}
#endif
//解锁延迟,也就是机器解锁后不立即启动,延迟2s-----Update arming delay state
if (ap.in_arming_delay && (!motors->armed() || millis()-arm_time_ms > ARMING_DELAY_SEC*1.0e3f || control_mode == THROW))
{
ap.in_arming_delay = false;
}
//输出所有的伺服通道--------------------------output any servo channels
SRV_Channels::calc_pwm(); //output_pwm
//立即触发,所有通道输出----------------------cork now, so that all channel outputs happen at once
hal.rcout->cork();
//在任何AUX通道上更新输出,手动通行-------------update output on any aux channels, for manual passthru
SRV_Channels::output_ch_all();
//检查我们是否执行电机测试---------------------check if we are performing the motor test
if (ap.motor_test)
{
motor_test_output(); //测试电机函数
} else
{
bool interlock = motors->armed() && !ap.in_arming_delay && (!ap.using_interlock || ap.motor_interlock_switch) && !ap.motor_emergency_stop;
if (!motors->get_interlock() && interlock)
{
motors->set_interlock(true);
Log_Write_Event(DATA_MOTORS_INTERLOCK_ENABLED);
} else if (motors->get_interlock() && !interlock)
{
motors->set_interlock(false);
Log_Write_Event(DATA_MOTORS_INTERLOCK_DISABLED);
}
//向马达发送输出信号----------------------send output signals to motors
motors->output();
}
//发送到所有通道------------------------------push all channels
hal.rcout->push();
}(1)故障测试代码(这里不分析)
#if ADVANCED_FAILSAFE == ENABLED
// this is to allow the failsafe module to deliberately crash
// the vehicle. Only used in extreme circumstances to meet the
// OBC rules
if (g2.afs.should_crash_vehicle()) //这是为了允许故障安全模块故意崩溃。车辆。只有在极端情况下才能满足OBC规则
{
g2.afs.terminate_vehicle();
return;
}
#endif(2)解锁延迟函数(这里可以通过地面站设置解锁延迟时间不分析)
//解锁延迟,也就是机器解锁后不立即启动,延迟2s-----Update arming delay state
if (ap.in_arming_delay && (!motors->armed() || millis()-arm_time_ms > ARMING_DELAY_SEC*1.0e3f || control_mode == THROW))
{
ap.in_arming_delay = false;
}(3)计算需要的PWM
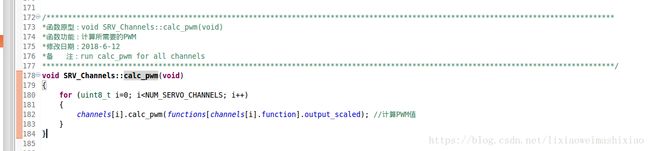
这里要注意上面(2)算的值怎么传送到这里的!!!(??)
SRV_Channels::calc_pwm(); //output_pwm
hal.rcout->cork();
SRV_Channels::output_ch_all();
if (ap.motor_test)
{
motor_test_output(); //测试电机函数
}
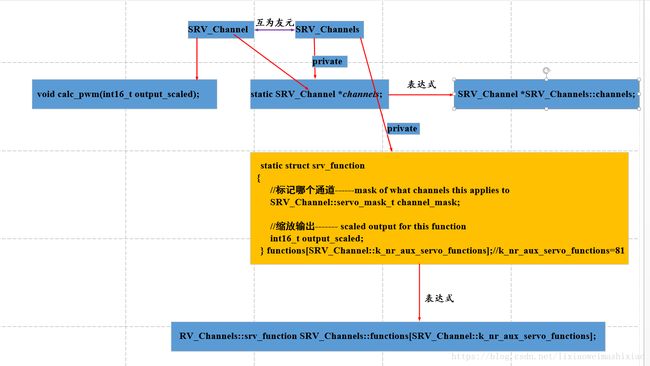
#define NUM_SERVO_CHANNELS 16
void SRV_Channel::calc_pwm(int16_t output_scaled)
{
if (have_pwm_mask & (1U<重点要分析这个函数怎么输入的值:
channels[i].calc_pwm(functions[channels[i].function].output_scaled); //计算PWM值**
我们先不分析先往后看代码
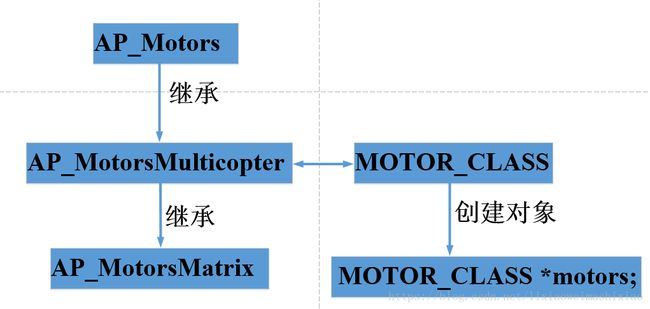
motors->output();
看下motors之间的类属关系
void AP_MotorsMulticopter::output()
{
//更新油门滤波,进行一阶低通滤波处理------------------------------------update throttle filter
update_throttle_filter();
//跟新电池电阻-(确保大机动运动时候,电池电压稳定)------------------------update battery resistance
update_battery_resistance();
//计算电池电压的最大升力值---------------------------------------------calc filtered battery voltage and lift_max
update_lift_max_from_batt_voltage();
// 输出设置阶段------------------------------------------------------run spool logic
output_logic();
//计算所需要的推力----------------------------------------------------calculate thrust
output_armed_stabilizing();
//申请对无人机结构补偿-------------------------------------------------apply any thrust compensation for the frame
thrust_compensation();
//将推力转换成PWM---------------------- convert rpy_thrust values to pwm
output_to_motors();
};1》》更新油门滤波update_throttle_filter();
void AP_MotorsMulticopter::update_throttle_filter()
{
if (armed())
{
_throttle_filter.apply(_throttle_in, 1.0f/_loop_rate); //低通滤波
// constrain filtered throttle
if (_throttle_filter.get() < 0.0f)
{
_throttle_filter.reset(0.0f);
}
if (_throttle_filter.get() > 1.0f)
{
_throttle_filter.reset(1.0f);
}
} else
{
_throttle_filter.reset(0.0f);
}
}2》》更新电池电压估计update_battery_resistance();
这里我们重点看下这个函数: output_armed_stabilizing();
void AP_MotorsMulticopter::update_battery_resistance()
{
// if disarmed reset resting voltage and current
if (!_flags.armed)
{
_batt_voltage_resting = _batt_voltage;
_batt_current_resting = _batt_current;
_batt_timer = 0;
} else if (_batt_voltage_resting > _batt_voltage && _batt_current_resting < _batt_current)
{
// update battery resistance when throttle is over hover throttle
float batt_resistance = (_batt_voltage_resting-_batt_voltage)/(_batt_current-_batt_current_resting);
if ((_batt_timer < 400) && ((_batt_current_resting*2.0f) < _batt_current)) {
if (get_throttle() >= get_throttle_hover()) {
// filter reaches 90% in 1/4 the test time
_batt_resistance += 0.05f*(batt_resistance - _batt_resistance);
_batt_timer += 1;
} else {
// initialize battery resistance to prevent change in resting voltage estimate
_batt_resistance = batt_resistance;
}
}
// make sure battery resistance value doesn't result in the predicted battery voltage exceeding the resting voltage
if(batt_resistance < _batt_resistance){
_batt_resistance = batt_resistance;
}
}
}3》》根据电压计算电池所能提供的最大升力
void AP_MotorsMulticopter::update_lift_max_from_batt_voltage()
{
// sanity check battery_voltage_min is not too small
// if disabled or misconfigured exit immediately
if((_batt_voltage_max <= 0) || (_batt_voltage_min >= _batt_voltage_max) || (_batt_voltage < 0.25f*_batt_voltage_min)) {
_batt_voltage_filt.reset(1.0f);
_lift_max = 1.0f;
return;
}
_batt_voltage_min = MAX(_batt_voltage_min, _batt_voltage_max * 0.6f);
// add current based voltage sag to battery voltage
float batt_voltage = _batt_voltage + (_batt_current-_batt_current_resting) * _batt_resistance;
batt_voltage = constrain_float(batt_voltage, _batt_voltage_min, _batt_voltage_max);
// filter at 0.5 Hz
float batt_voltage_filt = _batt_voltage_filt.apply(batt_voltage/_batt_voltage_max, 1.0f/_loop_rate);
// calculate lift max
_lift_max = batt_voltage_filt*(1-_thrust_curve_expo) + _thrust_curve_expo*batt_voltage_filt*batt_voltage_filt;
}4》》电机状态机设置
**SHUT_DOWN :Motors停转无输出,Servos输出保持中位或测试条件值
SPIN_WHEN_ARMED :Motors停转无输出或者开始输出旋转,Servos开始输出
SPOOL_UP :Motors最大油门输出,Servos正常输出
THROTTLE_UNLIMITED :Motors正常输出,Servos正常输出
SPOOL_DOWN :Motors最小输出,Servos正常输出**
void AP_MotorsMulticopter::output_logic()
{
if (_flags.armed) {
_disarm_safety_timer = 100;
} else if (_disarm_safety_timer != 0) {
_disarm_safety_timer--;
}
// force desired and current spool mode if disarmed or not interlocked
if (!_flags.armed || !_flags.interlock) {
_spool_desired = DESIRED_SHUT_DOWN;
_spool_mode = SHUT_DOWN;
}
if (_spool_up_time < 0.05) {
// prevent float exception
_spool_up_time.set(0.05);
}
switch (_spool_mode) {
case SHUT_DOWN:
// Motors should be stationary.
// Servos set to their trim values or in a test condition.
// set limits flags
limit.roll_pitch = true;
limit.yaw = true;
limit.throttle_lower = true;
limit.throttle_upper = true;
// make sure the motors are spooling in the correct direction
if (_spool_desired != DESIRED_SHUT_DOWN) {
_spool_mode = SPIN_WHEN_ARMED;
break;
}
// set and increment ramp variables
_spin_up_ratio = 0.0f;
_throttle_thrust_max = 0.0f;
break;
case SPIN_WHEN_ARMED: {
// Motors should be stationary or at spin when armed.
// Servos should be moving to correct the current attitude.
// set limits flags
limit.roll_pitch = true;
limit.yaw = true;
limit.throttle_lower = true;
limit.throttle_upper = true;
// set and increment ramp variables
float spool_step = 1.0f/(_spool_up_time*_loop_rate);
if (_spool_desired == DESIRED_SHUT_DOWN){
_spin_up_ratio -= spool_step;
// constrain ramp value and update mode
if (_spin_up_ratio <= 0.0f) {
_spin_up_ratio = 0.0f;
_spool_mode = SHUT_DOWN;
}
} else if(_spool_desired == DESIRED_THROTTLE_UNLIMITED) {
_spin_up_ratio += spool_step;
// constrain ramp value and update mode
if (_spin_up_ratio >= 1.0f) {
_spin_up_ratio = 1.0f;
_spool_mode = SPOOL_UP;
}
} else { // _spool_desired == SPIN_WHEN_ARMED
float spin_up_armed_ratio = 0.0f;
if (_spin_min > 0.0f) {
spin_up_armed_ratio = _spin_arm / _spin_min;
}
_spin_up_ratio += constrain_float(spin_up_armed_ratio-_spin_up_ratio, -spool_step, spool_step);
}
_throttle_thrust_max = 0.0f;
break;
}
case SPOOL_UP:
// Maximum throttle should move from minimum to maximum.
// Servos should exhibit normal flight behavior.
// initialize limits flags
limit.roll_pitch = false;
limit.yaw = false;
limit.throttle_lower = false;
limit.throttle_upper = false;
// make sure the motors are spooling in the correct direction
if (_spool_desired != DESIRED_THROTTLE_UNLIMITED ){
_spool_mode = SPOOL_DOWN;
break;
}
// set and increment ramp variables
_spin_up_ratio = 1.0f;
_throttle_thrust_max += 1.0f/(_spool_up_time*_loop_rate);
// constrain ramp value and update mode
if (_throttle_thrust_max >= MIN(get_throttle(), get_current_limit_max_throttle())) {
_throttle_thrust_max = get_current_limit_max_throttle();
_spool_mode = THROTTLE_UNLIMITED;
} else if (_throttle_thrust_max < 0.0f) {
_throttle_thrust_max = 0.0f;
}
break;
case THROTTLE_UNLIMITED:
// Throttle should exhibit normal flight behavior.
// Servos should exhibit normal flight behavior.
// initialize limits flags
limit.roll_pitch = false;
limit.yaw = false;
limit.throttle_lower = false;
limit.throttle_upper = false;
// make sure the motors are spooling in the correct direction
if (_spool_desired != DESIRED_THROTTLE_UNLIMITED) {
_spool_mode = SPOOL_DOWN;
break;
}
// set and increment ramp variables
_spin_up_ratio = 1.0f;
_throttle_thrust_max = get_current_limit_max_throttle();
break;
case SPOOL_DOWN:
// Maximum throttle should move from maximum to minimum.
// Servos should exhibit normal flight behavior.
// initialize limits flags
limit.roll_pitch = false;
limit.yaw = false;
limit.throttle_lower = false;
limit.throttle_upper = false;
// make sure the motors are spooling in the correct direction
if (_spool_desired == DESIRED_THROTTLE_UNLIMITED) {
_spool_mode = SPOOL_UP;
break;
}
// set and increment ramp variables
_spin_up_ratio = 1.0f;
_throttle_thrust_max -= 1.0f/(_spool_up_time*_loop_rate);
// constrain ramp value and update mode
if (_throttle_thrust_max <= 0.0f){
_throttle_thrust_max = 0.0f;
}
if (_throttle_thrust_max >= get_current_limit_max_throttle()) {
_throttle_thrust_max = get_current_limit_max_throttle();
} else if (is_zero(_throttle_thrust_max)) {
_spool_mode = SPIN_WHEN_ARMED;
}
break;
}
}5》》计算所需要的推力output_armed_stabilizing();
void AP_MotorsMatrix::output_armed_stabilizing()
{
uint8_t i; // general purpose counter
float roll_thrust; // roll thrust input value, +/- 1.0
float pitch_thrust; // pitch thrust input value, +/- 1.0
float yaw_thrust; // yaw thrust input value, +/- 1.0
float throttle_thrust; // throttle thrust input value, 0.0 - 1.0
float throttle_thrust_best_rpy; // throttle providing maximum roll, pitch and yaw range without climbing
float rpy_scale = 1.0f; // this is used to scale the roll, pitch and yaw to fit within the motor limits
float rpy_low = 0.0f; // lowest motor value
float rpy_high = 0.0f; // highest motor value
float yaw_allowed = 1.0f; // amount of yaw we can fit in
float unused_range; // amount of yaw we can fit in the current channel
float thr_adj; // the difference between the pilot's desired throttle and throttle_thrust_best_rpy
//申请电压和气压补偿----------------------apply voltage and air pressure compensation
roll_thrust = _roll_in * get_compensation_gain(); //横滚推力计算
pitch_thrust = _pitch_in * get_compensation_gain(); //俯仰推力计算
yaw_thrust = _yaw_in * get_compensation_gain(); //偏航推力计算
throttle_thrust = get_throttle() * get_compensation_gain(); //垂直升力计算
//检查油门值是0或者比限制的值低------------------sanity check throttle is above zero and below current limited throttle
if (throttle_thrust <= 0.0f)
{
throttle_thrust = 0.0f;
limit.throttle_lower = true;
}
if (throttle_thrust >= _throttle_thrust_max)
{
throttle_thrust = _throttle_thrust_max;
limit.throttle_upper = true;
}
_throttle_avg_max = constrain_float(_throttle_avg_max, throttle_thrust, _throttle_thrust_max); //油门最大值
// calculate throttle that gives most possible room for yaw which is the lower of:
// 1. 0.5f - (rpy_low+rpy_high)/2.0 - this would give the maximum possible margin above the highest motor and below the lowest
// 2. the higher of:
// a) the pilot's throttle input
// b) the point _throttle_rpy_mix between the pilot's input throttle and hover-throttle
// Situation #2 ensure we never increase the throttle above hover throttle unless the pilot has commanded this.
// Situation #2b allows us to raise the throttle above what the pilot commanded but not so far that it would actually cause the copter to rise.
// We will choose #1 (the best throttle for yaw control) if that means reducing throttle to the motors (i.e. we favor reducing throttle *because* it provides better yaw control)
// We will choose #2 (a mix of pilot and hover throttle) only when the throttle is quite low. We favor reducing throttle instead of better yaw control because the pilot has commanded it
// calculate amount of yaw we can fit into the throttle range
// this is always equal to or less than the requested yaw from the pilot or rate controller
throttle_thrust_best_rpy = MIN(0.5f, _throttle_avg_max);
// calculate roll and pitch for each motor
// calculate the amount of yaw input that each motor can accept
for (i=0; i 0.0f)
{
unused_range = fabsf((1.0f - (throttle_thrust_best_rpy + _thrust_rpyt_out[i]))/_yaw_factor[i]);
if (yaw_allowed > unused_range)
{
yaw_allowed = unused_range;
}
} else
{
unused_range = fabsf((throttle_thrust_best_rpy + _thrust_rpyt_out[i])/_yaw_factor[i]);
if (yaw_allowed > unused_range) {
yaw_allowed = unused_range;
}
}
}
}
}
// todo: make _yaw_headroom 0 to 1
yaw_allowed = MAX(yaw_allowed, (float)_yaw_headroom/1000.0f);
if (fabsf(yaw_thrust) > yaw_allowed)
{
yaw_thrust = constrain_float(yaw_thrust, -yaw_allowed, yaw_allowed);
limit.yaw = true;
}
// add yaw to intermediate numbers for each motor
rpy_low = 0.0f;
rpy_high = 0.0f;
for (i=0; i rpy_high)
{
rpy_high = _thrust_rpyt_out[i];
}
}
}
// check everything fits
throttle_thrust_best_rpy = MIN(0.5f - (rpy_low+rpy_high)/2.0, _throttle_avg_max);
if (is_zero(rpy_low)){
rpy_scale = 1.0f;
} else {
rpy_scale = constrain_float(-throttle_thrust_best_rpy/rpy_low, 0.0f, 1.0f);
}
// calculate how close the motors can come to the desired throttle
thr_adj = throttle_thrust - throttle_thrust_best_rpy;
if (rpy_scale < 1.0f){
// Full range is being used by roll, pitch, and yaw.
limit.roll_pitch = true;
limit.yaw = true;
if (thr_adj > 0.0f) {
limit.throttle_upper = true;
}
thr_adj = 0.0f;
} else {
if (thr_adj < -(throttle_thrust_best_rpy+rpy_low)){
// Throttle can't be reduced to desired value
thr_adj = -(throttle_thrust_best_rpy+rpy_low);
} else if (thr_adj > 1.0f - (throttle_thrust_best_rpy+rpy_high)){
// Throttle can't be increased to desired value
thr_adj = 1.0f - (throttle_thrust_best_rpy+rpy_high);
limit.throttle_upper = true;
}
}
// add scaled roll, pitch, constrained yaw and throttle for each motor
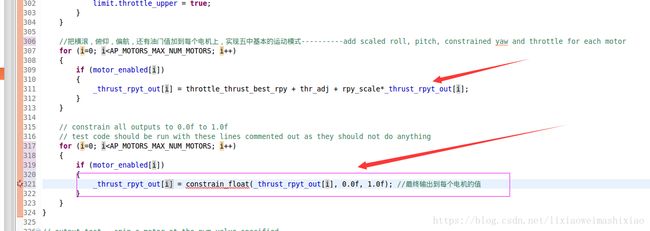
for (i=0; i 其中有一些需要注意的参数:_roll_factor[i],_pitch_factor[i],_yaw_factor[i]是有正负的,可以看出是来自:
void AP_Motors6DOF::setup_motors(motor_frame_class frame_class, motor_frame_type frame_type)
{
// remove existing motors
for (int8_t i=0; i- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
这里找到了_roll_in,_pitch_in,_yaw_in姿态角速度PID运算后怎么传送,并进行电机分配转换成每个电机需要的PWM值的计算过程,这样整个过程基本就打通了。
我们重点关注这个值:thrust_rpyt_out[i]
6》》申请结构补偿thrust_compensation()
void AP_MotorsMatrix::thrust_compensation(void)
{
if (_thrust_compensation_callback)
{
_thrust_compensation_callback(_thrust_rpyt_out, AP_MOTORS_MAX_NUM_MOTORS); //最大8旋翼
}
}thrust_compensation_fn_t _thrust_compensation_callback;
void set_thrust_compensation_callback(thrust_compensation_fn_t callback)
{
_thrust_compensation_callback = callback;
}7》》输出PWM到电机—output_to_motors
void AP_MotorsMatrix::output_to_motors()
{
int8_t i;
int16_t motor_out[AP_MOTORS_MAX_NUM_MOTORS]; // final pwm values sent to the motor
switch (_spool_mode)
{
case SHUT_DOWN:
{
// sends minimum values out to the motors
// set motor output based on thrust requests
for (i=0; i最终写入的值: rc_write(i, motor_out[i]); //最终写入的值
void AP_Motors::rc_write(uint8_t chan, uint16_t pwm)
{
if (_motor_map_mask & (1U< 250)
{
pwm = 250;
}
}
hal.rcout->write(chan, pwm); //写入PWM到电机
} 可以看到最后调用硬件抽象层hal.rcout->write
这里最后会调用AP_HAL_PX4里面的,为什么,可以看我的博客,apm怎么实现一个硬件抽象层支持不同的飞控板
void PX4RCOutput::write(uint8_t ch, uint16_t period_us)
{
if (ch >= PX4_NUM_OUTPUT_CHANNELS) {
return;
}
if (!(_enabled_channels & (1U<= _max_channel) {
_max_channel = ch + 1;
}
if (_output_mode == MODE_PWM_BRUSHED16KHZ) {
// map from the PWM range to 0 t0 100% duty cycle. For 16kHz
// this ends up being 0 to 500 pulse width in units of
// 125usec.
const uint32_t period_max = 1000000UL/(16000/8);
if (period_us <= _esc_pwm_min) {
period_us = 0;
} else if (period_us >= _esc_pwm_max) {
period_us = period_max;
} else {
uint32_t pdiff = period_us - _esc_pwm_min;
period_us = pdiff*period_max/(_esc_pwm_max - _esc_pwm_min);
}
}
/*
only mark an update is needed if there has been a change, or we
are in oneshot mode. In oneshot mode we always need to send the
output
*/
if (period_us != _period[ch] ||
_output_mode == MODE_PWM_ONESHOT) {
_period[ch] = period_us;
_need_update = true;
}
}