移动开发之设计模式- 责任链模式(IOS&Android)
资源
完全参照 责任链模式|菜鸟教程但不包括IOS代码
责任链模式
顾名思义,责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern)为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链。这种模式给予请求的类型,对请求的发送者和接收者进行解耦。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
在这种模式中,通常每个接收者都包含对另一个接收者的引用。如果一个对象不能处理该请求,那么它会把相同的请求传给下一个接收者,依此类推。
介绍
意图: 避免请求发送者与接收者耦合在一起,让多个对象都有可能接收请求,将这些对象连接成一条链,并且沿着这条链传递请求,直到有对象处理它为止。
主要解决: 职责链上的处理者负责处理请求,客户只需要将请求发送到职责链上即可,无须关心请求的处理细节和请求的传递,所以职责链将请求的发送者和请求的处理者解耦了。
何时使用: 在处理消息的时候以过滤很多道。
如何解决: 拦截的类都实现统一接口。
关键代码: Handler 里面聚合它自己,在 HanleRequest 里判断是否合适,如果没达到条件则向下传递,向谁传递之前 set 进去。
应用实例:
1、红楼梦中的"击鼓传花"。
2、JS 中的事件冒泡。
3、JAVA WEB 中 Apache Tomcat 对 Encoding 的处理,Struts2 的拦截器,jsp servlet 的 Filter。
优点:
1、降低耦合度。它将请求的发送者和接收者解耦。
2、简化了对象。使得对象不需要知道链的结构。
3、增强给对象指派职责的灵活性。通过改变链内的成员或者调动它们的次序,允许动态地新增或者删除责任。
4、增加新的请求处理类很方便。
缺点:
1、不能保证请求一定被接收。
2、系统性能将受到一定影响,而且在进行代码调试时不太方便,可能会造成循环调用。
3、可能不容易观察运行时的特征,有碍于除错。
使用场景:
1、有多个对象可以处理同一个请求,具体哪个对象处理该请求由运行时刻自动确定。
2、在不明确指定接收者的情况下,向多个对象中的一个提交一个请求。
3、可动态指定一组对象处理请求。
注意事项: 在 JAVA WEB 中遇到很多应用。
#Android
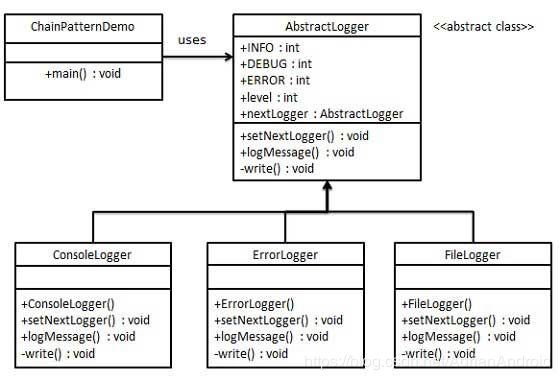
AbstractLogger.java
public abstract class AbstractLogger {
public static int INFO = 1;
public static int DEBUG = 2;
public static int ERROR = 3;
protected int level;
//责任链中的下一个元素
protected AbstractLogger nextLogger;
public void setNextLogger(AbstractLogger nextLogger){
this.nextLogger = nextLogger;
}
public void logMessage(int level, String message){
if(this.level <= level){
write(message);
}
if(nextLogger !=null){
nextLogger.logMessage(level, message);
}
}
abstract protected void write(String message);
}
ConsoleLogger.java
public class ConsoleLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public ConsoleLogger(int level){
this.level = level;
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("Standard Console::Logger: " + message);
}
}
ErrorLogger.java
public class ErrorLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public ErrorLogger(int level){
this.level = level;
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("Error Console::Logger: " + message);
}
}
FileLogger.java
public class FileLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public FileLogger(int level){
this.level = level;
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("File::Logger: " + message);
}
}
ChainPatternDemo.java
public class ChainPatternDemo {
private static AbstractLogger getChainOfLoggers(){
AbstractLogger errorLogger = new ErrorLogger(AbstractLogger.ERROR);
AbstractLogger fileLogger = new FileLogger(AbstractLogger.DEBUG);
AbstractLogger consoleLogger = new ConsoleLogger(AbstractLogger.INFO);
errorLogger.setNextLogger(fileLogger);
fileLogger.setNextLogger(consoleLogger);
return errorLogger;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractLogger loggerChain = getChainOfLoggers();
loggerChain.logMessage(AbstractLogger.INFO,
"This is an information.");
loggerChain.logMessage(AbstractLogger.DEBUG,
"This is an debug level information.");
loggerChain.logMessage(AbstractLogger.ERROR,
"This is an error information.");
}
}
RESULT
Standard Console::Logger: This is an information.
File::Logger: This is an debug level information.
Standard Console::Logger: This is an debug level information.
Error Console::Logger: This is an error information.
File::Logger: This is an error information.
Standard Console::Logger: This is an error information.
IOS
AbstractLogger.h
#import
typedef enum LEVEL{
_INFO = 1,
_DEBUG = 2,
_ERROR = 3
}level;
@interface AbstractLogger : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) AbstractLogger * nextLogger;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int level;
-(void)setNextLoggering:(AbstractLogger*)nextLogger;
-(void)logMessage:(int)level message:(NSString*)message;
-(void)write:(NSString*)message;
@end
AbstractLogger.m
#import "AbstractLogger.h"
@interface AbstractLogger ()
@end
@implementation AbstractLogger
- (void)setNextLoggering:(AbstractLogger *)nextLogger{
static int count;
NSLog(@"setNextLogger %d", count++);
NSLog(@"%@", [NSString stringWithUTF8String:object_getClassName(self)]);
self.nextLogger = nextLogger;
}
- (void)logMessage:(int)level message:(NSString *)message{
if(self.level <= level) {
[self write:message];
}
if(self.nextLogger) {
[self.nextLogger logMessage:level message:message];
}
}
- (void)write:(NSString *)message{
}
@end
ConsoleLogger.h
#import
#import "AbstractLogger.h"
@interface ConsoleLogger : AbstractLogger
-(instancetype)initWithLevel:(int)level;
@end
ConsoleLogger.m
#import "ConsoleLogger.h"
@implementation ConsoleLogger
- (instancetype)initWithLevel:(int)level
{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
self.level = level;
}
return self;
}
- (void)write:(NSString *)message{
NSLog(@"Standard Console::Logger:%@", message);
}
@end
ErrorLogger.h
#import "AbstractLogger.h"
@interface ErrorLogger : AbstractLogger
- (instancetype)initWithLevel:(int)level;
@end
ErrorLogger.m
#import "ErrorLogger.h"
@implementation ErrorLogger
- (instancetype)initWithLevel:(int)level
{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
self.level = level;
}
return self;
}
-(void)write:(NSString*)message{
NSLog(@"ERROR Console::Logger:%@", message);
}
@end
FileLogger.h
#import "AbstractLogger.h"
@interface FileLogger : AbstractLogger
- (instancetype)initWithLevel:(int)level;
@end
FileLogger.m
#import "FileLogger.h"
@implementation FileLogger
- (instancetype)initWithLevel:(int)level
{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
self.level = level;
}
return self;
}
-(void)write:(NSString*)message{
NSLog(@"ERROR Console::Logger : %@", message);
}
@end
ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
AbstractLogger *loggerChain = [self getChainOfLoggers];
[loggerChain logMessage:_INFO message:@"This is an information."];
[loggerChain logMessage:_DEBUG message:@"This is an debug level information."];
[loggerChain logMessage:_ERROR message:@"This is an error information"];
}
-(AbstractLogger*)getChainOfLoggers{
AbstractLogger *errorLogger = [[ErrorLogger alloc]initWithLevel:_ERROR];
AbstractLogger *fileLogger = [[FileLogger alloc] initWithLevel:_DEBUG];
AbstractLogger *consoleLogger = [[ConsoleLogger alloc] initWithLevel:_INFO];
[errorLogger setNextLoggering:fileLogger];
[fileLogger setNextLoggering:consoleLogger];
return errorLogger;
}
结果
setNextLogger 0
ErrorLogger
setNextLogger 1
FileLogger
Standard Console::Logger:This is an information.
ERROR Console::Logger : This is an debug level information.
Standard Console::Logger:This is an debug level information.
ERROR Console::Logger:This is an error information
ERROR Console::Logger : This is an error information
Standard Console::Logger:This is an error information