从源码角度分析Spring batch里ItemReader的使用
想要成为技术大牛,必需要看源码,从源码分析。下面分析几种springBatch里的ItemReader子类。
ItemReader
所以子类的参数或通过spring注入或创建默认。
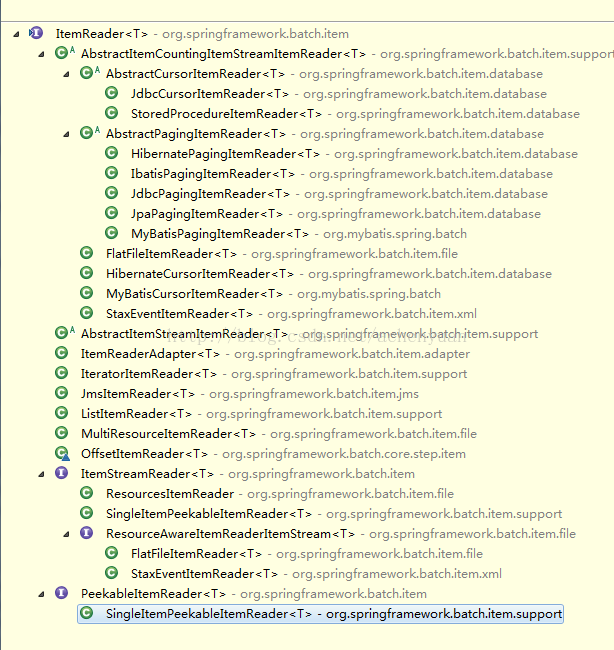
所有子类如下图:
挑几个常用的做介绍。
文件读取类
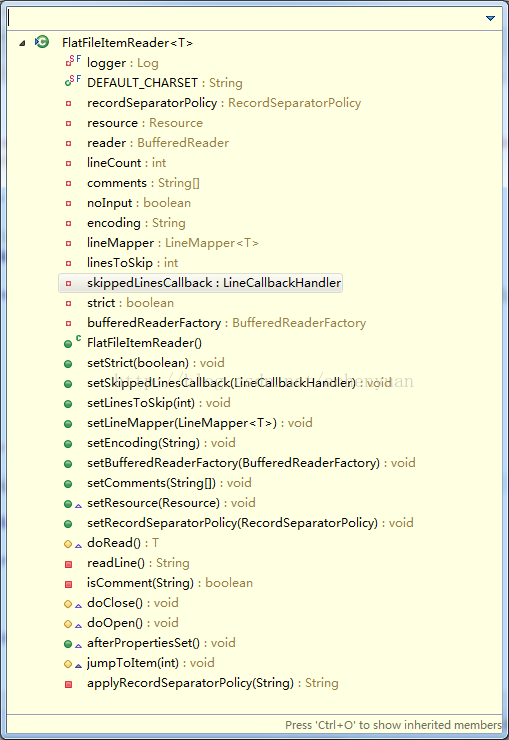
FlatFileItemReader:文件读取类,属性及方法如下:原来该类通过BufferedReader一行一行读取文件数据,同时以#开头的视做注释,跳过读取。真正做事的是doRead方法。而doRead():
protected T doRead() throws Exception {
if (noInput) {
return null;
}
String line = readLine();
if (line == null) {
return null;
}
else {
try {
return lineMapper.mapLine(line, lineCount);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new FlatFileParseException("Parsing error at line: " + lineCount + " in resource=["
+ resource.getDescription() + "], input=[" + line + "]", ex, line, lineCount);
}
}
}
在读取之前会有打开的操作doOpen():
protected void doOpen() throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(resource, "Input resource must be set");
Assert.notNull(recordSeparatorPolicy, "RecordSeparatorPolicy must be set");
noInput = true;
if (!resource.exists()) {
if (strict) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Input resource must exist (reader is in 'strict' mode): " + resource);
}
logger.warn("Input resource does not exist " + resource.getDescription());
return;
}
if (!resource.isReadable()) {
if (strict) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Input resource must be readable (reader is in 'strict' mode): "
+ resource);
}
logger.warn("Input resource is not readable " + resource.getDescription());
return;
}
reader = bufferedReaderFactory.create(resource, encoding);
for (int i = 0; i < linesToSkip; i++) {
String line = readLine();
if (skippedLinesCallback != null) {
skippedLinesCallback.handleLine(line);
}
}
noInput = false;
}
见红色字体,必需保证资源存在可读,同时初始化一个BufferedReader实例。
配置例子:
假设数据是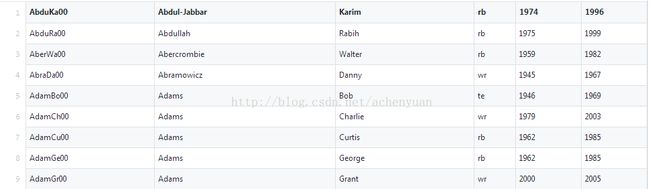
那reader可如下配置:
这样数据和红色字段指定的names字段就会自动映射。
故,想要使用FlatFileItemReader必需配resource和lineMapper两个属性,其它可选配。指定names字段,这样,字段映射成一个对象传给ItemWriter
数据库操作:
由于持久层有hiberate,ibatis,mybatis,所以不同的框架读取不一样:
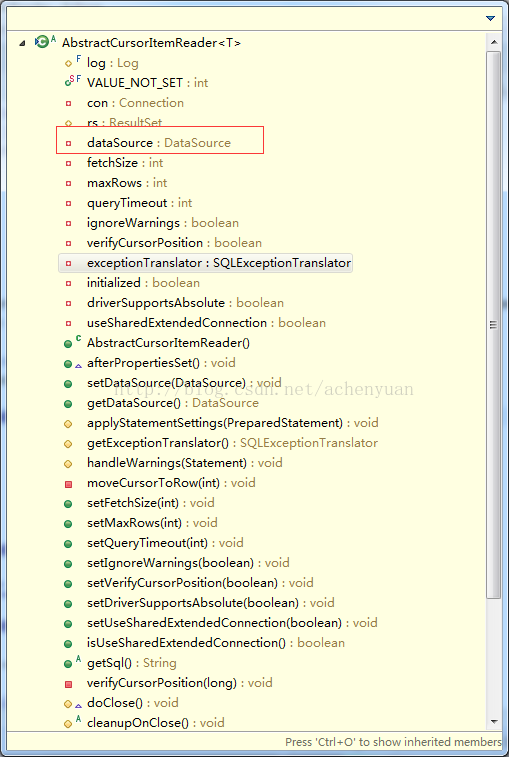
游标读取方式:JdbcCursorItemReader。通过查看JdbcCursorItemReader
的代码,我们发现必要参数是sql, dataSource及rowMapper必需注入。
AbstractCursorItemReader.doRead():
protected T doRead() throws Exception {
if (rs == null) {
throw new ReaderNotOpenException("Reader must be open before it can be read.");
}
try {
if (!rs.next()) {
return null;
}
int currentRow = getCurrentItemCount();
T item = readCursor(rs, currentRow);
verifyCursorPosition(currentRow);
return item;
}
catch (SQLException se) {
throw getExceptionTranslator().translate("Attempt to process next row failed", getSql(), se);
}
}
不难发现rs是执行sql语句返回的结果集,该方法返回当前游标的的item,注意类型是T即泛型。所以,dataSource指定数据源,sql即指定查询语句,rowMapper对当前游标位置的数据进行包装,得到的结果即是指定的结构对象,我一直强调泛型,因为我们用返回的结果即是泛型指定的类型。
配置例子:
CustomerCreditRowMapper.java:
public class CustomerCreditRowMapper implements RowMapper {
public static final String ID_COLUMN = "id";
public static final String NAME_COLUMN = "name";
public static final String CREDIT_COLUMN = "credit";
@Override
public CustomerCredit mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
CustomerCredit customerCredit = new CustomerCredit();
customerCredit.setId(rs.getInt(ID_COLUMN));
customerCredit.setName(rs.getString(NAME_COLUMN));
customerCredit.setCredit(rs.getBigDecimal(CREDIT_COLUMN));
return customerCredit;
}
Ibatis读取方式:
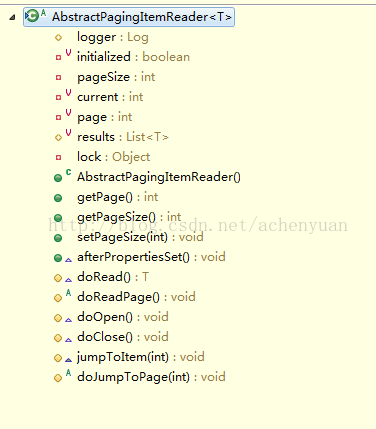
先看IbatisPagingItemReader的父类AbstractPagingItemReader类结构图:分别可设置页号page,页尺寸pageSize默认10等,重点看看doRead()方法:
@Override
protected T doRead() throws Exception {
synchronized (lock) {
if (results == null || current >= pageSize) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Reading page " + getPage());
}
doReadPage();
page++;
if (current >= pageSize) {
current = 0;
}
}
int next = current++;
//返回下一个item
if (next < results.size()) {
return results.get(next);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
}
具体读操作由子类doReadPage方法完成,故现在看看IbatisPagingItemReader
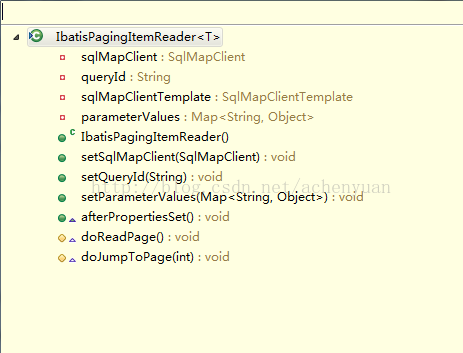
配queryId(映射文件xml里的方法名称),sqlMapCLient实例即是ibatis的配置文件,还要配dataSource.看看它是怎么完成查询的
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void doReadPage() {
Map parameters = new HashMap();
if (parameterValues != null) {
parameters.putAll(parameterValues);
}
parameters.put("_page", getPage());
parameters.put("_pagesize", getPageSize());
parameters.put("_skiprows", getPage() * getPageSize());
if (results == null) {
results = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
}
else {
results.clear();
}
results.addAll(sqlMapClientTemplate.queryForList(queryId, parameters));//过程以目了然
}
所以IbatisPagingItemReader必需配的参数为queryId,sqlMapCLient, dataSource,其它选配。
配置例子:
ibatis-config.xml:
ibatis-customer-credit.xml:
update CUSTOMER set CREDIT = #credit# where NAME = #name#
Ps:不需要对结果集包装,因为ibatis里将读取的数据映射。和spring-batch框架没关系
总结,以上只介绍了几咱读取的类,常用读取的要么文件要么数据库,会这两种类型即可,其实简单。